Spring的事务管理
事务
事务:是逻辑上一组操作,要么全都成功,要么全都失败.
事务特性(ACID)
原子性:事务不可分割
一致性:事务执行的前后,数据完整性保持一致
隔离性:一个事务执行的时候,不应该受到其他事务的打扰
持久性:一旦结束,数据就永久的保存到数据库
如果不考虑隔离性
脏读:一个事务读到另一个事务未提交数据
不可重复读:一个事务读到另一个事务已经提交数据(update)导致一个事务多次查询结果不一致
虚读:一个事务读到另一个事务已经提交数据(insert)导致一个事务多次查询结果不一致
事务的隔离级别
未提交读:以上情况都有可能发生。
已提交读:避免脏读,但不可重复读,虚读是有可能发生。
可重复读:避免脏读,不可重复读,但是虚读有可能发生。
串行的:避免以上所有情况.
Spring中事务管理
Spring提供事务管理API(三个接口)
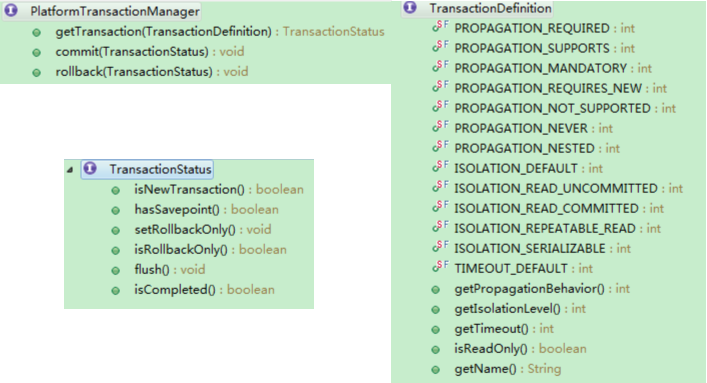
PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器
commit(TransactionStatus status)
getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition)
rollback(TransactionStatus status)
TransactionDefinition:事务定义信息(隔离、传播、超时、只读)
ISOLATION_XXX:事务隔离级别
PROPAGATION_XXX:事务的传播行为(不是JDBC中有的,为了解决实际开发问题.)
TransactionStatus:事务状态
是否有保存点
是否一个新的事务
事务是否已经提交
关系:PlatformTransactionManager通过TransactionDefinition设置事务相关信息管理事务,管理事务过程中,产生一些事务状态:状态由TransactionStatus记录
API详解
PlatformTransactionManager
Spring为不同的持久化框架提供了不同PlatformTransactionManager接口实现
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager : 使用Spring JDBC或iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager : 使用Hibernate3.0版本进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager 使用JPA进行持久化时使用
org.springframework.jdo.JdoTransactionManager 当持久化机制是Jdo时使用
org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager 使用一个JTA实现来管理事务,在一个事务跨越多个资源时必须使用
TransactionDefinition接口
ISOLATION_DEFAULT:默认级别(Mysql:repeatable_read oracle:read_commited)
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE
事务的传播行为:(不是JDBC事务管理,用来解决实际开发的问题)传播行为:解决业务层之间的调用的事务的关系
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED :支持当前事务,如果不存在 就新建一个
A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,B就开启一个新的事务.(A,B是在一个事务中。)
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS :支持当前事务,如果不存在,就不使用事务
A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,B就不使用事务.
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY :支持当前事务,如果不存在,抛出异常
A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,抛出异常.
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务,创建一个新的事务
A,B 如果A有事务,B将A的事务挂起,重新创建一个新的事务.(A,B不在一个事务中.事务互不影响.)
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务
A,B 非事务的方式运行,A有事务,就会挂起当前的事务.
PROPAGATION_NEVER 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常
PROPAGATION_NESTED 如果当前事务存在,则嵌套事务执行(基于SavePoint技术)
A,B A有事务,A执行之后,将A事务执行之后的内容保存到SavePoint.B事务有异常的话,用户需要自己设置事务提交还是回滚.
Spring的事务管理(分为两类)
编程式事务管理:手动编写代码完成事务管理(麻烦,实际中很少用)
声明式事务管理:不需要手动编写代码,配置(推荐使用)
事务操作的环境搭建
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int() NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar() NOT NULL,
`money` double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT= DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('', 'aaa', '');
INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('', 'bbb', '');
INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('', 'ccc', '');
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 转出的方法
* @param from :转出的人
* @param money :要转账金额
*/
public void out(String from,Double money);
/**
* 转出的方法
* @param to :转入的人
* @param money :要转账金额
*/
public void in(String to,Double money);
}
AccountDao
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
/**
* 转出的方法
* @param from :转出的人
* @param money :要转账金额
*/
public void out(String from, Double money) {
String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";
this.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, money,from);
}
/**
* 转出的方法
* @param to :转入的人
* @param money :要转账金额
*/
public void in(String to, Double money) {
String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";
this.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, money , to);
}
}
AccountDaoImpl
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账的方法
* @param from:从哪转出
* @param to:转入的人
* @param money:转账金额
*/
public void transfer(String from,String to,Double money);
}
AccountService
Spring的事务管理
手动编码的方式完成事务管理(缺点:代码量增加,代码有侵入性)
在AccountService中使用TransactionTemplate,TransactionTemplate依赖DataSourceTransactionManager,DataSourceTransactionManager依赖DataSource构造
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) {
this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate;
}
public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {
accountDao.out(from, money);
//int d = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(to, money);
}
});
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部属性文件. -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 业务层类 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo1.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 在业务层注入Dao -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<!-- 在业务层注入事务的管理模板 -->
<property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"/>
</bean>
<!-- 持久层类 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo1.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入连接池的对象,通过连接池对象创建模板. -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理的模板 -->
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 需要注入连接池,通过连接池获得连接 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class SpringTest1 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void demo1(){
// 完成转账
accountService.transfer("aaa", "bbb", 100d);
}
}
声明式事务管理(原始方式,基于TransactionProxyFactoryBean,缺点:就是需要为每一个管理事务的类生成代理.需要为每个类都需要进行配置)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) {
accountDao.out(from, money);
//int d = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(to, money);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部属性文件. -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 业务层类 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo2.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 在业务层注入Dao -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 持久层类 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo2.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入连接池的对象,通过连接池对象创建模板. -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置生成代理对象 -->
<bean id="accountServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<property name="target" ref="accountService"/>
<!-- 注入事务管理器 -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
<!-- 事务的属性设置 -->
<!-- prop格式:PROPAGATION,ISOLATION,readOnly,-Exception,+Exception
顺序:传播行为、隔离级别、事务是否只读、发生哪些异常可以回滚事务(所有的异常都回滚)、发生了哪些异常不回滚 -->
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<prop key="transfer">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext2.xml")
public class SpringTest2 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountServiceProxy")//千万注意:注入代理对象
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void demo1(){
accountService.transfer("aaa", "bbb", 100d);
}
}
声明式事务管理:(自动代理.基于切面 ******)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) {
accountDao.out(from, money);
//int d = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(to, money);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部属性文件. -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 业务层类 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo3.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 在业务层注入Dao -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 持久层类 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo3.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入连接池的对象,通过连接池对象创建模板. -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 定义一个增强 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!-- 增强(事务)的属性的配置 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!--
isolation:DEFAULT :事务的隔离级别.
propagation :事务的传播行为.
read-only :false.不是只读
timeout :-1
no-rollback-for :发生哪些异常不回滚
rollback-for :发生哪些异常回滚事务
-->
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="DEFAULT"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- aop配置定义切面和切点的信息 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 定义切点:哪些类的哪些方法应用增强 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.AccountService+.*(..))" id="mypointcut"/>
<!-- 定义切面: -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext3.xml")
public class SpringTest3 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountService")//注入Service对象,不需要注入代理对象(生成这个类的时候,已经是代理对象)
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void demo1(){
accountService.transfer("aaa", "bbb", 100d);
}
}
基于注解的事务管理
//注解中有属性值:isolation,propagation,readOnly...
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) {
accountDao.out(from, money);
int d = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(to, money);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部属性文件. -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 业务层类 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo4.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 在业务层注入Dao -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 持久层类 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="cn.yzu.spring3.demo4.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入连接池的对象,通过连接池对象创建模板. -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启注解的事务管理 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext4.xml")
public class SpringTest4 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void demo1(){
accountService.transfer("aaa", "bbb", 100d);
}
}
Spring的事务管理的更多相关文章
- spring笔记--事务管理之声明式事务
事务简介: 事务管理是企业级应用开发中必不可少的技术,主要用来确保数据的完整性和一致性, 事务:就是一系列动作,它们被当作一个独立的工作单元,这些动作要么全部完成,要么全部不起作用. Spring中使 ...
- Spring应用——事务管理
事务基础:请参看:http://www.cnblogs.com/solverpeng/p/5720306.html 一.Spring 事务管理 1.前提:事务管理器 在使用 Spring 声明式事务管 ...
- spring+mybatis事务管理
spring+mybatis事务管理 最近在和朋友做一个项目,考虑用springmvc+mybatis来做,之前在公司工作吧,对于数据库这块的配置也有人再弄,最近因为这个项目,我就上网学习了一些关于数 ...
- spring,mybatis事务管理配置与@Transactional注解使用[转]
spring,mybatis事务管理配置与@Transactional注解使用[转] spring,mybatis事务管理配置与@Transactional注解使用 概述事务管理对于企业应用来说是至关 ...
- Spring高级事务管理难点剖析
1Spring事务传播行为 所谓事务传播行为就是多个事务方法相互调用时,事务如何在这些方法间传播.Spring支持7种事务传播行为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED(加入已有事务) 如果当前没 ...
- CSDN上看到的一篇有关Spring JDBC事务管理的文章(内容比较全) (转)
JDBC事务管理 Spring提供编程式的事务管理(Programmatic transaction manage- ment)与声明式的事务管理(Declarative transaction ma ...
- Spring之事务管理
事务管理对于企业应用至关重要.它保证了用户的每一次操作都是可靠的,即便出现了异常的访问情况,也不至于破坏后台数据的完整性. 就像银行的自助取款机,通常都能正常为客户服务,但是也难免遇到 ...
- Mybatis整合Spring实现事务管理的源码分析
一:前言 没有完整看完,但是看到了一些关键的地方,这里做个记录,过程会有点乱,以后逐渐补充最终归档为完整流程:相信看过框架源码的都知道过程中无法完全确定是怎样的流程,毕竟不可能全部都去测试一遍 ,但是 ...
- Hibernate与Spring的事务管理
什么是事务 这个问题比较大,按照我的理解就是,一个事务内的n个操作,要么全部完成,一旦有一个操作有问题,那么所有的操作都全部回滚. Jdbc的事务 首先,大家已经知道了,事务说白了就是一个词----统 ...
随机推荐
- php如何防止图片盗用/盗链的两种方法(转)
图片防盗链有什么用? 防止其它网站盗用你的图片,浪费你宝贵的流量.本文章向大家介绍php防止图片盗用/盗链的两种方法 Apache图片重定向方法 设置images目录不充许http访问 Apache服 ...
- angularjs-$http.post请求传递参数,后台Controller接受不到原因
现象回显 js文件 app.controller('indexCtrl', function($scope, $state, $http) { $scope.login = function() { ...
- vtkTubeFilter实例
filter that generates tubes around lines vtkTubeFilter is a filter that generates a tube around each ...
- Android之弹出/隐藏系统软键盘
Android弹出/隐藏系统软键盘的代码如下: InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getSystemService(Context.INPUT ...
- SQL语句生成指定范围内随机数
1.生成随机实型数据 create procedure awf_RandDouble @min dec(14,2), @max dec(14,2), @result dec(14,2) output ...
- 网络第二节——AFNworking
/** 要使用常规的AFN网络访问 AFHTTPRequestOperationManager *manager = [AFHTTPRequestOperationManager manager]; ...
- XCode8目录整理后的几个警告消除,Missing file
Git目录没有及时更新导致 终端进入目录运行如下命令 git rm main.m git rm Info.plist git rm AppDelegate.h git rm AppDelegate.m ...
- 163邮件出错:不允许使用邮箱名称。 服务器响应为: authentication is required,smtp7,C8CowEDpS0+Uke9VvSmXBg--.546S2 1441763733
原因:用163邮箱发邮件,需开启smtp服务,开启服务时,要求使用客户端授权码. 在.net中,使用smtp发邮件,在验证中使用的密码,是上面所讲的客户端授权码,而不是注册和web登录时用的邮箱密码. ...
- dreamweaver cs6 mac破解版
http://www.sdifenzhou.com/dreamweaver-cs6-mac.html
- linux commands
abrt-cli --since ;查看abrt捕捉的异常 alias ;别名,alias rm='rm -i':使用“ \rm ” 使用原命令 alsamixer ;图形音量调节,q 增加左声道, ...
