Django - 常用配置
一、logging配置
Django项目常用的logging配置
settings.py
LOGGING = {
'version': 1,
'disable_existing_loggers': False,
'formatters': {
'standard': {
'format': '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]'
'[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]'
},
'simple': {
'format': '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s'
},
'collect': {
'format': '%(message)s'
}
},
'filters': {
'require_debug_true': {
'()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue',
},
},
'handlers': {
'console': {
'level': 'DEBUG',
'filters': ['require_debug_true'], # 只有在Django debug为True时才在屏幕打印日志
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
'formatter': 'simple'
},
'default': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_info.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 3,
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
'error': {
'level': 'ERROR',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_err.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
'collect': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_collect.log"),
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'collect',
'encoding': "utf-8"
}
},
'loggers': {
# 默认的logger应用如下配置
'': {
'handlers': ['default', 'console', 'error'], # 上线之后可以把'console'移除
'level': 'DEBUG',
'propagate': True,
},
# 名为 'collect'的logger还单独处理
'collect': {
'handlers': ['console', 'collect'],
'level': 'INFO',
}
},
}
Python logger流示图
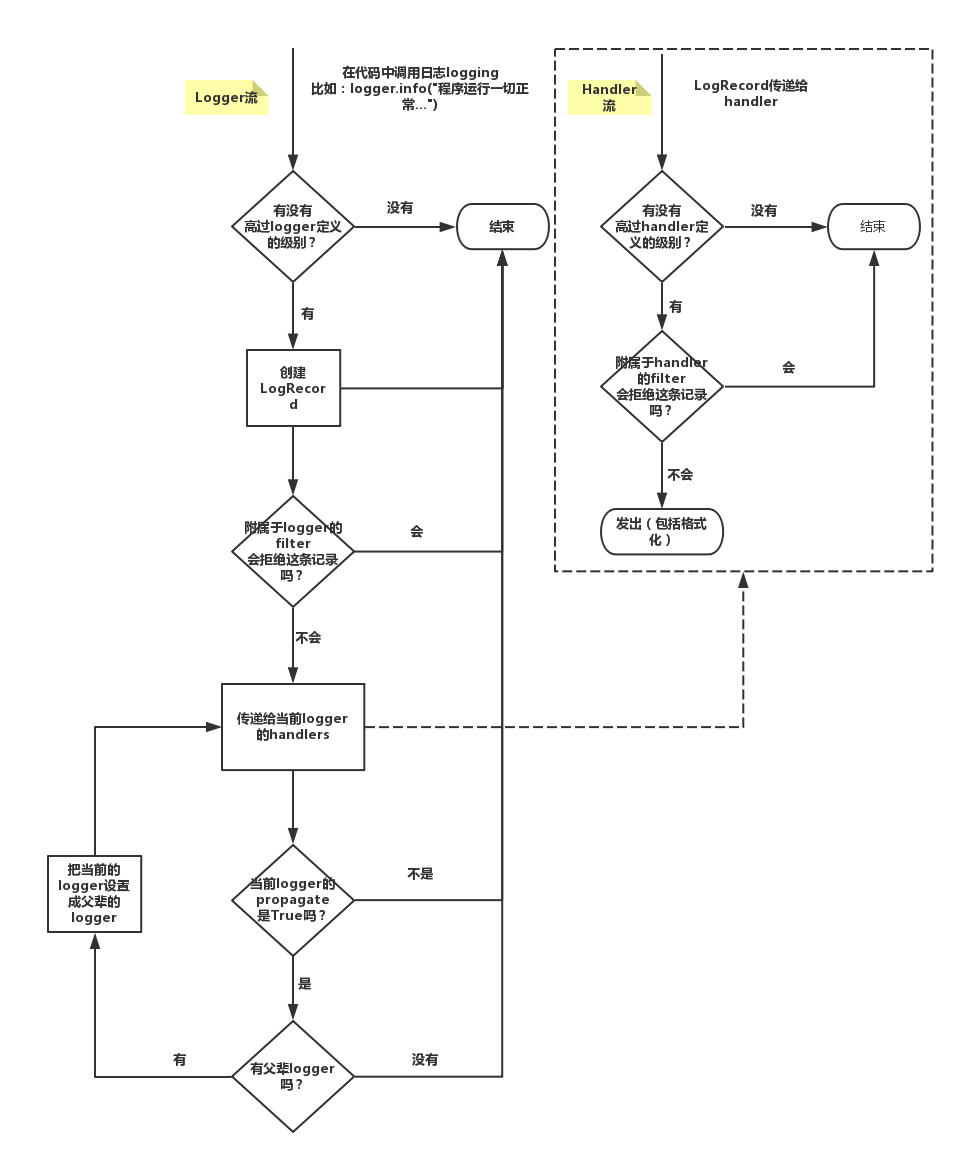
使用:

settings.py
"""
Django settings for about_middleware project. Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 2.0.1. For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/settings/ For the full list of settings and their values, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/settings/
""" import os # Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...)
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production
# See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/howto/deployment/checklist/ # SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = 's011rs!(ga_n!j#*1@!-c2is3)xaw()87bpj=ffjhel^$vzi5v' # SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True # 真正上线 这是 false ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] # Application definition INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01.apps.App01Config',
] MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware', # 注册两个自定义的中间件
'my_middleware.MD1',
'my_middleware.MD2', ]
# 中间件 https://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/p/8761803.html from django.middleware.security import SecurityMiddleware
from django.middleware.csrf import CsrfViewMiddleware
from django.middleware.clickjacking import XFrameOptionsMiddleware # process_request(self,request)
# process_view(self, request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs)
# process_template_response(self,request,response)
# process_exception(self, request, exception)
# process_response(self, request, response) ROOT_URLCONF = 'about_middleware.urls' TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')]
,
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
] WSGI_APPLICATION = 'about_middleware.wsgi.application' # Database
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/settings/#databases DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
}
} # Password validation
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
] # Internationalization
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/i18n/ LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' USE_I18N = True USE_L10N = True USE_TZ = True # Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/howto/static-files/ STATIC_URL = '/static/' # https://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/p/8763264.html
# django 的日志配置项
BASE_LOG_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'log')
LOGGING = {
'version': 1, # 保留字
'disable_existing_loggers': False, # 禁用已经存在的 logger 实例
'formatters': {
# 详细的日志格式
'standard': {
'format': '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]'
'[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]'
},
# 简单的日志格式
'simple': {
'format': '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s'
},
# 定义一个特殊的日志格式
'collect': {
'format': '%(message)s'
}
},
# 过滤器
'filters': {
# DEBUG = True 的情况 才过滤
'require_debug_true': {
'()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue',
},
},
# 处理器
'handlers': {
# 在终端打印
'console': {
'level': 'DEBUG',
'filters': ['require_debug_true'], # 只有在Django debug为True时才在屏幕打印日志
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
'formatter': 'simple'
},
# 默认
'default': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_info.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M 一般配500M
'backupCount': 3, # 最多备份3个
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
# 专门用来记 错误日志
'error': {
'level': 'ERROR',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_err.log"), # 日志文件
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'standard',
'encoding': 'utf-8',
},
# 专门 定义一个 收集特定信息的日志
'collect': {
'level': 'INFO',
'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切
'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_collect.log"),
'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 50, # 日志大小 50M
'backupCount': 5,
'formatter': 'collect',
'encoding': "utf-8"
}
},
'loggers': {
# 默认的logger应用如下配置
'': {
'handlers': ['default', 'console', 'error'], # 上线之后可以把'console'移除
'level': 'DEBUG',
'propagate': True, # 向不向更高级别的logger传递
},
# 名为 'collect'的logger还单独处理
'collect': {
'handlers': ['console', 'collect'],
'level': 'INFO',
}
},
}
settings
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # Create your views here. import logging
# 生成一个以当前文件名为名字的logger实例
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
collect_logger = logging.getLogger('collect') # 生成一个名为collect的实例 def index(requset):
logger.debug('一个debug萌萌的请求...')
logger.info('一个info萌萌的请求...')
'''
这是视图函数index的doc信息
:param requset:
:return:
'''
print('@'*120)
print('这是app01里面的index函数')
# print(requset.s9) # raise ValueError('hehe,抛异常') # return HttpResponse('OK') rep = HttpResponse('OK')
collect_logger.info('这是collect_logger日志')
collect_logger.info('hello:collect') # def render():
# return HttpResponse('不常用')
#
# rep.render = render
return rep
views
二、静态文件配置
settings.py
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static')
]
项目/static
/plugins/sweetalert # 插件
下载 dist css js 引入
https://github.com/lipis/bootstrap-sweetalert
https://lipis.github.io/bootstrap-sweetalert/

/bootstrap-3.3.7/css. fonts. js. # 下载
js ... # 下载
css ...
使用:
<script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/init_ajax.js"></script>
<script src="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/plugins/sweetalert/sweetalert.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript">
//给删除按钮绑定事件
$('.delete').click(function () {
var id = $(this).parent().prev().prev().text();
var $currentTr = $(this).parent().parent();
swal({
title: "确定要删除吗? ",
text: "删了就找不回来了",
type: "warning",
showCancelButton: true, // 显不显示取消按钮
confirmButtonClass: "btn-danger",
confirmButtonText: "是,就是删除", //取消按钮上的文字
closeOnConfirm: false
},
function(){
$.ajax({
url:'/delete_publisher/',
type:'post',
data:{'publisher_id':id},
success:function (arg) {
var ret = JSON.parse(arg);
if(ret.status === 0){
$currentTr.remove();
swal("删除成功!", "你可以跑路了", "success");
}else{
swal(ret.msg, "你可以尝试在删一次", "error");
}
}
});
});
}); </script>
三、mysql配置
settings.py
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'bms',
'HOST':'127.0.0.1',
'PORT':3306,
'USER':'root',
'PASSWORD':'',
}
}
在项目bms __init__ 下设置
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
四、ajax post (csrf-token)请求前配置
项目/static/init_ajax.js
// 从cooikie 取 csft token 的值
function getCookie(name) {
var cookieValue = null;
if (document.cookie && document.cookie !== '') {
var cookies = document.cookie.split(';');
for (var i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
var cookie = jQuery.trim(cookies[i]);
// Does this cookie string begin with the name we want?
if (cookie.substring(0, name.length + 1) === (name + '=')) {
cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(cookie.substring(name.length + 1));
break;
}
}
}
return cookieValue;
}
var csrftoken = getCookie('csrftoken'); // 将csrftoken 设置到ajax 请求头中,后续的ajax请求就会自动携带这个csrf token
function csrfSafeMethod(method) {
// these HTTP methods do not require CSRF protection
return (/^(GET|HEAD|OPTIONS|TRACE)$/.test(method));
} $.ajaxSetup({
beforeSend: function (xhr, settings) {
if (!csrfSafeMethod(settings.type) && !this.crossDomain) {
xhr.setRequestHeader("X-CSRFToken", csrftoken);
}
}
});
<script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/init_ajax.js"></script>
五、事务
import os if __name__ == '__main__':
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "BMS.settings")
import django
django.setup() import datetime
from app01 import models try:
from django.db import transaction
with transaction.atomic():
new_publisher = models.Publisher.objects.create(name="火星出版社")
models.Book.objects.create(title="橘子物语", publish_date=datetime.date.today(), publisher_id=10) # 指定一个不存在的出版社id
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
六、Django终端打印SQL语句
settings.py
LOGGING = {
'version': 1,
'disable_existing_loggers': False,
'handlers': {
'console':{
'level':'DEBUG',
'class':'logging.StreamHandler',
},
},
'loggers': {
'django.db.backends': {
'handlers': ['console'],
'propagate': True,
'level':'DEBUG',
},
}
}
七、在Python脚本中调用Django环境
项目/myscript.py
import os if __name__ == '__main__':
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "BMS.settings")
import django
django.setup() from app01 import models books = models.Book.objects.all()
print(books)
测试数据,批量插入数据:
myscript.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import os if __name__ == '__main__':
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "BMS.settings")
import django
django.setup() # 创建300个出版社
from app01 import models # Publisher.objects.create(name='水星第{}出版社'.format(i)) # obj = Publisher(name='火星出版社')
# obj.save() # ret = []
# for i in range(300):
# obj = Publisher(name='水星第{}出版社'.format(i))
# ret.append(obj) # ret = [models.Publisher(name='水星第{}出版社'.format(i)) for i in range(300)] # 批量创建300个出版社对象
# models.Publisher.objects.bulk_create(ret) # 只提交一次 # 创建300本书
import random
ret = [models.Book(title='番茄物语{}'.format(i),price=random.randint(10, 90),publisher_id=1) for i in range(300)]
models.Book.objects.bulk_create(ret)
八、自定义分页组件
项目/utils/mypage.py
'''
自定义分页组件 '''
class Pagination(object): def __init__(self, data_num, current_page,url_prefix, per_page = 10, max_show = 11):
"""
进行初始化
:param data_num: 数据总数
:param current_page: 当前页
:param url_prefix: 生成得页码得链接前缀
:param per_page: 每页显示多少条数据
:param max_show: 页面最多显示多少个页码
"""
self.data_num = data_num
self.per_page = per_page
self.max_show = max_show
self.url_prefix = url_prefix # 把页码数算出来
self.page_num, more = divmod(self.data_num, self.per_page)
if more:
self.page_num += 1 try:
current_page = int(current_page)
except Exception as e:
current_page = 1
if current_page <= 0: # 如果页面数是 负数
current_page = 1
elif current_page > self.page_num: # 如果页面 大于 总页面
current_page = self.page_num
self.current_page = current_page # 页码数得一半
self.half_show = self.max_show // 2 if self.current_page - self.half_show <= 1:
self.page_start = 1
self.page_end = self.max_show
elif self.current_page + self.half_show >= self.page_num: # 如果右边 越界了
self.page_start = self.page_num - self.max_show + 1
self.page_end = self.page_num
else:
self.page_start = self.current_page - self.half_show
self.page_end = self.current_page + self.half_show @property
def start(self):
return (self.current_page-1) * self.per_page # 数据从哪开始切 @property
def end(self):
return self.current_page * self.per_page # 数据切到哪 def page_html(self):
# 生成页码
li = []
# 加一个首页
li.append('<li><a href="{}?page=1">首页</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix))
# 加一个上一页
if self.current_page == 1:
li.append(
'<li class="disabled"><a href="#"><span aria-hidden="true">«</span></a></li>')
else:
li.append('<li><a href="{0}?page={1}"><span aria-hidden="true">«</span></a></li>'.format(
self.url_prefix,self.current_page - 1))
for i in range(self.page_start, self.page_end + 1):
if i == self.current_page:
tmp = '<li class="active"><a href="{0}?page={1}">{1}</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,i)
else:
tmp = '<li><a href="{0}?page={1}">{1}</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,i)
li.append(tmp)
# 加一个下一页
if self.current_page == self.page_num:
li.append(
'<li class="disabled"><a href="#"><span aria-hidden="true">»</span></a></li>')
else:
li.append('<li><a href="{0}?page={1}"><span aria-hidden="true">»</span></a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,
self.current_page + 1))
li.append('<li><a href="{0}?page={1}">尾页</a></li>'.format(self.url_prefix,self.page_num)) return "".join(li)

views.py
def publisher_list(request):
data = Publisher.objects.all()
data_num = data.count() # 数据得总数
current_page = request.GET.get('page', 1)
from utils import mypage
obj = mypage.Pagination(data_num,current_page,request.path)
publisher_list = data[obj.start:obj.end]
page_html = obj.page_html()
return render(
request,
'publisher_list.html',
{'publisher_list': publisher_list,'page_html':page_html}
)
publisher_list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>publisher_list</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/plugins/sweetalert/sweetalert.css">
<style type="text/css">
.sweet-alert h2{padding-top: 20px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/logout">注销</a>
<div class="container">
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>ID</th>
<th>出版社名称</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for publisher in publisher_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ publisher.id }}</td>
<td>{{ publisher.name }}</td>
<td>
{# https://github.com/lipis/bootstrap-sweetalert #}
<button class="btn btn-danger delete">删除</button>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %} </tbody>
</table>
<nav aria-label="...">
<ul class="pagination">
{{ page_html|safe }}
</ul>
</nav>
</div> <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/init_ajax.js"></script>
<script src="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/plugins/sweetalert/sweetalert.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript">
//给删除按钮绑定事件
$('.delete').click(function () {
var id = $(this).parent().prev().prev().text();
var $currentTr = $(this).parent().parent();
swal({
title: "确定要删除吗? ",
text: "删了就找不回来了",
type: "warning",
showCancelButton: true, // 显不显示取消按钮
confirmButtonClass: "btn-danger",
confirmButtonText: "是,就是删除", //取消按钮上的文字
closeOnConfirm: false
},
function(){
$.ajax({
url:'/delete_publisher/',
type:'post',
data:{'publisher_id':id},
success:function (arg) {
var ret = JSON.parse(arg);
if(ret.status === 0){
$currentTr.remove();
swal("删除成功!", "你可以跑路了", "success");
}else{
swal(ret.msg, "你可以尝试在删一次", "error");
}
}
});
});
}); </script> </body>
</html>
九、django分页组件(CBV)

re_path(r'^book_list/',views.BookList.as_view(),name="book_list"),
# 类视图 要调用as_view()
# 以ip和端口后面什么都没有,就能匹配上url
re_path(r'^$',views.publisher_list),
views.py
# 使用django 内置得分页
from django.core.paginator import Paginator,EmptyPage,PageNotAnInteger
class BookList(View):
@method_decorator(check_login)
def get(self,request):
current_page = request.GET.get('page',1)
data = Book.objects.all()
# 用内置得分页类 得到一个分页对象
page_obj = Paginator(data,10)
try:
# 尝试去取 current_page
ret = page_obj.page(current_page)
except PageNotAnInteger:
ret = page_obj.page(1) # 返回第一页
except EmptyPage:
ret = page_obj.page(page_obj.num_pages) # 返回最后一页
return render(request,'book_list2.html',{'book_list':ret,})
book_list2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>book_list</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是书籍列表页</h1>
<a href="/logout">注销</a> <div class="container">
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>ID</th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ book.id }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %} </tbody>
</table>
<nav aria-label="...">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if book_list.has_previous %}
<li><a href="/book_list?page={{ book_list.previous_page_number }}">«</a></li>
{% else %}
<li class="disabled"><a href="#">«</a></li>
{% endif %}
<li class="active"><a href="/book_list?page={{ book_list.number }}">{{ book_list.number }}</a></li>
{% if book_list.has_next %}
<li><a href="/book_list?page={{ book_list.next_page_number}}">»</a></li>
{% else %}
<li class="disabled"><a href="#">»</a></li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
</div> <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="/static/bootstrap-3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
十、django缓存 - redis
http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5246483.html
由于Django是动态网站,所有每次请求均会去数据进行相应的操作,当程序访问量大时,耗时必然会更加明显,最简单解决方式是使用:缓存,缓存将一个某个views的返回值保存至内存或者memcache中,5分钟内再有人来访问时,则不再去执行view中的操作,而是直接从内存或者Redis中之前缓存的内容拿到,并返回。
Django中提供了6种缓存方式:
- 开发调试
- 内存
- 文件
- 数据库
- Memcache缓存(python-memcached模块)
- Memcache缓存(pylibmc模块)
1、配置
a、开发调试

# 此为开始调试用,实际内部不做任何操作
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.dummy.DummyCache', # 引擎
'TIMEOUT': 300, # 缓存超时时间(默认300,None表示永不过期,0表示立即过期)
'OPTIONS':{
'MAX_ENTRIES': 300, # 最大缓存个数(默认300)
'CULL_FREQUENCY': 3, # 缓存到达最大个数之后,剔除缓存个数的比例,即:1/CULL_FREQUENCY(默认3)
},
'KEY_PREFIX': '', # 缓存key的前缀(默认空)
'VERSION': 1, # 缓存key的版本(默认1)
'KEY_FUNCTION' 函数名 # 生成key的函数(默认函数会生成为:【前缀:版本:key】)
}
} # 自定义key
def default_key_func(key, key_prefix, version):
"""
Default function to generate keys. Constructs the key used by all other methods. By default it prepends
the `key_prefix'. KEY_FUNCTION can be used to specify an alternate
function with custom key making behavior.
"""
return '%s:%s:%s' % (key_prefix, version, key) def get_key_func(key_func):
"""
Function to decide which key function to use. Defaults to ``default_key_func``.
"""
if key_func is not None:
if callable(key_func):
return key_func
else:
return import_string(key_func)
return default_key_func

b、内存

# 此缓存将内容保存至内存的变量中
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.locmem.LocMemCache',
'LOCATION': 'unique-snowflake',
}
} # 注:其他配置同开发调试版本

c、文件

# 此缓存将内容保存至文件
# 配置: CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.filebased.FileBasedCache',
'LOCATION': '/var/tmp/django_cache',
}
}
# 注:其他配置同开发调试版本

d、数据库

# 此缓存将内容保存至数据库
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.db.DatabaseCache',
'LOCATION': 'my_cache_table', # 数据库表
}
}
# 注:执行创建表命令 python manage.py createcachetable

e、Memcache缓存(python-memcached模块)

# 此缓存使用python-memcached模块连接memcache
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': 'unix:/tmp/memcached.sock',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11211',
]
}
}

f、Memcache缓存(pylibmc模块)

# 此缓存使用pylibmc模块连接memcache
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': '/tmp/memcached.sock',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11211',
]
}
}

g. Redis缓存(依赖:pip3 install django-redis)

CACHES = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "django_redis.cache.RedisCache",
"LOCATION": "redis://127.0.0.1:6379",
"OPTIONS": {
"CLIENT_CLASS": "django_redis.client.DefaultClient",
"CONNECTION_POOL_KWARGS": {"max_connections": 100}
# "PASSWORD": "密码",
}
}
}

from django_redis import get_redis_connection
conn = get_redis_connection("default")
2、应用
a. 全站使用

使用中间件,经过一系列的认证等操作,如果内容在缓存中存在,则使用FetchFromCacheMiddleware获取内容并返回给用户,当返回给用户之前,判断缓存中是否已经存在,如果不存在则UpdateCacheMiddleware会将缓存保存至缓存,从而实现全站缓存
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',
# 其他中间件...
'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',
]
CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_ALIAS = ""
CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_SECONDS = ""
CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_KEY_PREFIX = ""

b. 单独视图缓存

方式一:
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page @cache_page(60 * 15)
def my_view(request):
... 方式二:
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page urlpatterns = [
url(r'^foo/([0-9]{1,2})/$', cache_page(60 * 15)(my_view)),
]

c、局部视图使用

a. 引入TemplateTag
{% load cache %}
b. 使用缓存
{% cache 5000 缓存key %}
缓存内容
{% endcache %}

更多:猛击这里
django缓存配置
由于Django是动态网站,所有每次请求均会去数据进行相应的操作,当程序访问量大时,耗时必然会更加明显,最简单解决方式是使用:缓存,缓存将一个某个views的返回值保存至内存或者memcache中,5分钟内再有人来访问时,则不再去执行view中的操作,而是直接从内存或者Redis中之前缓存的内容拿到,并返回。
Django中提供了6种缓存方式:
- 开发调试
- 内存
- 文件
- 数据库
- Memcache缓存(python-memcached模块)
- Memcache缓存(pylibmc模块)
通用配置

'TIMEOUT': 300, # 缓存超时时间(默认300,None表示永不过期,0表示立即过期)
'OPTIONS':{
'MAX_ENTRIES': 300, # 最大缓存个数(默认300)
'CULL_FREQUENCY': 3, # 缓存到达最大个数之后,剔除缓存个数的比例,即:1/CULL_FREQUENCY(默认3)
},
'KEY_PREFIX': '', # 缓存key的前缀(默认空)
'VERSION': 1, # 缓存key的版本(默认1)
'KEY_FUNCTION' 函数名 # 生成key的函数(默认函数会生成为:【前缀:版本:key】)

以上六中模式都可以使用
自定义key

def default_key_func(key, key_prefix, version):
"""
Default function to generate keys. Constructs the key used by all other methods. By default it prepends
the `key_prefix'. KEY_FUNCTION can be used to specify an alternate
function with custom key making behavior.
"""
return '%s:%s:%s' % (key_prefix, version, key) def get_key_func(key_func):
"""
Function to decide which key function to use. Defaults to ``default_key_func``.
"""
if key_func is not None:
if callable(key_func):
return key_func
else:
return import_string(key_func)
return default_key_func

开发调试


# 此为开始调试用,实际内部不做任何操作
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.dummy.DummyCache', # 引擎
通用配置
}
}


内存


# 此缓存将内容保存至内存的变量中
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.locmem.LocMemCache',
'LOCATION': 'unique-snowflake',
通用配置
}
} # 注:其他配置同开发调试版本


文件


# 此缓存将内容保存至文件
# 配置: CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.filebased.FileBasedCache',
'LOCATION': '/var/tmp/django_cache',
通用配置
}
}
# 注:其他配置同开发调试版本


数据库


# 此缓存将内容保存至数据库
# 配置:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.db.DatabaseCache',
'LOCATION': 'my_cache_table', # 数据库表
通用配置
}
}
# 注:执行创建表命令 python manage.py createcachetable


Memcache缓存(python-memcached模块)


# 此缓存使用python-memcached模块连接memcache
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': 'unix:/tmp/memcached.sock',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11211',
]
}
}


Memcache缓存(pylibmc模块)


# 此缓存使用pylibmc模块连接memcache
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': '/tmp/memcached.sock',
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': [
'172.19.26.240:11211',
'172.19.26.242:11211',
]
}
}


缓存的应用
单独视图缓存
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page @cache_page(60 * 15)
def my_view(request):
...
即通过装饰器的方式实现,导入模块之后,在需要缓存的函数前加@cache_page(60 * 15) 60*15表示缓存时间是15分钟
例子如下:


from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
@cache_page(10)
def cache(request):
import time
ctime = time.time()
return render(request,"cache.html",{"ctime":ctime})


前端页面如下:


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1>
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1>
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1> </body>
</html>


这样在前端页面在获取的ctime的时候就会被缓存10秒钟,10秒钟之后才会变化,但是这样的话就相当月所有的调用ctime的地方都被缓存了
局部缓存


引入TemplateTag
{% load cache %}
使用缓存
{% cache 5000 缓存key %}
缓存内容
{% endcache %}


更改前端代码如下:


{% load cache %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1>
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1>
{% cache 10 c1 %}
<h1>{{ ctime }}</h1>
{% endcache %}
</body>
</html>


这样就实现了最后一个ctime缓存,其他两个不缓存
全站缓存
全站缓存的时候,需要在中间件的最上面添加:
'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',
在中间件的最下面添加:
'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',
其中'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware'里面只有process_response方法,在'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware'中只有process_request方法,所以最开始是直接跳过UpdateCacheMiddleware,然后从第一个到最后一个中间件的resquest,第一次没有缓存座椅匹配urls路由关系依次进过中间件的process_view,到达views函数,再经过process_exception最后经过response,到达FetchFromCacheMiddleware
使用中间件,经过一系列的认证等操作,如果内容在缓存中存在,则使用FetchFromCacheMiddleware获取内容并返回给用户,当返回给用户之前,判断缓存中是否已经存在,如果不存在则UpdateCacheMiddleware会将缓存保存至缓存,从而实现全站缓存
MIDDLEWARE = [ 'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',#放到第一个中间件位置 # 其他中间件... 'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',#放到最后一个 ] CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_ALIAS = "" CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_SECONDS = "" # 可设置缓存时间 CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_KEY_PREFIX = ""Django - 常用配置的更多相关文章
- 最全的Django入门及常用配置
Django 常用配置 Django 安装 pipx install django x 为python解释器版本2 or 3 如果你想安装指定版本的django,使用pip install djang ...
- django->基本操作和新建项目常用配置
一.安装django pip install django==2.1.5 -U #安装django/升级最新版本 二.创建.启动django项目 django-admin startproject m ...
- Django常用命令及参数配置(Django 1.8.6)
常用命令 #新建Django项目 django-admin startproject mysite(项目名) #新建一个APP cd mysite python manager.py startapp ...
- Django - 日志工作中常用配置
工作中常用配置 # 日志配置 BASE_LOG_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "log") LOGGING = { 'version': 1, # 保留 ...
- Django笔记&教程 1-2 二 常用配置
Django 自学笔记兼学习教程第1章第2节--二 常用配置 点击查看教程总目录 新手建议简单浏览本文,不理解的建议跳过,不要强行理解. Django的设置涉及多个模块,需要了解Django的一些相关 ...
- django-debug-toolbar和Django 日志配置
django-debug-toolbar介绍 django-debug-toolbar 是一组可配置的面板,可显示有关当前请求/响应的各种调试信息,并在单击时显示有关面板内容的更多详细信息. gith ...
- python 全栈开发,Day96(Django REST framework 视图,django logging配置,django-debug-toolbar使用指南)
昨日内容回顾 1. Serializer(序列化) 1. ORM对应的query_set和ORM对象转换成JSON格式的数据 1. 在序列化类中定义自定义的字段:SerializerMethodFie ...
- Pycharm常用配置
Pycharm常用配置 pycharm中的设置是可以导入和导出的,file>export settings 可以保存当前pycharm中的设置为jar文件,重装时可以直接import setti ...
- 12: nginx原理及常用配置
1.1 nginx基本介绍 1.nginx高并发原理( 多进程+epoll实现高并发 ) 1. Nginx 在启动后,会有一个 master 进程和多个相互独立的 worker 进程. 2. 每个子进 ...
随机推荐
- sqlserver 字符串split
select value from TF_NJVALUES('3C457A2D-188B-4D99-A822-2968054E1FB8,3C457A2D-188B-4D99-A822-2968054E ...
- PL/SQL developer(绿色版)安装及配置
1.PL/SQL Developer下载地址:百度网盘: 2.tsname.ora配置: orcl = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS )) ) (CO ...
- jquery-插入兄弟元素
1.after方法 在匹配元素集合中的每个元素的 后面 插入参数所指定的内容,作为其兄弟节点 参数类型说明: 1)普通字符串(可包含各种html标签) $('div').after('html字符串' ...
- hbase shell学习-2
一个学生成绩表的例子来演示hbase的用法. name grade course math english Tom 5 97 87 Jim 4 89 80 表的创建:语法:create '表名称',' ...
- git分支合并的冲突解决方法
本次学习的是解决不同分支提交的内容不同导致合并冲突,及怎样解决冲突. 基本命令: git log --graph查看分支合并图 具体步骤: 新建分支branch1,并修改rea ...
- error MSB8031
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=286820 下载
- ubuntu 执行make menuconfig ARCH=arm
1.ubuntu 执行make menuconfig ARCH=arm出错了!! *** Unable to find the ncurses libraries or the *** require ...
- 一、NHibernate配置所支持的属性
属性名 用途 dialect 设置NHibernate的Dialect类名 - 允许NHibernate针对特定的关系数据库生成优化的SQL 可用值: full.classname.of.Dialec ...
- Nginx 链接
Nginx反向代理以及负载均衡配置:http://www.cnblogs.com/Miss-mickey/p/6734831.html
- CH7-WEB开发(集成在一起)
