HDU 2829 - Lawrence - [斜率DP]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2829
You are to write a program to help Lawrence figure out how to best use his limited resources. You have some information from British Intelligence. First, the rail line is completely linear---there are no branches, no spurs. Next, British Intelligence has assigned a Strategic Importance to each depot---an integer from 1 to 100. A depot is of no use on its own, it only has value if it is connected to other depots. The Strategic Value of the entire railroad is calculated by adding up the products of the Strategic Values for every pair of depots that are connected, directly or indirectly, by the rail line. Consider this railroad:
Its Strategic Value is 4*5 + 4*1 + 4*2 + 5*1 + 5*2 + 1*2 = 49.
Now, suppose that Lawrence only has enough resources for one attack. He cannot attack the depots themselves---they are too well defended. He must attack the rail line between depots, in the middle of the desert. Consider what would happen if Lawrence attacked this rail line right in the middle:
The Strategic Value of the remaining railroad is 4*5 + 1*2 = 22. But, suppose Lawrence attacks between the 4 and 5 depots:
The Strategic Value of the remaining railroad is 5*1 + 5*2 + 1*2 = 17. This is Lawrence's best option.
Given a description of a railroad and the number of attacks that Lawrence can perform, figure out the smallest Strategic Value that he can achieve for that railroad.
Input
There will be several data sets. Each data set will begin with a line with two integers, n and m. n is the number of depots on the railroad (1≤n≤1000), and m is the number of attacks Lawrence has resources for (0≤m<n). On the next line will be n integers, each from 1 to 100, indicating the Strategic Value of each depot in order. End of input will be marked by a line with n=0 and m=0, which should not be processed.
Output
For each data set, output a single integer, indicating the smallest Strategic Value for the railroad that Lawrence can achieve with his attacks. Output each integer in its own line.
Sample Input
4 1
4 5 1 2
4 2
4 5 1 2
0 0
Sample Output
17
2
题意:
给出一条笔直无分叉的铁路上有n个仓库,每个仓库有一个v[i]代表价值;
每两个仓库之间算作一段铁路,现在有m次攻击机会,一次攻击可以炸毁一段铁路;
m次攻击后,剩余的总价值为:Σ(v[i]*v[j]),i和j为所有任意两个互相可到达的仓库。
现要求选定m段铁路进行攻击炸毁,然后使得总价值最小。
题解:
设dp[i][j]是前i个仓库,炸掉j段铁路后,剩余总价值的最小值。(显然,j<i)
设w[a][b]表示铁路完好的情况下,从a仓库到b仓库的总价值,即:
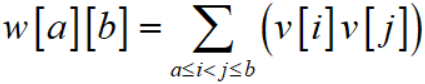
那么,就有:
dp[i][j] = min( dp[k][j-1] + w[k+1][i] ),j≤k<i;
方程的意义是:炸毁仓库k和仓库k+1之间的那段铁路(即第k段铁路),算出总价值,枚举k找到最小的。
那么如何计算w[k+1][i]呢?
假设$sum\left[ i \right] = \sum\limits_{k = 1}^i {v\left[ k \right]}$,那么就有:
w[1][i] = w[1][k] + w[k+1][i] + (v[1]+v[2]+…+v[k]) × (v[k+1]+v[k+2]+…+v[i])
= w[1][k] + w[k+1][i] + sum[k] × (sum[i]-sum[k])
即w[k+1][i] = w[1][i] - w[1][k] - sum[k] × (sum[i]-sum[k])
我们把w[k+1][i]的计算式带入状态转移方程得到:
dp[i][j] = min{ dp[k][j-1] + w[1][i] - w[1][k] - sum[k] × (sum[i]-sum[k]) }
那么,对于这个DP,j一个循环、i一个循环、k一个循环,就是O(n3)的时间复杂度;
需要斜率优化,优化到O(n2)即可。
对于第a段铁路和第b段铁路(1≤a<b<i),我们若有:
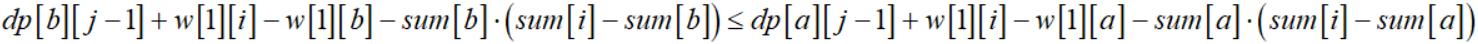
可以说第b段铁路优于第a段铁路。
对上式进行变形可得:
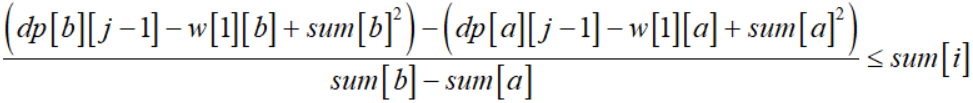
我们假设:
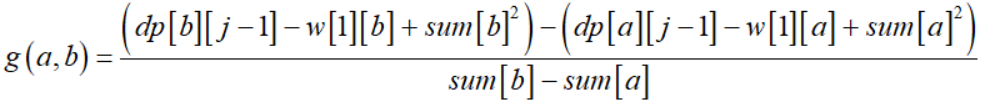
那么
选择炸毁第b段铁路优于炸毁第a段铁路 <=> g(a,b) ≤ sum[i]
选择炸毁第b段铁路劣于炸毁第a段铁路 <=> g(a,b) > sum[i]
然后后面的操作就和HDU3507http://www.cnblogs.com/dilthey/p/8745843.html差不多了:
①在计算dp[i][j]时,若有j≤a<b<c<i,只要满足g(a,b) ≥ g(b,c),则b点必然被淘汰.
证明:若g(b,c) ≤ sum[i],则选择第c段铁路优于第b段铁路,b淘汰;
若g(b,c) > sum[i],则g(a,b) > sum[i],则选第b段铁路差于第a段,b淘汰。
②若在计算dp[i][j]时,k点被淘汰,则计算dp[i+1][j]时,k点必然也被淘汰.
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e3+; int n,m;
int sum[maxn]; //前缀和
int w[maxn]; //w[1][i]
int dp[maxn][maxn];
int q[maxn],head,tail; double g(int a,int b,int j)
{
double up = (dp[b][j-]-w[b]+sum[b]*sum[b]) - (dp[a][j-]-w[a]+sum[a]*sum[a]);
double down = sum[b]-sum[a];
return up/down;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) && n+m>)
{
sum[]=;
for(int i=,tmp;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);
sum[i]=sum[i-]+tmp;
w[i]=w[i-]+sum[i-]*tmp;
} for(int i=;i<=n;i++) dp[i][]=w[i];
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
head=tail=;
q[tail++]=j;
for(int i=j+,a,b;i<=n;i++)
{
while(head+<tail)
{
a=q[head], b=q[head+];
if(g(a,b,j)<=sum[i]) head++;
else break;
}
int k=q[head];
dp[i][j]=dp[k][j-]+w[i]-w[k]-sum[k]*(sum[i]-sum[k]); while(head+<tail)
{
a=q[tail-], b=q[tail-];
if(g(a,b,j)>=g(b,i,j)) tail--;
else break;
}
q[tail++]=i;
}
} printf("%d\n",dp[n][m]);
}
}
注意点:
本题看到v[i]在1到100之间,所以不会出现sum[b]-sum[a]=0这种除数为零的情况,所以可以直接求g(a,b),而不用再转成乘法比大小。
斜率DP也算是有一定的套路,能够优化一维的时间复杂度,所以刚开始做斜率DP的时候,应先从普通的DP进行考虑(包括条件初始化、状态转移的顺序之类),然后再考虑加入斜率优化。
HDU 2829 - Lawrence - [斜率DP]的更多相关文章
- hdu 2829 Lawrence(斜率优化DP)
题目链接:hdu 2829 Lawrence 题意: 在一条直线型的铁路上,每个站点有各自的权重num[i],每一段铁路(边)的权重(题目上说是战略价值什么的好像)是能经过这条边的所有站点的乘积之和. ...
- HDU 2829 Lawrence (斜率优化DP或四边形不等式优化DP)
题意:给定 n 个数,要你将其分成m + 1组,要求每组数必须是连续的而且要求得到的价值最小.一组数的价值定义为该组内任意两个数乘积之和,如果某组中仅有一个数,那么该组数的价值为0. 析:DP状态方程 ...
- HDU 2829 Lawrence (斜率DP)
斜率DP 设dp[i][j]表示前i点,炸掉j条边的最小值.j<i dp[i][j]=min{dp[k][j-1]+cost[k+1][i]} 又由得出cost[1][i]=cost[1][k] ...
- HDU 3480 - Division - [斜率DP]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3480 Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory L ...
- ACM-ICPC 2016 沈阳赛区现场赛 I. The Elder && HDU 5956(斜率DP)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5956 题意:一颗树上每条边有个权值,每个节点都有新闻要送到根节点就是1节点,运送过程中如果不换青蛙就是 ...
- HDU 2829 Lawrence(斜率优化DP O(n^2))
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2829 题目大意:有一段铁路有n个站,每个站可以往其他站运送粮草,现在要炸掉m条路使得粮草补给最小,粮草 ...
- HDU 2829 [Lawrence] DP斜率优化
解题思路 首先肯定是考虑如何快速求出一段铁路的价值. \[ \sum_{i=1}^k \sum_{j=1, j\neq i}^kA[i]A[j]=(\sum_{i=1}^kA[i])^2-\sum_{ ...
- HDU.2829.Lawrence(DP 斜率优化)
题目链接 \(Description\) 给定一个\(n\)个数的序列,最多将序列分为\(m+1\)段,每段的价值是这段中所有数两两相乘的和.求最小总价值. \(Solution\) 写到这突然懒得写 ...
- HDU 2829 Lawrence(四边形优化DP O(n^2))
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2829 题目大意:有一段铁路有n个站,每个站可以往其他站运送粮草,现在要炸掉m条路使得粮草补给最小,粮草 ...
随机推荐
- 10 -- 深入使用Spring -- 5...2 在Spring中使用Quartz
10.5.2 在Spring中使用Quartz Spring 的任务调度抽象层简化了任务调度,在Quartz基础上提供了更好的调度抽象.本系统使用Quartz框架来完成任务调度,创建Quartz的作业 ...
- grid网格的流动定位
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- SpringBoot Cmd运行Jar文件指定active文件的命令如下
SpringBoot Cmd运行Jar文件指定active文件的命令如下 SpringBoot 命令行指定配置文件运行 ================================ ©Copyri ...
- 【Cesium】flyTo
// 1. Fly to a position with a top-down view viewer.camera.flyTo({ destination : Cesium.Cartesian3.f ...
- hbase2.0.0-安装部署
依赖hadoop 环境,我这边的版本是hadoop-2.6.5 选择hbase2.0.0版本的时候,去官网查看支持的hadoop版本 1.伪分布式安装 下载:http://mirror.bit.edu ...
- mysql5.7 服务无法启动的问题解决方法
解决办法: 1.把MySQL文件低下的data文件删掉,如果没有的话,就不用管了: 2.在mysql安装路径下,执行mysqld --initialize命令进行初始化,mysql会自动帮你重新创建d ...
- 【RF库XML测试】Element Attribute Should Be
Name:Element Attribute Should BeSource:XML <test library>Arguments:[ source | name | expected ...
- HttpClient(五)-- 模拟表单上传文件
1.maven依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId ...
- Linux下的/proc目录介绍
proc被称为虚拟文件系统,它是一个控制中心,可以通过更改其中某些文件改变内核运行状态, 它也是内核提空给我们的查询中心,用户可以通过它查看系统硬件及当前运行的进程信息. Linux中许多工具的数据来 ...
- Jar命令
JAR包是Java中所特有一种压缩文档,其实大家就可以把它理解为.zip包;当然也是有区别的,JAR包中有一个META-INF\MANIFEST.MF文件,当你打成JAR包时,它会自动生成. 一.ja ...
