Useful NumPy functions: Reshape, Argpartition, Clip, Extract, Setdiff1d
In everyday data processing for Machine Learning and Data Science projects, we encounter unique situations, those require boilerplate code to solve the problem. Over the period some of those are converted into base features provided by the core language or the package itself as per need and usage from the community. Here I am sharing 5 elegant python Numpy functions, which can be used for efficient and neat data manipulation.
1) Use of -1 in Reshape
Numpy allows us to reshape a matrix provided new shape should be compatible with the original shape. One interesting aspect of this new shape is, we can give one of the shape parameter as -1. It simply means that it is an unknown dimension and we want Numpy to figure it out. Numpy will figure this by looking at the ‘length of the array and remaining dimensions’ and making sure it satisfies the above mentioned criteria. Let's see one example now.

Pictorial representation of different reshape with one dimension as -1
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])
a.shape
(2, 4)
Suppose we give row as 1 and -1 as column then Numpy will able to find column as 8.
a.reshape(1,-1)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
Suppose we give row as -1 and 1 as column then Numpy will able to find row as 8.
a.reshape(-1,1)
array([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[7],
[8]])
Similarly below are possible.
a.reshape(-1,4)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])a.reshape(-1,2)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])a.reshape(2,-1)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])a.reshape(4,-1)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
This is also applicable to any higher level tensor reshape as well but only one dimension can be given -1.
a.reshape(2,2,-1)
array([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]], [[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])a.reshape(2,-1,1)
array([[[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]], [[5],
[6],
[7],
[8]]])
If we try to reshape a non-compatible shape or more than one unknown shape then there will be an error message.
a.reshape(-1,-1)
ValueError: can only specify one unknown dimensiona.reshape(3,-1)
ValueError: cannot reshape array of size 8 into shape (3,newaxis)
To summarize, when reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements as the old shape, meaning the products of the two shapes’ dimensions must be equal. When using a -1, the dimension corresponding to the -1 will be the product of the dimensions of the original array divided by the product of the dimensions given to reshape so as to maintain the same number of elements.
2) Argpartition : Find N maximum values in an array
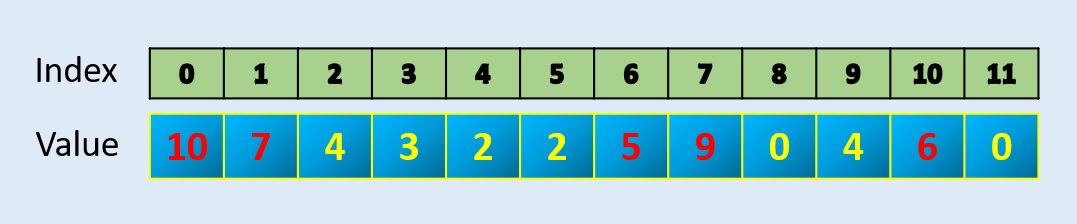
Numpy has a function called argpartition which can efficiently find largest of N values index and in-turn N values. It gives index and then you can sort if you need sorted values.
array = np.array([10, 7, 4, 3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])index = np.argpartition(array, -5)[-5:]
index
array([ 6, 1, 10, 7, 0], dtype=int64)np.sort(array[index])
array([ 5, 6, 7, 9, 10])
3) Clip : How to keep values in an array within an interval
In many data problem or algorithm (like PPO in Reinforcement Learning) we need to keep all values within an upper and lower limit. Numpy has a built in function called Clip that can be used for such purpose. Numpy clip() function is used to Clip (limit) the values in an array. Given an interval, values outside the interval are clipped to the interval edges. For example, if an interval of [-1, 1] is specified, values smaller than -1 become -1, and values larger than 1 become 1.

Clip example with min value 2 and maximum value 6
#Example-1
array = np.array([10, 7, 4, 3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])
print (np.clip(array,2,6))[6 6 4 3 2 2 5 6 2 4 6 2]#Example-2
array = np.array([10, -1, 4, -3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])
print (np.clip(array,2,5))[5 2 4 2 2 2 5 5 2 4 5 2]
4) Extract: To extract specific elements from an array based on condition
We can use Numpy extract() function to extract specific elements from an array that matches the condition.
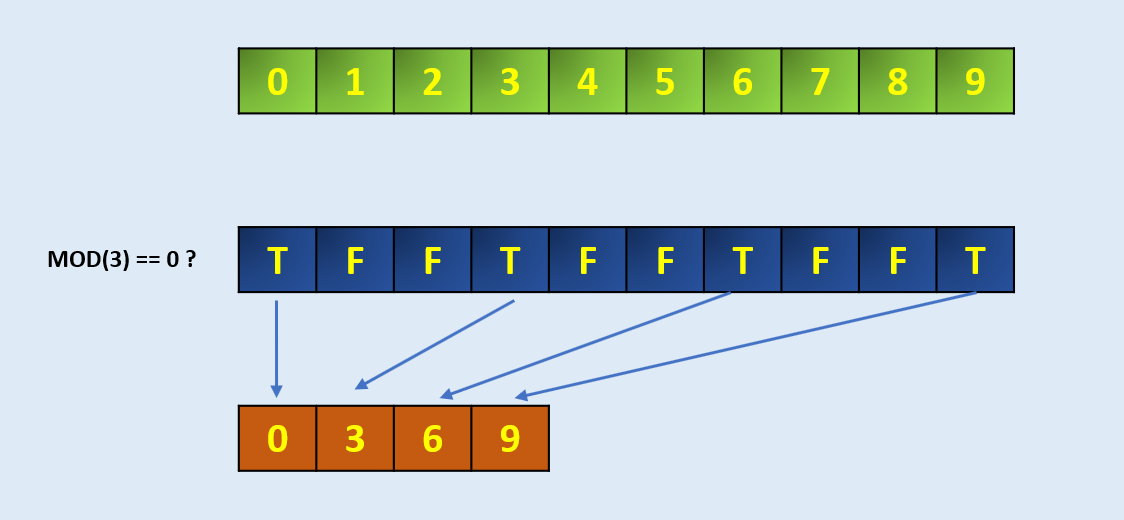
arr = np.arange(10)
arrarray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])# Define the codition, here we take MOD 3 if zero
condition = np.mod(arr, 3)==0
conditionarray([ True, False, False, True, False, False, True, False, False,True])np.extract(condition, arr)
array([0, 3, 6, 9])
Similarly, we can use direct condition with combination of AND and OR if required like
np.extract(((arr > 2) & (arr < 8)), arr)array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
5) setdiff1d : How to find unique values in an array compared to another
Return the unique values in an array that are not in present in another array. This is equivalent to set difference of two arrays.
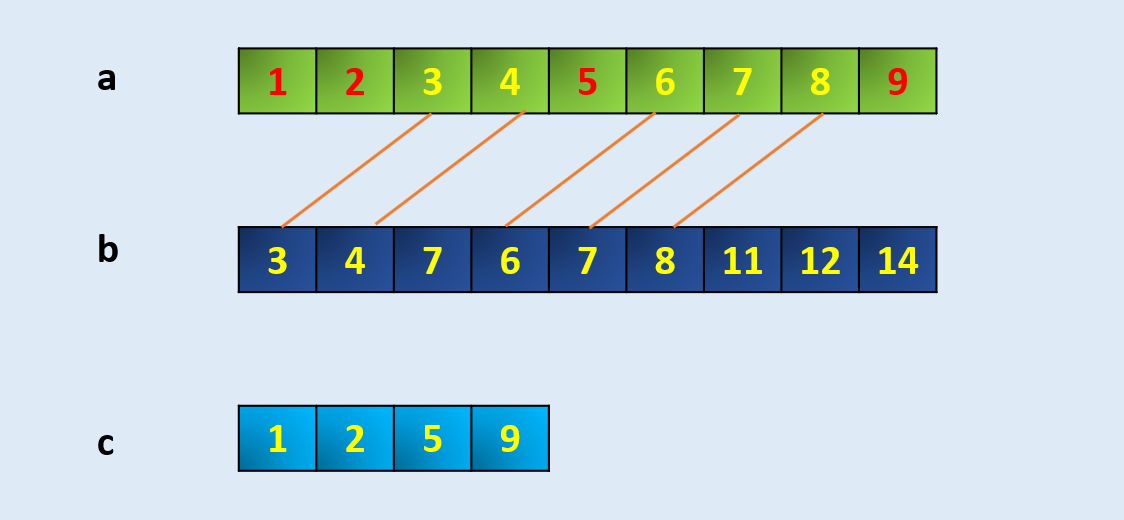
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
b = np.array([3,4,7,6,7,8,11,12,14])
c = np.setdiff1d(a,b)
carray([1, 2, 5, 9])
Final Note :
These are 5 Numpy functions which are not used frequently by the community but they are neat and elegant. In my view, we should use them whenever there is similar situation as these provide not just less code but mostly smart way of achieving a solution for a complex problem.
Useful NumPy functions: Reshape, Argpartition, Clip, Extract, Setdiff1d的更多相关文章
- numpy中的argpartition
numpy.argpartition(a, kth, axis=-1, kind='introselect', order=None) 在快排算法中,有一个典型的操作:partition.这个操作指: ...
- numpy 矩阵变换 reshape ravel flatten
1. 两者的区别在于返回拷贝(copy)还是返回视图(view),numpy.flatten()返回一份拷贝,对拷贝所做的修改不会影响(reflects)原始矩阵,而numpy.ravel()返回的是 ...
- python库numpy的reshape的终极解释
a = np.arange(2*4*4) b = a.reshape(1,4,4,2) #应该这样按反序来理解:最后一个2是一个只有2个元素的向量,最后的4,2代表4×2的矩阵,最 ...
- 小白眼中的AI之~Numpy基础
周末码一文,明天见矩阵- 其实Numpy之类的单讲特别没意思,但不稍微说下后面说实际应用又不行,所以大家就练练手吧 代码裤子: https://github.com/lotapp/BaseCode ...
- numpy基本用法
numpy 简介 numpy的存在使得python拥有强大的矩阵计算能力,不亚于matlab. 官方文档(https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quick ...
- numpy快速指南
Quickstart tutorial 引用https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quickstart.html Prerequisites Before ...
- 课程一(Neural Networks and Deep Learning),第二周(Basics of Neural Network programming)—— 3、Python Basics with numpy (optional)
Python Basics with numpy (optional)Welcome to your first (Optional) programming exercise of the deep ...
- Python Basics with Numpy
Welcome to your first assignment. This exercise gives you a brief introduction to Python. Even if yo ...
- Python Basics with numpy (optional)
Python Basics with Numpy (optional assignment) Welcome to your first assignment. This exercise gives ...
随机推荐
- 类再生(合成、继承、final)
类再生 有两种方法达到代码复用的效果:合成.继承. 合成的语法 合成就是形成对象,把复用的代码置入对象句柄. 在类内字段使用基本数据会初始化为零,但对象句柄会初始化为null.在下面的程序中若没有ne ...
- prometheus被OOM杀死
参考https://www-01.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=ibm10882172 提升内存配置 2.5版本后新增--query.max-samples 这个参数 ...
- final,finally,finalize之间的区别。
fianl:可以修饰类.变量.方法.修饰类不能被继承,修饰变量只能赋值一次,修饰方法不能被重写. finally是try语句体中的一个语句体,不能单独使用,用来释放资源. finalize()是在ja ...
- 2019 游族网络java面试笔试题 (含面试题解析)
本人5年开发经验.18年年底开始跑路找工作,在互联网寒冬下成功拿到阿里巴巴.今日头条.游族网络等公司offer,岗位是Java后端开发,因为发展原因最终选择去了游族网络,入职一年时间了,也成为了面 ...
- ASP.NET Core 2.2在中间件内使用有作用域的服务
服务生存期 为每个注册的服务选择适当的生存期.可以使用以下生存期配置ASP.NET Core服务: 暂时 暂时生存期服务 (AddTransient) 是每次从服务容器进行请求时创建的. 这种生存期适 ...
- Eureka设计原理
1. Eureka设计原理 1.1. 前言 目前我越来越关注技术原理层面的东西,开始考虑中间件设计背后,要考虑哪些因素,为什么要这样设计,有什么优化的地方,这次来讨论Eureka 1.2. 设计问题 ...
- 21、解决关于 vue项目中 点击按钮路由多了个问号
在vue项目开发过程中,点击按钮结果页面刷新了一遍 后来发现路径变成了 localhost:8080/?#/login 原因: 这里是 form 表单,点击了button 按钮,触发了他的默认事件,就 ...
- 动态路由 RIP
不同网段之间进行通信,中间有多个路由器的情况下,我们可以通过配置RIP动态路由来实现数据转发. 实验拓扑 如图所示连接,地址规划如下: 名称 接口 IP地址 R1 f0/0 192.168.10.1/ ...
- Django之mysql数据库配置
在settings.py中配置 DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', # 数据库引擎 'NAME': 'my ...
- SaltStack--使用salt-ssh
SaltStack使用salt-ssh模式 salt-ssh 介绍 参考官档 salt-ssh是 0.17.0 新引入的一个功能,不需要minion对客户端进行管理,也可以不需要master:salt ...
