Transaction-Mybatis源码
github地址:https://github.com/dchack/Mybatis-source-code-learn (欢迎star)
TransactionFactory
官方文档:
在 MyBatis 中有两种类型的事务管理器(也就是 type=”[JDBC|MANAGED]”):
JDBC – 这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
MANAGED – 这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。例如:
<transactionManager type="MANAGED"><property name="closeConnection" value="false"/></transactionManager>提示如果你正在使用 Spring + MyBatis,则没有必要配置事务管理器, 因为 Spring 模块会使用自带的管理器来覆盖前面的配置。
以上配置transactionManager属性来配置使用哪一种TransactionFactory的代码,肯定在MybatisXMLConfigBuilder中可以找到:
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {if (context != null) {String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();factory.setProperties(props);return factory;}throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");}
从TransactionFactory入手:
public interface TransactionFactory {/*** Sets transaction factory custom properties.* @param props*/void setProperties(Properties props);/*** Creates a {@link Transaction} out of an existing connection.* @param conn Existing database connection* @return Transaction* @since 3.1.0*/Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);/*** Creates a {@link Transaction} out of a datasource.* @param dataSource DataSource to take the connection from* @param level Desired isolation level* @param autoCommit Desired autocommit* @return Transaction* @since 3.1.0*/Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);}
TransactionFactory接口描述实现者需要从Connection或DataSource生产org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction出来。
接口实现类如下:
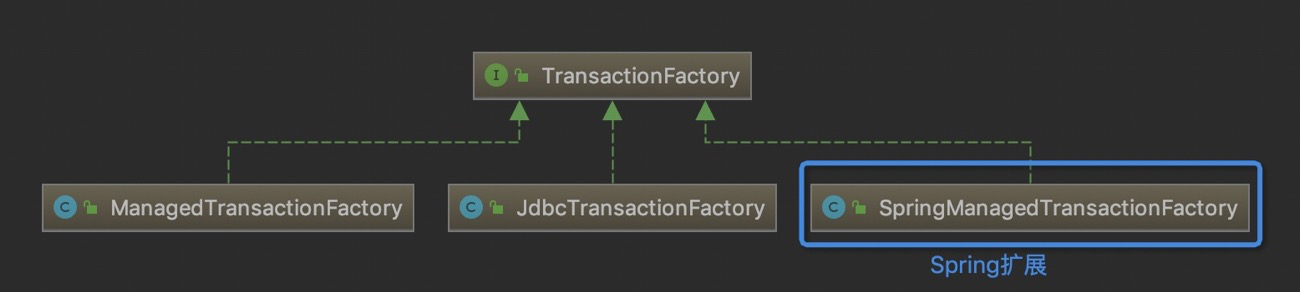
他们各自生产的Transaction分别是:
- JdbcTransaction
- ManagedTransaction
- SpringManagedTransaction
Transaction接口:
/*** Wraps a database connection.* Handles the connection lifecycle that comprises: its creation, preparation, commit/rollback and close.** @author Clinton Begin*/public interface Transaction {/*** Retrieve inner database connection* @return DataBase connection* @throws SQLException*/Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;/*** Commit inner database connection.* @throws SQLException*/void commit() throws SQLException;/*** Rollback inner database connection.* @throws SQLException*/void rollback() throws SQLException;/*** Close inner database connection.* @throws SQLException*/void close() throws SQLException;/*** Get transaction timeout if set* @throws SQLException*/Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;}
抽象出了控制connection生命周期的核心接口:getConnection(create),commit,rollback,close。
JdbcTransaction的实现:
三个操作方法:commit,rollback,close,都是connection的封装而已,commit,rollback执行的条件需要已经生成好connection并且AutoCommit没有设置true,close方法会调用resetAutoCommit方法重置Connection的autoCommit属性为true:
@Overridepublic void commit() throws SQLException {if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.commit();}}@Overridepublic void rollback() throws SQLException {if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.rollback();}}@Overridepublic void close() throws SQLException {if (connection != null) {resetAutoCommit();if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.close();}}
重置autoCommit属性方法:
protected void resetAutoCommit() {try {if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {// MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed.// Some databases start transactions with select statements// and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection.// A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection.// Sybase throws an exception here.if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");}connection.setAutoCommit(true);}} catch (SQLException e) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);}}}
在看下getConnection方法的实现:
@Overridepublic Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {if (connection == null) {openConnection();}return connection;}protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");}connection = dataSource.getConnection();if (level != null) {connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());}setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);}
openConnection中设置了事务隔离级别(transaction isolation level)和autoCommmit。
事务隔离级别在TransactionIsolationLevel枚举中可以看到:
public enum TransactionIsolationLevel {NONE(Connection.TRANSACTION_NONE),READ_COMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED),READ_UNCOMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED),REPEATABLE_READ(Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ),SERIALIZABLE(Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE);private final int level;private TransactionIsolationLevel(int level) {this.level = level;}public int getLevel() {return level;}}
在java.sql.Connection中的定义和注释如下:
/*** A constant indicating that transactions are not supported.*/int TRANSACTION_NONE = 0;/*** A constant indicating that* dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur.* This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read* by another transaction before any changes in that row have been* committed (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back,* the second transaction will have retrieved an invalid row.*/int TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;/*** A constant indicating that* dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads and phantom* reads can occur. This level only prohibits a transaction* from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it.*/int TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;/*** A constant indicating that* dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are prevented; phantom* reads can occur. This level prohibits a transaction from* reading a row with uncommitted changes in it, and it also* prohibits the situation where one transaction reads a row,* a second transaction alters the row, and the first transaction* rereads the row, getting different values the second time* (a "non-repeatable read").*/int TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;/*** A constant indicating that* dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads are prevented.* This level includes the prohibitions in* <code>TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ</code> and further prohibits the* situation where one transaction reads all rows that satisfy* a <code>WHERE</code> condition, a second transaction inserts a row that* satisfies that <code>WHERE</code> condition, and the first transaction* rereads for the same condition, retrieving the additional* "phantom" row in the second read.*/int TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;
关于事务隔离级别
几个概念:
- 脏读:读取的数据可以取到其他未提交事务修改的数据
- 不可重复读:一个事务中多次读取相同的数据,因其他事务在中间修改了这个数据,导致第一个事务多次读的数据会不相同
- 幻读:就是在一个事务提交时发现之前查的条件发生了改变
隔离级别:
- 提交读(READ_COMMITTED)只能读取到已经提交的数据
- 未提交读(READ_UNCOMMITTED)允许脏读
- 可重复读(REPEATABLE_READ)在同一事务中保证多次读取的数据是一致的
- 串行读(SERIALIZABLE)每次读都需要获取表级锁,读写互相阻塞
mysql中查看隔离级别设置:
select @@global.tx_isolation;
另外我们也看到JdbcTransaction中是需要autoCommmit设置true的,否则是不能完成事务功能的。
ManagedTransaction
从类注释上可以看到:ManagedTransaction是将事务的生命周期交给容器管理,可以理解它都是空实现,比如commit,rollback,close可以通过closeConnection字段来关闭。
SpringManagedTransaction
后续进入Mybatis扩展模块时展开。
Transaction-Mybatis源码的更多相关文章
- MyBatis 源码篇-Transaction
本章简单介绍一下 MyBatis 的事务模块,这块内容比较简单,主要为后面介绍 mybatis-spring-1.**.jar(MyBatis 与 Spring 集成)中的事务模块做准备. 类图结构 ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-MyBatis-Spring 剖析
本章通过分析 mybatis-spring-x.x.x.jar Jar 包中的源码,了解 MyBatis 是如何与 Spring 进行集成的. Spring 配置文件 MyBatis 与 Spring ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-DataSource
本章介绍 MyBatis 提供的数据源模块,为后面与 Spring 集成做铺垫,从以下三点出发: 描述 MyBatis 数据源模块的类图结构: MyBatis 是如何集成第三方数据源组件的: Pool ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-插件模块
本章主要描述 MyBatis 插件模块的原理,从以下两点出发: MyBatis 是如何加载插件配置的? MyBatis 是如何实现用户使用自定义拦截器对 SQL 语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截的? 示 ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-日志模块2
上一章的案例,配置日志级别为 debug,执行一个简单的查询操作,会将 JDBC 操作打印出来.本章通过 MyBatis 日志部分源码分析它是如何实现日志打印的. 在 MyBatis 的日志模块中有一 ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-日志模块1
在 Java 开发中常用的日志框架有 Log4j.Log4j2.Apache Common Log.java.util.logging.slf4j 等,这些日志框架对外提供的接口各不相同.本章详细描述 ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-资源加载
本章主要描述 MyBatis 资源加载模块中的 ClassLoaderWrapper 类和 Java 加载配置文件的三种方式. ClassLoaderWrapper 上一章的案例,使用 org.apa ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-SQL 执行的流程
本章通过一个简单的例子,来了解 MyBatis 执行一条 SQL 语句的大致过程是怎样的. 案例代码如下所示: public class MybatisTest { @Test public void ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-整体架构
MyBatis 的整体架构分为三层, 分别是基础支持层.核心处理层和接口层,如下图所示. 基础支持层 反射模块 该模块对 Java 原生的反射进行了良好的封装,提供了更加简洁易用的 API ,方便上层 ...
- MyBatis源码分析-SQL语句执行的完整流程
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简 ...
随机推荐
- kuangbin专题专题四 Silver Cow Party POJ - 3268
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3268 题意:点X处开办排队,其他点的牛到X点去参加派对,然后从X点回到各自的点,通路是单向的,所有牛都要走最短路, 求出所有 ...
- django最小程序开发流程
1.建立工程 在工程目录下打开cmd,输入以下命令.其中mysite是项目名称. django-admin startproject mysite 命令运行完后,在该目录下会出现一个名为mysite的 ...
- CentOS7.5搭建NFS(Network File System)
NFS(Network File System)即网络文件系统,是由Sun公司开发的一种通过网络方式共享文件系统的通用共享解决方案.可以将远程Linux系统上的文件共享资源挂载到本地主机(Linux客 ...
- 到底该不该用RTOS——rtos的优点
我现在要不要学习RTOS? 学习RTOS有什么好处? 我的项目要不要跑RTOS? ······等等一些关于RTOS的问题,其实归根结底还是你对RTOS了解的不够,项目开发的经验还不足等. 针对这部分朋 ...
- Futex同步机制简介
http://blog.csdn.net/u013234805/article/details/24796551 Futex是fast userspacemutex的缩写,意思是快速用户空间互斥体.它 ...
- JS中判断空对象
js 判断空对象 首先要区分一个概念,空对象和空引用: 空对象:{}是指不含任何属性的对象,当然对象属性包括字面值和函数. 空引用:obj=null 是指变量值指向null变量,当然在js默认不赋值的 ...
- 为什么学习JavaScript设计模式,因为它是核心
那么什么是设计模式呢?当我们在玩游戏的时候,我们会去追求如何最快地通过,去追求获得已什么高效率的操作获得最好的奖品:下班回家,我们打开手机app查询最便捷的路线去坐车:叫外卖时候,也会找附近最近又实惠 ...
- uniapp 组件传参
父组件 <v-sub @returnDate=returnDate :backGround=backGround></v-sub> import vSub from " ...
- K8s的存储卷使用总结
K8s的存储卷: 它有四种存储卷: 1. emptyDir: 空目录,这种存储卷会随着Pod的删除而被清空,它一般作为缓存目录使用,或临时目录, 当做缓存目录时,通常会将一块内存空间映射到该目录上,让 ...
- Foxmail: 错误信息::ssl连接错误, errorCode: 5,各种解决方案的大杂烩。
1. 收件数据过多,删除部分邮件可解决 我尝试失败,在foxmail把收件箱全部删完了没解决. 2. 网上最常见的解决方法 https://help.foxmail.com/cgi-bin/hel ...
