动态树之LCT(link-cut tree)讲解
动态树是一类要求维护森林的连通性的题的总称,这类问题要求维护某个点到根的某些数据,支持树的切分,合并,以及对子树的某些操作。其中解决这一问题的某些简化版(不包括对子树的操作)的基础数据结构就是LCT(link-cut tree)。
LCT的大体思想类似于树链剖分中的轻重链剖分(轻重链剖分请移步http://www.cnblogs.com/BLADEVIL/p/3479713.html),轻重链剖分是处理出重链来,由于重链的定义和树链剖分是处理静态树所限,重链不会变化,变化的只是重链上的边或点的权值,由于这个性质,我们用线段树来维护树链剖分中的重链,但是LCT解决的是动态树问题(包含静态树),所以需要用更灵活的splay来维护这里的“重链”(splay请移步http://www.cnblogs.com/BLADEVIL/p/3464458.html)。
定义:
首先来定义一些量:
access(X):表示访问X点(之后会有说明)。
Preferred child(偏爱子节点):如果最后被访问的点在X的儿子P节点的子树中,那么称P为X的Preferred child,如果一个点被访问,他的Preferred child为null(即没有)。
Preferred edge(偏爱边):每个点到自己的Preferred child的边被称为Preferred edge。
Preferred path(偏爱路径):由Preferred edge组成的不可延伸的路径称为Preferred path。
这样我们可以发现一些比较显然的性质,每个点在且仅在一条Preferred path上,也就是所有的Preferred path包含了这棵树上的所有的点,这样一颗树就可以由一些Preferred path来表示(类似于轻重链剖分中的重链),我们用splay来维护每个条Preferred path,关键字为深度,也就是每棵splay中的点左子树的深度都比当前点小,右节点的深度都比当前节点
的深度大。这样的每棵splay我们称为Auxiliary tree(辅助树),每个Auxiliary tree的根节点保存这个Auxiliary tree与上一棵Auxiliary tree中的哪个点相连。这个点称作他的Path parent。
看一个例子
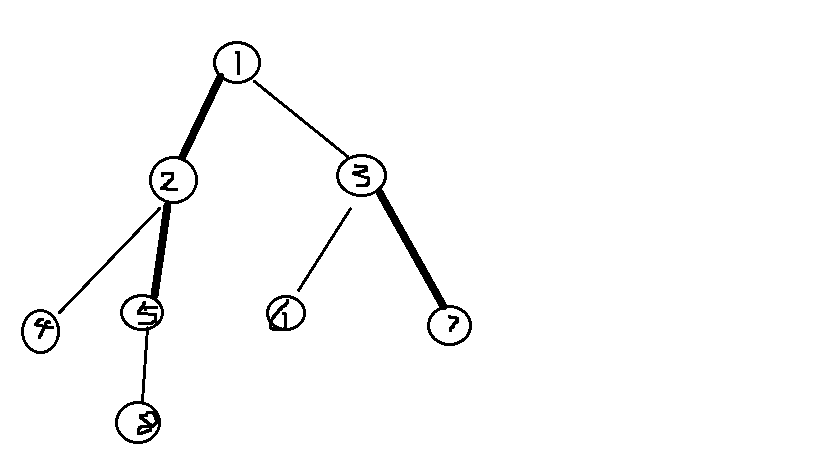
粗的边是Preferred path。那么3-7这个Auxiliary tree中,Path parent为1节点,每个单独的点单独在一棵splay中。以上描述的几个量可以存储这棵树,并且维护相应的信息。
操作:
access(X):首先由于preferred path的定义,如果一个点被访问,那么这个点到根节点的所有的边都会变成preferred edge,由于每个点只有一个preferred child,所以这个点到根节点路径上的所有的点都会和原来的preferred child断开,连接到这条新的preferred path上。假设访问X点,那么先将X点旋转到对应Auxiliary tree的根节点,然后因为被访问的点是没有preferred child的,所以将Auxiliary tree中根节点(X)与右子树的边断掉,左节点保留,将这个树的path parent旋转到对应Auxiliary tree的根节点,断掉右子树,连接这个点与X点,相当于合并两棵Auxiliary tree,不断地重复这一操作,直到当前X所在Auxiliary tree的path parent为null时停止,表示已经完成当前操作。
procedure access(x:longint);
var
y :longint;
begin
splay(x);//旋转
while father[x]<>0 do
begin
y:=father[x];
splay(y);
root[son[y,1]]:=true;//son为子节点son[x,0]代表左子结点,son[x,1]代表右子结点
root[x]:=false;//当前点是否为对应Auxiliary tree的根节点
son[y,1]:=x;
update(y);//更新y点的信息
splay(x);
end;
end;
find root(x):找到某一点所在树的根节点(维护森林时使用)。只需要access(X),然后将X节点旋到对应Auxiliary tree的根节点,然后找到这个Auxiliary tree中最左面的点。
function find root(x:longint):longint;
begin
access(x);
splay(x);//将X旋转到根节点
exit(find(x,-maxlongint));//找到子树中最左面的点
end;
cut(x):断掉X节点和其父节点相连的边。首先access(X),然后将X旋转到对应Auxiliary tree的根节点,然后断掉Auxiliary tree中X和左节点相连的边。
procedure cut(x:longint);
begin
access(x);
splay(x);//旋转x点到根节点
father[son[x,0]]:=0;
root[son[x,0]]:=true;//设置左子树根节点
son[x,0]:=-1;
end;
link(join)(x,y):连接点x到y点上。即让x称为y的子节点。因为x为y的子节点后,在原x的子树中,x点到根节点的所有的点的深度会被翻转过来,所以先access(x),然后在对应的Auxiliary tree中将x旋转到根节点,,然后将左子树翻转(splay中的reverse操作),然后access(y),将y旋转到对应Auxiliary tree中的根节点,将x连到y就行了。
procedure link(x,y:longint);
begin
access(x);
splay(x);
reverse(son[x,0]);
access(y);
splay(y);
son[y,1]:=x;
father[x]:=y;
root[x]:=false;
end;
access操作是LCT的基础,应该熟练掌握并且理解。
时间复杂度:
证明access以及其他操作的时间复杂度是均摊log2N的,具体证明参考杨哲的论文《QTREE 解法的一些研究》。
基础题,bzoj 2002:http://61.187.179.132/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2002
/**************************************************************
Problem: 2002
User: BLADEVIL
Language: Pascal
Result: Accepted
Time:2372 ms
Memory:4328 kb
****************************************************************/
//By BLADEVIL
var
n, m :longint;
father, size :array[-1..200010] of longint;
son :array[-1..200010,0..2] of longint;
root :array[-1..200010] of boolean;
procedure update(x:longint);
begin
size[x]:=size[son[x,0]]+size[son[x,1]]+1;
end;
procedure left_rotate(x:longint);
var
y :longint;
begin
y:=son[x,1];
son[x,1]:=son[y,0];
father[son[x,1]]:=x;
son[y,0]:=x;
if x=son[father[x],0] then
son[father[x],0]:=y else
if x=son[father[x],1] then
son[father[x],1]:=y;
father[y]:=father[x];
father[x]:=y;
root[y]:=root[x] xor root[y];
root[x]:=root[x] xor root[y];
update(x); update(y);
end;
procedure right_rotate(x:longint);
var
y :longint;
begin
y:=son[x,0];
son[x,0]:=son[y,1];
father[son[x,0]]:=x;
son[y,1]:=x;
if x=son[father[x],0] then
son[father[x],0]:=y else
if x=son[father[x],1] then
son[father[x],1]:=y;
father[y]:=father[x];
father[x]:=y;
root[y]:=root[y] xor root[x];
root[x]:=root[y] xor root[x];
update(x); update(y);
end;
procedure splay(x:longint);
begin
while not root[x] do
if x=son[father[x],1] then
left_rotate(father[x]) else
right_rotate(father[x]);
end;
procedure access(x:longint);
var
y :longint;
begin
splay(x);
while father[x]<>0 do
begin
y:=father[x];
splay(y);
root[son[y,1]]:=true;
root[x]:=false;
son[y,1]:=x;
update(y);
splay(x);
end;
end;
procedure init;
var
i :longint;
begin
read(n);
for i:=1 to n do
begin
read(father[i]);
father[i]:=father[i]+i;
if father[i]>n then father[i]:=n+1;
end;
read(m);
end;
procedure main;
var
i :longint;
x, y, z :longint;
begin
for i:=1 to n+1 do size[i]:=1;
fillchar(root,sizeof(root),true);
for i:=1 to m do
begin
read(x);
if x=1 then
begin
read(y); inc(y);
access(y);
writeln(size[son[y,0]]);
end else
begin
read(y,z); inc(y);
splay(y);
father[son[y,0]]:=father[y];
root[son[y,0]]:=true;
son[y,0]:=0;
size[y]:=size[son[y,1]]+1;
father[y]:=y+z;
if father[y]>n then father[y]:=n+1;
end;
end;
end;
begin
init;
main;
end.
动态树之LCT(link-cut tree)讲解的更多相关文章
- LCT(link cut tree) 动态树
模板参考:https://blog.csdn.net/saramanda/article/details/55253627 综合各位大大博客后整理的模板: #include<iostream&g ...
- 动态树(LCT、Top Tree、ETT)
LCT Upd: 一个细节:假如我们要修改某个节点的数据,那么要先把它makeroot再修改,改完之后pushup. LCT是一种维护森林的数据结构,本质是用Splay维护实链剖分. 实链剖分大概是这 ...
- 【学习笔记】LCT link cut tree
大概就是供自己复习的吧 1. 细节讲解 安利两篇blog: Menci 非常好的讲解与题单 2.模板 把 $ rev $ 和 $ pushdown $ 的位置记清 #define lc son[x][ ...
- Link Cut Tree学习笔记
从这里开始 动态树问题和Link Cut Tree 一些定义 access操作 换根操作 link和cut操作 时间复杂度证明 Link Cut Tree维护链上信息 Link Cut Tree维护子 ...
- LCT总结——概念篇+洛谷P3690[模板]Link Cut Tree(动态树)(LCT,Splay)
为了优化体验(其实是强迫症),蒟蒻把总结拆成了两篇,方便不同学习阶段的Dalao们切换. LCT总结--应用篇戳这里 概念.性质简述 首先介绍一下链剖分的概念(感谢laofu的讲课) 链剖分,是指一类 ...
- LuoguP3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树) LCT模板
P3690 [模板]Link Cut Tree (动态树) 题目背景 动态树 题目描述 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两 ...
- P3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树)
P3690 [模板]Link Cut Tree (动态树) 认父不认子的lct 注意:不 要 把 $fa[x]$和$nrt(x)$ 混 在 一 起 ! #include<cstdio> v ...
- 【刷题】洛谷 P3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树)
题目背景 动态树 题目描述 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两个整数(x,y),代表询问从x到y的路径上的点的权值的xor ...
- LG3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树)
题意 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两个整数(x,y),代表询问从x到y的路径上的点的权值的xor和.保证x到y是联通的 ...
- 洛谷P3690 [模板] Link Cut Tree [LCT]
题目传送门 Link Cut Tree 题目背景 动态树 题目描述 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两个整数(x,y),代 ...
随机推荐
- Android—定位
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { private Button ...
- XML语言基础2 DTD
XML DTD 文档类型定义(DTD)可定义合法的XML文档构建模块.它使用一系列合法的元素来定义文档结构. DTD可被声明于XML文档中,也可以作为一个外部的引用. 内部的DOCTYPE声明 假如D ...
- java获取注册ip
String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for"); if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || &q ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(12):Hadoop命令中
阅读目录 序 HDFS Commands User Commands Administration Commands Debug Commands 引用 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共 ...
- Python学习笔记2-解析数据
Import os; -- Python自带 print(os.getcwd()) -- 获得当前工作目录 os.chdir('/Users/longlong/Documents') -- 转换到/U ...
- StarkSoft题库管理系统(二)--生成word格式试卷
一.功能介绍 1.自定义试题库管理系统目录.难易程度,题型,知识库等. 2.试题录入. 3.强大的试题编辑功能,并与通常应用编辑工具有共通. 4.灵活的试卷构造功能,用户可自定 ...
- Android 上实现像微信一样的用Fragment来实现的Tab切页效果 提供源码下载
网有不少的例子,但是要么是像微信一样可是没有使用Fragment实现,要么是只实现了一个很简单的切换,没有下面的菜单页.这个例子有实现了,我觉得暂时够我用了##实现类:+ MainTabFragmen ...
- java中对象产生初始化过程
以前面试的时候,很多公司的笔试题中有关new一个对象有关一系列初始化的过程的选择题目.请看下面的题目. class Parent { static { System.out.println(" ...
- 【转】What is an SDET
What is an SDET? SDET stands for Software Development Engineer in Test (or Software Design Engineer ...
- 手把手教你玩GDB
第一部分牛刀小试:启动GDB开始调试 1. 编译带调试信息的可执行程序:用gcc(g++)编译的时候带上-g选项即可 2. 启动GDB开始调试 (1)gdb program ...
