Codeforces Round #175 (Div. 2) A~D 题解
A.Slightly Decreasing Permutations
Permutation p is an ordered set of integers p1, p2, ..., pn, consisting of n distinct positive integers, each of them doesn't exceed n. We'll denote the i-th element of permutation p as pi. We'll call number n the size or the length of permutation p1, p2, ..., pn.
The decreasing coefficient of permutation p1, p2, ..., pn is the number of such i (1 ≤ i < n), that pi > pi + 1.
You have numbers n and k. Your task is to print the permutation of length n with decreasing coefficient k.
The single line contains two space-separated integers: n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k < n) — the permutation length and the decreasing coefficient.
In a single line print n space-separated integers: p1, p2, ..., pn — the permutation of length n with decreasing coefficient k.
If there are several permutations that meet this condition, print any of them. It is guaranteed that the permutation with the sought parameters exists.
5 2
1 5 2 4 3
3 0
1 2 3
3 2
3 2 1
构造题;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<time.h>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 2000005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mclr(x,a) memset((x),a,sizeof(x))
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 100000007;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n, k; int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> k;
if (k == 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cout << i << ' ';
return 0;
} for (int i = 1; i < n - k; i++) {
cout << i << ' ';
}
for (int i = n; i >= n - k; i--)cout << i << ' '; return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Petya and Vasya are playing a game. Petya's got n non-transparent glasses, standing in a row. The glasses' positions are indexed with integers from 1 to n from left to right. Note that the positions are indexed but the glasses are not.
First Petya puts a marble under the glass in position s. Then he performs some (possibly zero) shuffling operations. One shuffling operation means moving the glass from the first position to position p1, the glass from the second position to position p2 and so on. That is, a glass goes from position i to position pi. Consider all glasses are moving simultaneously during one shuffling operation. When the glasses are shuffled, the marble doesn't travel from one glass to another: it moves together with the glass it was initially been put in.
After all shuffling operations Petya shows Vasya that the ball has moved to position t. Vasya's task is to say what minimum number of shuffling operations Petya has performed or determine that Petya has made a mistake and the marble could not have got from position s to position t.
The first line contains three integers: n, s, t (1 ≤ n ≤ 105; 1 ≤ s, t ≤ n) — the number of glasses, the ball's initial and final position. The second line contains n space-separated integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the shuffling operation parameters. It is guaranteed that all pi's are distinct.
Note that s can equal t.
If the marble can move from position s to position t, then print on a single line a non-negative integer — the minimum number of shuffling operations, needed to get the marble to position t. If it is impossible, print number -1.
4 2 1
2 3 4 1
3
4 3 3
4 1 3 2
0
4 3 4
1 2 3 4
-1
3 1 3
2 1 3
-1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<time.h>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mclr(x,a) memset((x),a,sizeof(x))
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 100000007;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n, s, t;
int p[maxn]; int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
n = rd(); s = rd(); t = rd();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)p[i] = rd();
if (s == t) {
puts("0"); return 0;
}
bool fg = 1;
int cnt = 0;
int pos = s;
while (1) {
pos = p[pos]; cnt++;
if (pos == s) {
fg = 0; break;
}
else if (pos == t) {
break;
}
}
if (fg == 0)cout << -1 << endl;
else {
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Permutation p is an ordered set of integers p1, p2, ..., pn, consisting of n distinct positive integers, each of them doesn't exceed n. We'll denote the i-th element of permutation p as pi. We'll call number n the size or the length of permutation p1, p2, ..., pn.
You have a sequence of integers a1, a2, ..., an. In one move, you are allowed to decrease or increase any number by one. Count the minimum number of moves, needed to build a permutation from this sequence.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·105) — the size of the sought permutation. The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Print a single number — the minimum number of moves.
Please, do not use the %lld specifier to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams or the %I64d specifier.
2
3 0
2
3
-1 -1 2
6
In the first sample you should decrease the first number by one and then increase the second number by one. The resulting permutation is (2, 1).
In the second sample you need 6 moves to build permutation (1, 3, 2).
贪心地从小到大排序;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<time.h>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 500005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mclr(x,a) memset((x),a,sizeof(x))
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 100000007;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n;
int a[maxn]; int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
n = rd();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i] = rd();
ll tot = 0;
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
tot += 1ll * abs(i - a[i]);
}
cout << (ll)tot << endl;
return 0;
}
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Permutation p is an ordered set of integers p1, p2, ..., pn, consisting of n distinct positive integers, each of them doesn't exceed n. We'll denote the i-th element of permutation p as pi. We'll call number n the size or the length of permutation p1, p2, ..., pn.
Petya decided to introduce the sum operation on the set of permutations of length n. Let's assume that we are given two permutations of length n: a1, a2, ..., an and b1, b2, ..., bn. Petya calls the sum of permutations a and b such permutation c of length n, where ci = ((ai - 1 + bi - 1) mod n) + 1 (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
Operation 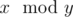 means taking the remainder after dividing number x by number y.
means taking the remainder after dividing number x by number y.
Obviously, not for all permutations a and b exists permutation c that is sum of a and b. That's why Petya got sad and asked you to do the following: given n, count the number of such pairs of permutations a and b of length n, that exists permutation c that is sum of a and b. The pair of permutations x, y (x ≠ y) and the pair of permutations y, x are considered distinct pairs.
As the answer can be rather large, print the remainder after dividing it by 1000000007 (109 + 7).
The single line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 16).
In the single line print a single non-negative integer — the number of such pairs of permutations a and b, that exists permutation c that is sum of a and b, modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
3
18
5
1800

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<time.h>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 500005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mclr(x,a) memset((x),a,sizeof(x))
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ ll ans[20];
ll fac[20];
ll a[20], b[20];
ll res;
bool use[20], vis[20];
int n;
void dfs(int pos,int up) {
if (pos == up + 1) {
res++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= up; i++) {
if (use[i])continue;
int C = (a[pos] + i - 2) % up + 1;
if (vis[C])continue;
use[i] = 1; vis[C] = 1;
dfs(pos + 1, up);
use[i] = 0; vis[C] = 0;
}
} int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
n = rd();
fac[0] = 1ll;
for (int i = 1; i <= 16; i++)fac[i] = (i*fac[i - 1]) % mod;
/* for (int j = 1; j <= 16; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= j; i++)a[i] = i;
ms(vis); ms(use);
res = 0; dfs(1, j);
printf("j=%d , ans=%d\n ", j, res);
}
*/
ans[1] = 1; ans[2] = 0; ans[3] = 3;
ans[4] = 0; ans[5] = 15; ans[6] = 0; ans[7] = 133;
ans[8] = 0; ans[9] = 2025; ans[10] = 0;
ans[11] = 37851; ans[12] = 0; ans[13] = 1030367;
ans[14] = 0; ans[15] = 36362925; ans[16] = 0;
cout << (ll)ans[n] * fac[n] % mod << endl; return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #175 (Div. 2) A~D 题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #612 (Div. 2) 前四题题解
这场比赛的出题人挺有意思,全部magic成了青色. 还有题目中的图片特别有趣. 晚上没打,开virtual contest打的,就会前三道,我太菜了. 最后看着题解补了第四道. 比赛传送门 A. An ...
- Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 2)A,B题解
Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 2) 昨天看到奋斗群的群赛,好奇的去做了一下, 大概花了3个小时Ak,我大概可以退役了吧 那下面来稍微总结一下 A. The Wall Iahu ...
- Codeforces Round #672 (Div. 2) A - C1题解
[Codeforces Round #672 (Div. 2) A - C1 ] 题目链接# A. Cubes Sorting 思路: " If Wheatley needs more th ...
- Codeforces Round #614 (Div. 2) A-E简要题解
链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1293 A. ConneR and the A.R.C. Markland-N 题意:略 思路:上下枚举1000次扫一遍,比较一下 ...
- Codeforces Round #610 (Div. 2) A-E简要题解
contest链接: https://codeforces.com/contest/1282 A. Temporarily unavailable 题意: 给一个区间L,R通有网络,有个点x,在x+r ...
- Codeforces Round #611 (Div. 3) A-F简要题解
contest链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1283 A. Minutes Before the New Year 题意:给一个当前时间,输出离第二天差多少分钟 ...
- Codeforces Round #499 (Div. 2) D. Rocket题解
题目: http://codeforces.com/contest/1011/problem/D This is an interactive problem. Natasha is going to ...
- Codeforces Round #499 (Div. 2) C Fly题解
题目 http://codeforces.com/contest/1011/problem/C Natasha is going to fly on a rocket to Mars and retu ...
- Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 2)C,D题解
接着是C,D的题解 C. Tourist Problem Iahub is a big fan of tourists. He wants to become a tourist himself, s ...
随机推荐
- C#使用 SharpAVI进行 屏幕录制
再 nuget 中 搜索 shapAvi 并添加引用 github 地址:https://github.com/baSSiLL/SharpAvi using SharpAvi; using Sharp ...
- 供参考的 php 学习路线
供参考的 php 学习路线 第一阶段第一讲,WEB基础 1.1 网站基本知识: 1.2 网络协议介绍: 1.3 B/S与C/S结构的区别: 1.4 WEB编程.网站开发技术介绍. ...
- 453. Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements 一次改2个数,变成统一的
[抄题]: Given a non-empty integer array of size n, find the minimum number of moves required to make a ...
- 搭建大数据hadoop完全分布式环境遇到的坑
搭建大数据hadoop完全分布式环境,遇到很多问题,这里记录一部分,以备以后查看. 1.在安装配置完hadoop以后,需要格式化namenode,输入指令:hadoop namenode -forma ...
- R dataframe 遗忘, which 矩阵搜索
A data frame is used for storing data tables. It is a list of vectors of equal length. For example, ...
- CF 1091E New Year and the Factorisation Collaboration
昨晚Good Bye 2018D题没做出来,车翻大了…… 官方题解 传送门 初赛知识:一个无向图所有顶点度数之和为偶数.然而这东西还有一个高端的名字:Handshaking lemma 但是 ...
- jquery表单数据反序列化为字典
.前台代码 <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="WebForm1 ...
- NSString 对象保存在哪? @“xxx”和 stringWithFormat:@"xxx" 区别?
NSString *str1=@"string";//这种是保存在常量池 NSString *str2=@"string"; NSLog(@"str1 ...
- (转)不定义JQuery插件,不要说会JQuery
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xcj26/p/3345556.html 一:导言 有些WEB开发者,会引用一个JQuery类库,然后在网页上写一写$("#" ...
- Mac OS X 下android环境搭建
安装jdk6.0版本以支持eclipse的安装 安装eclipse 安装jdk8.0版本,实际开发中用到的jdk 配置java环境变量 打开shell命令窗口(终端) 检测输入java -versio ...
