FASTX-Toolkit组件用法
FASTX-Toolkit组件用法
- Command Line Arguments
- FASTQ-to-FASTA
- FASTQ/A Quality Statistics
- FASTQ Quality chart
- FASTQ/A Nucleotide Distribution chart
- FASTQ/A Clipper
- FASTQ/A Renamer
- FASTQ/A Trimmer
- FASTQ/A Collapser
- FASTQ/A Artifacts Filter
- FASTQ Quality Filter
- FASTQ/A Reverse Complement
- FASTA Formatter
- FASTA nucleotides changer
- FASTA Clipping Histogram
- FASTX Barcode Splitter
- 示例:FASTQ信息
- 示例:FASTQ/A操作
- 示例:fastx_barcode_splitter.pl操作
命令行参数
- 大多数子工具都可以使用 -h 参数查看具体用法。
- 大多数子工具默认从环境输入STDIN读取数据,STDOUT输出数据,或者使用-i参数指定的文件中读取数据,然后输出到-o参数指定的输出文件中。
- 部分工具不输出,或者使用-v参数简短输出。
如果输出信息到环境STDOUT,运行信息就会输出到环境STDERR。
如果输出信息到文件,运行信息就会输出到环境STDOUT。 - 部分工具使用-z参数以压缩方式输出。
FASTQ-to-FASTA
$ fastq_to_fasta -h
usage: fastq_to_fasta [-h] [-r] [-n] [-v] [-z] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-r] = Rename sequence identifiers to numbers.
[-n] = keep sequences with unknown (N) nucleotides.
Default is to discard such sequences.
[-v] = Verbose - report number of sequences.
If [-o] is specified, report will be printed to STDOUT.
If [-o] is not specified (and output goes to STDOUT),
report will be printed to STDERR.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTX Statistics
$ fastx_quality_stats -h
usage: fastx_quality_stats [-h] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6 (C) 2008 by Assaf Gordon (gordon@cshl.edu)
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
If FASTA file is given, only nucleotides
distribution is calculated (there's no quality info).
[-o OUTFILE] = TEXT output file. default is STDOUT. The output TEXT file will have the following fields (one row per column):
column = column number (1 to 36 for a 36-cycles read solexa file)
count = number of bases found in this column.
min = Lowest quality score value found in this column.
max = Highest quality score value found in this column.
sum = Sum of quality score values for this column.
mean = Mean quality score value for this column.
Q1 = 1st quartile quality score.
med = Median quality score.
Q3 = 3rd quartile quality score.
IQR = Inter-Quartile range (Q3-Q1).
lW = 'Left-Whisker' value (for boxplotting).
rW = 'Right-Whisker' value (for boxplotting).
A_Count = Count of 'A' nucleotides found in this column.
C_Count = Count of 'C' nucleotides found in this column.
G_Count = Count of 'G' nucleotides found in this column.
T_Count = Count of 'T' nucleotides found in this column.
N_Count = Count of 'N' nucleotides found in this column.
max-count = max. number of bases (in all cycles)
FASTQ Quality Chart
$ fastq_quality_boxplot_graph.sh -h
Solexa-Quality BoxPlot plotter
Generates a solexa quality score box-plot graph Usage: /usr/local/bin/fastq_quality_boxplot_graph.sh [-i INPUT.TXT] [-t TITLE] [-p] [-o OUTPUT] [-p] - Generate PostScript (.PS) file. Default is PNG image.
[-i INPUT.TXT] - Input file. Should be the output of "solexa_quality_statistics" program.
[-o OUTPUT] - Output file name. default is STDOUT.
[-t TITLE] - Title (usually the solexa file name) - will be plotted on the graph.
FASTA/Q Nucleotide Distribution
$ fastx_nucleotide_distribution_graph.sh -h
FASTA/Q Nucleotide Distribution Plotter Usage: /usr/local/bin/fastx_nucleotide_distribution_graph.sh [-i INPUT.TXT] [-t TITLE] [-p] [-o OUTPUT] [-p] - Generate PostScript (.PS) file. Default is PNG image.
[-i INPUT.TXT] - Input file. Should be the output of "fastx_quality_statistics" program.
[-o OUTPUT] - Output file name. default is STDOUT.
[-t TITLE] - Title - will be plotted on the graph.
FASTA/Q Clipper
$ fastx_clipper -h
usage: fastx_clipper [-h] [-a ADAPTER] [-D] [-l N] [-n] [-d N] [-c] [-C] [-o] [-v] [-z] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-a ADAPTER] = ADAPTER string. default is CCTTAAGG (dummy adapter).
[-l N] = discard sequences shorter than N nucleotides. default is 5.
[-d N] = Keep the adapter and N bases after it.
(using '-d 0' is the same as not using '-d' at all. which is the default).
[-c] = Discard non-clipped sequences (i.e. - keep only sequences which contained the adapter).
[-C] = Discard clipped sequences (i.e. - keep only sequences which did not contained the adapter).
[-k] = Report Adapter-Only sequences.
[-n] = keep sequences with unknown (N) nucleotides. default is to discard such sequences.
[-v] = Verbose - report number of sequences.
If [-o] is specified, report will be printed to STDOUT.
If [-o] is not specified (and output goes to STDOUT),
report will be printed to STDERR.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-D] = DEBUG output.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTA/Q Renamer
$ fastx_renamer -h
usage: fastx_renamer [-n TYPE] [-h] [-z] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE]
Part of FASTX Toolkit 0.0.10 by A. Gordon (gordon@cshl.edu) [-n TYPE] = rename type:
SEQ - use the nucleotides sequence as the name.
COUNT - use simply counter as the name.
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTA/Q Trimmer
$ fastx_trimmer -h
usage: fastx_trimmer [-h] [-f N] [-l N] [-z] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-f N] = First base to keep. Default is 1 (=first base).
[-l N] = Last base to keep. Default is entire read.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTA/Q Collapser
$ fastx_collapser -h
usage: fastx_collapser [-h] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-v] = verbose: print short summary of input/output counts
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTQ/A Artifacts Filter
$ fastx_artifacts_filter -h
usage: fastq_artifacts_filter [-h] [-v] [-z] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-v] = Verbose - report number of processed reads.
If [-o] is specified, report will be printed to STDOUT.
If [-o] is not specified (and output goes to STDOUT),
report will be printed to STDERR.
FASTQ Quality Filter
$ fastq_quality_filter -h
usage: fastq_quality_filter [-h] [-v] [-q N] [-p N] [-z] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-q N] = Minimum quality score to keep.
[-p N] = Minimum percent of bases that must have [-q] quality.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
[-v] = Verbose - report number of sequences.
If [-o] is specified, report will be printed to STDOUT.
If [-o] is not specified (and output goes to STDOUT),
report will be printed to STDERR.
FASTQ/A Reverse Complement
$ fastx_reverse_complement -h
usage: fastx_reverse_complement [-h] [-r] [-z] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] version 0.0.6
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
FASTA Formatter
$ fasta_formatter -h
usage: fasta_formatter [-h] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] [-w N] [-t] [-e]
Part of FASTX Toolkit 0.0.7 by gordon@cshl.edu [-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
[-w N] = max. sequence line width for output FASTA file.
When ZERO (the default), sequence lines will NOT be wrapped -
all nucleotides of each sequences will appear on a single
line (good for scripting).
[-t] = Output tabulated format (instead of FASTA format).
Sequence-Identifiers will be on first column,
Nucleotides will appear on second column (as single line).
[-e] = Output empty sequences (default is to discard them).
Empty sequences are ones who have only a sequence identifier,
but not actual nucleotides. Input Example:
>MY-ID
AAAAAGGGGG
CCCCCTTTTT
AGCTN Output example with unlimited line width [-w 0]:
>MY-ID
AAAAAGGGGGCCCCCTTTTTAGCTN Output example with max. line width=7 [-w 7]:
>MY-ID
AAAAAGG
GGGTTTT
TCCCCCA
GCTN Output example with tabular output [-t]:
MY-ID AAAAAGGGGGCCCCCTTTTAGCTN example of empty sequence:
(will be discarded unless [-e] is used)
>REGULAR-SEQUENCE-1
AAAGGGTTTCCC
>EMPTY-SEQUENCE
>REGULAR-SEQUENCE-2
AAGTAGTAGTAGTAGT
GTATTTTATAT
FASTA Nucleotides Changer
$ fasta_nucleotide_changer -h
usage: fasta_nucleotide_changer [-h] [-z] [-v] [-i INFILE] [-o OUTFILE] [-r] [-d] version 0.0.7
[-h] = This helpful help screen.
[-z] = Compress output with GZIP.
[-v] = Verbose mode. Prints a short summary.
with [-o], summary is printed to STDOUT.
Otherwise, summary is printed to STDERR.
[-i INFILE] = FASTA/Q input file. default is STDIN.
[-o OUTFILE] = FASTA/Q output file. default is STDOUT.
[-r] = DNA-to-RNA mode - change T's into U's.
[-d] = RNA-to-DNA mode - change U's into T's.
FASTA Clipping Histogram
$ fasta_clipping_histogram.pl
Create a Linker Clipping Information Histogram usage: fasta_clipping_histogram.pl INPUT_FILE.FA OUTPUT_FILE.PNG INPUT_FILE.FA = input file (in FASTA format, can be GZIPped)
OUTPUT_FILE.PNG = histogram image
FASTX Barcode Splitter
$ fastx_barcode_splitter.pl
Barcode Splitter, by Assaf Gordon (gordon@cshl.edu), 11sep2008 This program reads FASTA/FASTQ file and splits it into several smaller files,
Based on barcode matching.
FASTA/FASTQ data is read from STDIN (format is auto-detected.)
Output files will be writen to disk.
Summary will be printed to STDOUT. usage: /usr/local/bin/fastx_barcode_splitter.pl --bcfile FILE --prefix PREFIX [--suffix SUFFIX] [--bol|--eol]
[--mismatches N] [--exact] [--partial N] [--help] [--quiet] [--debug] Arguments: --bcfile FILE - Barcodes file name. (see explanation below.)
--prefix PREFIX - File prefix. will be added to the output files. Can be used
to specify output directories.
--suffix SUFFIX - File suffix (optional). Can be used to specify file
extensions.
--bol - Try to match barcodes at the BEGINNING of sequences.
(What biologists would call the 5' end, and programmers
would call index 0.)
--eol - Try to match barcodes at the END of sequences.
(What biologists would call the 3' end, and programmers
would call the end of the string.)
NOTE: one of --bol, --eol must be specified, but not both.
--mismatches N - Max. number of mismatches allowed. default is 1.
--exact - Same as '--mismatches 0'. If both --exact and --mismatches
are specified, '--exact' takes precedence.
--partial N - Allow partial overlap of barcodes. (see explanation below.)
(Default is not partial matching)
--quiet - Don't print counts and summary at the end of the run.
(Default is to print.)
--debug - Print lots of useless debug information to STDERR.
--help - This helpful help screen. Example (Assuming 's_2_100.txt' is a FASTQ file, 'mybarcodes.txt' is
the barcodes file): $ cat s_2_100.txt | /usr/local/bin/fastx_barcode_splitter.pl --bcfile mybarcodes.txt --bol --mismatches 2 \
--prefix /tmp/bla_ --suffix ".txt" Barcode file format
-------------------
Barcode files are simple text files. Each line should contain an identifier
(descriptive name for the barcode), and the barcode itself (A/C/G/T),
separated by a TAB character. Example: #This line is a comment (starts with a 'number' sign)
BC1 GATCT
BC2 ATCGT
BC3 GTGAT
BC4 TGTCT For each barcode, a new FASTQ file will be created (with the barcode's
identifier as part of the file name). Sequences matching the barcode
will be stored in the appropriate file. Running the above example (assuming "mybarcodes.txt" contains the above
barcodes), will create the following files:
/tmp/bla_BC1.txt
/tmp/bla_BC2.txt
/tmp/bla_BC3.txt
/tmp/bla_BC4.txt
/tmp/bla_unmatched.txt
The 'unmatched' file will contain all sequences that didn't match any barcode. Barcode matching
---------------- ** Without partial matching: Count mismatches between the FASTA/Q sequences and the barcodes.
The barcode which matched with the lowest mismatches count (providing the
count is small or equal to '--mismatches N') 'gets' the sequences. Example (using the above barcodes):
Input Sequence:
GATTTACTATGTAAAGATAGAAGGAATAAGGTGAAG Matching with '--bol --mismatches 1':
GATTTACTATGTAAAGATAGAAGGAATAAGGTGAAG
GATCT (1 mismatch, BC1)
ATCGT (4 mismatches, BC2)
GTGAT (3 mismatches, BC3)
TGTCT (3 mismatches, BC4) This sequence will be classified as 'BC1' (it has the lowest mismatch count).
If '--exact' or '--mismatches 0' were specified, this sequence would be
classified as 'unmatched' (because, although BC1 had the lowest mismatch count,
it is above the maximum allowed mismatches). Matching with '--eol' (end of line) does the same, but from the other side
of the sequence. ** With partial matching (very similar to indels): Same as above, with the following addition: barcodes are also checked for
partial overlap (number of allowed non-overlapping bases is '--partial N'). Example:
Input sequence is ATTTACTATGTAAAGATAGAAGGAATAAGGTGAAG
(Same as above, but note the missing 'G' at the beginning.) Matching (without partial overlapping) against BC1 yields 4 mismatches:
ATTTACTATGTAAAGATAGAAGGAATAAGGTGAAG
GATCT (4 mismatches) Partial overlapping would also try the following match:
-ATTTACTATGTAAAGATAGAAGGAATAAGGTGAAG
GATCT (1 mismatch) Note: scoring counts a missing base as a mismatch, so the final
mismatch count is 2 (1 'real' mismatch, 1 'missing base' mismatch).
If running with '--mismatches 2' (meaning allowing upto 2 mismatches) - this
seqeunce will be classified as BC1.
示例: FASTQ信息
Genrating Quality Information on BC54.fq:
$ fastx_quality_stats -i BC54.fq -o bc54_stats.txt
$ fastq_quality_boxplot_graph.sh -i bc54_stats.txt -o bc54_quality.png -t "My Library"
$ fastx_nucleotide_distribution_graph.sh -i bc54_stats.txt -o bc54_nuc.png -t "My Library"
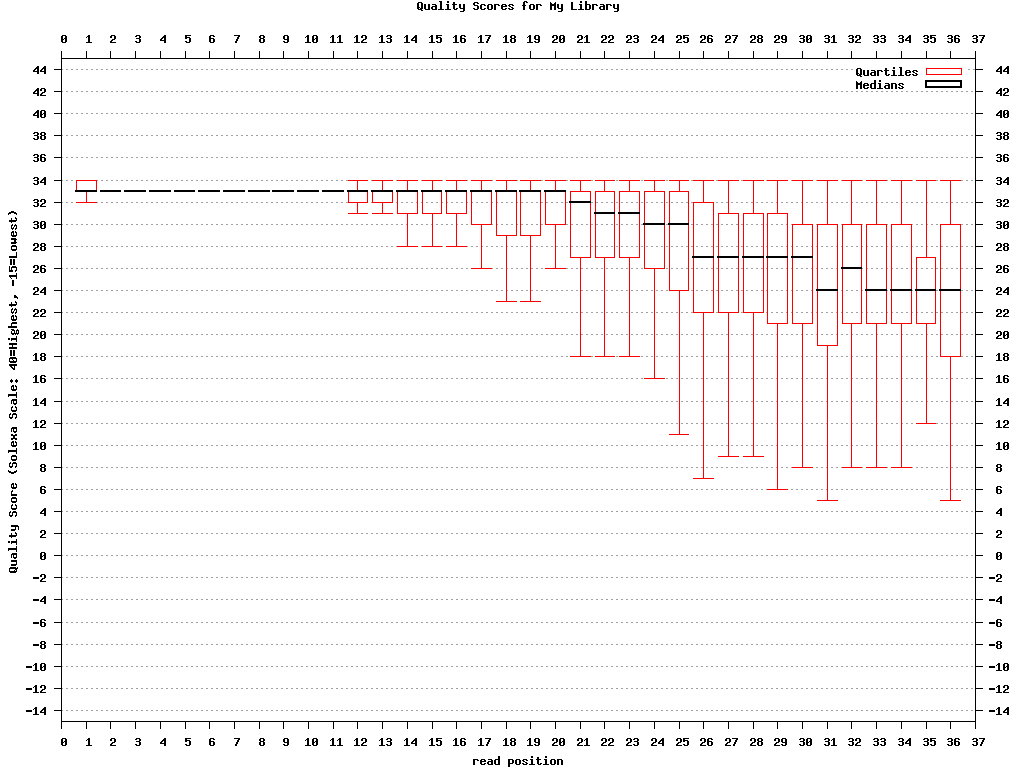 bc54_quality.png (click to enlarge) |
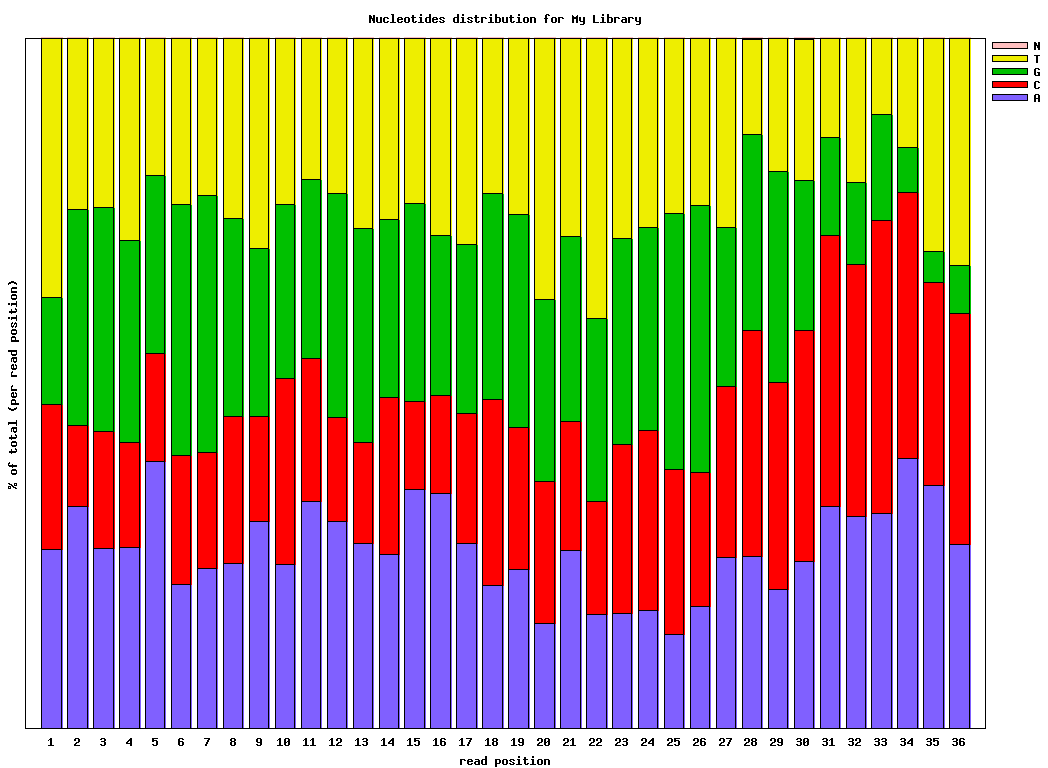 bc54_nuc.png (click to enlarge) |
示例: FASTQ/A操作
Common pre-processing work-flow:
- Covnerting FASTQ to FASTA
- Clipping the Adapter/Linker
- Trimming to 27nt (if you're analyzing miRNAs, for example)
- Collapsing the sequences
- Plotting the clipping results
Using the FASTX-toolkit from the command line:
$ fastq_to_fasta -v -n -i BC54.fq -o BC54.fa
Input: 100000 reads.
Output: 100000 reads.
$ fastx_clipper -v -i BC54.fa -a CTGTAGGCACCATCAATTCGTA -o BC54.clipped.fa
Clipping Adapter: CTGTAGGCACCATCAATTCGTA
Min. Length: 15
Input: 100000 reads.
Output: 92533 reads.
discarded 468 too-short reads.
discarded 6939 adapter-only reads.
discarded 60 N reads.
$ fastx_trimmer -v -f 1 -l 27 -i BC54.clipped.fa -o BC54.trimmed.fa
Trimming: base 1 to 27
Input: 92533 reads.
Output: 92533 reads.
$ fastx_collapser -v -i BC54.trimmed.fa -o BC54.collapsed.fa
Collapsd 92533 reads into 36431 unique sequences.
$ fasta_clipping_histogram.pl BC54.collapsed.fa bc54_clipping.png (alternatively, run it all together with shell pipes ) $ cat BC54.fq | fastq_to_fasta -n | fastx_clipper -l 15 -a CTGTAGGCACCATCAATTCGTA | \
fastx_trimmer -f 1 -l 27 | fastx_collapser > bc54.final.fa
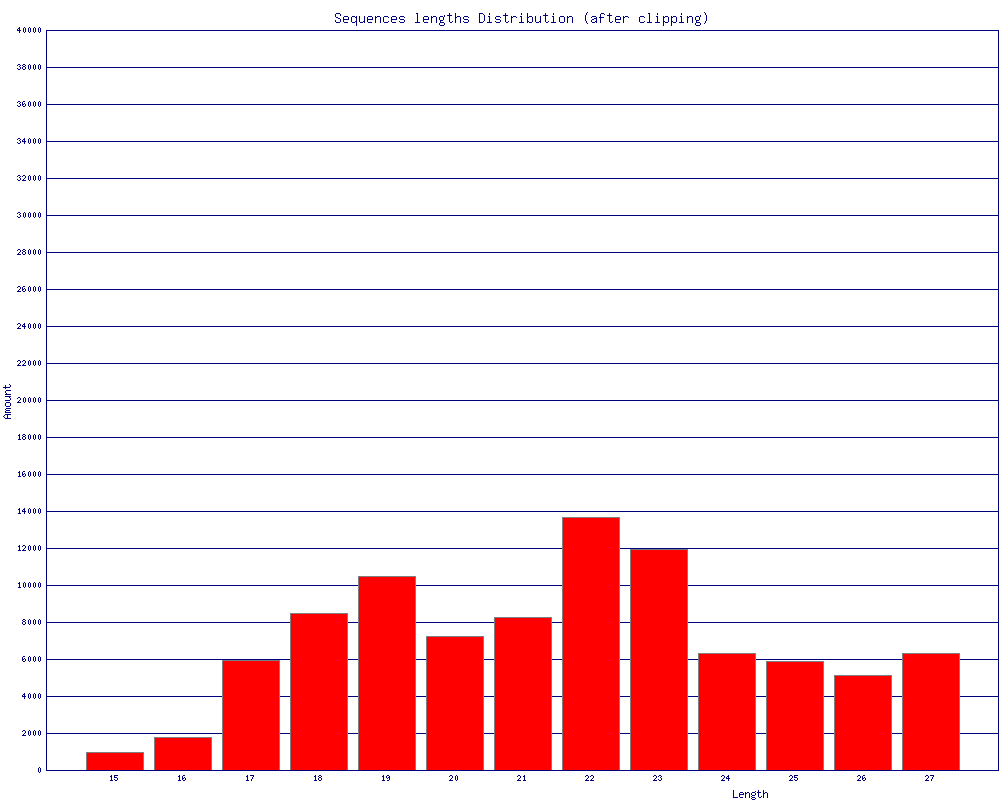 bc54_clipping.png (click to enlarge) |
Mapping (or any other kind of analysis) of the Clipped + Collapsed FASTA file will be:
- quicker - each unique sequence appears only once in the FASTA file.
- more accurate - the Adapter/Linker sequence was removed from the 3' end, and will affect the mapping results.
示例:fastx_barcode_splitter.pl操作
使用shell多进程快速分割多个fq.gz文件。
#! /bin/bash # 编写*.fq.gz样本分割函数
function split_fq() {
zcat $1 |/usr/local/bin/fastx_barcode_splitter.pl --bcfile barcodes.txt --bol --mismatches 0 --prefix $(basename $1 .fq.gz) --suffix ".fq"
} tempfifo=$$.fifo # $$表示当前执行文件的PID
fqlist=$1 # $1表示fq列表文件
mkfifo $tempfifo
exec 1000<>$tempfifo
rm -f $tmpfifo # 先向管道中写入8个空行,控制并发数量,其实此时并没有写入而是等下面的read操作时才实际写入。
for ((i=1;i<=8;i++))
do
echo "">&1000 &
done # read -u从文件描述符中读取一行,然后执行相关操作,若读不到则会阻塞在这里,从而实现进程控制
while read fq
do
read -u1000
{
split_fq $fq
# 执行完成后写回管道
echo "">&1000
} &
done < $fplist
wait
参考资料:
http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/commandline.html
FASTX-Toolkit组件用法的更多相关文章
- Easyui主要组件用法
Easyui主要组件用法说明: 1. combogrid用法 说明:combogrid可提供翻页列表的数据选择并可进行数据的过滤查询(查询的传人参数为q,可在控制器中获取这个参数传过来的值,下面的示 ...
- Linux 使用记1 fastx toolkit安装问题
1 安装fastx toolkit的时候,步骤按https://blog.csdn.net/LotusWang0723/article/details/78723409 其中可能会出现如下报错 tex ...
- Vuejs的指令及组件用法总结
vuejs介绍 Vue.js是当下很火的一个JavaScript MVVM库,它是以数据驱动和组件化的思想构建的.相比于Angular.js,Vue.js提供了更加简洁.更易于理解的API,使得我们能 ...
- Flutter中Expanded组件用法
Flutter中Expanded组件用法 Expanded组件可以使Row.Column.Flex等子组件在其主轴方向上展开并填充可用空间(例如,Row在水平方向,Column在垂直方向).如果多个子 ...
- React的组件用法
React.createClass() 中文翻译 https://discountry.github.io/react/3.4K ( https://doc.react-china.org868 ) ...
- ReactNative系列组件用法(一)
首先我们来认识view 改变一些特性,再来看看项目的变化 我们新增flex布局的一些属性,再来看看项目的变化 接下来我们来看看如果获取屏幕的分辨率 关于图片的用法,reactNative这里也是很神奇 ...
- Unity3D UGUI下拉菜单/Dropdown组件用法、总结
Unity3D中UGUI实现下拉菜单 本文提供全流程,中文翻译. Chinar 坚持将简单的生活方式,带给世人!(拥有更好的阅读体验 -- 高分辨率用户请根据需求调整网页缩放比例) Chinar -- ...
- VUE入门实例,模版组件用法
这里每一个例子可以直接拷进body运行. 本系列为学习记录,并非大神教学案例. 仅仅整理用法,至于VUE的原理,设计模式等等暂不讨论,文中如有不对,还请大家帮忙指正,万分感激. 下一篇会写父子组件交互 ...
- WP开发-Toolkit组件 列表采集器(ListPicker)的使用
列表采集器ListPicker在作用上与html中的<select/>标签一样 都是提供多选一功能,区别在于ListPicker可以自定义下拉状态和非下拉状态的样式. 1.模板设置 Lis ...
随机推荐
- Java知识点梳理——泛型
1.定义:泛型的本质是参数化类型,就是将类型由原来的具体的类型参数化,这种参数类型可以用在类.接口.方法中,分别称为泛型类.泛型接口.泛型方法: 2.泛型类:泛型类的声明和非泛型类的声明类似,除了在类 ...
- 九度OJ 1147:Jugs(罐子) (模拟、游戏)
时间限制:1 秒 内存限制:32 兆 特殊判题:是 提交:243 解决:200 题目描述: In the movie "Die Hard 3", Bruce Willis and ...
- VC调用Delphi DLL
别的没什么,是一定可以调用成功的.但是意外的是,ShowMessage函数在DLL里也可以轻易被调用.此外,Delphi里的var 相当于VC里的引用,需要在函数原型里正确标识,否则传递普通变量甚至常 ...
- global 全局变量的用法
说明:i 和foo()都为全局变量,i 是在模块文件顶层注册的,所以为全局变量,他能够在函数内部进行引用而不需要再特意声明是全局变量,且foo()函数也是全局变量 1.当没有局部变量时,print(i ...
- selector + shape
selector_shape.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <selector xmln ...
- 20145239 《Java程序设计》第5周学习总结
20145239 <Java程序设计>第5周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 (一)掌握try...catch...finally处理异常的方法: 程序中有许多意想不到的错误,所以我们要学会一些 ...
- 我的.emacs文件,用于C/C++及shell编程。
1. [代码]我的.emacs文件,用于C/C++及shell编程.;;我的配置;;1.基本配置;;外观配置***************;;禁用启动画面(setq inhibit-startup-m ...
- jenkins maven tomcat做持续集成
maven 采用 maven 3.0以上的版本.tomcat 采用 tomcat 7.0 以上的版本 1. tomcat 配置用户账号和权限 tomcat-users.xml <role rol ...
- c# 实现WebSocket
用C# ASP.NET MVC 实现WebSocket ,对于WebSocket想必都很了解了,不多说. 东西做的很粗糙 只能实现基本的聊天功能,不过基本的通信实现了,那么后序的扩展应该也不难(个人这 ...
- T61
你参加了这次科学讨论会,有什么体会?What have you learned from the symposium?那墙有点斜.The wall is a little out of the per ...
