java源码 -- TreeMap
简介

TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
源码
TreeMap属性
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; //比较器,是自然排序,还是定制排序 ,使用final修饰,表明一旦赋值便不允许改变
private transient Entry<K,V> root = null; //红黑树的根节点
private transient int size = 0; //TreeMap中存放的键值对的数量
private transient int modCount = 0; //修改的次数
TreeMap构造器
//构造方法,comparator用键的顺序做比较
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//构造方法,提供比较器,用指定比较器排序
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//将m中的元素转化到TreeMap中,按照键的顺序做比较排序
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
//构造方法,指定的参数为SortedMap
//采用m的比较器排序
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
/**
*最后一个构造函数不同于上一个构造函数,在上一个构造函数中传入的参数是Map,Map不是有序的,所以要逐个添加。
*而该构造函数的参数是SortedMap是一个有序的Map,我们通过buildFromSorted()来创建对应的Map。
*/
//首先调用此方法,进行初步的整理。将size设置为有序的SortedMap的size
private void buildFromSorted(int size, Iterator<?> it,
java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
V defaultVal)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.size = size;
root = buildFromSorted(0, 0, size-1, computeRedLevel(size),
it, str, defaultVal);
}
// 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap
// 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。
// level 当前树的级别,初始调用为0, 其实就是根节点级别; lo 这个子树的第一个元素索引,初始值应该为0;这个子树的最后一个元素索引。初始值应为size-1; redLevel 节点应该是红色的级别。
// it 如果非空,则从该迭代器读取的条目或键创建新条目;如果非空,则从键创建新条目,并可能以序列化形式从该流读取值; defaultVal 如果非null,则此默认值用于映射中的每个值。
private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi, int redLevel, Iterator<?> it, java.io.ObjectInputStream str, V defaultVal)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
if (hi < lo) return null;
// 获取中间元素
int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1; Entry<K,V> left = null;
// 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。
if (lo < mid)
left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel,
it, str, defaultVal); // 获取middle节点对应的key和value
K key;
V value;
if (it != null) {
if (defaultVal==null) {
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>)it.next();
key = (K)entry.getKey();
value = (V)entry.getValue();
} else {
key = (K)it.next();
value = defaultVal;
}
} else { // use stream
key = (K) str.readObject();
value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject());
} Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<>(key, value, null); // 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。
if (level == redLevel)
middle.color = RED;
// 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
if (left != null) {
middle.left = left;
left.parent = middle;
} if (mid < hi) {
// 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。
Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel,
it, str, defaultVal); // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
middle.right = right;
right.parent = middle;
} return middle;
}
要理解buildFromSorted,重点说明以下几点: 第一,buildFromSorted是通过递归将SortedMap中的元素逐个关联。
第二,buildFromSorted返回middle节点(中间节点)作为root。
第三,buildFromSorted添加到红黑树中时,只将level == redLevel的节点设为红色。第level级节点,实际上是buildFromSorted转换成红黑树后的最底端(假设根节点在最上方)的节点;只将红黑树最底端的阶段着色为红色,其余都是黑色。
TreeMap方法
/ /查询操作
public int size() {
return size;
}
//返回指定key是否存在
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null; //调用getEntry方法
}
//返回指定value是否存在
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
//返回key的value值
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
return comparator;
}
//返回第一个key
public K firstKey() {
return key(getFirstEntry());
}
//返回最后一个key
public K lastKey() {
return key(getLastEntry());
}
//在TreeMap添加Map集合
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
int mapSize = map.size(); //获取参数map集合的大小
// 如果TreeMap的大小是0,且map的大小不是0,且map是已排序的“key-value对”
if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) {
Comparator<?> c = ((SortedMap<?,?>)map).comparator();
// 如果TreeMap和map的比较器相等;
// 则将map的元素全部拷贝到TreeMap中,然后返回!
if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) {
++modCount;
try {
buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(),
null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
return;
}
}
// 调用AbstractMap中的putAll();
// AbstractMap中的putAll()又会调用到TreeMap的put()
super.putAll(map);
}
// 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// 若“比较器”为null,则通过getEntryUsingComparator()获取“键”为key的节点
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//root根节点赋值给p
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
// 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子”
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
// 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子”
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
// 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
// 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点(对应TreeMap的比较器不是null的情况)
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
// 将p设为根节点
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
// 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子”
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
// 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子”
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
// 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
// 获取TreeMap中大于等于key的最小的节点(等于最好,不等于就找大于)
// 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key小),就返回null
final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
// 情况一:若“p的key” > key。
// 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=“p的左孩子”
// 否则,返回p
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
// 情况二:若“p的key” < key。
} else if (cmp > 0) {
// 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=“p的右孩子”
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
// 情况三:若“p的key” = key。
} else
return p;
}
return null;
}
// 获取TreeMap中 小于等于 key的最大的节点;(优先小于 没有找小于)
// 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key小),就返回null
// getFloorEntry的原理和getCeilingEntry类似,这里不再多说。
final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
return p; }
return null;
}
// 获取TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点,若不存在,就返回null。
// 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getHigherEntry进行理解。
final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
// 获取TreeMap中小于key的最大的节点。若不存在,就返回null。
// 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getLowerEntry进行理解
final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
//将“key value” 添加到TreeMap中。掌握"红黑树"数据结构,很容易理解TreeMap
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//红黑树是以key来进行排序的,所以这里以key来进行查找。
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 新建红黑树的节点(e)
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e); //维持红黑树的特性
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
} // 删除TreeMap中的键为key的节点,并返回节点的值
public V remove(Object key) {
// 找到键为key的节点
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
// 保存节点的值
V oldValue = p.value;
// 删除节点
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
// 清空红黑树
public void clear() {
modCount++;
size = 0;
root = null;
}
// 克隆一个TreeMap,并返回Object对象
public Object clone() {
TreeMap<?,?> clone;
try {
clone = (TreeMap<?,?>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
} // Put clone into "virgin" state (except for comparator)
clone.root = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
clone.entrySet = null;
clone.navigableKeySet = null;
clone.descendingMap = null; // Initialize clone with our mappings
try {
clone.buildFromSorted(size, entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
} return clone;
}
NavigableMap API methods(Navigable英译:可航行的)
// 获取第一个节点(对外接口)。
public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(getFirstEntry());
} // 获取最后一个节点(对外接口)。
public Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
return exportEntry(getLastEntry());
} // 获取第一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。
public Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
// 获取第一个节点
Entry<K,V> p = getFirstEntry();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p);
// 删除第一个节点
if (p != null)
deleteEntry(p);
return result;
} // 获取最后一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。
public Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
// 获取最后一个节点
Entry<K,V> p = getLastEntry();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p);
// 删除最后一个节点
if (p != null)
deleteEntry(p);
return result;
} // 返回小于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null
public Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getLowerEntry(key));
} // 返回小于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
public K lowerKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getLowerEntry(key));
} // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null
public Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getFloorEntry(key));
} // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
public K floorKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getFloorEntry(key));
} // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null
public Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getCeilingEntry(key));
} // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key));
} // 返回大于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null
public Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getHigherEntry(key));
} // 返回大于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
public K higherKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getHigherEntry(key));
}
视图菜单
// TreeMap的红黑树节点对应的集合
private transient EntrySet entrySet;
// KeySet为KeySet导航类
private transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySet;
// descendingMap为键值对的倒序“映射”
private transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap;
//返回TreeMap “键的集合”
public Set<K> keySet() {
return navigableKeySet();
}
// 获取“可导航”的Key的集合
// 实际上是返回KeySet类的对象。
public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
KeySet<K> nks = navigableKeySet;
return (nks != null) ? nks : (navigableKeySet = new KeySet<>(this));
}
public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
}
// 返回“TreeMap的值对应的集合”
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs = values;
if (vs == null) {
vs = new Values();
values = vs;
}
return vs;
}
// 获取TreeMap的Entry的集合,实际上是返回EntrySet类的对象。
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
} // 获取TreeMap的降序Map
// 实际上是返回DescendingSubMap类的对象
public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {
NavigableMap<K, V> km = descendingMap;
return (km != null) ? km :
(descendingMap = new DescendingSubMap<>(this,
true, null, true,
true, null, true));
} // 获取TreeMap的子Map
// 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
false, fromKey, fromInclusive,
false, toKey, toInclusive);
} // 获取“Map的头部”
// 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
true, null, true,
false, toKey, inclusive);
}
// 获取“Map的尾部”。
//范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
false, fromKey, inclusive,
true, null, true);
}
// 获取“子Map”。
// 范围是从fromKey(包括) 到 toKey(不包括)
public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
}
//获取“Map的头部”
//范围从第一个节点 到 toKey(不包括)
public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
return headMap(toKey, false);
}
// 获取“Map的尾部”。
// 范围是从 fromKey(包括) 到 最后一个节点
public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
return tailMap(fromKey, true);
}
//替换指定key的value值
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p!=null && Objects.equals(oldValue, p.value)) {
p.value = newValue;
return true;
}
return false;
}
//替换指定key的值,并返回旧值
public V replace(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p!=null) {
V oldValue = p.value;
p.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
return null;
}
//输出所有key和value。通过BiConsumer方式
public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
int expectedModCount = modCount;
for (Entry<K, V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) {
action.accept(e.key, e.value); if (expectedModCount != modCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
//替换集合
public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Objects.requireNonNull(function);
int expectedModCount = modCount; for (Entry<K, V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) {
e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value); if (expectedModCount != modCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
视图类的支持
Values值集合,通过TreeMap的值形成的一个集合。封装成一个内部类Values。Values继承AbstractCollection
//它的方法比较简单,不是很复杂
class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return new ValueIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
//大小即是TreeMap大小
public int size() {
return TreeMap.this.size();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return TreeMap.this.containsValue(o);
} public boolean remove(Object o) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) {
if (valEquals(e.getValue(), o)) {
deleteEntry(e);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} public void clear() {
TreeMap.this.clear();
} public Spliterator<V> spliterator() {
return new ValueSpliterator<K,V>(TreeMap.this, null, null, 0, -1, 0);
}
}
EntrySet键集合。封装成一个内部类EntrySet。 EntrySet继承AbstractSet
class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
// EntrySet中是否包含“键值对Object”
public boolean contains(Object o) {
//判断是否为Map.Entry类型
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object value = entry.getValue();
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
return p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value);
}
// 删除EntrySet中的“键值对Object”
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//判断是否为Map.Entry类型
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object value = entry.getValue();
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) {
deleteEntry(p); //删除对应的元素
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int size() {
return TreeMap.this.size();
}
public void clear() {
TreeMap.this.clear();
}
public Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator<K,V>(TreeMap.this, null, null, 0, -1, 0);
}
}
TreeMap迭代器的基类
上面的方法用到了ValueIterator、PrivateEntryIterator、EntryIterator等一些与迭代相关的内容
PrivateEntryIterator 它是众多迭代器的父类
abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
Entry<K,V> next; //指向next的引用
Entry<K,V> lastReturned; //保留上一次返回节点的引用
int expectedModCount; //并发记录
//构造方法
PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
}
//判断是否有下一个节点
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
//返回下一个节点
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next; //赋值下一个节点
if (e == null) //空 抛异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount) //fail-fast 不能在并发中修改
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
//返回前一个节点
final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = predecessor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
//删除节点
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 删除的条目将由它们的后继条目替换
if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
next = lastReturned;
deleteEntry(lastReturned); //删除节点 然后重新平衡树
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
}
}
EntryIterator 节点的迭代器
final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { //继承PrivateEntryIterator抽象类
EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
ValueIterator 值的迭代器
final class ValueIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<V> { //继承PrivateEntryIterator抽象类
ValueIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public V next() {
return nextEntry().value; //返回节点值
}
}
KeyIterator 键的迭代器
final class KeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> { //继承PrivateEntryIterator抽象类
KeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public K next() {
return nextEntry().key; //返回节点键值
}
}
DescendingKeyIterator 反向键的迭代器
final class DescendingKeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> {
DescendingKeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
//返回上一个节点键
public K next() {
return prevEntry().key;
}
//删除元素
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
deleteEntry(lastReturned);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
// Little utilities 小工具
//比较两个键值大小
final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2)
: comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
}
//值是否相等
static final boolean valEquals(Object o1, Object o2) {
return (o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2));
}
//返回简化不变的节点
static <K,V> Map.Entry<K,V> exportEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
return (e == null) ? null :
new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<>(e);
}
//返回key 如果空 返回null
static <K,V> K keyOrNull(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
return (e == null) ? null : e.key;
}
//返回key,空抛异常
static <K> K key(Entry<K,?> e) {
if (e==null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return e.key;
}
SubMaps内核映射和子映射
NavigableSubMap是一个继承于AbstractMap的抽象类。 它包括2个子类——"(升序)AscendingSubMap"和"(降序)DescendingSubMap"。NavigableSubMap为它的两个子类实现了许多公共API。
NavigableSubMap的源码。
abstract static class NavigableSubMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2102997345730753016L; final TreeMap<K,V> m; final K lo, hi;
final boolean fromStart, toEnd;
final boolean loInclusive, hiInclusive; NavigableSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
if (!fromStart && !toEnd) {
if (m.compare(lo, hi) > 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey > toKey");
} else {
if (!fromStart) // type check
m.compare(lo, lo);
if (!toEnd)
m.compare(hi, hi);
} this.m = m;
this.fromStart = fromStart;
this.lo = lo;
this.loInclusive = loInclusive;
this.toEnd = toEnd;
this.hi = hi;
this.hiInclusive = hiInclusive;
} // internal utilities
//判断key是否太小
final boolean tooLow(Object key) {
//SubMap不包括“起始节点”
//并且,key小于最小键(lo)或者等于最小键,但是SubMap不包括最小键内
//则判断key太小,其他情况都不是太小!
if (!fromStart) {
int c = m.compare(key, lo);
if (c < 0 || (c == 0 && !loInclusive)) //小于最小键 | 等于最小键,但是最小键不在SubMap内
return true; //则key太小
}
return false;
}
//判断key是否太大,与tooLow原理相同
final boolean tooHigh(Object key) {
if (!toEnd) {
int c = m.compare(key, hi);
if (c > 0 || (c == 0 && !hiInclusive))
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断key是否在lo~li开区间(不包含lo li)范围内
final boolean inRange(Object key) {
return !tooLow(key) && !tooHigh(key);
}
// 判断key是否在封闭区间内
final boolean inClosedRange(Object key) {
return (fromStart || m.compare(key, lo) >= 0) //包含起始节点lo,且key大于lo
&& (toEnd || m.compare(hi, key) >= 0); //包含结束节点li,且key小于li
}
// 判断key是否在区间内, inclusive是区间开关标志
final boolean inRange(Object key, boolean inclusive) {
return inclusive ? inRange(key) : inClosedRange(key);
} //返回最低的Entry节点
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowest() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
(fromStart ? m.getFirstEntry() : //若“包含起始节点”,则调用getFirstEntry()返回第一个节点
(loInclusive ? m.getCeilingEntry(lo) : //否则的话,若包括lo,则调用getCeilingEntry(lo)获取大于/等于lo的最小的Entry;
m.getHigherEntry(lo))); //否则,调用getHigherEntry(lo)获取大于lo的最小Entry
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
}
//返回最高的Entry节点
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighest() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
(toEnd ? m.getLastEntry() : // 若“包含结束节点”,则调用getLastEntry()返回最后一个节点
(hiInclusive ? m.getFloorEntry(hi) : // 否则的话,若包括hi,则调用getFloorEntry(hi)获取小于/等于hi的最大的Entry;
m.getLowerEntry(hi))); // 否则,调用getLowerEntry(hi)获取大于hi的最大Entry
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
} // 返回"大于/等于key的最小的Entry"
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absCeiling(K key) {
// 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
// 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了!
if (tooLow(key))
return absLowest();
// 获取“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getCeilingEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
} // 返回"大于key的最小的Entry"
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHigher(K key) {
// 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于key的最小Entry”
// 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了,而不一定是“大于key的最小Entry”!
if (tooLow(key))
return absLowest();
// 获取“大于key的最小Entry”
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getHigherEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
} // 返回"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absFloor(K key) {
// 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于/等于key的最大Entry”
// 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了!
if (tooHigh(key))
return absHighest();
// 获取"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getFloorEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
} // 返回"小于key的最大的Entry"
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLower(K key) {
// 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于key的最大Entry”
// 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了,而不一定是“小于key的最大Entry”!
if (tooHigh(key))
return absHighest();
// 获取"小于key的最大的Entry"
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getLowerEntry(key);
return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
} // 返回“大于最大节点中的最小节点”,不存在的话,返回null
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighFence() {
return (toEnd ? null : (hiInclusive ?
m.getHigherEntry(hi) :
m.getCeilingEntry(hi)));
} // 返回“小于最小节点中的最大节点”,不存在的话,返回null
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowFence() {
return (fromStart ? null : (loInclusive ?
m.getLowerEntry(lo) :
m.getFloorEntry(lo)));
} // 下面几个abstract方法是需要NavigableSubMap的实现类实现的方法
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest();
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest();
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key);
abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key);
// 返回“顺序”的键迭代器
abstract Iterator<K> keyIterator();
// 返回“逆序”的键迭代器
abstract Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator(); // 返回SubMap是否为空。空的话,返回true,否则返回false
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.isEmpty() : entrySet().isEmpty();
} // 返回SubMap的大小
public int size() {
return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.size() : entrySet().size();
} // 返回SubMap是否包含键key
public final boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return inRange(key) && m.containsKey(key);
} // 将key-value 插入SubMap中
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (!inRange(key))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key out of range");
return m.put(key, value);
} // 获取key对应值
public final V get(Object key) {
return !inRange(key)? null : m.get(key);
} // 删除key对应的键值对
public final V remove(Object key) {
return !inRange(key)? null : m.remove(key);
} // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键值对”
public final Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subCeiling(key));
} // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键”
public final K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subCeiling(key));
} // 获取“大于key的最小键值对”
public final Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subHigher(key));
} // 获取“大于key的最小键”
public final K higherKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subHigher(key));
} // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键值对”
public final Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subFloor(key));
} // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键”
public final K floorKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subFloor(key));
} // 获取“小于key的最大键值对”
public final Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(subLower(key));
} // 获取“小于key的最大键”
public final K lowerKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(subLower(key));
} // 获取"SubMap的第一个键"
public final K firstKey() {
return key(subLowest());
} // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键"
public final K lastKey() {
return key(subHighest());
} // 获取"SubMap的第一个键值对"
public final Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(subLowest());
} // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键值对"
public final Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
return exportEntry(subHighest());
} // 返回"SubMap的第一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subLowest();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
if (e != null)
m.deleteEntry(e);
return result;
} // 返回"SubMap的最后一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subHighest();
Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
if (e != null)
m.deleteEntry(e);
return result;
} // Views
transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMapView = null;
transient EntrySetView entrySetView = null;
transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySetView = null; // 返回NavigableSet对象,实际上返回的是当前对象的"Key集合"。
public final NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
KeySet<K> nksv = navigableKeySetView;
return (nksv != null) ? nksv :
(navigableKeySetView = new TreeMap.KeySet(this));
} // 返回"Key集合"对象
public final Set<K> keySet() {
return navigableKeySet();
} // 返回“逆序”的Key集合
public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
} // 排列fromKey(包含) 到 toKey(不包含) 的子map
public final SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
} // 返回当前Map的头部(从第一个节点 到 toKey, 不包括toKey)
public final SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
return headMap(toKey, false);
} // 返回当前Map的尾部[从 fromKey(包括fromKeyKey) 到 最后一个节点]
public final SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
return tailMap(fromKey, true);
} // Map的Entry的集合
abstract class EntrySetView extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
private transient int size = -1, sizeModCount; // 获取EntrySet的大小
public int size() {
// 若SubMap是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则SubMap大小就是原TreeMap的大小
if (fromStart && toEnd)
return m.size();
// 若SubMap不是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则调用iterator()遍历EntrySetView中的元素
if (size == -1 || sizeModCount != m.modCount) {
sizeModCount = m.modCount;
size = 0;
Iterator i = iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
size++;
i.next();
}
}
return size;
} // 判断EntrySetView是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> n = absLowest();
return n == null || tooHigh(n.key);
} // 判断EntrySetView是否包含Object
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
K key = entry.getKey();
if (!inRange(key))
return false;
TreeMap.Entry node = m.getEntry(key);
return node != null &&
valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue());
} // 从EntrySetView中删除Object
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
K key = entry.getKey();
if (!inRange(key))
return false;
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key);
if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(),entry.getValue())){
m.deleteEntry(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
} // SubMap的迭代器
abstract class SubMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
// 上一次被返回的Entry
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
// 指向下一个Entry
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> next;
// “栅栏key”。根据SubMap是“升序”还是“降序”具有不同的意义
final K fenceKey;
int expectedModCount; // 构造函数
SubMapIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
// 每创建一个SubMapIterator时,保存修改次数
// 若后面发现expectedModCount和modCount不相等,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
// 这就是所说的fast-fail机制的原理!
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
fenceKey = fence == null ? null : fence.key;
} // 是否存在下一个Entry
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null && next.key != fenceKey;
} // 返回下一个Entry
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// next指向e的后继节点
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
} // 返回上一个Entry
final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// next指向e的前继节点
next = predecessor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
} // 删除当前节点(用于“升序的SubMap”)。
// 删除之后,可以继续升序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
final void removeAscending() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。
// 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。
// 根据“红黑树”的特性可知:
// 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。
// 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,'新的当前节点'实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。
// 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。
if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
next = lastReturned;
m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
} // 删除当前节点(用于“降序的SubMap”)。
// 删除之后,可以继续降序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
final void removeDescending() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
} } // SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
final class SubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
SubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(first, fence);
}
// 获取下一个节点(升序)
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
// 删除当前节点(升序)
public void remove() {
removeAscending();
}
} // SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
final class SubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
SubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(first, fence);
}
// 获取下一个节点(升序)
public K next() {
return nextEntry().key;
}
// 删除当前节点(升序)
public void remove() {
removeAscending();
}
} // 降序SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
final class DescendingSubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(last, fence);
} // 获取下一个节点(降序)
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return prevEntry();
}
// 删除当前节点(降序)
public void remove() {
removeDescending();
}
} // 降序SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
final class DescendingSubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
super(last, fence);
}
// 获取下一个节点(降序)
public K next() {
return prevEntry().key;
}
// 删除当前节点(降序)
public void remove() {
removeDescending();
}
}
}
子类(升序)AscendingSubMap
static final class AscendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866124060L;
AscendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
}
//获得比较器
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
return m.comparator();
}
//截取 子Map
public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
// 截取之前判断是否超出范围
if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
return new AscendingSubMap<>(m,
false, fromKey, fromInclusive,
false, toKey, toInclusive);
}
// “截取”子Map,headMap通过构造方法便可以实现
public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
return new AscendingSubMap<>(m,
fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
false, toKey, inclusive);
}
//和heapMap类似
public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {
if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
return new AscendingSubMap<>(m,
false, fromKey, inclusive,
toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
}
public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() {
NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView;
return (mv != null) ? mv :
(descendingMapView =
new DescendingSubMap<>(m,
fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
toEnd, hi, hiInclusive));
}
Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
}
Spliterator<K> keySpliterator() {
return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
}
Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
}
final class AscendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new SubMapEntryIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
}
}
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySetView es = entrySetView;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySetView = new AscendingEntrySetView());
}
// 父类中抽象方法的实现,都很简单
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absLowest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absHighest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absLower(key); }
}
子类(降序)DescendingSubMap
static final class DescendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866120460L;
DescendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
}
//反转的比较器,是将原始比较器反转得到的
private final Comparator<? super K> reverseComparator =
Collections.reverseOrder(m.comparator);
//获取反转比较器
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
return reverseComparator;
}
//获取子Map。 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
return new DescendingSubMap<>(m,
false, toKey, toInclusive,
false, fromKey, fromInclusive);
}
// 获取“Map的头部”。范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
return new DescendingSubMap<>(m,
false, toKey, inclusive,
toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
}
// 获取“Map的尾部”。范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {
if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
return new DescendingSubMap<>(m,
fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
false, fromKey, inclusive);
}
// 获取对应的降序Map
public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() {
NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView;
return (mv != null) ? mv :
(descendingMapView =
new AscendingSubMap<>(m,
fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
toEnd, hi, hiInclusive));
}
// 返回“升序Key迭代器”
Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
}
Spliterator<K> keySpliterator() {
return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
}
// 返回“降序Key迭代器”
Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
}
// “降序EntrySet集合”类,实现了iterator()final class DescendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
}
}
// 返回“降序EntrySet集合”
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySetView es = entrySetView;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySetView = new DescendingEntrySetView());
}
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absHighest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absLowest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absLower(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
}
一个内部类是SubMap,它比较特别。这个类存在仅仅为了序列化兼容之前的版本不支持NavigableMap TreeMap。它被翻译成一个旧版本AscendingSubMap子映射到一个新版本。这个类是从来没有以其他方式使用。
// SubMap 继承自AbstractMap;这个类存在仅仅为了序列化兼容之前的版本不支持NavigableMap TreeMap。它被翻译成一个旧版本AscendingSubMap子映射到一个新版本。这个类是从来没有以其他方式使用。
private class SubMap extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements SortedMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6520786458950516097L;
// 标识是否从map的开始到结尾都属于子map
private boolean fromStart = false, toEnd = false;
// 开始位置和结束位置的key
private K fromKey, toKey;
private Object readResolve() {
return new AscendingSubMap(TreeMap.this,
fromStart, fromKey, true,
toEnd, toKey, false);
}
// 结合类定义和类的说明就明白为什么提供了这么多方法但是都不能用了
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { throw new InternalError(); }
public K lastKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
public K firstKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { throw new InternalError(); }
}
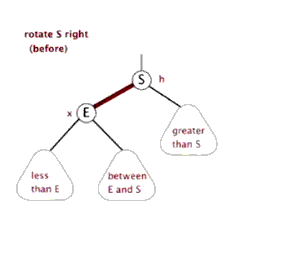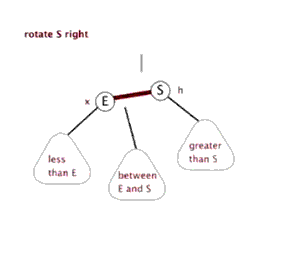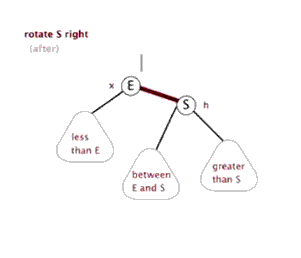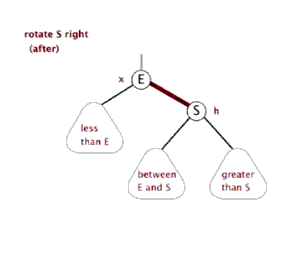
下面的源码是TreeMap的核心代码,我们知道TreeMap原理是通过红黑树实现的,那么它是怎么维持红黑树的特性的呢? (红黑树数据结构:https://www.cnblogs.com/FondWang/p/11906824.html)
//两个记录红黑点的属性
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
红黑树结构代码
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left; //左孩子节点
Entry<K,V> right; //右孩子节点
Entry<K,V> parent; //父节点
boolean color = BLACK; //红黑树用来表示节点颜色的属性,默认为黑色
//构造方法,用指定的key,value ,parent初始化,color默认为黑色
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
//获取key
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
//获取value
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
//设置新值,返回旧值
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
//重写equals方法
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
//两个节点的key相等,value相等,这两个节点才相等
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
//重写hashCode()方法
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
//key和vale hash值得异或运算,相同则为零,不同则为1
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
getFirstEntry 获取第一个节点,就是红黑树最后一层的左子树的第一个节点
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null) //循环到第一个节点
p = p.left;
return p;
}
getLastEntry 获取最后一个节点,就是红黑树最后一层的右子树的最后一个节点
final Entry<K,V> getLastEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.right != null) //循环到最后一个节点
p = p.right;
return p;
}
successor 比较核心的方法。返回当前节点的后继节点,就是找大于当前节点的最小节点。如1、3、4、9、6 找4的后继节点,就是6 大于4的最小节点值。(也可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/iwts_24/article/details/87165743)
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) { //右子树的最小左孩子
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else { //该节点没有右子树但是有比该结点大的祖先结点。如果当前结点就是最大值,这就需要返回null了
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
predecessor 与上面原理一样。返回当前节点的前继节点,就是找小于当前节点的最大节点。
static <K,V> Entry<K,V> predecessor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.left != null) { //左子树的最大右孩子
Entry<K,V> p = t.left;
while (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
return p;
} else { //该节点没有左子树但是有比该结点小的祖先结点。如果当前结点就是最小值,这就需要返回null了
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.left) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
下面是一些平衡操作
//节点为null,即为黑节点
private static <K,V> boolean colorOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color);
}
//返回父节点
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null ? null: p.parent);
}
//设置节点颜色
private static <K,V> void setColor(Entry<K,V> p, boolean c) {
if (p != null)
p.color = c;
}
//返回左孩子
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> leftOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null: p.left;
}
//返回右孩子
private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> rightOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
return (p == null) ? null: p.right;
}
下面就是真正核心代码,平衡红黑树的操作
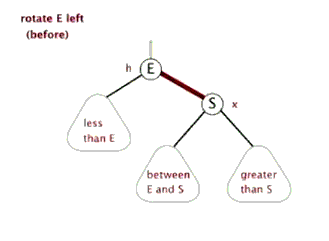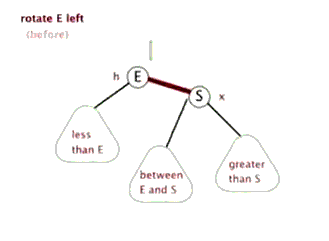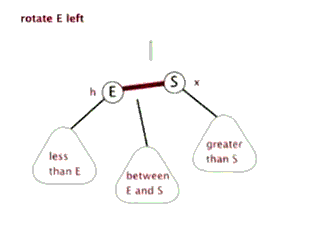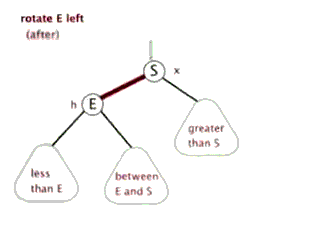
//左旋转
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;//获取P的右子节点,其实这里就相当于新增节点N
p.right = r.left; //将R的左子树设置为P的右子树
//若R的左子树不为空,则将P设置为R左子树的父亲
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
//将P的父亲设置R的父亲
r.parent = p.parent;
//如果P的父亲为空,则将R设置为跟节点
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
//如果P为其父节点(G)的左子树,则将R设置为P父节点(G)左子树
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
//否则R设置为P的父节点(G)的右子树
else
p.parent.right = r;
//将P设置为R的左子树
r.left = p;
//将R设置为P的父节点
p.parent = r;
}
}
//右旋转
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
//将L设置为P的左子树
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
//将L的右子树设置为P的左子树
p.left = l.right;
//若L的右子树不为空,则将P设置L的右子树的父节点
if (l.right != null)
l.right.parent = p;
//将P的父节点设置为L的父节点
l.parent = p.parent;
//如果P的父节点为空,则将L设置根节点
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
//若P为其父节点的右子树,则将L设置为P的父节点的右子树
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
//否则将L设置为P的父节点的左子树
else
p.parent.left = l;
//将P设置为L的右子树
l.right = p;
//将L设置为P的父节点
p.parent = l;
}
}
我们在添加删除节点时,肯定会打破红黑树的性质,所以要进行平衡调整操作。通过fixAfterInsertion()和 fixAfterDeletion()
方法调整
fixAfterInsertion(e); 添加调整的过程务必会涉及到红黑树的左旋、右旋、着色三个基本操作。
/**
* 新增节点后的修复操作
* x 表示新增节点
*/
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
x.color = RED; //新增节点的颜色为红色 //循环 直到 x不是根节点,且x的父节点不为红色
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
//如果X的父节点(P)是其父节点的父节点(G)的左节点
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
//获取X的叔节点(U)
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
//如果X的叔节点(U) 为红色
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
//将X的父节点(P)设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//将X的叔节点(U)设置为黑色
setColor(y, BLACK);
//将X的父节点的父节点(G)设置红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
}
//如果X的叔节点(U为黑色)
else {
//如果X节点为其父节点(P)的右子树,则进行左旋转
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
//将X的父节点作为X
x = parentOf(x);
//右旋转
rotateLeft(x);
} //将X的父节点(P)设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//将X的父节点的父节点(G)设置红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//以X的父节点的父节点(G)为中心右旋转
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
//如果X的父节点(P)是其父节点的父节点(G)的右节点
else {
//获取X的叔节点(U)
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
//如果X的叔节点(U) 为红色
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
//将X的父节点(P)设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//将X的叔节点(U)设置为黑色
setColor(y, BLACK);
//将X的父节点的父节点(G)设置红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
}
//如果X的叔节点(U为黑色);这里会存在两种情况
else {
//如果X节点为其父节点(P)的右子树,则进行左旋转
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
//将X的父节点作为X
x = parentOf(x);
//右旋转
rotateRight(x);
}
//将X的父节点(P)设置为黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
//将X的父节点的父节点(G)设置红色
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//以X的父节点的父节点(G)为中心右旋转
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
//将根节点G强制设置为黑色
root.color = BLACK;
}
fixAfterDeletion(e); 删除后的调整过程
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
// 循环处理,条件为x不是root节点且是黑色的(因为红色不会对红黑树的性质造成破坏,所以不需要调整)
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
// x是一个左孩子
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
// 获取x的兄弟节点sib
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
// sib是红色的
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
// 将sib设置为黑色
setColor(sib, BLACK);
// 将父节点设置成红色
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
// 左旋父节点
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
// sib移动到旋转后x的父节点p的右孩子(参见左旋示意图,获取的节点是旋转前p的右孩子r的左孩子rl)
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
// sib的两个孩子的颜色都是黑色(null返回黑色)
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// 将sib设置成红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// x移动到x的父节点
x = parentOf(x);
} else {// sib的左右孩子都是黑色的不成立
// sib的右孩子是黑色的
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// 将sib的左孩子设置成黑色
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
// sib节点设置成红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// 右旋操作
rotateRight(sib);
// sib移动到旋转后x父节点的右孩子
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
// sib设置成和x的父节点一样的颜色
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
// x的父节点设置成黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
// sib的右孩子设置成黑色
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
// 左旋操作
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
// 设置调整完的条件:x = root跳出循环
x = root;
}
} else { // x是一个右孩子
// 获取x的兄弟节点
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
// 如果sib是红色的
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
// 将sib设置为黑色
setColor(sib, BLACK);
// 将x的父节点设置成红色
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
// 右旋
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
// sib移动到旋转后x父节点的左孩子
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
// sib的两个孩子的颜色都是黑色(null返回黑色)
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// sib设置为红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// x移动到x的父节点
x = parentOf(x);
} else { // sib的两个孩子的颜色都是黑色(null返回黑色)不成立
// sib的左孩子是黑色的,或者没有左孩子
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
// 将sib的右孩子设置成黑色
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
// sib节点设置成红色
setColor(sib, RED);
// 左旋
rotateLeft(sib);
// sib移动到x父节点的左孩子
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
// sib设置成和x的父节点一个颜色
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
// x的父节点设置成黑色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
// sib的左孩子设置成黑色
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
// 右旋
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
// 设置跳出循环的标识
x = root;
}
}
}
// 将x设置为黑色
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
到此TreeMap就分析完了,其实大部分时间都在整理红黑树,在数据结构中树是比较难懂的一个,其算法也比较复杂,对于树的理解一定要多看图画图,要明白这么做是为了解决什么问题,这么做又有什么好处,当然看一遍看不懂就要多看几遍了。
还有最后一些序列化和排序的方法暂时整理,待有时间再弄。
java源码 -- TreeMap的更多相关文章
- 如何阅读Java源码 阅读java的真实体会
刚才在论坛不经意间,看到有关源码阅读的帖子.回想自己前几年,阅读源码那种兴奋和成就感(1),不禁又有一种激动. 源码阅读,我觉得最核心有三点:技术基础+强烈的求知欲+耐心. 说到技术基础,我打个比 ...
- 如何阅读Java源码
刚才在论坛不经意间,看到有关源码阅读的帖子.回想自己前几年,阅读源码那种兴奋和成就感(1),不禁又有一种激动.源码阅读,我觉得最核心有三点:技术基础+强烈的求知欲+耐心. 说到技术基础,我打个比方吧, ...
- Java 源码学习线路————_先JDK工具包集合_再core包,也就是String、StringBuffer等_Java IO类库
http://www.iteye.com/topic/1113732 原则网址 Java源码初接触 如果你进行过一年左右的开发,喜欢用eclipse的debug功能.好了,你现在就有阅读源码的技术基础 ...
- [收藏] Java源码阅读的真实体会
收藏自http://www.iteye.com/topic/1113732 刚才在论坛不经意间,看到有关源码阅读的帖子.回想自己前几年,阅读源码那种兴奋和成就感(1),不禁又有一种激动. 源码阅读,我 ...
- 【java集合框架源码剖析系列】java源码剖析之TreeSet
本博客将从源码的角度带领大家学习TreeSet相关的知识. 一TreeSet类的定义: public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E&g ...
- 如何阅读Java源码?
阅读本文大概需要 3.6 分钟. 阅读Java源码的前提条件: 1.技术基础 在阅读源码之前,我们要有一定程度的技术基础的支持. 假如你从来都没有学过Java,也没有其它编程语言的基础,上来就啃< ...
- Java源码阅读的真实体会(一种学习思路)
Java源码阅读的真实体会(一种学习思路) 刚才在论坛不经意间,看到有关源码阅读的帖子.回想自己前几年,阅读源码那种兴奋和成就感(1),不禁又有一种激动. 源码阅读,我觉得最核心有三点:技术基础+强烈 ...
- Java源码阅读的真实体会(一种学习思路)【转】
Java源码阅读的真实体会(一种学习思路) 刚才在论坛不经意间,看到有关源码阅读的帖子.回想自己前几年,阅读源码那种兴奋和成就感(1),不禁又有一种激动. 源码阅读,我觉得最核心有三点:技术基础+ ...
- Android反编译(一)之反编译JAVA源码
Android反编译(一) 之反编译JAVA源码 [目录] 1.工具 2.反编译步骤 3.实例 4.装X技巧 1.工具 1).dex反编译JAR工具 dex2jar http://code.go ...
随机推荐
- EasyUEFI---EFI/UEFI boot option management
EasyUEFI owns comprehensive EFI/UEFI boot option management functions, such as create, delete, edit, ...
- js 返回两数(包含这两数)之间的随机数函数
function selectFrom( lowerValue, upperValue ){ var choices = upperValue - lowerValue + 1; return Mat ...
- Jenkins部署maven项目到远端服务器
jenkins服务器地址:192.168.1.203 项目部署机器地址:192.168.1.201,192.168.1.200 代码托管github 虽然比较low,但是入门是可以的! Jenkins ...
- vue-cli构建路径加载资源出错问题
这份文档是对应 @vue/cli 3.x 版本的,官方文档https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/guide/ 项目打包执行npm run build的时候,打开dist目录的index.h ...
- 解决微信小程序要求TLS版本不低于1.2问题
客官,本文可在我的小站中看到哦 昨天项目服务器发生意外,其上的IIS服务无法使用,导致项目后台瘫痪,倒腾一番最终以无法修复告终,启用备用的服务器,从安装IIS环境开始,然后最后所有的东西都准备就绪,却 ...
- 本周JavaScript学习小结
应组长杨老师号召,写个js阶段性学习小结. emmm这周学了Linux进程通讯,学正则表达式尝试完成第一次编程作业,中秋还去平潭露营(所以...js学得很少hhh). 现在还处于感性认识阶段,浏览了一 ...
- GIS 空间分析案例教程-坐标高斯投影正反算
GIS 空间分析案例教程-坐标高斯投影正反算 商务科技合作:向日葵,135-4855__4328,xiexiaokui#qq.com 特点: 1. 地理处理工具,可以与任何arcgis 工具和语言集成 ...
- vue页面刷新重定向
在App.vue中,添加如下代码: created(){ if(this.$router.path !== '/RealTimeMonitoring'){ this.$router.replace(' ...
- mybatis的xml中也可以通过传入标记参数然后用 choose写选择语句【我】
mybatis的xml中也可以通过传入标记参数然后用 choose写选择语句
- VS2015编译GDAL库出现宏重复定义 snprintf: 宏重定义
E:\OpenSourceGraph\gdal-1.10.0\gdal\port cpl_config.h 20行 #define HAVE_VPRINTF 1#define HAVE_ ...