【转】CUDA之Dynamic Parallelism详解
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/Bruce_0712/article/details/63683264
CUDA之Dynamic Parallelism详解(一)
1. 循环的并行化:
(1)循环固定
(2)内循环依赖于外循环
without dynamic parallelism
with dynamic parallelism
examples:
- 顶
- 0
- 踩
- 0
CUDA 5.0中引入动态并行化,使得在device端执行的kernel的线程也能跟在host上一样launch kernels,只有支持CC3.5或者以上的设备中才能支持。动态并行化使用CUDA Device Runtime library(cudadevrt),它是一个能在device code中调用的CUDA runtime子集。
编译链接
为了支持动态并行化,必须使用两步分离编译和链接的过程:首先,设定-c和-rdc=true(–relocatable-device-code=true)来生成relocatable device code来进行后续链接,可以使用-dc(–device -c)来合并这两个选项;然后将上一步目标文件和cudadevrt库进行连接生成可执行文件,-lcudadevrt。过程如下图
C++
|
1
2
|
nvcc -arch=sm_35 -dc myprog.cu -o myprog.o
nvcc -arch=sm_35 myprog.o -lcudadevrt -o myprog
|
或者简化成一步
C++
|
1
|
nvcc -arch=sm_35 -rdc=true myprog.cu -lcudadevrt -o myprog.o
|
执行、同步
在CUDA编程模型中,一组执行的kernel的线程块叫做一个grid。在CUDA动态并行化,parent grid能够调用child grids。child grid继承parant grid的特定属性和限制,如L1 cache、shared_memory、栈大小。如果一个parent grid有M个block和N个thread,如果对child kernel launch没有控制的话,那个将产生M*N个child kernel launch。如果想一个block产生一个child kernel,那么只需要其中一个线程launch a kernel就行。如下
C++
|
1
2
3
|
if(threadIdx.x == 0) {
child_k <<< (n + bs - 1) / bs, bs >>> ();
}
|
grid lanuch是完全嵌套的,child grids总是在发起它们的parent grids结束前完成,这可以看作是一个一种隐式的同步。

如果parent kernel需要使用child kernel的计算结果,也可以使用CudaDeviceSynchronize(void)进行显示的同步,这个函数会等待一个线程块发起的所有子kernel结束。往往不知道一个线程块中哪些子kernel已经执行,可以通过下述方式进行一个线程块级别的同步
C++
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void threadBlockDeviceSynchronize(void) {
__syncthreads();
if(threadIdx.x == 0)
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
__syncthreads();
}
|
CudaDeviceSynchronize(void)调用开销较大,不是必须的时候,尽量减少使用,同时不要在父kernel退出时调用,因为结束时存在上述介绍的隐式同步。
内存一致
当子 grids开始与结束之间,父grids和子grids有完全一致的global memory view。
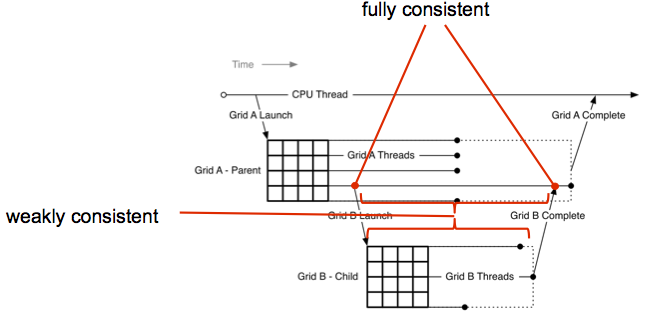
当子kernel launch的时候,global memory视图不一致。
C++
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
__device__ int v = 0;
__global__ void child_k(void) {
printf("v = %d\n", v);
}
__global__ void parent_k(void) {
v = 1;
child_k <<< 1, 1 >>>> ();
v = 2; // RACE CONDITION
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
|
在子kernel launch之后,显示同步之前,parent grid不能对 child grid读取的内存做写入操作,否则会造成race condition。
向Child grids传递指针
指针的传递存在限制:
- 可以传递的指针:global memory(包括__device__变量和malloc分配的内存),zero-copy host端内存,常量内存。
- 不可以传递的指针:shared_memory(__shared__变量), local memory(包括stack变量)
Device Streams和Events
所有在device上创建的streams都是non-blocking的,不支持默认NULL stream的隐式同步。创建流的方式如下
C++
|
1
2
|
cudaStream_t s;
cudaStreamCreateWithFlags(&s, cudaStreamNonBlocking);
|
一旦一个device stream被创建,它能被一个线程块中其他线程使用。只有当这个线程块完成执行的时候,这个stream才能被其他线程块或者host使用。反之亦然。
Event也是支持的,不过有限制,只支持在不同stream之间使用cudaStreamWaitEvent()指定执行顺序,而不能使用event来计时或者同步。
Recursion Depth和Device Limits
递归深度包括两个概念:
- nesting depth:递归grids的最大嵌套层次,host端的为0;
- synchronization depth:cudaDeviceSynchronize()能调用的最大嵌套层次,host端为1,cudaLimitDevRuntimeSyncDepth应该设定为maximum 所以你吃肉你咋体on depth加1,设定方式如
cudaDeviceLimit(cudaLimitDevRuntimeSyncDepth, 4).
maximum nesting depth有硬件限制,在CC3.5中, 对depth 的限制为24. synchronization depth也一样。
从外到内,直到最大同步深度,每一次层会保留一部分内存来保存父block的上下文数据,即使这些内存没有被使用。所以递归深度的设定需要考虑到每一层所预留的内存。
另外还有一个限制是待处理的子grid数量。pending launch buffer用来维持launch queue和追踪当前执行kernel的状态。通过
C++
|
1
|
cudaDeviceSetLimit(cudaLimitDevRuntimePendingLaunchCount, 32768);
|
来设定合适的限制。否则通过cudaGetLastError()调用可以返回CudaErrorLaunchPendingCountExceeded的错误。
动态并行化执行有点类似树的结构,但与CPU上树处理也有些不同。类似深度小,分支多,比较茂密的树的执行结构,比较适合动态并行化的处理。深度大,每层节点少的树的执行结构,则不适合动态并行化。
| characteristic | tree processing | dynamic parallelism |
| node | thin (1 thread) | thick (many threads) |
| branch degree | small (usually < 10) | large (usually > 100) |
| depth | large | small |
到目前为止,所有kernel都是在host端调用,GPU的工作完全在CPU的控制下。CUDA Dynamic Parallelism允许GPU kernel在device端创建调用。Dynamic Parallelism使递归更容易实现和理解,由于启动的配置可以由device上的thread在运行时决定,这也减少了host和device之间传递数据和执行控制。我们接下来会分析理解使用Dynamic Parallelism。
Nested Execution
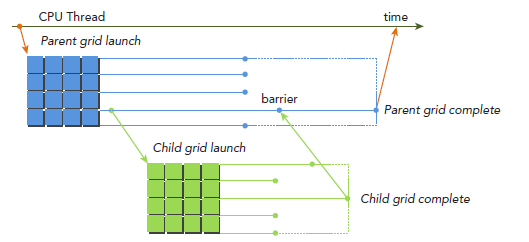
在host调用kernel和在device调用kernel的语法完全一样。kernel的执行则被分为两种类型:parent和child。一个parent thread,parent block或者parent grid可以启动一个新的grid,即child grid。child grid必须在parent 之前完成,也就是说,parent必须等待所有child完成。
当parent启动一个child grid时,在parent显式调用synchronize之前,child不保证会开始执行。parent和child共享同一个global和constant memory,但是有不同的shared 和local memory。不难理解的是,只有两个时刻可以保证child和parent见到的global memory完全一致:child刚开始和child完成。所有parent对global memory的操作对child都是可见的,而child对global memory的操作只有在parent进行synchronize操作后对parent才是可见的。
Nested Hello World on the GPU
为了更清晰的讲解Dynamic Parallelism,我们改编最开始写的hello world程序。下图显示了使用Dynamic Parallelism的执行过程,host调用parent grid(每个block八个thread)。thread 0调用一个child grid(每个block四个thread),thread 0 的第一个thread又调用一个child grid(每个block两个thread),依次类推。

下面是具体的代码,每个thread会先打印出Hello World;然后,每个thread再检查自己是否该停止。

__global__ void nestedHelloWorld(int const iSize,int iDepth) {
int tid = threadIdx.x;
printf("Recursion=%d: Hello World from thread %d block %d\n",iDepth,tid,blockIdx.x);
// condition to stop recursive execution
if (iSize == 1) return;
// reduce block size to half
int nthreads = iSize>>1;
// thread 0 launches child grid recursively
if(tid == 0 && nthreads > 0) {
nestedHelloWorld<<<1, nthreads>>>(nthreads,++iDepth);
printf("-------> nested execution depth: %d\n",iDepth);
}
}

编译:
$ nvcc -arch=sm_35 -rdc=true nestedHelloWorld.cu -o nestedHelloWorld -lcudadevrt
-lcudadevrt是用来连接runtime库的,跟gcc连接库一样。-rdc=true使device代码可重入,这是DynamicParallelism所必须的,至于原因则将是一个比较大的话题,以后探讨。
代码的输出为:

./nestedHelloWorld Execution Configuration: grid 1 block 8
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 1
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 2
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 3
Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0

这里的01234….输出顺序挺诡异的,太规整了,我们暂且认为CUDA对printf做过修改吧。还有就是,按照CPU递归程序的经验,这里的输出顺序就更怪了,当然,肯定不是编译器错误或者CUDA的bug,大家可以在调用kernel后边加上cudaDeviceSynchronize,就可以看到“正常”的顺序了,原因也就清楚了。
使用nvvp可以查看执行情况,空白说明parent在等待child执行结束:
$nvvp ./nesttedHelloWorld
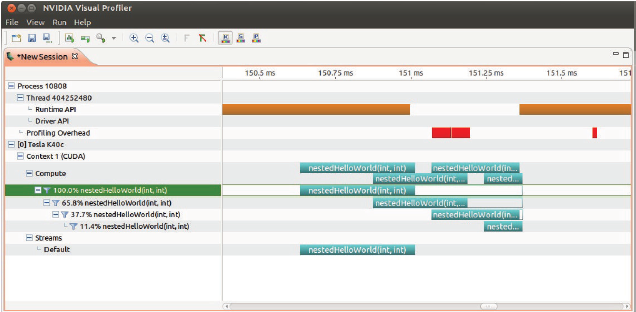
接着,我们尝试使用两个block而不是一个:
$ ./nestedHelloWorld 2
输出是:

./nestedHelloWorld 2Execution Configuration: grid 2 block 8
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 1
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 2 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 3 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 4 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 5 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 6 block 0
Recursion=0: Hello World from thread 7 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 1
-------> nested execution depth: 1
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 2 block 0
Recursion=1: Hello World from thread 3 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 2
-------> nested execution depth: 2
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=2: Hello World from thread 1 block 0
-------> nested execution depth: 3
-------> nested execution depth: 3
Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0
Recursion=3: Hello World from thread 0 block 0

从上面结果来看,首先应该注意到,所有child的block的id都是0。下图是调用过程,parent有两个block了,但是所有child都只有一个blcok:
nestedHelloWorld<<<1, nthreads>>>(nthreads, ++iDepth);
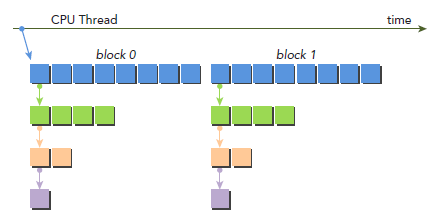
注意:Dynamic Parallelism只有在CC3.5以上才被支持。通过Dynamic Parallelism调用的kernel不能执行于不同的device(物理上实际存在的)上。调用的最大深度是24,但实际情况是,kernel要受限于memory资源,其中包括为了同步parent和child而需要的额外的memory资源。
Nested Reduction
学过算法导论之类的算法书应该知道,因为递归比较消耗资源的,所以如果可以的话最好是展开,而这里要讲的恰恰相反,我们要实现递归,这部分主要就是再次证明DynamicParallelism的好处,有了它就可以实现像C那样写递归代码了。
下面的代码就是一份实现,和之前一样,每个child的有一个block,block中第一个thread调用kernel,不同的是,parent的grid有很多的block。第一步还是讲global memory的地址g_idata转化为每个block本地地址。然后,if判断是否该退出,退出的话,就将结果拷贝回global memory。如果不该退出,就进行本地reduction,一般的线程执行in-place(就地)reduction,然后,同步block来保证所有部分和的计算。thread0再次产生一个只有一个block和当前一半数量thread的child grid。

__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduce (int *g_idata, int *g_odata,
unsigned int isize) {
// set thread ID
unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x;
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
int *odata = &g_odata[blockIdx.x];
// stop condition
if (isize == 2 && tid == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]+idata[1];
return;
}
// nested invocation
int istride = isize>>1;
if(istride > 1 && tid < istride) {
// in place reduction
idata[tid] += idata[tid + istride];
}
// sync at block level
__syncthreads();
// nested invocation to generate child grids
if(tid==0) {
gpuRecursiveReduce <<<1, istride>>>(idata,odata,istride);
// sync all child grids launched in this block
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
// sync at block level again
__syncthreads();
}

编译运行,下面结果是运行在Kepler K40上面:
$ nvcc -arch=sm_35 -rdc=true nestedReduce.cu -o nestedReduce -lcudadevrt
./nestedReduce starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c
array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512
cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576
gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
相较于neighbored,nested的结果是非常差的。
从上面结果看,2048个block被初始化了。每个block执行了8个recursion,16384个child block被创建,__syncthreads也被调用了16384次。这都是导致效率很低的原因。
当一个child grid被调用后,他看到的memory是和parent完全一样的,因为child只需要parent的一部分数据,block在每个child grid的启动前的同步操作是不必要的,修改后:

__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduceNosync (int *g_idata, int *g_odata,unsigned int isize) {
// set thread ID
unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x;
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int *odata = &g_odata[blockIdx.x];
// stop condition
if (isize == 2 && tid == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0] + idata[1];
return;
}
// nested invoke
int istride = isize>>1;
if(istride > 1 && tid < istride) {
idata[tid] += idata[tid + istride];
if(tid==0) {
gpuRecursiveReduceNosync<<<1, istride>>>(idata,odata,istride);
}
}
}

运行输出,时间减少到原来的三分之一:
./nestedReduceNoSync starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c
array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512
cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576
gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nestedNosyn elapsed 0.059125 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
不过,性能还是比neighbour-paired要慢。接下来在做点改动,主要想法如下图所示,kernel的调用增加了一个参数iDim,这是因为每次递归调用,child block的大小就减半,parent 的blockDim必须传递给child grid,从而使每个thread都能计算正确的global memory偏移地址。注意,所有空闲的thread都被移除了。相较于之前的实现,每次都会有一半的thread空闲下来而被移除,也就释放了一半的计算资源。


__global__ void gpuRecursiveReduce2(int *g_idata, int *g_odata, int iStride,int const iDim) {
// convert global data pointer to the local pointer of this block
int *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*iDim;
// stop condition
if (iStride == 1 && threadIdx.x == 0) {
g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]+idata[1];
return;
}
// in place reduction
idata[threadIdx.x] += idata[threadIdx.x + iStride];
// nested invocation to generate child grids
if(threadIdx.x == 0 && blockIdx.x == 0) {
gpuRecursiveReduce2 <<<gridDim.x,iStride/2>>>(
g_idata,g_odata,iStride/2,iDim);
}
}

编译运行:

./nestedReduce2 starting reduction at device 0: Tesla K40c
array 1048576 grid 2048 block 512
cpu reduce elapsed 0.000689 sec cpu_sum: 1048576
gpu Neighbored elapsed 0.000532 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nested elapsed 0.172036 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nestedNosyn elapsed 0.059125 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>
gpu nested2 elapsed 0.000797 sec gpu_sum: 1048576<<<grid 2048 block 512>>>

从这个结果看,数据又好看了不少,可以猜测,大约是由于调用了较少的child grid,我们可以用nvprof来验证下:
$ nvprof ./nestedReduce2
部分输出结果如下,第二列上显示了dievice kernel 的调用次数,第一个和第二个创建了16384个child grid。gpuRecursiveReduce2八层nested Parallelism只创建了8个child。
Calls (host) Calls (device) Avg Min Max Name
1 16384 441.48us 2.3360us 171.34ms gpuRecursiveReduce
1 16384 51.140us 2.2080us 57.906ms gpuRecursiveReduceNosync
1 8 56.195us 22.048us 100.74us gpuRecursiveReduce2
1 0 352.67us 352.67us 352.67us reduceNeighbored
对于一个给定的算法,我们可以有很多种实现方式,避免大量的nested 调用可以提升很多性能。同步对算法的正确性至关重要,但也是一个消耗比较大的操作,block内部的同步操作倒是可以去掉。因为在device上运行nested程序需要额外的资源,nested调用是有限的。
【转】CUDA之Dynamic Parallelism详解的更多相关文章
- 详解动态规划(Dynamic Programming)& 背包问题
详解动态规划(Dynamic Programming)& 背包问题 引入 有序号为1~n这n项工作,每项工作在Si时间开始,在Ti时间结束.对于每项工作都可以选择参加与否.如果选择了参与,那么 ...
- CUDA ---- Dynamic Parallelism
Dynamic Parallelism 到目前为止,所有kernel都是在host端调用,GPU的工作完全在CPU的控制下.CUDA Dynamic Parallelism允许GPU kernel在d ...
- c# 把一个匿名对象赋值给一个Object类型的变量后,怎么取这个变量? c# dynamic动态类型和匿名类 详解C# 匿名对象(匿名类型)、var、动态类型 dynamic 深入浅析C#中的var和dynamic
比如有一个匿名对象,var result =......Select( a=>new { id=a.id, name=a.name});然后Object obj = result ;我怎 ...
- Kintinuous 相关论文 Volume Fusion 详解
近几个月研读了不少RGBD-SLAM的相关论文,Whelan的Volume Fusion系列文章的效果确实不错,而且开源代码Kintinuous结构清晰,易于编译和运行,故把一些学习时自己的理解和经验 ...
- suricata.yaml (一款高性能的网络IDS、IPS和网络安全监控引擎)默认配置文件(图文详解)
不多说,直接上干货! 前期博客 基于CentOS6.5下Suricata(一款高性能的网络IDS.IPS和网络安全监控引擎)的搭建(图文详解)(博主推荐) 或者 基于Ubuntu14.04下Suric ...
- C#进阶系列——WebApi 接口返回值不困惑:返回值类型详解
前言:已经有一个月没写点什么了,感觉心里空落落的.今天再来篇干货,想要学习Webapi的园友们速速动起来,跟着博主一起来学习吧.之前分享过一篇 C#进阶系列——WebApi接口传参不再困惑:传参详解 ...
- 3.awk数组详解及企业实战案例
awk数组详解及企业实战案例 3.打印数组: [root@nfs-server test]# awk 'BEGIN{array[1]="zhurui";array[2]=" ...
- C#进阶系列——WebApi 接口参数不再困惑:传参详解
前言:还记得刚使用WebApi那会儿,被它的传参机制折腾了好久,查阅了半天资料.如今,使用WebApi也有段时间了,今天就记录下API接口传参的一些方式方法,算是一个笔记,也希望能帮初学者少走弯路.本 ...
- ElasticSearch第四步-查询详解
ElasticSearch系列学习 ElasticSearch第一步-环境配置 ElasticSearch第二步-CRUD之Sense ElasticSearch第三步-中文分词 ElasticSea ...
随机推荐
- 简单的SpringWebFlow例子及遇到的问题
这段时间在看<Spring 实战>里面有讲Spring Web Flow,觉得里面的例子过于复杂,不适合新手,于是在网上找了个例子,跟着写 以下是项目的目录,我是基于maven搭建项目的 ...
- 拿到iframe页面里面的变量及元素的方法
先严重差评一下,用这种方法window.parent.document.frames['layui-layer-iframe1']不行!而且frames方法存在浏览器不兼容问题(貌似火狐不行) 页面d ...
- Spring Boot 揭秘与实战(四) 配置文件篇 - 有哪些很棒的特性
文章目录 1. 使用属性文件2. YAML文件 1.1. 自定义属性 1.2. 参数引用 1.3. 随机数属性 1.4. application-{profile}.properties参数加载 3. ...
- C++和C在linux下 和在windows下有什么区别?
一.函数库的区别 linux下的C函数库和windows下的函数库系统调用的机制不一样,Glibc包含了主要的C库.这个库提供了基本例程,用于分配内存.搜索目录.打开关闭文件.读写文件.字串处理.模式 ...
- 【leetcode】26-RemoveDuplicatesfromSortedArray
problem RemoveDuplicatesfromSortedArray 注意数组为空的情况要首先考虑,并给出返回值: 注意也要同时给出新的数组的数值: 注意数组最后两个元素的处理: class ...
- 在 Mac 安装Docker
https://blog.csdn.net/jpiverson/article/details/50685817 https://legacy.gitbook.com/book/yeasy/docke ...
- numpy中的复合数组
1.复合数组的创建 # 复合数组,最重要的是定义dtype a = np.array([('ABC', [1, 2, 3])], dtype="U3, 3i4") print(a) ...
- [LeetCode&Python] Problem 606. Construct String from Binary Tree
You need to construct a string consists of parenthesis and integers from a binary tree with the preo ...
- UGUI中Event Trigger的基本用法
UGUI中Event Trigger的基本用法 本文提供全流程,中文翻译. Chinar 坚持将简单的生活方式,带给世人!(拥有更好的阅读体验 -- 高分辨率用户请根据需求调整网页缩放比例) Chin ...
- day03用户交互、基本数据类型、运算符
用户交互 在实际应用中,我们经常需要用户输入相应信息,根据用户输入信息进行反馈,此时我们需要input/output信息 python中提供了便捷的输入方法input()和print() 在pytho ...





