Android开发之五大布局篇
一、Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种:
线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件。
相对布局(RelativeLayout):相对其它组件的布局方式。
绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout):按照绝对坐标来布局组件。
表格布局(TableLayout):按照行列方式布局组件。
帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件。
二、布局:
1、线性布局:线性布局是按照垂直或者水平方向来布局,通过“android:orientation”属性可以设置线性布局的方向。属性值有垂直(vertical)和水平(horizontal)两种。
常用的属性:
android:orientation:可以设置布局的方向,以列或行来显示。
android:gravity:用来控制组件的对齐方式,相对于父元素的重力方向。
layout_weight:控制各个组件在布局中的相对大小,对未占用空间水平或垂直分配权重值。
相关知识:
android:layout_gravity 本元素相对于父元素的重力方向 android:gravity 本元素所有子元素的重力方向 android:orientation 线性布局以列或行来显示内部子元素 android:layout_weight 子元素对未占用空间水平或垂直分配权重值 当 android:orientation="vertical" 时, 只有水平方向的设置才起作用,垂直方向的设置不起作用。即:left,right,center_horizontal 是生效的。!!!! 当 android:orientation="horizontal" 时, 只有垂直方向的设置才起作用,水平方向的设置不起作用。即:top,bottom,center_vertical 是生效的。!!!! android:layout_gravity 和 android:gravity 的区别 android:gravity对元素本身起作用-本身元素显示在什么位置 android:layout_gravity相对与它的父元素-元素显示在父元素的什么位置。 如:Button控件 android:layout_gravity 表示button在界面上的位置 android:gravity表示button上的字在button上的位置。 可选值[多选时用“|”分开] top、bottom、left、right、center_vertical、fill_vertical、center_horizontal、fill_horizontal、center、fill、clip_vertical。 top 将对象放在其容器的顶部,不改变其大小. bottom 将对象放在其容器的底部,不改变其大小. left将对象放在其容器的左侧,不改变其大小. right将对象放在其容器的右侧,不改变其大小. center_vertical 将对象纵向居中,不改变其大小. 垂直对齐方式:垂直方向上居中对齐。 fill_vertical 必要的时候增加对象的纵向大小,以完全充满其容器. 垂直方向填充 center_horizontal 将对象横向居中,不改变其大小水平对齐方式:水平方向上居中对齐 fill_horizontal 必要的时候增加对象的横向大小,以完全充满其容器. 水平方向填充 center 将对象横纵居中,不改变其大小. fill 必要的时候增加对象的横纵向大小,以完全充满其容器. clip_vertical 附加选项,用于按照容器的边来剪切对象的顶部和/或底部的内容. 剪切基于其纵向对齐设置:顶部对齐时,剪切底部;底部对齐时剪切顶部;除此之外剪切顶部和底部.垂直方向裁剪 clip_horizontal 附加选项,用于按照容器的边来剪切对象的左侧和/或右侧的内容. 剪切基于其横向对齐设置:左侧对齐时,剪切右侧;右侧对齐时剪切左侧;除此之外剪切左侧和右侧.水平方向裁剪 例子 TextView要让文本垂直/水平居中显示,有两种情况需要考虑: 1、layout_width/layout_height为wrap_content,此时要让TextView在父控件上居中显示,必须设置layout_gravity=”center”。 2、layout_width/layout_height为fill_parent,此时由于TextView已占据父窗体所有空间,必须设置gravity=”center”。
2、相对布局:相对布局是按照组件之间的相对位置来布局,比如在某个组件的左边,右边,上面和下面等。
RelativeLayout用到的一些重要的属性:
RelativeLayout用到的一些重要的属性:
第一类:属性值为true或false
android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent 相对于父元素完全居中
android:layout_alignParentBottom 贴紧父元素的下边缘
android:layout_alignParentLeft 贴紧父元素的左边缘
android:layout_alignParentRight 贴紧父元素的右边缘
android:layout_alignParentTop 贴紧父元素的上边缘
android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing 如果对应的兄弟元素找不到的话就以父元素做参照物
第二类:属性值必须为id的引用名“@id/id-name”
android:layout_below 在某元素的下方
android:layout_above 在某元素的的上方
android:layout_toLeftOf 在某元素的左边
android:layout_toRightOf 在某元素的右边
android:layout_alignTop 本元素的上边缘和某元素的的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 本元素的左边缘和某元素的的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 本元素的下边缘和某元素的的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 本元素的右边缘和某元素的的右边缘对齐
第三类:属性值为具体的像素值,如30dip,40px
android:layout_marginBottom 离某元素底边缘的距离
android:layout_marginLeft 离某元素左边缘的距离
android:layout_marginRight 离某元素右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginTop 离某元素上边缘的距离
EditText的android:hint
设置EditText为空时输入框内的提示信息。
android:gravity
android:gravity属性是对该view 内容的限定.比如一个button 上面的text. 你可以设置该text 在view的靠左,靠右等位置.以button为例,android:gravity="right"则button上面的文字靠右
android:layout_gravity
android:layout_gravity是用来设置该view相对与起父view 的位置.比如一个button 在linearlayout里,你想把该button放在靠左、靠右等位置就可以通过该属性设置.以button为例,android:layout_gravity="right"则button靠右
android:layout_alignParentRight
使当前控件的右端和父控件的右端对齐。这里属性值只能为true或false,默认false。
android:scaleType:
android:scaleType是控制图片如何resized/moved来匹对ImageView的size。ImageView.ScaleType / android:scaleType值的意义区别:
CENTER /center 按图片的原来size居中显示,当图片长/宽超过View的长/宽,则截取图片的居中部分显示
CENTER_CROP / centerCrop 按比例扩大图片的size居中显示,使得图片长(宽)等于或大于View的长(宽)
CENTER_INSIDE / centerInside 将图片的内容完整居中显示,通过按比例缩小或原来的size使得图片长/宽等于或小于View的长/宽
FIT_CENTER / fitCenter 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,居中显示
FIT_END / fitEnd 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的下部分位置
FIT_START / fitStart 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的上部分位置
FIT_XY / fitXY 把图片 不按比例扩大/缩小到View的大小显示
MATRIX / matrix 用矩阵来绘制,动态缩小放大图片来显示。
** 要注意一点,Drawable文件夹里面的图片命名是不能大写的。
3、表格布局:表格布局是一个ViewGroup以表格显示它的子视图(view)元素,即行和列标识一个视图的位置。
android:shrinkColumns:收缩指定的列以适合屏幕,不会挤出屏幕
android:stretchColumns:尽量把指定的列填充空白部分
android:layout_column:控件放在指定的列
android:layout_span:该控件所跨越的列数
android:foreground:设置该帧布局容器的前景图像
android:foregroundGravity:设置前景图像显示的位置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00BFFF" //淡蓝
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="260dp"
android:layout_height="260dp"
android:background="#FFC0CB" //粉
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="220dp"
android:layout_height="220dp"
android:background="#0000FF" // 蓝
/> </FrameLayout>
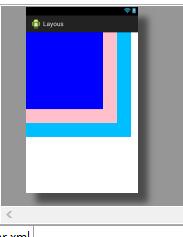
6、嵌套布局(线性布局与相对布局)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="177dp"
android:background="#FF4500"
android:text="111" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="162dp"
android:background="#BCBFEF"
android:text="222" /> <RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="406dp" >
<TextView
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="124dp"
android:layout_height="134dp"
android:background="#c2c2c2"
android:text="ccc" /> <TextView
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textView3"
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="123dp"
android:layout_height="136dp"
android:background="#FF4500"
android:text="bbb" /> <TextView
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textView4"
android:id="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_width="119dp"
android:layout_height="136dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#c4c4c4"
android:text="ttt" /> </RelativeLayout> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="123dp"
android:layout_height="136dp"
android:background="#FF4500"
android:text="bbb" /> <TextView
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_width="119dp"
android:layout_height="136dp"
android:background="#c4c4c4"
android:text="ttt" /> </LinearLayout>

Android开发之五大布局篇的更多相关文章
- Android开发-之五大布局
在html中大家都知道布局是什么意思了,简单来说就是将页面划分模块,比如html中的div.table等.那么Android中也是这样的.Android五大布局让界面更加美化,开发起来也更加方便.当然 ...
- Android中的五大布局
Android中的五大布局 1.了解布局 一个丰富的界面总是要由很多个控件组成的,那我们如何才能让各个控件都有条不紊地 摆放在界面上,而不是乱糟糟的呢?这就需要借助布局来实现了.布局是一种可用于放置很 ...
- android开发学习---layout布局、显示单位和如何进行单元测试
一.五大布局(layout) android中的用五大布局:LinearLayout (线性布局).AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局).RelativeLayout(相对布局).TableLay ...
- Android开发5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- android中的五大布局(控件的容器,可以放button等控件)
一.android中五大布局相当于是容器,这些容器里可以放控件也可以放另一个容器,子控件和布局都需要制定属性. 1.相对布局:RelativeLayout @1控件默认堆叠排列,需要制定控件的相对位置 ...
- Android开发之环境配置篇
Android环境配置: 一.JDK(不用安装) 1.拷贝 D:\Java\jdk1.8.0_91 文件内容 2. 安卓ADT ADT(Android Development Tools):安装ADT ...
- android开发 静态碎片布局实现
实现思维: 1.需要写2个或者多个子布局 2.写一个Java的class去实现将子布局与父类布局铺满.(一个子布局对应一个class) 3.在父类布局中导入fragment布局,并且添加android ...
- .Net程序猿玩转Android开发---(6)线性布局LinearLayout
LinearLayout控件是Android中重要的布局控件,是一个线性控件,所谓线性控件的意思是指该控件里面的内容仅仅能水平或垂直排列.也就 ...
- Android中的五大布局和logcat打印日志
在android中的布局有五大类,有的时候你可能用到一种,但有的时候你也可能需要两种或者三种布局同时一起使用.这五种布局为别为:LinearLayout(线性布局),FrameLayout(框架布局) ...
随机推荐
- jquery实现拖拽进度条并显示百分比的特效
#box{position: relative; width: 200px; height: 50px; border: 1px solid #eee; margin: 50px auto 0;} # ...
- Codeforces Round #516(Div 2)
比赛链接:传送门 A. Make a triangle!(简单思维) 题目大意: 给你三条边,问你最多加多少长度能使这三条边能构成三角形. 思路: 最大边小于答案加另外两条边的和. #include ...
- 20155208实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
20155208实验二 Java面向对象程序设计 一.实验内容 1.初步掌握单元测试和TDD 2.理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 3.初步掌握UML建模 4.熟悉S.O.L.I.D原则 5 ...
- dijksta 模板
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f ]; ]; ][]; void dijkstra(i ...
- 2017-2018-2 20165313实验三 《敏捷开发与XP实践》
实验报告封面 实验内容及步骤 实验一 1.试验要求: 参考http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6371315.html#SECCODESTANDARD安装alibaba 插 ...
- Windows server 2008 R2 安装指引
1.虚拟机实验安装win server 2008 R2 企业版, 安装环境: 虚拟机版本:VM 14 本地系统:win 7 64 位 专业版 打开VM14,新建虚拟机,选择自定义高级(此处也可以选择典 ...
- SELECT INTO 和 INSERT INTO SELECT 两种表复制语句详解(SQL数据库和Oracle数据库的区别)
https://www.cnblogs.com/mq0036/p/4155136.html 我们经常会遇到需要表复制的情况,如将一个table1的数据的部分字段复制到table2中,或者将整个tabl ...
- LeetCode – Most Common Word
Given a paragraph and a list of banned words, return the most frequent word that is not in the list ...
- 将koa+vue部署到服务器
很久很久以前,就对前后端如何分离,后端如何把代码部署到服务器有浓厚的兴趣,最近在阿里云上申请了一个服务器,试试水吧! 本文参考了文章<基于Node的Koa2项目从创建到打包到云服务器指南> ...
- CONTINUOUS MIGRATION
转自:https://pgloader.io/blog/continuous-migration/ After having been involved in many migration proje ...
