转载自系统技术非业余研究
http://blog.yufeng.info/archives/1239
我们在系统调优或者定位问题的时候,经常会发现多线程程序的效率很低,但是又不知道问题出在哪里,就知道上下文切换很多,但是为什么上下文切换,是谁导致切换,我们就不知道了。上下文切换可以用dstat这样的工具查看,比如:
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- -net/total- ---paging-- ---system-- |
usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw |
9 2 87 2 0 1|7398k 31M| 0 0 | 9.8k 11k| 16k 64k |
20 4 69 3 0 4| 26M 56M| 34M 172M| 0 0 | 61k 200k |
21 5 64 6 0 3| 26M 225M| 35M 175M| 0 0 | 75k 216k |
21 5 66 4 0 4| 25M 119M| 34M 173M| 0 0 | 66k 207k |
19 4 68 5 0 3| 23M 56M| 33M 166M| 0 0 | 60k 197k |
$sudo stap -e 'global cnt; probe scheduler.cpu_on {cnt<<<1;} probe timer.s(1){printf("%d\n", @count(cnt)); delete cnt;}' |
每秒高达200k左右的的上下文切换, 谁能告诉我发生了什么? 好吧,latencytop来救助了!
它的官网:http://www.latencytop.org/
Skipping audio, slower servers, everyone knows the symptoms of latency. But to know what’s going on in the system, what’s causing the latency, how to fix it… that’s a hard question without good answers right now.
LatencyTOP is a Linux* tool for software developers (both kernel and userspace), aimed at identifying where in the system latency is happening, and what kind of operation/action is causing the latency to happen so that the code can be changed to avoid the worst latency hiccups.
它是Intel贡献的另外一个性能查看器,还有一个是powertop,都是很不错的工具.
Latencytop通过在内核上下文切换的时候,记录被切换的进程的内核栈,然后通过匹配内核栈的函数来判断是什么原因导致上下文切换,同时他把几十种容易引起切换的场景的函数都记录起来,这样在判断系统问题的时候能容易定位到问题。
latencytop分成2个部分,内核部分和应用部分。内核部分负责调用栈的收集并且通过/proc来暴露, 应用部分负责显示.
工作界面截图如下:
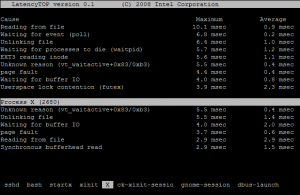
latencytop在2.6.256后被内核吸收成为其中一部分,只要编译的时候打开该选项就好,如何确认呢?
$ cat /proc/latency_stats |
Latency Top version : v0.1 |
看到这个就好了, 遗憾的是RHEL6竟然带了latencytop应用部分,而没有打开编译选项,让我们情何以堪呢?
在ubuntu下可以这么安装:
$ apt-get install latencytop |
$ sudo latencytop #就可以使用了 |
但是latencytop比较傻的是默认是开图像界面的,我们很不习惯,我们要文本界面, 自己动手把!
$ apt-get source latencytop |
$ diff -up Makefile.orig Makefile |
--- Makefile.orig 2011-03-29 20:10:29.025845447 +0800 |
+++ Makefile 2011-03-28 14:48:11.232318002 +0800 |
重新make下就好了, 文本界面出现了. 具体使用参看 man latencytop。
fcicq同学说:
加个 –nogui 参数就好了. 不需要重新编译.
谢谢!
好了,那么latencytop支持多少种的延迟原因呢?让latencytop.trans告诉你,我们也可以自己修改这个文件,把新的延迟原因加上去。
$ cat /usr/share/latencytop/latencytop.trans |
1 vfs_read Reading from file |
1 vfs_write Writing to file |
1 __mark_inode_dirty Marking inode dirty |
1 vfs_readdir Reading directory content |
1 vfs_unlink Unlinking file |
1 blocking_notifier_call_chain Blocking notifier |
1 lock_super Superblock lock contention |
1 vfs_create Creating a file |
1 KAS_ScheduleTimeout Binary AMD driver delay |
1 firegl_lock_device Binary AMD driver delay |
2 __bread Synchronous buffer read |
2 do_generic_mapping_read Reading file data |
2 sock_sendmsg Sending data over socket |
2 do_sys_open Opening file |
2 do_sys_poll Waiting for event (poll) |
2 core_sys_select Waiting for event (select) |
2 proc_reg_read Reading from /proc file |
2 __pollwait Waiting for event (poll) |
2 sys_fcntl FCNTL system call |
2 scsi_error_handler SCSI error handler |
2 proc_root_readdir Reading /proc directory |
2 ksoftirqd Waking ksoftirqd |
2 do_unlinkat Unlinking file |
2 __wait_on_buffer Waiting for buffer IO to complete |
2 pdflush pdflush() kernel thread |
2 kjournald kjournald() kernel thread |
2 blkdev_ioctl block device IOCTL |
2 kauditd_thread kernel audit daemon |
2 __filemap_fdatawrite_range fdatasync system call |
2 do_sync_write synchronous write |
2 kthreadd kthreadd kernel thread |
2 usb_port_resume Waking up USB device |
2 usb_autoresume_device Waking up USB device |
2 kswapd kswapd() kernel thread |
2 md_thread Raid resync kernel thread |
2 i915_wait_request Waiting for GPU command to complete |
2 request_module Loading a kernel module |
3 tty_wait_until_sent Waiting for TTY to finish sending |
3 pipe_read Reading from a pipe |
3 pipe_write Writing to a pipe |
3 pipe_wait Waiting for pipe data |
3 read_block_bitmap Reading EXT3 block bitmaps |
3 scsi_execute_req Executing raw SCSI command |
3 sys_wait4 Waiting for a process to die |
3 sr_media_change Checking for media change |
3 sr_do_ioctl SCSI cdrom ioctl |
3 sd_ioctl SCSI disk ioctl |
3 sr_cd_check Checking CDROM media present |
3 ext3_read_inode Reading EXT3 inode |
3 htree_dirblock_to_tree Reading EXT3 directory htree |
3 ext3_readdir Reading EXT3 directory |
3 ext3_bread Synchronous EXT3 read |
3 ext3_free_branches Unlinking file on EXT3 |
3 ext3_get_branch Reading EXT3 indirect blocks |
3 ext3_find_entry EXT3: Looking for file |
3 __ext3_get_inode_loc Reading EXT3 inode |
3 ext3_delete_inode EXT3 deleting inode |
3 sync_page Writing a page to disk |
3 tty_poll Waiting for TTY data |
3 tty_read Waiting for TTY input |
3 tty_write Writing data to TTY |
3 update_atime Updating inode atime |
3 page_cache_sync_readahead Pagecache sync readahead |
3 do_fork Fork() system call |
3 sys_mkdirat Creating directory |
3 lookup_create Creating file |
3 inet_sendmsg Sending TCP/IP data |
3 tcp_recvmsg Receiving TCP/IP data |
3 link_path_walk Following symlink |
3 path_walk Walking directory tree |
3 sys_getdents Reading directory content |
3 unix_stream_recvmsg Waiting for data on unix socket |
3 ext3_mkdir EXT3: Creating a directory |
3 journal_get_write_access EXT3: Waiting for journal access |
3 synchronize_rcu Waiting for RCU |
3 input_close_device Closing input device |
3 mousedev_close_device Closing mouse device |
3 mousedev_release Closing mouse device |
3 mousedev_open Opening mouse device |
3 kmsg_read Reading from dmesg |
3 sys_futex Userspace lock contention |
3 do_futex Userspace lock contention |
3 vt_waitactive vt_waitactive IOCTL |
3 acquire_console_sem Waiting for console access |
3 filp_close Closing a file |
3 sync_inode (f)syncing an inode to disk |
3 ata_exec_internal_sg Executing internal ATA command |
3 writeback_inodes Writing back inodes |
3 ext3_orphan_add EXT3 adding orphan |
3 ext3_mark_inode_dirty EXT3 marking inode dirty |
3 ext3_unlink EXT3 unlinking file |
3 ext3_create EXT3 Creating a file |
3 log_do_checkpoint EXT3 journal checkpoint |
3 generic_delete_inode Deleting an inode |
3 proc_delete_inode Removing /proc file |
3 do_truncate Truncating file |
3 sys_execve Executing a program |
3 journal_commit_transaction EXT3: committing transaction |
3 __stop_machine_run Freezing the kernel (for module load) |
3 sys_munmap unmapping memory |
3 sys_mmap mmaping memory |
3 sync_buffer Writing buffer to disk (synchronous) |
3 inotify_inode_queue_event Inotify event |
3 proc_lookup Looking up /proc file |
3 generic_make_request Creating block layer request |
3 get_request_wait Creating block layer request |
3 alloc_page_vma Allocating a VMA |
#3 __d_lookup Looking up a dentry |
3 blkdev_direct_IO Direct block device IO |
3 sys_mprotect mprotect() system call |
3 shrink_icache_memory reducing inode cache memory footprint |
3 vfs_stat_fd stat() operation |
3 cdrom_open opening cdrom device |
3 sys_epoll_wait Waiting for event (epoll) |
3 sync_sb_inodes Syncing inodes |
3 tcp_connect TCP/IP connect |
3 ata_scsi_ioctl ATA/SCSI disk ioctl |
3 do_rmdir Removing directory |
3 vfs_rmdir Removing directory |
3 sys_flock flock() on a file |
3 usbdev_open opening USB device |
3 lock_kernel Big Kernel Lock contention |
3 blk_execute_rq Submitting block IO |
3 scsi_cmd_ioctl SCSI ioctl command |
3 acpi_ec_transaction ACPI hardware access |
3 journal_get_undo_access Waiting for EXT3 journal undo operation |
3 i915_irq_wait Waiting for GPU interrupt |
3 i915_gem_throttle_ioctl Throttling GPU while waiting for commands |
5 do_page_fault Page fault |
5 handle_mm_fault Page fault |
5 filemap_fault Page fault |
5 sync_filesystems Syncing filesystem |
5 sys_nanosleep Application requested delay |
5 sys_pause Application requested delay |
5 evdev_read Reading keyboard/mouse input |
5 do_fsync fsync() on a file (type 'F' for details) |
5 __log_wait_for_space Waiting for EXT3 journal space |
延迟原因非常的详细.
本来到这里,我要介绍的要介绍了,但是且慢,由于这个东西要在2.6.26后的系统上使用,我们的线上系统大部分是RHEL 5U4, 2.6.18的, 我们如何使用呢?
这时候 systemtap 一如既往的前来救助了!
systemtap 1.4版本以后带了个latencytop.stp, 也是intel的贡献. 那我们试验下穷人家的latencytop.
它在那里呢?
Systemtap translator/driver (version 1.5 /0.137 non-git sources) |
Copyright (C) 2005-2011 Red Hat, Inc. and others |
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. |
enabled features: AVAHI LIBRPM LIBSQLITE3 NSS BOOST_SHARED_PTR TR1_UNORDERED_MAP NLS |
$ ls -al /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
-rwxr-xr-x 1 chuba users 16240 Feb 17 22:02/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
$ sudo stap -t --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
ERROR: Skipped too many probes, check MAXSKIPPED or try again with stap -t for moredetails. |
WARNING: Number of errors: 0, skipped probes: 101 |
WARNING: Skipped due to global 'dequeue' lock timeout: 2 |
WARNING: Skipped due to global 'this_sleep' lock timeout: 99 |
kernel.trace("deactivate_task")!, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:47:1), hits: 254, cycles: 680min/43327avg/2248467max, from: kernel.trace("deactivate_task") |
kernel.trace("activate_task")!, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:58:1), hits: 255, cycles: 890min/502549avg/2271568max, from: kernel.trace("activate_task") |
kernel.function("finish_task_switch@kernel/sched.c:1969")?, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:78:7), hits: 509, cycles: 213min/1002207avg/5382852max, from: kernel.function("finish_task_switch") from: scheduler.cpu_on |
begin, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:123:1), hits: 1, cycles: 1802min/1802avg/1802max, from: begin |
begin, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:131:1), hits: 1, cycles: 227979min/227979avg/227979max, from: begin |
Pass 5: run failed. Try again with another '--vp 00001' option. |
出错了! 原因是lock timeout, 原来stap的全局变量是用锁保护的,现在超时了!知道原因好办,打个patch吧!
$ diff -up translate.cxx.orig translate.cxx |
--- translate.cxx.orig 2011-03-22 21:26:52.000000000 +0800 |
+++ /translate.cxx 2011-03-29 20:31:28.000000000 +0800 |
@@ -5802,10 +5802,10 @@ translate_pass (systemtap_session& s) |
s.op->newline() << "#define MAXACTION_INTERRUPTIBLE (MAXACTION * 10)"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef TRYLOCKDELAY"; |
- s.op->newline() << "#define TRYLOCKDELAY 10 /* microseconds */"; |
+ s.op->newline() << "#define TRYLOCKDELAY 50 /* microseconds */"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef MAXTRYLOCK"; |
- s.op->newline() << "#define MAXTRYLOCK 100 /* 1 millisecond total */"; |
+ s.op->newline() << "#define MAXTRYLOCK 500 /* 1 millisecond total */"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef MAXMAPENTRIES"; |
s.op->newline() << "#define MAXMAPENTRIES 2048"; |
$ sudo stap --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
ERROR: probe overhead exceeded threshold |
WARNING: Number of errors: 1, skipped probes: 0 |
Pass 5: run failed. Try again with another '--vp 00001' option. |
#又错了,这次原因是probe overhead exceeded threshold, 看下代码我们知道,脚本的开销太大了,超过正常的负载,通过查看代码可以用STP_NO_OVERLOAD来解除这个限制 |
$ sudo stap -DSTP_NO_OVERLOAD --all-modules -DMAXSKIPPED=1024 /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
Reason Count Average(us) Maximum(us) Percent% |
Userspace lock contention 345 16409195 83258717 45% |
migration() kernel thread 1733 402701 3571412 5% |
Reading from a pipe 212 2922207 52151180 4% |
Waking ksoftirqd 16 16082822 59266312 2% |
Waiting for event (select) 99 2113310 28510974 1% |
kjournald() kernel thread 148 1313447 13983084 1% |
Application requested delay 94 1059898 10011409 0% |
Waiting for event (select) 38 2259444 29057362 0% |
Waiting for event (poll) 1 57582711 57582711 0% |
Application requested delay 3 19030709 36000553 0% |
Waiting for event (select) 39 1341880 5847683 0% |
这次看到结果了,哈哈,小高兴一把。但是在繁忙的系统上这个脚本的资源占用特别多,也是不爽的。 幸运的是这个脚本支持查看某个进程的延迟情况, 就是在 latencytap.stp 后面加个-x 参数。
这个脚本设计应该是支持进程ID, 但是结果写成了线程ID,属于bug!!!
动手改下吧:
$ diff -u latencytap.stp.orig latencytap.stp |
--- latencytap.stp.orig 2011-02-17 22:02:40.000000000 +0800 |
+++ latencytap.stp 2011-03-29 20:43:51.000000000 +0800 |
-function log_event:long (p:long) { return (!traced_pid || traced_pid == p) } |
+function log_event:long (p:long) { return (!traced_pid || traced_pid == task_pid(p)) } |
#func names from hex addresses |
function func_backtrace:string (ips:string) |
# check to see if task is in appropriate state: |
- if (log_event($p->pid) && (s & 3)) { |
+ if (log_event($p) && (s & 3)) { |
dequeue[$p] = gettimeofday_us(); |
probe kernel.trace("activate_task") !, |
kernel.function("activate_task") { |
- if (!log_event($p->pid)) next |
+ if (!log_event($p)) next |
$ sudo stap --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp -x $$ |
#如果发现出来的Reason是空行, 就把latencytap.stp里面的debug=0, 改成debug=1 |
这下终于爽了,旧内核用systemtap版本的,新内核用内核版本的,世界和谐!
通过对线上MySQL的诊断发现大部分时间花在mutex锁的竞争上来,我说过了,我会收拾你的,等着瞧!
玩得开心!
Related posts:
- SystemTap–Linux下的万能观测工具
- Systemtap的另类用法
- 再谈systemtap在ubuntu 10.10下的安装
- Systemtap辅助设置tcp_init_cwnd,免对操作系统打Patch
- 突破systemtap脚本对资源使用的限制
我们在系统调优或者定位问题的时候,经常会发现多线程程序的效率很低,但是又不知道问题出在哪里,就知道上下文切换很多,但是为什么上下文切换,是谁导致切换,我们就不知道了。上下文切换可以用dstat这样的工具查看,比如:
----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- -net/total- ---paging-- ---system-- |
usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| recv send| in out | int csw |
9 2 87 2 0 1|7398k 31M| 0 0 | 9.8k 11k| 16k 64k |
20 4 69 3 0 4| 26M 56M| 34M 172M| 0 0 | 61k 200k |
21 5 64 6 0 3| 26M 225M| 35M 175M| 0 0 | 75k 216k |
21 5 66 4 0 4| 25M 119M| 34M 173M| 0 0 | 66k 207k |
19 4 68 5 0 3| 23M 56M| 33M 166M| 0 0 | 60k 197k |
$sudo stap -e 'global cnt; probe scheduler.cpu_on {cnt<<<1;} probe timer.s(1){printf("%d\n", @count(cnt)); delete cnt;}' |
每秒高达200k左右的的上下文切换, 谁能告诉我发生了什么? 好吧,latencytop来救助了!
它的官网:http://www.latencytop.org/
Skipping audio, slower servers, everyone knows the symptoms of latency. But to know what’s going on in the system, what’s causing the latency, how to fix it… that’s a hard question without good answers right now.
LatencyTOP is a Linux* tool for software developers (both kernel and userspace), aimed at identifying where in the system latency is happening, and what kind of operation/action is causing the latency to happen so that the code can be changed to avoid the worst latency hiccups.
它是Intel贡献的另外一个性能查看器,还有一个是powertop,都是很不错的工具.
Latencytop通过在内核上下文切换的时候,记录被切换的进程的内核栈,然后通过匹配内核栈的函数来判断是什么原因导致上下文切换,同时他把几十种容易引起切换的场景的函数都记录起来,这样在判断系统问题的时候能容易定位到问题。
latencytop分成2个部分,内核部分和应用部分。内核部分负责调用栈的收集并且通过/proc来暴露, 应用部分负责显示.
工作界面截图如下:

latencytop在2.6.256后被内核吸收成为其中一部分,只要编译的时候打开该选项就好,如何确认呢?
$ cat /proc/latency_stats |
Latency Top version : v0.1 |
看到这个就好了, 遗憾的是RHEL6竟然带了latencytop应用部分,而没有打开编译选项,让我们情何以堪呢?
在ubuntu下可以这么安装:
$ apt-get install latencytop |
$ sudo latencytop #就可以使用了 |
但是latencytop比较傻的是默认是开图像界面的,我们很不习惯,我们要文本界面, 自己动手把!
$ apt-get source latencytop |
$ diff -up Makefile.orig Makefile |
--- Makefile.orig 2011-03-29 20:10:29.025845447 +0800 |
+++ Makefile 2011-03-28 14:48:11.232318002 +0800 |
重新make下就好了, 文本界面出现了. 具体使用参看 man latencytop。
fcicq同学说:
加个 –nogui 参数就好了. 不需要重新编译.
谢谢!
好了,那么latencytop支持多少种的延迟原因呢?让latencytop.trans告诉你,我们也可以自己修改这个文件,把新的延迟原因加上去。
$ cat /usr/share/latencytop/latencytop.trans |
1 vfs_read Reading from file |
1 vfs_write Writing to file |
1 __mark_inode_dirty Marking inode dirty |
1 vfs_readdir Reading directory content |
1 vfs_unlink Unlinking file |
1 blocking_notifier_call_chain Blocking notifier |
1 lock_super Superblock lock contention |
1 vfs_create Creating a file |
1 KAS_ScheduleTimeout Binary AMD driver delay |
1 firegl_lock_device Binary AMD driver delay |
2 __bread Synchronous buffer read |
2 do_generic_mapping_read Reading file data |
2 sock_sendmsg Sending data over socket |
2 do_sys_open Opening file |
2 do_sys_poll Waiting for event (poll) |
2 core_sys_select Waiting for event (select) |
2 proc_reg_read Reading from /proc file |
2 __pollwait Waiting for event (poll) |
2 sys_fcntl FCNTL system call |
2 scsi_error_handler SCSI error handler |
2 proc_root_readdir Reading /proc directory |
2 ksoftirqd Waking ksoftirqd |
2 do_unlinkat Unlinking file |
2 __wait_on_buffer Waiting for buffer IO to complete |
2 pdflush pdflush() kernel thread |
2 kjournald kjournald() kernel thread |
2 blkdev_ioctl block device IOCTL |
2 kauditd_thread kernel audit daemon |
2 __filemap_fdatawrite_range fdatasync system call |
2 do_sync_write synchronous write |
2 kthreadd kthreadd kernel thread |
2 usb_port_resume Waking up USB device |
2 usb_autoresume_device Waking up USB device |
2 kswapd kswapd() kernel thread |
2 md_thread Raid resync kernel thread |
2 i915_wait_request Waiting for GPU command to complete |
2 request_module Loading a kernel module |
3 tty_wait_until_sent Waiting for TTY to finish sending |
3 pipe_read Reading from a pipe |
3 pipe_write Writing to a pipe |
3 pipe_wait Waiting for pipe data |
3 read_block_bitmap Reading EXT3 block bitmaps |
3 scsi_execute_req Executing raw SCSI command |
3 sys_wait4 Waiting for a process to die |
3 sr_media_change Checking for media change |
3 sr_do_ioctl SCSI cdrom ioctl |
3 sd_ioctl SCSI disk ioctl |
3 sr_cd_check Checking CDROM media present |
3 ext3_read_inode Reading EXT3 inode |
3 htree_dirblock_to_tree Reading EXT3 directory htree |
3 ext3_readdir Reading EXT3 directory |
3 ext3_bread Synchronous EXT3 read |
3 ext3_free_branches Unlinking file on EXT3 |
3 ext3_get_branch Reading EXT3 indirect blocks |
3 ext3_find_entry EXT3: Looking for file |
3 __ext3_get_inode_loc Reading EXT3 inode |
3 ext3_delete_inode EXT3 deleting inode |
3 sync_page Writing a page to disk |
3 tty_poll Waiting for TTY data |
3 tty_read Waiting for TTY input |
3 tty_write Writing data to TTY |
3 update_atime Updating inode atime |
3 page_cache_sync_readahead Pagecache sync readahead |
3 do_fork Fork() system call |
3 sys_mkdirat Creating directory |
3 lookup_create Creating file |
3 inet_sendmsg Sending TCP/IP data |
3 tcp_recvmsg Receiving TCP/IP data |
3 link_path_walk Following symlink |
3 path_walk Walking directory tree |
3 sys_getdents Reading directory content |
3 unix_stream_recvmsg Waiting for data on unix socket |
3 ext3_mkdir EXT3: Creating a directory |
3 journal_get_write_access EXT3: Waiting for journal access |
3 synchronize_rcu Waiting for RCU |
3 input_close_device Closing input device |
3 mousedev_close_device Closing mouse device |
3 mousedev_release Closing mouse device |
3 mousedev_open Opening mouse device |
3 kmsg_read Reading from dmesg |
3 sys_futex Userspace lock contention |
3 do_futex Userspace lock contention |
3 vt_waitactive vt_waitactive IOCTL |
3 acquire_console_sem Waiting for console access |
3 filp_close Closing a file |
3 sync_inode (f)syncing an inode to disk |
3 ata_exec_internal_sg Executing internal ATA command |
3 writeback_inodes Writing back inodes |
3 ext3_orphan_add EXT3 adding orphan |
3 ext3_mark_inode_dirty EXT3 marking inode dirty |
3 ext3_unlink EXT3 unlinking file |
3 ext3_create EXT3 Creating a file |
3 log_do_checkpoint EXT3 journal checkpoint |
3 generic_delete_inode Deleting an inode |
3 proc_delete_inode Removing /proc file |
3 do_truncate Truncating file |
3 sys_execve Executing a program |
3 journal_commit_transaction EXT3: committing transaction |
3 __stop_machine_run Freezing the kernel (for module load) |
3 sys_munmap unmapping memory |
3 sys_mmap mmaping memory |
3 sync_buffer Writing buffer to disk (synchronous) |
3 inotify_inode_queue_event Inotify event |
3 proc_lookup Looking up /proc file |
3 generic_make_request Creating block layer request |
3 get_request_wait Creating block layer request |
3 alloc_page_vma Allocating a VMA |
#3 __d_lookup Looking up a dentry |
3 blkdev_direct_IO Direct block device IO |
3 sys_mprotect mprotect() system call |
3 shrink_icache_memory reducing inode cache memory footprint |
3 vfs_stat_fd stat() operation |
3 cdrom_open opening cdrom device |
3 sys_epoll_wait Waiting for event (epoll) |
3 sync_sb_inodes Syncing inodes |
3 tcp_connect TCP/IP connect |
3 ata_scsi_ioctl ATA/SCSI disk ioctl |
3 do_rmdir Removing directory |
3 vfs_rmdir Removing directory |
3 sys_flock flock() on a file |
3 usbdev_open opening USB device |
3 lock_kernel Big Kernel Lock contention |
3 blk_execute_rq Submitting block IO |
3 scsi_cmd_ioctl SCSI ioctl command |
3 acpi_ec_transaction ACPI hardware access |
3 journal_get_undo_access Waiting for EXT3 journal undo operation |
3 i915_irq_wait Waiting for GPU interrupt |
3 i915_gem_throttle_ioctl Throttling GPU while waiting for commands |
5 do_page_fault Page fault |
5 handle_mm_fault Page fault |
5 filemap_fault Page fault |
5 sync_filesystems Syncing filesystem |
5 sys_nanosleep Application requested delay |
5 sys_pause Application requested delay |
5 evdev_read Reading keyboard/mouse input |
5 do_fsync fsync() on a file (type 'F' for details) |
5 __log_wait_for_space Waiting for EXT3 journal space |
延迟原因非常的详细.
本来到这里,我要介绍的要介绍了,但是且慢,由于这个东西要在2.6.26后的系统上使用,我们的线上系统大部分是RHEL 5U4, 2.6.18的, 我们如何使用呢?
这时候 systemtap 一如既往的前来救助了!
systemtap 1.4版本以后带了个latencytop.stp, 也是intel的贡献. 那我们试验下穷人家的latencytop.
它在那里呢?
Systemtap translator/driver (version 1.5 /0.137 non-git sources) |
Copyright (C) 2005-2011 Red Hat, Inc. and others |
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. |
enabled features: AVAHI LIBRPM LIBSQLITE3 NSS BOOST_SHARED_PTR TR1_UNORDERED_MAP NLS |
$ ls -al /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
-rwxr-xr-x 1 chuba users 16240 Feb 17 22:02/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
$ sudo stap -t --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
ERROR: Skipped too many probes, check MAXSKIPPED or try again with stap -t for moredetails. |
WARNING: Number of errors: 0, skipped probes: 101 |
WARNING: Skipped due to global 'dequeue' lock timeout: 2 |
WARNING: Skipped due to global 'this_sleep' lock timeout: 99 |
kernel.trace("deactivate_task")!, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:47:1), hits: 254, cycles: 680min/43327avg/2248467max, from: kernel.trace("deactivate_task") |
kernel.trace("activate_task")!, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:58:1), hits: 255, cycles: 890min/502549avg/2271568max, from: kernel.trace("activate_task") |
kernel.function("finish_task_switch@kernel/sched.c:1969")?, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:78:7), hits: 509, cycles: 213min/1002207avg/5382852max, from: kernel.function("finish_task_switch") from: scheduler.cpu_on |
begin, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:123:1), hits: 1, cycles: 1802min/1802avg/1802max, from: begin |
begin, (/usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp:131:1), hits: 1, cycles: 227979min/227979avg/227979max, from: begin |
Pass 5: run failed. Try again with another '--vp 00001' option. |
出错了! 原因是lock timeout, 原来stap的全局变量是用锁保护的,现在超时了!知道原因好办,打个patch吧!
$ diff -up translate.cxx.orig translate.cxx |
--- translate.cxx.orig 2011-03-22 21:26:52.000000000 +0800 |
+++ /translate.cxx 2011-03-29 20:31:28.000000000 +0800 |
@@ -5802,10 +5802,10 @@ translate_pass (systemtap_session& s) |
s.op->newline() << "#define MAXACTION_INTERRUPTIBLE (MAXACTION * 10)"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef TRYLOCKDELAY"; |
- s.op->newline() << "#define TRYLOCKDELAY 10 /* microseconds */"; |
+ s.op->newline() << "#define TRYLOCKDELAY 50 /* microseconds */"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef MAXTRYLOCK"; |
- s.op->newline() << "#define MAXTRYLOCK 100 /* 1 millisecond total */"; |
+ s.op->newline() << "#define MAXTRYLOCK 500 /* 1 millisecond total */"; |
s.op->newline() << "#endif"; |
s.op->newline() << "#ifndef MAXMAPENTRIES"; |
s.op->newline() << "#define MAXMAPENTRIES 2048"; |
$ sudo stap --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
ERROR: probe overhead exceeded threshold |
WARNING: Number of errors: 1, skipped probes: 0 |
Pass 5: run failed. Try again with another '--vp 00001' option. |
#又错了,这次原因是probe overhead exceeded threshold, 看下代码我们知道,脚本的开销太大了,超过正常的负载,通过查看代码可以用STP_NO_OVERLOAD来解除这个限制 |
$ sudo stap -DSTP_NO_OVERLOAD --all-modules -DMAXSKIPPED=1024 /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp |
Reason Count Average(us) Maximum(us) Percent% |
Userspace lock contention 345 16409195 83258717 45% |
migration() kernel thread 1733 402701 3571412 5% |
Reading from a pipe 212 2922207 52151180 4% |
Waking ksoftirqd 16 16082822 59266312 2% |
Waiting for event (select) 99 2113310 28510974 1% |
kjournald() kernel thread 148 1313447 13983084 1% |
Application requested delay 94 1059898 10011409 0% |
Waiting for event (select) 38 2259444 29057362 0% |
Waiting for event (poll) 1 57582711 57582711 0% |
Application requested delay 3 19030709 36000553 0% |
Waiting for event (select) 39 1341880 5847683 0% |
这次看到结果了,哈哈,小高兴一把。但是在繁忙的系统上这个脚本的资源占用特别多,也是不爽的。 幸运的是这个脚本支持查看某个进程的延迟情况, 就是在 latencytap.stp 后面加个-x 参数。
这个脚本设计应该是支持进程ID, 但是结果写成了线程ID,属于bug!!!
动手改下吧:
$ diff -u latencytap.stp.orig latencytap.stp |
--- latencytap.stp.orig 2011-02-17 22:02:40.000000000 +0800 |
+++ latencytap.stp 2011-03-29 20:43:51.000000000 +0800 |
-function log_event:long (p:long) { return (!traced_pid || traced_pid == p) } |
+function log_event:long (p:long) { return (!traced_pid || traced_pid == task_pid(p)) } |
#func names from hex addresses |
function func_backtrace:string (ips:string) |
# check to see if task is in appropriate state: |
- if (log_event($p->pid) && (s & 3)) { |
+ if (log_event($p) && (s & 3)) { |
dequeue[$p] = gettimeofday_us(); |
probe kernel.trace("activate_task") !, |
kernel.function("activate_task") { |
- if (!log_event($p->pid)) next |
+ if (!log_event($p)) next |
$ sudo stap --all-modules /usr/share/doc/systemtap/examples/profiling/latencytap.stp -x $$ |
#如果发现出来的Reason是空行, 就把latencytap.stp里面的debug=0, 改成debug=1 |
这下终于爽了,旧内核用systemtap版本的,新内核用内核版本的,世界和谐!
通过对线上MySQL的诊断发现大部分时间花在mutex锁的竞争上来,我说过了,我会收拾你的,等着瞧!
玩得开心!
- 最新深度技术GHOST XP系统旗舰增强版 V2016年
来自系统妈:http://www.xitongma.com 深度技术GHOST xp系统旗舰增强版 V2016年 系统概述 深度技术ghost xp系统旗舰增强版集合微软JAVA虚拟机IE插件,增强浏 ...
- 深度技术GHOST WIN7系统32.64位j极速安装版 V2016年
系统来自系统妈:http://www.xitongma.com 深度技术GHOST win7系统64位j极速安装版 V2016年3月 系统概述 深度技术ghost win7系统64位j极速安装版 版 ...
- 工信部公示网络安全示范项目 网易云易盾“自适应DDoS攻击深度检测和防御系统”入选
本文由 网易云发布. 工信部官网 2017年年底,经专家评审和遴选,中华人民共和国工业和信息化部(以下简称“工信部”)公示了2017年电信和互联网行业网络安全试点示范项目,网易云易盾的“自适应DDo ...
- Deepin深度应用商店和系统更新不正常的解决方法
Deepin深度应用商店和系统更新不正常的解决方法 2020-02-04 10:25:09作者:i8520稿源:深度站 如果你的Deepin深度应用商店和系统更新不正常,可采用以下方法来解决问题. 解 ...
- 深度技术GHOST WIN7系统32,64位旗舰稳定版
系统来自系统妈:http://www.xitongma.com 系统概述 深度技术ghost win8 X86(32位)旗舰稳定版系统集成了SATA/RAID/SCSI驱动,支持P45. MCP78. ...
- 基于深度学习的车辆检测系统(MATLAB代码,含GUI界面)
摘要:当前深度学习在目标检测领域的影响日益显著,本文主要基于深度学习的目标检测算法实现车辆检测,为大家介绍如何利用\(\color{#4285f4}{M}\color{#ea4335}{A}\colo ...
- 深度学习笔记------windows系统下进行Linux-Ubuntu14.04双系统安装笔记(二)
在上一篇文章中介绍了新手如何安装Ubuntu14.04的双系统,本文会说明Ubuntu系统下搜狗输入法的安装,并就我遇见的一些bug给出最简单的解决办法. 第一部分.搜狗输入法的安装 本身搜狗输入法的 ...
- 深度探索QT窗口系统(五篇)
窗口作为界面编程中最重要的部分,没有窗口就没有界面,是窗口让我们摆脱了DOS时代,按钮是一个窗口,文本框是一个窗口,标签页是一个窗口,...一个窗口可以由多个窗口组成,每天我们都在与窗口打交道,当你打 ...
- 深度(deepin)系统不能ssh root用户登录
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config找到这一部分信息刚进去信息应该是这样 # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m #PermitRootLogin proh ...
随机推荐
- FSMC stm32
1.FSMC机制 FSMC(Flexihie Static Memory Controller,可变静态存储控制器)是STM32系列中内部集成256 KB以上FlaSh,后缀为xC.xD和xE的高存储 ...
- DP重新学
白书上的DP讲义:一 二 DAG上的dp 不要好高骛远去学这种高端东西,学了也写不对,剩下的几天把基本的dp和搜索搞下,就圆满了.不要再学新算法了,去九度把现有的算法写个痛. 学了数位DP和记忆搜索, ...
- __toString()与__call()
__toString()适用于直接输出类,用此方法,可以避免出错:__call()适用于使用类当中没有定义的函数(方法) <!DOCTYPE html> <html> < ...
- c# 只允许一个实例运行
1.单件模式,Singleton,应用程序只能允许一个实例在运行.这是最好的解决方法2.查询系统进程里是不是已经运行.private void Form1_Load(object sender, Ev ...
- 前App Store高管揭秘:关于“苹果推荐”的七大真相
相信你已经看过很多这样那样关于如何获得苹果商店推荐的攻略了,但其实很多人依然陷入了很大的误区.前不久采访了前App Store团队高管Greg Essig,向各位开发者揭示关于获得苹果推荐的真相. 在 ...
- CF700C (枚举+tarjan)
Problem Break up (CF700C) 题目大意 给一张n个点,m条边的无向图,有边权,和起点S,终点T. (n<=1000 , m<=30000) 要求最多割掉2条边,使得S ...
- vim-airline的theme
仓库位置: https://github.com/vim-airline/vim-airline-themes 这些内置的这些主题,可以直接使用,方法是在.vimrc中写 let g:airline_ ...
- 【题解】【DP】【Leetcode】Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top. Each time you can either climb ...
- hdu 4252 A Famous City
题意:一张相片上的很多建筑相互遮住了,根据高低不同就在相片上把一座高楼的可见部分作为一个矩形,并用数字描述其高度,若一张相片上的两个建筑群中间有空地,高度则为0;求最少有多少个建筑; 分析: 输入的0 ...
- js foreach比for多出两个undefined
项目中发现,javascript 用foreach会比for多出两个undefined, //会多两个undefined for (var i in _SysFunctions_S) {} //正常 ...


