fasttext源码剖析
fasttext源码剖析
目的:记录结合多方资料以及个人理解的剖析代码;
https://heleifz.github.io/14732610572844.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/peghoty/p/3857839.html
一:代码总体模块关联图:

核心模块是fasttext.cc以及model.cc模块,但是辅助模块也很重要,是代码的螺丝钉,以及实现了数据采取什么样子数据结构进行组织,这里的东西值得学习借鉴,而且你会发现存储训练数据的结构比较常用的手段,后期可以对比多个源码的训练数据的结构对比。
部分:螺丝钉代码的剖析
二:dictionary模版

1 /**
2 * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
3 * All rights reserved.
4 *
5 * This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
6 * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
7 * of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
8 */
9
10 #include "dictionary.h"
11
12 #include <assert.h>
13
14 #include <iostream>
15 #include <algorithm>
16 #include <iterator>
17 #include <unordered_map>
18
19 namespace fasttext {
20
21 const std::string Dictionary::EOS = "</s>";
22 const std::string Dictionary::BOW = "<";
23 const std::string Dictionary::EOW = ">";
24
25 Dictionary::Dictionary(std::shared_ptr<Args> args) {
26 args_ = args;
27 size_ = 0;
28 nwords_ = 0;
29 nlabels_ = 0;
30 ntokens_ = 0;
31 word2int_.resize(MAX_VOCAB_SIZE);//建立全词的索引,hash值在0~MAX_VOCAB_SIZE-1之间
32 for (int32_t i = 0; i < MAX_VOCAB_SIZE; i++) {
33 word2int_[i] = -1;
34 }
35 }
36 //根据字符串,进行hash,hash后若是冲突则线性探索,找到其对应的hash位置
37 int32_t Dictionary::find(const std::string& w) const {
38 int32_t h = hash(w) % MAX_VOCAB_SIZE;
39 while (word2int_[h] != -1 && words_[word2int_[h]].word != w) {
40 h = (h + 1) % MAX_VOCAB_SIZE;
41 }
42 return h;
43 }
44 //向words_添加词,词可能是标签词
45 void Dictionary::add(const std::string& w) {
46 int32_t h = find(w);
47 ntokens_++;//已处理的词
48 if (word2int_[h] == -1) {
49 entry e;
50 e.word = w;
51 e.count = 1;
52 e.type = (w.find(args_->label) == 0) ? entry_type::label : entry_type::word;//与给出标签相同,则表示标签词
53 words_.push_back(e);
54 word2int_[h] = size_++;
55 } else {
56 words_[word2int_[h]].count++;
57 }
58 }
59 //返回纯词个数--去重
60 int32_t Dictionary::nwords() const {
61 return nwords_;
62 }
63 //标签词个数---去重
64 int32_t Dictionary::nlabels() const {
65 return nlabels_;
66 }
67 //返回已经处理的词数---可以重复
68 int64_t Dictionary::ntokens() const {
69 return ntokens_;
70 }
71 //获取纯词的ngram
72 const std::vector<int32_t>& Dictionary::getNgrams(int32_t i) const {
73 assert(i >= 0);
74 assert(i < nwords_);
75 return words_[i].subwords;
76 }
77 //获取纯词的ngram,根据词串
78 const std::vector<int32_t> Dictionary::getNgrams(const std::string& word) const {
79 int32_t i = getId(word);
80 if (i >= 0) {
81 return getNgrams(i);
82 }
83 //若是该词没有被入库词典中,未知词,则计算ngram
84 //这就可以通过其他词的近似ngram来获取该词的ngram
85 std::vector<int32_t> ngrams;
86 computeNgrams(BOW + word + EOW, ngrams);
87 return ngrams;
88 }
89 //是否丢弃的判断标准---这是由于无用词会出现过多的词频,需要被丢弃,
90 bool Dictionary::discard(int32_t id, real rand) const {
91 assert(id >= 0);
92 assert(id < nwords_);
93 if (args_->model == model_name::sup) return false;//非词向量不需要丢弃
94 return rand > pdiscard_[id];
95 }
96 //获取词的id号
97 int32_t Dictionary::getId(const std::string& w) const {
98 int32_t h = find(w);
99 return word2int_[h];
100 }
101 //词的类型
102 entry_type Dictionary::getType(int32_t id) const {
103 assert(id >= 0);
104 assert(id < size_);
105 return words_[id].type;
106 }
107 //根据词id获取词串
108 std::string Dictionary::getWord(int32_t id) const {
109 assert(id >= 0);
110 assert(id < size_);
111 return words_[id].word;
112 }
113 //hash规则
114 uint32_t Dictionary::hash(const std::string& str) const {
115 uint32_t h = 2166136261;
116 for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
117 h = h ^ uint32_t(str[i]);
118 h = h * 16777619;
119 }
120 return h;
121 }
122 //根据词计算其ngram情况
123 void Dictionary::computeNgrams(const std::string& word,
124 std::vector<int32_t>& ngrams) const {
125 for (size_t i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
126 std::string ngram;
127 if ((word[i] & 0xC0) == 0x80) continue;
128 for (size_t j = i, n = 1; j < word.size() && n <= args_->maxn; n++) {//n-1个词背景
129 ngram.push_back(word[j++]);
130 while (j < word.size() && (word[j] & 0xC0) == 0x80) {
131 ngram.push_back(word[j++]);
132 }
133 if (n >= args_->minn && !(n == 1 && (i == 0 || j == word.size()))) {
134 int32_t h = hash(ngram) % args_->bucket;//hash余数值
135 ngrams.push_back(nwords_ + h);
136 }
137 }
138 }
139 }
140 //初始化ngram值
141 void Dictionary::initNgrams() {
142 for (size_t i = 0; i < size_; i++) {
143 std::string word = BOW + words_[i].word + EOW;
144 words_[i].subwords.push_back(i);
145 computeNgrams(word, words_[i].subwords);
146 }
147 }
148 //读取词
149 bool Dictionary::readWord(std::istream& in, std::string& word) const
150 {
151 char c;
152 std::streambuf& sb = *in.rdbuf();
153 word.clear();
154 while ((c = sb.sbumpc()) != EOF) {
155 if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == '\v' || c == '\f' || c == '\0') {
156 if (word.empty()) {
157 if (c == '\n') {//若是空行,则增加一个EOS
158 word += EOS;
159 return true;
160 }
161 continue;
162 } else {
163 if (c == '\n')
164 sb.sungetc();//放回,体现对于换行符会用EOS替换
165 return true;
166 }
167 }
168 word.push_back(c);
169 }
170 // trigger eofbit
171 in.get();
172 return !word.empty();
173 }
174 //读取文件---获取词典;初始化舍弃规则,初始化ngram
175 void Dictionary::readFromFile(std::istream& in) {
176 std::string word;
177 int64_t minThreshold = 1;//阈值
178 while (readWord(in, word)) {
179 add(word);
180 if (ntokens_ % 1000000 == 0 && args_->verbose > 1) {
181 std::cout << "\rRead " << ntokens_ / 1000000 << "M words" << std::flush;
182 }
183 if (size_ > 0.75 * MAX_VOCAB_SIZE) {//词保证是不超过75%
184 minThreshold++;
185 threshold(minThreshold, minThreshold);//过滤小于minThreshold的词,顺便排序了
186 }
187 }
188 threshold(args_->minCount, args_->minCountLabel);//目的是排序,顺带过滤词,指定过滤
189
190 initTableDiscard();
191 initNgrams();
192 if (args_->verbose > 0) {
193 std::cout << "\rRead " << ntokens_ / 1000000 << "M words" << std::endl;
194 std::cout << "Number of words: " << nwords_ << std::endl;
195 std::cout << "Number of labels: " << nlabels_ << std::endl;
196 }
197 if (size_ == 0) {
198 std::cerr << "Empty vocabulary. Try a smaller -minCount value." << std::endl;
199 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
200 }
201 }
202 //缩减词,且排序词
203 void Dictionary::threshold(int64_t t, int64_t tl) {
204 sort(words_.begin(), words_.end(), [](const entry& e1, const entry& e2) {
205 if (e1.type != e2.type) return e1.type < e2.type;//不同类型词,将标签词排在后面
206 return e1.count > e2.count;//同类则词频降序排
207 });//排序,根据词频
208 words_.erase(remove_if(words_.begin(), words_.end(), [&](const entry& e) {
209 return (e.type == entry_type::word && e.count < t) ||
210 (e.type == entry_type::label && e.count < tl);
211 }), words_.end());//删除阈值以下的词
212 words_.shrink_to_fit();//剔除
213 //更新词典的信息
214 size_ = 0;
215 nwords_ = 0;
216 nlabels_ = 0;
217 for (int32_t i = 0; i < MAX_VOCAB_SIZE; i++) {
218 word2int_[i] = -1;//重置
219 }
220 for (auto it = words_.begin(); it != words_.end(); ++it) {
221 int32_t h = find(it->word);//重新构造hash
222 word2int_[h] = size_++;
223 if (it->type == entry_type::word) nwords_++;
224 if (it->type == entry_type::label) nlabels_++;
225 }
226 }
227 //初始化丢弃规则---
228 void Dictionary::initTableDiscard() {//t采样的阈值,0表示全部舍弃,1表示不采样
229 pdiscard_.resize(size_);
230 for (size_t i = 0; i < size_; i++) {
231 real f = real(words_[i].count) / real(ntokens_);//f概率高
232 pdiscard_[i] = sqrt(args_->t / f) + args_->t / f;//与论文貌似不一样?????
233 }
234 }
235 //返回词的频数--所以词的词频和
236 std::vector<int64_t> Dictionary::getCounts(entry_type type) const {
237 std::vector<int64_t> counts;
238 for (auto& w : words_) {
239 if (w.type == type) counts.push_back(w.count);
240 }
241 return counts;
242 }
243 //增加ngram,
244 void Dictionary::addNgrams(std::vector<int32_t>& line, int32_t n) const {
245 int32_t line_size = line.size();
246 for (int32_t i = 0; i < line_size; i++) {
247 uint64_t h = line[i];
248 for (int32_t j = i + 1; j < line_size && j < i + n; j++) {
249 h = h * 116049371 + line[j];
250 line.push_back(nwords_ + (h % args_->bucket));
251 }
252 }
253 }
254 //获取词行
255 int32_t Dictionary::getLine(std::istream& in,
256 std::vector<int32_t>& words,
257 std::vector<int32_t>& labels,
258 std::minstd_rand& rng) const {
259 std::uniform_real_distribution<> uniform(0, 1);//均匀随机0~1
260 std::string token;
261 int32_t ntokens = 0;
262 words.clear();
263 labels.clear();
264 if (in.eof()) {
265 in.clear();
266 in.seekg(std::streampos(0));
267 }
268 while (readWord(in, token)) {
269 if (token == EOS) break;//表示一行的结束
270 int32_t wid = getId(token);
271 if (wid < 0) continue;//表示词的id木有,代表未知词,则跳过
272 entry_type type = getType(wid);
273 ntokens++;//已经获取词数
274 if (type == entry_type::word && !discard(wid, uniform(rng))) {//随机采取样,表示是否取该词
275 words.push_back(wid);//词的收集--词肯定在nwords_以下
276 }
277 if (type == entry_type::label) {//标签词全部采取,肯定在nwords_以上
278 labels.push_back(wid - nwords_);//也就是labels的值需要加上nwords才能够寻找到标签词
279 }
280 if (words.size() > MAX_LINE_SIZE && args_->model != model_name::sup) break;//词向量则有限制句子长度
281 }
282 return ntokens;
283 }
284 //获取标签词,根据的是标签词的lid
285 std::string Dictionary::getLabel(int32_t lid) const {//标签词
286 assert(lid >= 0);
287 assert(lid < nlabels_);
288 return words_[lid + nwords_].word;
289 }
290 //保存词典
291 void Dictionary::save(std::ostream& out) const {
292 out.write((char*) &size_, sizeof(int32_t));
293 out.write((char*) &nwords_, sizeof(int32_t));
294 out.write((char*) &nlabels_, sizeof(int32_t));
295 out.write((char*) &ntokens_, sizeof(int64_t));
296 for (int32_t i = 0; i < size_; i++) {//词
297 entry e = words_[i];
298 out.write(e.word.data(), e.word.size() * sizeof(char));//词
299 out.put(0);//字符串结束标志位
300 out.write((char*) &(e.count), sizeof(int64_t));
301 out.write((char*) &(e.type), sizeof(entry_type));
302 }
303 }
304 //加载词典
305 void Dictionary::load(std::istream& in) {
306 words_.clear();
307 for (int32_t i = 0; i < MAX_VOCAB_SIZE; i++) {
308 word2int_[i] = -1;
309 }
310 in.read((char*) &size_, sizeof(int32_t));
311 in.read((char*) &nwords_, sizeof(int32_t));
312 in.read((char*) &nlabels_, sizeof(int32_t));
313 in.read((char*) &ntokens_, sizeof(int64_t));
314 for (int32_t i = 0; i < size_; i++) {
315 char c;
316 entry e;
317 while ((c = in.get()) != 0) {
318 e.word.push_back(c);
319 }
320 in.read((char*) &e.count, sizeof(int64_t));
321 in.read((char*) &e.type, sizeof(entry_type));
322 words_.push_back(e);
323 word2int_[find(e.word)] = i;//建立索引
324 }
325 initTableDiscard();//初始化抛弃规则
326 initNgrams();//初始化ngram词
327 }
328
329 }

个人觉得有必要说明的地方:
1:关于字符串映射过程,以及如何建立一套索引的,详情见下图:涉及的函数主要是find,内部实现需要hash函数建立hash规则,借助2个vector来进行关联。StrToHash(find函数) HashToIndex(word2int数组) IndexToStruct(words_数组)

2:初始化几个有用的表,目的是加速运行速度
1)初始化ngram表,即每个词都对应一个ngram的表的id列表。比如词 "我想你" ,通过computeNgrams函数可以计算出相应ngram的词索引,假设ngram的词最短为2,最长为3,则就是"<我","我想","想你","你>",<我想","我想你","想你>"的子词组成,这里有"<>"因为这里会自动添加这样的词的开始和结束位。这里注意代码实现中的"(word[j] & 0xC0) == 0x80)"这里是考虑utf-8的汉字情况,来使得能够取出完整的一个汉字作为一个"字"
2) 初始化initTableDiscard表,对每个词根据词的频率获取相应的丢弃概率值,若是给定的阈值小于这个表的值那么就丢弃该词,这里是因为对于频率过高的词可能就是无用词,所以丢弃。比如"的","是"等;这里的实现与论文中有点差异,这里是当表中的词小于某个值表示该丢弃,这里因为这里没有对其求1-p形式,而是p+p^2。若是同理转为同方向,则论文是p,现实是p+p^2,这样的做法是使得打压更加宽松点,也就是更多词会被当作无用词丢弃。(不知道原因)
3:外界使用该.cc的主线,一是readFromFile函数,加载词;二是getLine,获取句的词。
类似的vector.cc,matrix.cc,args.cc等代码解析如下:

1 /**
2 * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
3 * All rights reserved.
4 *
5 * This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
6 * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
7 * of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
8 */
9
10 #include "matrix.h"
11
12 #include <assert.h>
13
14 #include <random>
15
16 #include "utils.h"
17 #include "vector.h"
18
19 namespace fasttext {
20
21 Matrix::Matrix() {
22 m_ = 0;
23 n_ = 0;
24 data_ = nullptr;
25 }
26
27 Matrix::Matrix(int64_t m, int64_t n) {
28 m_ = m;
29 n_ = n;
30 data_ = new real[m * n];
31 }
32
33 Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix& other) {
34 m_ = other.m_;
35 n_ = other.n_;
36 data_ = new real[m_ * n_];
37 for (int64_t i = 0; i < (m_ * n_); i++) {
38 data_[i] = other.data_[i];
39 }
40 }
41
42 Matrix& Matrix::operator=(const Matrix& other) {
43 Matrix temp(other);
44 m_ = temp.m_;
45 n_ = temp.n_;
46 std::swap(data_, temp.data_);
47 return *this;
48 }
49
50 Matrix::~Matrix() {
51 delete[] data_;
52 }
53
54 void Matrix::zero() {
55 for (int64_t i = 0; i < (m_ * n_); i++) {
56 data_[i] = 0.0;
57 }
58 }
59 //随机初始化矩阵-均匀随机
60 void Matrix::uniform(real a) {
61 std::minstd_rand rng(1);
62 std::uniform_real_distribution<> uniform(-a, a);
63 for (int64_t i = 0; i < (m_ * n_); i++) {
64 data_[i] = uniform(rng);
65 }
66 }
67 //加向量
68 void Matrix::addRow(const Vector& vec, int64_t i, real a) {
69 assert(i >= 0);
70 assert(i < m_);
71 assert(vec.m_ == n_);
72 for (int64_t j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
73 data_[i * n_ + j] += a * vec.data_[j];
74 }
75 }
76 //点乘向量
77 real Matrix::dotRow(const Vector& vec, int64_t i) {
78 assert(i >= 0);
79 assert(i < m_);
80 assert(vec.m_ == n_);
81 real d = 0.0;
82 for (int64_t j = 0; j < n_; j++) {
83 d += data_[i * n_ + j] * vec.data_[j];
84 }
85 return d;
86 }
87 //存储
88 void Matrix::save(std::ostream& out) {
89 out.write((char*) &m_, sizeof(int64_t));
90 out.write((char*) &n_, sizeof(int64_t));
91 out.write((char*) data_, m_ * n_ * sizeof(real));
92 }
93 //加载
94 void Matrix::load(std::istream& in) {
95 in.read((char*) &m_, sizeof(int64_t));
96 in.read((char*) &n_, sizeof(int64_t));
97 delete[] data_;
98 data_ = new real[m_ * n_];
99 in.read((char*) data_, m_ * n_ * sizeof(real));
100 }
101
102 }


/**
* Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*/ #include "vector.h" #include <assert.h> #include <iomanip> #include "matrix.h"
#include "utils.h" namespace fasttext { Vector::Vector(int64_t m) {
m_ = m;
data_ = new real[m];
} Vector::~Vector() {
delete[] data_;
} int64_t Vector::size() const {
return m_;
} void Vector::zero() {
for (int64_t i = 0; i < m_; i++) {
data_[i] = 0.0;
}
}
//数乘向量
void Vector::mul(real a) {
for (int64_t i = 0; i < m_; i++) {
data_[i] *= a;
}
}
//向量相加
void Vector::addRow(const Matrix& A, int64_t i) {
assert(i >= 0);
assert(i < A.m_);
assert(m_ == A.n_);
for (int64_t j = 0; j < A.n_; j++) {
data_[j] += A.data_[i * A.n_ + j];
}
}
//加数乘向量
void Vector::addRow(const Matrix& A, int64_t i, real a) {
assert(i >= 0);
assert(i < A.m_);
assert(m_ == A.n_);
for (int64_t j = 0; j < A.n_; j++) {
data_[j] += a * A.data_[i * A.n_ + j];
}
}
//向量与矩阵相乘得到的向量
void Vector::mul(const Matrix& A, const Vector& vec) {
assert(A.m_ == m_);
assert(A.n_ == vec.m_);
for (int64_t i = 0; i < m_; i++) {
data_[i] = 0.0;
for (int64_t j = 0; j < A.n_; j++) {
data_[i] += A.data_[i * A.n_ + j] * vec.data_[j];
}
}
}
//最大分量
int64_t Vector::argmax() {
real max = data_[0];
int64_t argmax = 0;
for (int64_t i = 1; i < m_; i++) {
if (data_[i] > max) {
max = data_[i];
argmax = i;
}
}
return argmax;
} real& Vector::operator[](int64_t i) {
return data_[i];
} const real& Vector::operator[](int64_t i) const {
return data_[i];
} std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Vector& v)
{
os << std::setprecision(5);
for (int64_t j = 0; j < v.m_; j++) {
os << v.data_[j] << ' ';
}
return os;
} }


1 /**
2 * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
3 * All rights reserved.
4 *
5 * This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
6 * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
7 * of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
8 */
9
10 #include "args.h"
11
12 #include <stdlib.h>
13 #include <string.h>
14
15 #include <iostream>
16
17 namespace fasttext {
18
19 Args::Args() {
20 lr = 0.05;
21 dim = 100;
22 ws = 5;
23 epoch = 5;
24 minCount = 5;
25 minCountLabel = 0;
26 neg = 5;
27 wordNgrams = 1;
28 loss = loss_name::ns;
29 model = model_name::sg;
30 bucket = 2000000;//允许的ngram词典大小2M
31 minn = 3;
32 maxn = 6;
33 thread = 12;
34 lrUpdateRate = 100;
35 t = 1e-4;//默认
36 label = "__label__";
37 verbose = 2;
38 pretrainedVectors = "";
39 }
40
41 void Args::parseArgs(int argc, char** argv) {
42 std::string command(argv[1]);
43 if (command == "supervised") {
44 model = model_name::sup;
45 loss = loss_name::softmax;
46 minCount = 1;
47 minn = 0;
48 maxn = 0;
49 lr = 0.1;
50 } else if (command == "cbow") {
51 model = model_name::cbow;
52 }
53 int ai = 2;
54 while (ai < argc) {
55 if (argv[ai][0] != '-') {
56 std::cout << "Provided argument without a dash! Usage:" << std::endl;
57 printHelp();
58 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
59 }
60 if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-h") == 0) {
61 std::cout << "Here is the help! Usage:" << std::endl;
62 printHelp();
63 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
64 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-input") == 0) {
65 input = std::string(argv[ai + 1]);
66 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-test") == 0) {
67 test = std::string(argv[ai + 1]);
68 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-output") == 0) {
69 output = std::string(argv[ai + 1]);
70 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-lr") == 0) {
71 lr = atof(argv[ai + 1]);
72 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-lrUpdateRate") == 0) {
73 lrUpdateRate = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
74 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-dim") == 0) {
75 dim = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
76 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-ws") == 0) {
77 ws = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
78 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-epoch") == 0) {
79 epoch = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
80 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-minCount") == 0) {
81 minCount = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
82 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-minCountLabel") == 0) {
83 minCountLabel = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
84 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-neg") == 0) {
85 neg = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
86 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-wordNgrams") == 0) {
87 wordNgrams = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
88 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-loss") == 0) {
89 if (strcmp(argv[ai + 1], "hs") == 0) {
90 loss = loss_name::hs;
91 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai + 1], "ns") == 0) {
92 loss = loss_name::ns;
93 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai + 1], "softmax") == 0) {
94 loss = loss_name::softmax;
95 } else {
96 std::cout << "Unknown loss: " << argv[ai + 1] << std::endl;
97 printHelp();
98 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
99 }
100 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-bucket") == 0) {
101 bucket = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
102 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-minn") == 0) {
103 minn = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
104 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-maxn") == 0) {
105 maxn = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
106 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-thread") == 0) {
107 thread = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
108 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-t") == 0) {
109 t = atof(argv[ai + 1]);
110 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-label") == 0) {
111 label = std::string(argv[ai + 1]);
112 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-verbose") == 0) {
113 verbose = atoi(argv[ai + 1]);
114 } else if (strcmp(argv[ai], "-pretrainedVectors") == 0) {
115 pretrainedVectors = std::string(argv[ai + 1]);
116 } else {
117 std::cout << "Unknown argument: " << argv[ai] << std::endl;
118 printHelp();
119 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
120 }
121 ai += 2;
122 }
123 if (input.empty() || output.empty()) {
124 std::cout << "Empty input or output path." << std::endl;
125 printHelp();
126 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
127 }
128 if (wordNgrams <= 1 && maxn == 0) {
129 bucket = 0;
130 }
131 }
132
133 void Args::printHelp() {
134 std::string lname = "ns";
135 if (loss == loss_name::hs) lname = "hs";
136 if (loss == loss_name::softmax) lname = "softmax";
137 std::cout
138 << "\n"
139 << "The following arguments are mandatory:\n"
140 << " -input training file path\n"
141 << " -output output file path\n\n"
142 << "The following arguments are optional:\n"
143 << " -lr learning rate [" << lr << "]\n"
144 << " -lrUpdateRate change the rate of updates for the learning rate [" << lrUpdateRate << "]\n"
145 << " -dim size of word vectors [" << dim << "]\n"
146 << " -ws size of the context window [" << ws << "]\n"
147 << " -epoch number of epochs [" << epoch << "]\n"
148 << " -minCount minimal number of word occurences [" << minCount << "]\n"
149 << " -minCountLabel minimal number of label occurences [" << minCountLabel << "]\n"
150 << " -neg number of negatives sampled [" << neg << "]\n"
151 << " -wordNgrams max length of word ngram [" << wordNgrams << "]\n"
152 << " -loss loss function {ns, hs, softmax} [ns]\n"
153 << " -bucket number of buckets [" << bucket << "]\n"
154 << " -minn min length of char ngram [" << minn << "]\n"
155 << " -maxn max length of char ngram [" << maxn << "]\n"
156 << " -thread number of threads [" << thread << "]\n"
157 << " -t sampling threshold [" << t << "]\n"
158 << " -label labels prefix [" << label << "]\n"
159 << " -verbose verbosity level [" << verbose << "]\n"
160 << " -pretrainedVectors pretrained word vectors for supervised learning []"
161 << std::endl;
162 }
163
164 void Args::save(std::ostream& out) {
165 out.write((char*) &(dim), sizeof(int));
166 out.write((char*) &(ws), sizeof(int));
167 out.write((char*) &(epoch), sizeof(int));
168 out.write((char*) &(minCount), sizeof(int));
169 out.write((char*) &(neg), sizeof(int));
170 out.write((char*) &(wordNgrams), sizeof(int));
171 out.write((char*) &(loss), sizeof(loss_name));
172 out.write((char*) &(model), sizeof(model_name));
173 out.write((char*) &(bucket), sizeof(int));
174 out.write((char*) &(minn), sizeof(int));
175 out.write((char*) &(maxn), sizeof(int));
176 out.write((char*) &(lrUpdateRate), sizeof(int));
177 out.write((char*) &(t), sizeof(double));
178 }
179
180 void Args::load(std::istream& in) {
181 in.read((char*) &(dim), sizeof(int));
182 in.read((char*) &(ws), sizeof(int));
183 in.read((char*) &(epoch), sizeof(int));
184 in.read((char*) &(minCount), sizeof(int));
185 in.read((char*) &(neg), sizeof(int));
186 in.read((char*) &(wordNgrams), sizeof(int));
187 in.read((char*) &(loss), sizeof(loss_name));
188 in.read((char*) &(model), sizeof(model_name));
189 in.read((char*) &(bucket), sizeof(int));
190 in.read((char*) &(minn), sizeof(int));
191 in.read((char*) &(maxn), sizeof(int));
192 in.read((char*) &(lrUpdateRate), sizeof(int));
193 in.read((char*) &(t), sizeof(double));
194 }
195
196 }

三:model.cc

/**
* Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*/ #include "model.h" #include <assert.h> #include <algorithm> #include "utils.h" namespace fasttext { Model::Model(std::shared_ptr<Matrix> wi,
std::shared_ptr<Matrix> wo,
std::shared_ptr<Args> args,
int32_t seed)
: hidden_(args->dim), output_(wo->m_), grad_(args->dim), rng(seed)
{
wi_ = wi;//输入--上下文
wo_ = wo;//参数矩阵,行对应于某个词的参数集合
args_ = args;//参数
isz_ = wi->m_;
osz_ = wo->m_;
hsz_ = args->dim;
negpos = 0;
loss_ = 0.0;
nexamples_ = 1;
initSigmoid();
initLog();
} Model::~Model() {
delete[] t_sigmoid;
delete[] t_log;
}
//小型逻辑回归
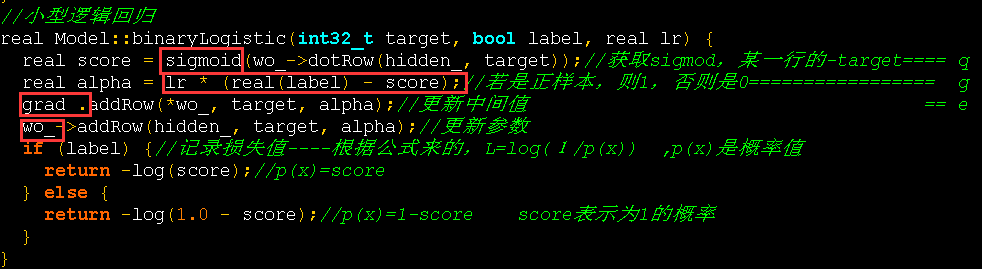
real Model::binaryLogistic(int32_t target, bool label, real lr) {
real score = sigmoid(wo_->dotRow(hidden_, target));//获取sigmod,某一行的-target==== q
real alpha = lr * (real(label) - score);//若是正样本,则1,否则是0================= g
grad_.addRow(*wo_, target, alpha);//更新中间值 == e
wo_->addRow(hidden_, target, alpha);//更新参数
if (label) {//记录损失值----根据公式来的,L=log(1/p(x)) ,p(x)是概率值
return -log(score);//p(x)=score
} else {
return -log(1.0 - score);//p(x)=1-score score表示为1的概率
}
}
//负采样的方式
real Model::negativeSampling(int32_t target, real lr) {//target表示目标词的index
real loss = 0.0;
grad_.zero();//e值的设置为0
for (int32_t n = 0; n <= args_->neg; n++) {//负采样的比例,这里数目
if (n == 0) {//正样例
loss += binaryLogistic(target, true, lr);
} else {//负样例--neg 个
loss += binaryLogistic(getNegative(target), false, lr);
}
}
return loss;
}
//层次softmax
real Model::hierarchicalSoftmax(int32_t target, real lr) {
real loss = 0.0;
grad_.zero();
const std::vector<bool>& binaryCode = codes[target];
const std::vector<int32_t>& pathToRoot = paths[target];
for (int32_t i = 0; i < pathToRoot.size(); i++) {//根据编码路劲搞,词到根目录的
loss += binaryLogistic(pathToRoot[i], binaryCode[i], lr);
}
return loss;
}
//计算softmax值,存入output中
void Model::computeOutputSoftmax(Vector& hidden, Vector& output) const {
output.mul(*wo_, hidden);//向量乘以矩阵---输出=参数转移矩阵*输入
real max = output[0], z = 0.0;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {//获取最大的内积值
max = std::max(output[i], max);
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {//求出每个内积值相对最大值的情况
output[i] = exp(output[i] - max);
z += output[i];//累计和,用于归一化
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {//求出softmax值
output[i] /= z;
}
} void Model::computeOutputSoftmax() {
computeOutputSoftmax(hidden_, output_);
}
//普通softmax计算
real Model::softmax(int32_t target, real lr) {
grad_.zero();
computeOutputSoftmax();
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {//遍历所有词---此次操作只是针对一个词的更新
real label = (i == target) ? 1.0 : 0.0;
real alpha = lr * (label - output_[i]);//中间参数
grad_.addRow(*wo_, i, alpha);//更新e值
wo_->addRow(hidden_, i, alpha);//更新参数
}
return -log(output_[target]);//损失值
}
//计算映射层的向量
void Model::computeHidden(const std::vector<int32_t>& input, Vector& hidden) const {
assert(hidden.size() == hsz_);
hidden.zero();
for (auto it = input.cbegin(); it != input.cend(); ++it) {//指定的行进行累加,也就是上下文的词向量
hidden.addRow(*wi_, *it);
}
hidden.mul(1.0 / input.size());//求均值为Xw
}
//比较,按照第一个降序
bool Model::comparePairs(const std::pair<real, int32_t> &l,
const std::pair<real, int32_t> &r) {
return l.first > r.first;
}
//模型预测函数
void Model::predict(const std::vector<int32_t>& input, int32_t k,
std::vector<std::pair<real, int32_t>>& heap,
Vector& hidden, Vector& output) const {
assert(k > 0);
heap.reserve(k + 1);
computeHidden(input, hidden);//计算映射层,input是上下文
if (args_->loss == loss_name::hs) {//层次softmax,遍历树结构
dfs(k, 2 * osz_ - 2, 0.0, heap, hidden);
} else {//其他则通过数组寻最大
findKBest(k, heap, hidden, output);
}
std::sort_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comparePairs);//堆排序,得到最终的排序的值,降序排
} void Model::predict(const std::vector<int32_t>& input, int32_t k,
std::vector<std::pair<real, int32_t>>& heap) {
predict(input, k, heap, hidden_, output_);
}
//vector寻找topk---获得一个最小堆
void Model::findKBest(int32_t k, std::vector<std::pair<real, int32_t>>& heap,
Vector& hidden, Vector& output) const {
computeOutputSoftmax(hidden, output);//计算soft值
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {//输出的大小
if (heap.size() == k && log(output[i]) < heap.front().first) {//小于topk中最小的那个,最小堆,损失值
continue;
}
heap.push_back(std::make_pair(log(output[i]), i));//加入堆中
std::push_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comparePairs);//做对排序
if (heap.size() > k) {//
std::pop_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comparePairs);//移动最小的那个到最后面,且堆排序
heap.pop_back();//删除最后一个元素
}
}
}
//层次softmax的topk获取
void Model::dfs(int32_t k, int32_t node, real score,
std::vector<std::pair<real, int32_t>>& heap,
Vector& hidden) const {//从根开始
if (heap.size() == k && score < heap.front().first) {//跳过
return;
} if (tree[node].left == -1 && tree[node].right == -1) {//表示为叶子节点
heap.push_back(std::make_pair(score, node));//根到叶子的损失总值,叶子也就是词了
std::push_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comparePairs);//维持最小堆,以损失值
if (heap.size() > k) {
std::pop_heap(heap.begin(), heap.end(), comparePairs);
heap.pop_back();
}
return;
} real f = sigmoid(wo_->dotRow(hidden, node - osz_));//计算出sigmod值,用于计算损失
dfs(k, tree[node].left, score + log(1.0 - f), heap, hidden);//左侧为1损失
dfs(k, tree[node].right, score + log(f), heap, hidden);
}
//更新操作
void Model::update(const std::vector<int32_t>& input, int32_t target, real lr) {
assert(target >= 0);
assert(target < osz_);
if (input.size() == 0) return;
computeHidden(input, hidden_);//计算映射层值
if (args_->loss == loss_name::ns) {//负采样的更新
loss_ += negativeSampling(target, lr);
} else if (args_->loss == loss_name::hs) {//层次soft
loss_ += hierarchicalSoftmax(target, lr);
} else {//普通soft
loss_ += softmax(target, lr);
}
nexamples_ += 1;//处理的样例数, if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {//分类
grad_.mul(1.0 / input.size());
}
for (auto it = input.cbegin(); it != input.cend(); ++it) {//获取指向常数的指针
wi_->addRow(grad_, *it, 1.0);//迭代加上上下文的词向量,来更新上下文的词向量
}
}
//根据词频的向量,构建哈夫曼树或者初始化负采样的表
void Model::setTargetCounts(const std::vector<int64_t>& counts) {
assert(counts.size() == osz_);
if (args_->loss == loss_name::ns) {
initTableNegatives(counts);
}
if (args_->loss == loss_name::hs) {
buildTree(counts);
}
}
//负采样的采样表获取
void Model::initTableNegatives(const std::vector<int64_t>& counts) {
real z = 0.0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < counts.size(); i++) {
z += pow(counts[i], 0.5);//采取是词频的0.5次方
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < counts.size(); i++) {
real c = pow(counts[i], 0.5);//c值
//0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2,2类似这种有序的,0表示第一个词,占个坑,随机读取时,越多则概率越大。所有词的随机化
//最多重复次数,若是c/z足够小,会导致重复次数很少,最小是1次
//NEGATIVE_TABLE_SIZE含义是一个词最多重复不能够超过的值
for (size_t j = 0; j < c * NEGATIVE_TABLE_SIZE / z; j++) {//该词映射到表的维度上的取值情况,也就是不等分区映射到等区分段上
negatives.push_back(i);
}
}
std::shuffle(negatives.begin(), negatives.end(), rng);//随机化一下,均匀随机化,
}
//对于词target获取负采样的值
int32_t Model::getNegative(int32_t target) {
int32_t negative;
do {
negative = negatives[negpos];//由于表是随机化的,取值就是随机采的
negpos = (negpos + 1) % negatives.size();//下一个,不断的累加的,由于表格随机的,所以不需要pos随机了
} while (target == negative);//若是遇到为正样本则跳过
return negative;
}
//构建哈夫曼树过程
void Model::buildTree(const std::vector<int64_t>& counts) {
tree.resize(2 * osz_ - 1);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < 2 * osz_ - 1; i++) {
tree[i].parent = -1;
tree[i].left = -1;
tree[i].right = -1;
tree[i].count = 1e15;
tree[i].binary = false;
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {
tree[i].count = counts[i];
}
int32_t leaf = osz_ - 1;
int32_t node = osz_;
for (int32_t i = osz_; i < 2 * osz_ - 1; i++) {
int32_t mini[2];
for (int32_t j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
if (leaf >= 0 && tree[leaf].count < tree[node].count) {
mini[j] = leaf--;
} else {
mini[j] = node++;
}
}
tree[i].left = mini[0];
tree[i].right = mini[1];
tree[i].count = tree[mini[0]].count + tree[mini[1]].count;
tree[mini[0]].parent = i;
tree[mini[1]].parent = i;
tree[mini[1]].binary = true;
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < osz_; i++) {
std::vector<int32_t> path;
std::vector<bool> code;
int32_t j = i;
while (tree[j].parent != -1) {
path.push_back(tree[j].parent - osz_);
code.push_back(tree[j].binary);
j = tree[j].parent;
}
paths.push_back(path);
codes.push_back(code);
}
}
//获取均匀损失值,平均每个样本的损失
real Model::getLoss() const {
return loss_ / nexamples_;
}
//初始化sigmod表
void Model::initSigmoid() {
t_sigmoid = new real[SIGMOID_TABLE_SIZE + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < SIGMOID_TABLE_SIZE + 1; i++) {
real x = real(i * 2 * MAX_SIGMOID) / SIGMOID_TABLE_SIZE - MAX_SIGMOID;
t_sigmoid[i] = 1.0 / (1.0 + std::exp(-x));
}
}
//初始化log函数的表,对于0~1之间的值
void Model::initLog() {
t_log = new real[LOG_TABLE_SIZE + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < LOG_TABLE_SIZE + 1; i++) {
real x = (real(i) + 1e-5) / LOG_TABLE_SIZE;
t_log[i] = std::log(x);
}
}
//log的处理
real Model::log(real x) const {
if (x > 1.0) {
return 0.0;
}
int i = int(x * LOG_TABLE_SIZE);
return t_log[i];
}
//获取sigmod值
real Model::sigmoid(real x) const {
if (x < -MAX_SIGMOID) {
return 0.0;
} else if (x > MAX_SIGMOID) {
return 1.0;
} else {
int i = int((x + MAX_SIGMOID) * SIGMOID_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_SIGMOID / 2);
return t_sigmoid[i];
}
} }

说明:
1:模型核心在于模型的更新即update函数,此时函数根据不同参数,选择不同的模型训练方法,共提供了3种方式

2:前两种方式的公有处理方式的提取,由于前两种方式的共有的更新。区别度在于选择部分词,还是将词累到共公节点上
四:fasttext.cc

/**
* Copyright (c) 2016-present, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*/ #include "fasttext.h" #include <math.h> #include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> namespace fasttext {
//获取词向量
void FastText::getVector(Vector& vec, const std::string& word) {
const std::vector<int32_t>& ngrams = dict_->getNgrams(word);
vec.zero();
for (auto it = ngrams.begin(); it != ngrams.end(); ++it) {
vec.addRow(*input_, *it);//ngram的累加
}
if (ngrams.size() > 0) {//ngram均值,来体现词向量
vec.mul(1.0 / ngrams.size());
}
}
//保存词向量
void FastText::saveVectors() {
std::ofstream ofs(args_->output + ".vec");
if (!ofs.is_open()) {
std::cout << "Error opening file for saving vectors." << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ofs << dict_->nwords() << " " << args_->dim << std::endl;
Vector vec(args_->dim);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < dict_->nwords(); i++) {
std::string word = dict_->getWord(i);//获取词
getVector(vec, word);//获取词的向量
ofs << word << " " << vec << std::endl;
}
ofs.close();
}
//保存模型
void FastText::saveModel() {
std::ofstream ofs(args_->output + ".bin", std::ofstream::binary);
if (!ofs.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Model file cannot be opened for saving!" << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
args_->save(ofs);
dict_->save(ofs);
input_->save(ofs);
output_->save(ofs);
ofs.close();
}
//加载模型
void FastText::loadModel(const std::string& filename) {
std::ifstream ifs(filename, std::ifstream::binary);
if (!ifs.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Model file cannot be opened for loading!" << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
loadModel(ifs);
ifs.close();
} void FastText::loadModel(std::istream& in) {
args_ = std::make_shared<Args>();
dict_ = std::make_shared<Dictionary>(args_);
input_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>();
output_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>();
args_->load(in);
dict_->load(in);
input_->load(in);
output_->load(in);
model_ = std::make_shared<Model>(input_, output_, args_, 0);//传的是指针,改变可以带回
if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {//构建模型的过程
model_->setTargetCounts(dict_->getCounts(entry_type::label));
} else {
model_->setTargetCounts(dict_->getCounts(entry_type::word));
}
}
//打印提示信息
void FastText::printInfo(real progress, real loss) {
real t = real(clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;//多少秒
real wst = real(tokenCount) / t;//每秒处理词数
real lr = args_->lr * (1.0 - progress);//学习率
int eta = int(t / progress * (1 - progress) / args_->thread);
int etah = eta / 3600;
int etam = (eta - etah * 3600) / 60;
std::cout << std::fixed;
std::cout << "\rProgress: " << std::setprecision(1) << 100 * progress << "%";//完成度
std::cout << " words/sec/thread: " << std::setprecision(0) << wst;//每秒每线程处理个数
std::cout << " lr: " << std::setprecision(6) << lr;//学习率
std::cout << " loss: " << std::setprecision(6) << loss;//损失度
std::cout << " eta: " << etah << "h" << etam << "m ";
std::cout << std::flush;
} void FastText::supervised(Model& model, real lr,
const std::vector<int32_t>& line,
const std::vector<int32_t>& labels) {
if (labels.size() == 0 || line.size() == 0) return;
std::uniform_int_distribution<> uniform(0, labels.size() - 1);
int32_t i = uniform(model.rng);
model.update(line, labels[i], lr);
}
//cbow模型
void FastText::cbow(Model& model, real lr,
const std::vector<int32_t>& line) {
std::vector<int32_t> bow;
std::uniform_int_distribution<> uniform(1, args_->ws);
for (int32_t w = 0; w < line.size(); w++) {
int32_t boundary = uniform(model.rng);//随机取个窗口--每个词的窗口不一样
bow.clear();
for (int32_t c = -boundary; c <= boundary; c++) {
if (c != 0 && w + c >= 0 && w + c < line.size()) {
const std::vector<int32_t>& ngrams = dict_->getNgrams(line[w + c]);//ngrams语言
bow.insert(bow.end(), ngrams.cbegin(), ngrams.cend());//加入上下文中
}
}
model.update(bow, line[w], lr);//根据上下文更新
}
}
//skipgram模型
void FastText::skipgram(Model& model, real lr,
const std::vector<int32_t>& line) {
std::uniform_int_distribution<> uniform(1, args_->ws);
for (int32_t w = 0; w < line.size(); w++) {
int32_t boundary = uniform(model.rng);//窗口随机
const std::vector<int32_t>& ngrams = dict_->getNgrams(line[w]);
for (int32_t c = -boundary; c <= boundary; c++) {//每个预测词的更新
if (c != 0 && w + c >= 0 && w + c < line.size()) {
model.update(ngrams, line[w + c], lr);//ngram作为上下文
}
}
}
}
//测试模型
void FastText::test(std::istream& in, int32_t k) {
int32_t nexamples = 0, nlabels = 0;
double precision = 0.0;
std::vector<int32_t> line, labels; while (in.peek() != EOF) {
dict_->getLine(in, line, labels, model_->rng);//获取句子
dict_->addNgrams(line, args_->wordNgrams);//对句子增加其ngram
if (labels.size() > 0 && line.size() > 0) {
std::vector<std::pair<real, int32_t>> modelPredictions;
model_->predict(line, k, modelPredictions);//预测
for (auto it = modelPredictions.cbegin(); it != modelPredictions.cend(); it++) {
if (std::find(labels.begin(), labels.end(), it->second) != labels.end()) {
precision += 1.0;//准确数
}
}
nexamples++;
nlabels += labels.size();
}
}
std::cout << std::setprecision(3);
std::cout << "P@" << k << ": " << precision / (k * nexamples) << std::endl;
std::cout << "R@" << k << ": " << precision / nlabels << std::endl;
std::cout << "Number of examples: " << nexamples << std::endl;
}
//预测
void FastText::predict(std::istream& in, int32_t k,
std::vector<std::pair<real,std::string>>& predictions) const {
std::vector<int32_t> words, labels;
dict_->getLine(in, words, labels, model_->rng);
dict_->addNgrams(words, args_->wordNgrams);
if (words.empty()) return;
Vector hidden(args_->dim);
Vector output(dict_->nlabels());
std::vector<std::pair<real,int32_t>> modelPredictions;
model_->predict(words, k, modelPredictions, hidden, output);
predictions.clear();
for (auto it = modelPredictions.cbegin(); it != modelPredictions.cend(); it++) {
predictions.push_back(std::make_pair(it->first, dict_->getLabel(it->second)));//不同标签的预测分
}
}
//预测
void FastText::predict(std::istream& in, int32_t k, bool print_prob) {
std::vector<std::pair<real,std::string>> predictions;
while (in.peek() != EOF) {
predict(in, k, predictions);
if (predictions.empty()) {
std::cout << "n/a" << std::endl;
continue;
}
for (auto it = predictions.cbegin(); it != predictions.cend(); it++) {
if (it != predictions.cbegin()) {
std::cout << ' ';
}
std::cout << it->second;
if (print_prob) {
std::cout << ' ' << exp(it->first);
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
//获取词向量
void FastText::wordVectors() {
std::string word;
Vector vec(args_->dim);
while (std::cin >> word) {
getVector(vec, word);//获取一个词的词向量,不仅仅是对已知的,还能对未知进行预测
std::cout << word << " " << vec << std::endl;
}
}
//句子的向量
void FastText::textVectors() {
std::vector<int32_t> line, labels;
Vector vec(args_->dim);
while (std::cin.peek() != EOF) {
dict_->getLine(std::cin, line, labels, model_->rng);//句子
dict_->addNgrams(line, args_->wordNgrams);//对应ngram
vec.zero();
for (auto it = line.cbegin(); it != line.cend(); ++it) {//句子的词以及ngram的索引
vec.addRow(*input_, *it);//将词的向量求出和
}
if (!line.empty()) {//求均值
vec.mul(1.0 / line.size());
}
std::cout << vec << std::endl;//表示句子的词向量
}
} void FastText::printVectors() {
if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {
textVectors();
} else {//词向量
wordVectors();
}
}
//训练线程
void FastText::trainThread(int32_t threadId) {
std::ifstream ifs(args_->input);
utils::seek(ifs, threadId * utils::size(ifs) / args_->thread); Model model(input_, output_, args_, threadId);
if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {
model.setTargetCounts(dict_->getCounts(entry_type::label));
} else {
model.setTargetCounts(dict_->getCounts(entry_type::word));
} const int64_t ntokens = dict_->ntokens();
int64_t localTokenCount = 0;
std::vector<int32_t> line, labels;
while (tokenCount < args_->epoch * ntokens) {//epoch迭代次数
real progress = real(tokenCount) / (args_->epoch * ntokens);//进度
real lr = args_->lr * (1.0 - progress);
localTokenCount += dict_->getLine(ifs, line, labels, model.rng);
if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {//分不同函数进行处理
dict_->addNgrams(line, args_->wordNgrams);
supervised(model, lr, line, labels);
} else if (args_->model == model_name::cbow) {
cbow(model, lr, line);
} else if (args_->model == model_name::sg) {
skipgram(model, lr, line);
}
if (localTokenCount > args_->lrUpdateRate) {//修正学习率
tokenCount += localTokenCount;
localTokenCount = 0;
if (threadId == 0 && args_->verbose > 1) {
printInfo(progress, model.getLoss());
}
}
}
if (threadId == 0 && args_->verbose > 0) {
printInfo(1.0, model.getLoss());
std::cout << std::endl;
}
ifs.close();
}
//加载Vectors过程, 字典
void FastText::loadVectors(std::string filename) {
std::ifstream in(filename);
std::vector<std::string> words;
std::shared_ptr<Matrix> mat; // temp. matrix for pretrained vectors
int64_t n, dim;
if (!in.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Pretrained vectors file cannot be opened!" << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
in >> n >> dim;
if (dim != args_->dim) {
std::cerr << "Dimension of pretrained vectors does not match -dim option"
<< std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
mat = std::make_shared<Matrix>(n, dim);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::string word;
in >> word;
words.push_back(word);
dict_->add(word);
for (size_t j = 0; j < dim; j++) {
in >> mat->data_[i * dim + j];
}
}
in.close(); dict_->threshold(1, 0);
input_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>(dict_->nwords()+args_->bucket, args_->dim);
input_->uniform(1.0 / args_->dim); for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int32_t idx = dict_->getId(words[i]);
if (idx < 0 || idx >= dict_->nwords()) continue;
for (size_t j = 0; j < dim; j++) {
input_->data_[idx * dim + j] = mat->data_[i * dim + j];
}
}
}
//训练
void FastText::train(std::shared_ptr<Args> args) {
args_ = args;
dict_ = std::make_shared<Dictionary>(args_);
if (args_->input == "-") {
// manage expectations
std::cerr << "Cannot use stdin for training!" << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
std::ifstream ifs(args_->input);
if (!ifs.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Input file cannot be opened!" << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
dict_->readFromFile(ifs);
ifs.close(); if (args_->pretrainedVectors.size() != 0) {
loadVectors(args_->pretrainedVectors);
} else {
input_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>(dict_->nwords()+args_->bucket, args_->dim);
input_->uniform(1.0 / args_->dim);
} if (args_->model == model_name::sup) {
output_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>(dict_->nlabels(), args_->dim);
} else {
output_ = std::make_shared<Matrix>(dict_->nwords(), args_->dim);
}
output_->zero(); start = clock();
tokenCount = 0;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < args_->thread; i++) {
threads.push_back(std::thread([=]() { trainThread(i); }));
}
for (auto it = threads.begin(); it != threads.end(); ++it) {
it->join();
}
model_ = std::make_shared<Model>(input_, output_, args_, 0); saveModel();
if (args_->model != model_name::sup) {
saveVectors();
}
} }
fasttext源码剖析的更多相关文章
- jQuery之Deferred源码剖析
一.前言 大约在夏季,我们谈过ES6的Promise(详见here),其实在ES6前jQuery早就有了Promise,也就是我们所知道的Deferred对象,宗旨当然也和ES6的Promise一样, ...
- Nodejs事件引擎libuv源码剖析之:高效线程池(threadpool)的实现
声明:本文为原创博文,转载请注明出处. Nodejs编程是全异步的,这就意味着我们不必每次都阻塞等待该次操作的结果,而事件完成(就绪)时会主动回调通知我们.在网络编程中,一般都是基于Reactor线程 ...
- Apache Spark源码剖析
Apache Spark源码剖析(全面系统介绍Spark源码,提供分析源码的实用技巧和合理的阅读顺序,充分了解Spark的设计思想和运行机理) 许鹏 著 ISBN 978-7-121-25420- ...
- 基于mybatis-generator-core 1.3.5项目的修订版以及源码剖析
项目简单说明 mybatis-generator,是根据数据库表.字段反向生成实体类等代码文件.我在国庆时候,没事剖析了mybatis-generator-core源码,写了相当详细的中文注释,可以去 ...
- STL"源码"剖析-重点知识总结
STL是C++重要的组件之一,大学时看过<STL源码剖析>这本书,这几天复习了一下,总结出以下LZ认为比较重要的知识点,内容有点略多 :) 1.STL概述 STL提供六大组件,彼此可以组合 ...
- SpringMVC源码剖析(四)- DispatcherServlet请求转发的实现
SpringMVC完成初始化流程之后,就进入Servlet标准生命周期的第二个阶段,即“service”阶段.在“service”阶段中,每一次Http请求到来,容器都会启动一个请求线程,通过serv ...
- 自己实现多线程的socket,socketserver源码剖析
1,IO多路复用 三种多路复用的机制:select.poll.epoll 用的多的两个:select和epoll 简单的说就是:1,select和poll所有平台都支持,epoll只有linux支持2 ...
- Java多线程9:ThreadLocal源码剖析
ThreadLocal源码剖析 ThreadLocal其实比较简单,因为类里就三个public方法:set(T value).get().remove().先剖析源码清楚地知道ThreadLocal是 ...
- JS魔法堂:mmDeferred源码剖析
一.前言 avalon.js的影响力愈发强劲,而作为子模块之一的mmDeferred必然成为异步调用模式学习之旅的又一站呢!本文将记录我对mmDeferred的认识,若有纰漏请各位指正,谢谢.项目请见 ...
随机推荐
- loadrunner——win7+LR11配置
一. 安装vmware虚拟机 下载安装vmware15后,可使用密钥为:CG392-4PX5J-H816Z-HYZNG-PQRG2 二. 安装win7系统 2.1下载win7镜像文件 2.2 vmwa ...
- SQL 与,或,非
SQL AND, OR and NOT(与,或不是运算符) AND&OR运算符用于根据一个以上的条件过滤记录. SQL AND & OR 运算符 WHERE子句可以与AND,OR和NO ...
- jsp网站访问次数统计的几种方法
我采用的是jsp网页,但是不管采用什么语言,原理是一样的. 第一种,单页面统计.就是说,只要点击这个页面就会统计一次. <body> <%!//在这种标记中定义的变量为全局变量 in ...
- 小程序解析HTML5
最近做项目的时候碰到一个问题,就是调用接口获取信息到页面上,内容与HTML5标签一起获取过来了.一起显示在微信端上.一般都是二次开发才有可能出现这种问题.通过查找方法,找到了一个可以把HTML5标签转 ...
- PHP FILTER_UNSAFE_RAW 过滤器
定义和用法 FILTER_UNSAFE_RAW 过滤器不进行任何过滤,去除或编码特殊字符. 该过滤器删除那些对应用程序有潜在危害的数据.它用于去除标签以及删除或编码不需要的字符. 如果不规定标志,则该 ...
- readUTF()和writeUTF()
readUTF()和writeUTF() 这是dataOutputStream 的方法~~使用utf-8编码 其实就是从unicode变过来的,utf8编码把unicode的ASCII编码变成1个字节 ...
- AndroidFine Error:Annotation processors must be explicitly declared now.
环境 Android Studio 3.0 Gradle 3.0.0 gradle 4.1 Error Error:Execution failed for task ':app:javaPreCom ...
- HDU 6697 Closest Pair of Segments (计算几何 暴力)
2019 杭电多校 10 1007 题目链接:HDU 6697 比赛链接:2019 Multi-University Training Contest 10 Problem Description T ...
- PostgreSQL——服务器基本设置与操作
一.编译安装: 环境准备: GNU make 版本 >=3.8 (make --version) ISO/ANSI C 编译器,至少須兼容 C89 标准,GCC 或 intel 編译器等均可 g ...
- Ubuntu12.04开机自动挂载windows分区
最近使用Ubuntu12.04时不知到怎么搞的原本能自动识别的Windows的C .D .E盘突然间无法识别了,于是上网搜了一下Ubuntu12.04下自动挂载Windows NTFS分区的方法. 还 ...
