设备驱动基础学习--platform driver简单实现
platform是一条虚拟的总线。设备用platform_device表示,驱动用platform_driver进行注册,Linux platform driver机制和传统的device driver机制(通过driver_register进行注册)相比,一个明显的优势在于platform机制将设备本身的资源注册进内核,由内核统一管理,在驱动中使用这些资源时通过platform device提供的标准结构进行申请并使用。这样提高了驱动和资源的独立性,并且具有较好的可移植性和安全性(这些标准接口是安全的)。
pltform机制本身使用并不复杂,由两部分组成:platform_device和platform_driver。通过platform机制开发底层驱动的大致流程为:定义platform_deive->注册platform_device->定义platform_driver->注册platform_driver。
platform driver的probe函数是平台总线实现匹配以后首先被调用的函数,因此在其中实现字符设备、块设备、网络设备驱动的初始化是有意义的,这样的设备驱动就是基于平台总线的设备驱动,便于维护。如果添加实际的设备到该平台总线设备驱动模型中,则可以在该函数中实现具体的设备驱动函数的初始化操作,包括设备号的申请,设备的初始化,添加。自动设备文件创建函数的添加等操作。或者是混杂字符设备的相关初始化操作。在remove函数中实现具体的设备的释放,包括设备的删除,设备号的注销等操作。
基于misc device实现一个简单的platform driver(仿照driver/char/sonypi.c).
fellowplat.h
#ifndef _FELLOW_MISC_H_
#define _FELLOW_MISC_H_
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
//#define FELLOW_MISC_MAJOR 199
//#define FELLOW_MISC_NR 2
struct miscdata {
int val;
char *str;
unsigned int size;
};
#define FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAGIC 'f'
#define FELLOW_MISC_IOC_PRINT _IO(FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAGIC, 1)
#define FELLOW_MISC_IOC_GET _IOR(FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAGIC, 2, struct miscdata)
#define FELLOW_MISC_IOC_SET _IOW(FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAGIC, 3, struct miscdata)
#define FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAXNR 3
#endif
fellowplat.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
//#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include "fellowplat.h"
struct fellowmisc_dev{
struct miscdevice misc;
struct miscdata data;
};
struct fellowmisc_dev *fellowmisc_devp;
int fellowmisc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filep)
{
filep->private_data = fellowmisc_devp;
return 0;
}
int fellowmisc_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filep)
{
return 0;
}
long fellowmisc_ioctl(struct file *filep,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{
int ret = 0;
struct fellowmisc_dev *devp = (struct fellowmisc_dev *)(filep->private_data);
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAGIC)
return -EINVAL;
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) > FELLOW_MISC_IOC_MAXNR)
return -EINVAL;
switch(cmd)
{
case FELLOW_MISC_IOC_PRINT:
printk("FELLOW_MISC_IOC_PRINT\n");
printk("val:%d, size: %d, str: %s\n", devp->data.val, devp->data.size, devp->data.str);
break;
case FELLOW_MISC_IOC_SET:
printk("FELLOW_MISC_IOC_SET\n");
ret = copy_from_user((unsigned char*)&(devp->data), (unsigned char *)arg, sizeof(struct miscdata));
printk("set val:%d, size: %d, str: %s\n", devp->data.val, devp->data.size, devp->data.str);
break;
case FELLOW_MISC_IOC_GET:
printk("FELLOW_MISC_IOC_GET\n");
ret = copy_to_user((unsigned char*)arg,(unsigned char*)&(devp->data), sizeof(struct miscdata));
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
return ret;
}
static const struct file_operations fellowmisc_fops ={
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = fellowmisc_open,
.release = fellowmisc_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = fellowmisc_ioctl,
};
static struct miscdevice fellow_misc = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = "fellowplat",
.fops = &fellowmisc_fops,
};
static struct platform_device *fellow_platform_device;
static int fellow_plat_drv_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
int error;
printk("fellow_plat_drv_probe\n");
fellowmisc_devp = kmalloc(sizeof(struct fellowmisc_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!fellowmisc_devp)
{
error = -ENOMEM;
return error;
}
memset(&(fellowmisc_devp->data), 0, sizeof(fellowmisc_devp->data));
fellowmisc_devp->misc = fellow_misc;
error = misc_register(&fellow_misc);
return error;
}
static int fellow_plat_drv_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
int error;
if (fellowmisc_devp)
kfree(fellowmisc_devp);
error = misc_deregister(&fellow_misc);
return error;
}
static struct platform_driver fellow_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "fellow",
},
.probe = fellow_plat_drv_probe,
.remove = fellow_plat_drv_remove,
};
static int fellowplat_init(void)
{
int error;
printk("fellowplat_init\n");
printk("fellow register driver\n");
error = platform_driver_register(&fellow_platform_driver);//注册platform driver
if (error)
return error;
fellow_platform_device = platform_device_alloc("fellow", -1);//名字与platform driver相同。
if (!fellow_platform_device) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_driver_unregister;
}
printk("fellow register device\n");
error = platform_device_add(fellow_platform_device);//添加platform device
if (error)
goto err_free_device;
return 0;
err_free_device:
platform_device_put(fellow_platform_device);
err_driver_unregister:
platform_driver_unregister(&fellow_platform_driver);
return error;
}
static void fellowplat_exit(void)
{
platform_device_unregister(fellow_platform_device);
platform_driver_unregister(&fellow_platform_driver);
}
MODULE_AUTHOR("fellow");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(fellowplat_init);
module_exit(fellowplat_exit);
app.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "fellowplat.h"
int main(void)
{
int fd = open("/dev/fellowplat", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open fail:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
int ret = 0;
struct miscdata data;
data.val = 18;
data.str = "fellow platform device";
data.size = sizeof("fellow platform device");
if ((ret = ioctl(fd, FELLOW_MISC_IOC_SET, &data)) < 0)
{
printf("ioctl set fail:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
struct miscdata getdata;
if ((ret = ioctl(fd, FELLOW_MISC_IOC_GET, &getdata)) < 0)
{
printf("ioctl get fail:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
printf("get val:%d, str:%s, size: %d\n", getdata.val, getdata.str, getdata.size);
if ((ret = ioctl(fd, FELLOW_MISC_IOC_PRINT, NULL)) < 0)
{
printf("ioctl print fail:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
close(fd);
return ret;
}
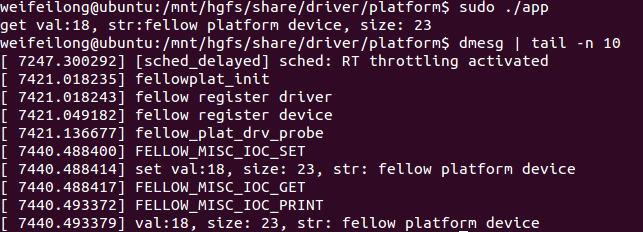
运行结果如下
设备驱动基础学习--platform driver简单实现的更多相关文章
- 设备驱动基础学习--misc device简单实现
在Linux驱动中把无法归类的五花八门的设备定义为混杂设备(用miscdevice结构体表述).miscdevice共享一个主设备号MISC_MAJOR(即10),但次设备号不同. 所有的miscde ...
- 设备驱动基础学习--poll
使用非阻塞I/O的应用程序通常会使用select()和poll()系统调用查询是否可对设备进行无阻塞的访问,这两个系统调用最终又会引发设备驱动中的poll()函数被执行,所以我们的问题就集中到了如何编 ...
- 设备驱动基础学习--/proc下增加节点
在需要创建一个由一系列数据顺序组合而成的/proc虚拟文件或一个较大的/proc虚拟文件时,推荐使用seq_file接口. 数据结构struct seq_fille定义在include/linux/s ...
- Hasen的linux设备驱动开发学习之旅--时钟
/** * Author:hasen * 參考 :<linux设备驱动开发具体解释> * 简单介绍:android小菜鸟的linux * 设备驱动开发学习之旅 * 主题:时钟 * Date ...
- Linux设备驱动模型之platform(平台)总线详解
/********************************************************/ 内核版本:2.6.35.7 运行平台:三星s5pv210 /*********** ...
- Introduction the naive“scull” 《linux设备驱动》 学习笔记
Introduction the naive "scull" 首先.什么是scull? scull (Simple Character Utility for Loading Lo ...
- 【驱动】Flash设备驱动基础·NOR·NAND
Flash存储器 ——>Flash存储器是近几年来发展最快的存储设备,通常也称作闪存.Flash属于EEPROM(电可擦除可编程只读存储器),是一类存取速度很高的存储器. ——>它既有RO ...
- 探究linux设备驱动模型之——platform虚拟总线(一)
说在前面的话 : 设备驱动模型系列的文章主要依据的内核版本是2.6.32的,因为我装的Linux系统差不多就是这个版本的(实际上我用的fedora 14的内核版本是2.6.35.13的.) ...
- Java基础学习-- 继承 的简单总结
代码参考:Java基础学习小记--多态 为什么要引入继承? 还是做一个媒体库,里面可以放CD,可以放DVD.如果把CD和DVD做成两个没有联系的类的话,那么在管理这个媒体库的时候,要单独做一个添加CD ...
随机推荐
- 多线程启动selenium,报NameError: name '__file__' is not defined
将__file__加上单引号就解决了: # 获取当前文件名,用于创建模型及结果文件的目录 file_name = os.path.basename('__file__').split('.') ...
- c语言 printf格式化输出
#include <iostream> #include<stdio.h> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int ...
- Win10 JDK 环境变量配置
1.安装JDK 到指定的目录 2.配置环境变量 2.1 配置 CLASSPATH .;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\dt.jar;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar; 2. ...
- Energy Consumption Of Low-Pressure Crystal Craft Lights
What kind of place is the low-pressure crystal light generally suitable for? Low-pressure crystal li ...
- linq和转换运算符
1.ToArray 两种常用用法 使用ILSPY查看Enumerable中的ToArray 源码分析:我们发现如果该类型可以转化为ICollection,我们最后执行CopyTo方法,如果不能转换为I ...
- 百度地图和echarts结合实例
1.由echart对象(bmapChart)获取百度地图对象(bdMap),echart对象(bmapChart)适用于所有的echart的操作和接口,百度地图对象(bdMap)适用于百度地图的所有接 ...
- codeforces 1288C. Two Arrays(dp)
链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1288/problem/C C. Two Arrays 题意:给定一个数n和一个数m,让构建两个数组a和b满足条件,1.数组中所有 ...
- laravel框架实现发送邮件的功能
1.在config 下的mail.php中配置(配置后面的两个就行了) 'from' => [ 'address' => env('MAIL_FROM_ADDRESS', '7623018 ...
- web项目中设置首页
1.在web.xml中设置以下代码: <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>login.jsp</welcome-file> < ...
- 牛客多校第一场 A Equivalent Prefixes 单调栈(笛卡尔树)
Equivalent Prefixes 单调栈(笛卡尔树) 题意: 给出两个数组u,v,每个数组都有n个不同的元素,RMQ(u,l,r)表示u数组中[l,r]区间里面的最小值标号是多少,求一个最大的m ...
