MNIST机器学习入门【学习笔记】
平台信息:
PC:ubuntu18.04、i5、anaconda2、cuda9.0、cudnn7.0.5、tensorflow1.10、GTX1060
作者:庄泽彬(欢迎转载,请注明作者)
说明:本文是在tensorflow社区的学习笔记,MNIST 手写数据入门demo
一、MNIST数据的下载,使用代码的方式:
input_data.py文件内容:
# Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Functions for downloading and reading MNIST data."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import gzip
import os
import numpy
from six.moves import urllib
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
SOURCE_URL = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
def maybe_download(filename, work_directory):
"""Download the data from Yann's website, unless it's already here."""
if not os.path.exists(work_directory):
os.mkdir(work_directory)
filepath = os.path.join(work_directory, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(SOURCE_URL + filename, filepath)
statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
return filepath
def _read32(bytestream):
dt = numpy.dtype(numpy.uint32).newbyteorder('>')
return numpy.frombuffer(bytestream.read(4), dtype=dt)[0]
def extract_images(filename):
"""Extract the images into a 4D uint8 numpy array [index, y, x, depth]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2051:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST image file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_images = _read32(bytestream)
rows = _read32(bytestream)
cols = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(rows * cols * num_images)
data = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
data = data.reshape(num_images, rows, cols, 1)
return data
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes=10):
"""Convert class labels from scalars to one-hot vectors."""
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
index_offset = numpy.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
labels_one_hot = numpy.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
return labels_one_hot
def extract_labels(filename, one_hot=False):
"""Extract the labels into a 1D uint8 numpy array [index]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2049:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST label file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_items = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(num_items)
labels = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
if one_hot:
return dense_to_one_hot(labels)
return labels
class DataSet(object):
def __init__(self, images, labels, fake_data=False):
if fake_data:
self._num_examples = 10000
else:
assert images.shape[0] == labels.shape[0], (
"images.shape: %s labels.shape: %s" % (images.shape,
labels.shape))
self._num_examples = images.shape[0]
# Convert shape from [num examples, rows, columns, depth]
# to [num examples, rows*columns] (assuming depth == 1)
assert images.shape[3] == 1
images = images.reshape(images.shape[0],
images.shape[1] * images.shape[2])
# Convert from [0, 255] -> [0.0, 1.0].
images = images.astype(numpy.float32)
images = numpy.multiply(images, 1.0 / 255.0)
self._images = images
self._labels = labels
self._epochs_completed = 0
self._index_in_epoch = 0
@property
def images(self):
return self._images
@property
def labels(self):
return self._labels
@property
def num_examples(self):
return self._num_examples
@property
def epochs_completed(self):
return self._epochs_completed
def next_batch(self, batch_size, fake_data=False):
"""Return the next `batch_size` examples from this data set."""
if fake_data:
fake_image = [1.0 for _ in xrange(784)]
fake_label = 0
return [fake_image for _ in xrange(batch_size)], [
fake_label for _ in xrange(batch_size)]
start = self._index_in_epoch
self._index_in_epoch += batch_size
if self._index_in_epoch > self._num_examples:
# Finished epoch
self._epochs_completed += 1
# Shuffle the data
perm = numpy.arange(self._num_examples)
numpy.random.shuffle(perm)
self._images = self._images[perm]
self._labels = self._labels[perm]
# Start next epoch
start = 0
self._index_in_epoch = batch_size
assert batch_size <= self._num_examples
end = self._index_in_epoch
return self._images[start:end], self._labels[start:end]
def read_data_sets(train_dir, fake_data=False, one_hot=False):
class DataSets(object):
pass
data_sets = DataSets()
if fake_data:
data_sets.train = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.validation = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.test = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
return data_sets
TRAIN_IMAGES = 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TRAIN_LABELS = 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
TEST_IMAGES = 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TEST_LABELS = 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
VALIDATION_SIZE = 5000
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_IMAGES, train_dir)
train_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_LABELS, train_dir)
train_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_IMAGES, train_dir)
test_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_LABELS, train_dir)
test_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
validation_images = train_images[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
validation_labels = train_labels[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
train_images = train_images[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
train_labels = train_labels[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
data_sets.train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels)
data_sets.validation = DataSet(validation_images, validation_labels)
data_sets.test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels)
return data_sets
新建test.py调用input_data.py进行下载手写识别的数据
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Oct 11 23:10:15 2018 @author: zhuang
""" import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
注意test.py与input_data.py要放在同一个目录下,运行test.py之后会在当前目录生成MNIST_data/ 存放下载的数据,下载的内容如下图

二、使用tensorflow构建模型进行训练
新建mnist-test.py内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Oct 12 11:43:37 2018 @author: zhuang
"""
import input_data
import tensorflow as tf mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) x = tf.placeholder("float",[None,784]) w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,w)+b) # 计算交叉熵
y_ = tf.placeholder("float",[None,10])
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y)) #梯度下降算法,以0.01的学习率更新参数
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init) #训练模型1000次
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y_:batch_ys}) #评估模型
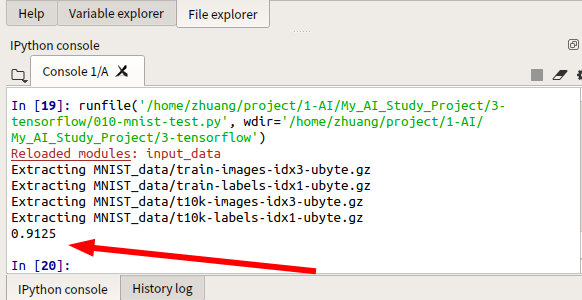
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,"float")) print sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels})
我们构建的模型手写识别的准确率在91%z左右
MNIST机器学习入门【学习笔记】的更多相关文章
- 机器学习入门学习笔记:(一)BP神经网络原理推导及程序实现
机器学习中,神经网络算法可以说是当下使用的最广泛的算法.神经网络的结构模仿自生物神经网络,生物神经网络中的每个神经元与其他神经元相连,当它“兴奋”时,想下一级相连的神经元发送化学物质,改变这些神经元的 ...
- [转]MNIST机器学习入门
MNIST机器学习入门 转自:http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/tensorflow-zh/tutorials/mnist_beginners.html?plg_ ...
- tensorfllow MNIST机器学习入门
MNIST机器学习入门 这个教程的目标读者是对机器学习和TensorFlow都不太了解的新手.如果你已经了解MNIST和softmax回归(softmax regression)的相关知识,你可以阅读 ...
- Hadoop入门学习笔记---part4
紧接着<Hadoop入门学习笔记---part3>中的继续了解如何用java在程序中操作HDFS. 众所周知,对文件的操作无非是创建,查看,下载,删除.下面我们就开始应用java程序进行操 ...
- Hadoop入门学习笔记---part3
2015年元旦,好好学习,天天向上.良好的开端是成功的一半,任何学习都不能中断,只有坚持才会出结果.继续学习Hadoop.冰冻三尺,非一日之寒! 经过Hadoop的伪分布集群环境的搭建,基本对Hado ...
- PyQt4入门学习笔记(三)
# PyQt4入门学习笔记(三) PyQt4内的布局 布局方式是我们控制我们的GUI页面内各个控件的排放位置的.我们可以通过两种基本方式来控制: 1.绝对位置 2.layout类 绝对位置 这种方式要 ...
- PyQt4入门学习笔记(一)
PyQt4入门学习笔记(一) 一直没有找到什么好的pyqt4的教程,偶然在google上搜到一篇不错的入门文档,翻译过来,留以后再复习. 原始链接如下: http://zetcode.com/gui/ ...
- Hadoop入门学习笔记---part2
在<Hadoop入门学习笔记---part1>中感觉自己虽然总结的比较详细,但是始终感觉有点凌乱.不够系统化,不够简洁.经过自己的推敲和总结,现在在此处概括性的总结一下,认为在准备搭建ha ...
- Hadoop入门学习笔记---part1
随着毕业设计的进行,大学四年正式进入尾声.任你玩四年的大学的最后一次作业最后在激烈的选题中尘埃落定.无论选择了怎样的选题,无论最后的结果是怎样的,对于大学里面的这最后一份作业,也希望自己能够尽心尽力, ...
- Scala入门学习笔记三--数组使用
前言 本篇主要讲Scala的Array.BufferArray.List,更多教程请参考:Scala教程 本篇知识点概括 若长度固定则使用Array,若长度可能有 变化则使用ArrayBuffer 提 ...
随机推荐
- android Instrumentation 转载
Android提供了一系列强大的测试工具,它针对Android的环境,扩展了业内标准的JUnit测试框架.尽管你可以使用JUnit测试Android工程,但Android工具允许你为应用程序的各个 ...
- msc文件
MSC微软管理控制台(Microsoft Management Control)文件.可以点击开始/运行,然后输入下列文件名就可以打开相应的控制窗口. 除第三个文件外,其他均在C:\WINDOWS\s ...
- oracle显示转换字段类型cast()函数
今天遇到一个查询类型转换的问题:表的字段是varchar2类型,然后查询到的结果要转换为number(20,2),刚开始的时候使用to_number()函数,发现不能满足需求.后来才知道,原来还有ca ...
- UILabel富文本 段落格式以及UILabel添加图片
之前文本整理有一点乱,这边重新整理一下,下面是效果图,一共两个UILabel, 富文本整理: /*NSForegroundColorAttributeName设置字体颜色,对象UIColor; NSP ...
- PAT 1103 Integer Factorization[难]
1103 Integer Factorization(30 分) The K−P factorization of a positive integer N is to write N as the ...
- pem转cer
openssl x509 -inform pem -in fullchain.pem -outform der -out fullchain.cer
- [LeetCode] 721. Accounts Merge_Medium tag: DFS recursive
Given a list accounts, each element accounts[i] is a list of strings, where the first element accoun ...
- Java的jdk1.6与jre1.8中存在的差异
一般来说: jdk每一个版本都是向后兼容的,说以低版本的代码是可以运行在高版本的虚拟机上的.而反过来则不可以,用1.6的编译器编辑的字节码文件是不可以运行在1.5版本的虚拟机上的. 但是今天我用Sun ...
- mysql buffer
php与mysql的连接有三种方式,mysql,mysqli,pdo.不管使用哪种方式进行连接,都有使用buffer和不使用buffer的区别. 什么叫使用buffer和不使用buffer呢? 客户端 ...
- chrome浏览器使用
1.如何打开多个历史网页.这个需求是这样的,有时候开了多个网页查找资料,但是又还没有做完,然后又需要重启电脑.显然重启电脑后再开启浏览器,一般都是显示浏览器的主页了,上次开的那些网页全部在历史记录里面 ...
