『科学计算』通过代码理解线性回归&Logistic回归模型
sklearn线性回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model def get_data():
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') scale_data = scale_n(data_original)
np.random.shuffle(scale_data)
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) train_X = data[:400, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:400, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[400:, :-1]
test_y = data[400:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y def scale_n(x):
return (x-x.mean(axis=0))/x.std(axis=0) if __name__=="__main__":
train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y = get_data() l_model = linear_model.Ridge(alpha = 1000) # 参数是正则化系数 l_model.fit(train_X,train_y) predict_train_y = l_model.predict(train_X) predict_train_y.shape = (predict_train_y.shape[0],1)
error = (predict_train_y-train_y)
rms_train = np.sqrt(np.mean(error**2, axis=0)) predict_test_y = l_model.predict(test_X)
predict_test_y.shape = (predict_test_y.shape[0],1)
error = (predict_test_y-test_y)
rms_test = np.sqrt(np.mean(error**2, axis=0)) print (rms_train, rms_test) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size), sorted(test_y), c='b', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.5, label='actual')
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size), sorted(predict_test_y), c='g', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.5, label='predicted')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylabel('House price ($1000s)')
plt.xlabel('House #')
plt.show()
sklearn模型调用民工三连:
l_model = linear_model.Ridge(alpha = 1000) # 模型装载 l_model.fit(train_X,train_y) # 模型训练 predict_train_y = l_model.predict(train_X) # 模型预测
手动线性回归模型
数据获取
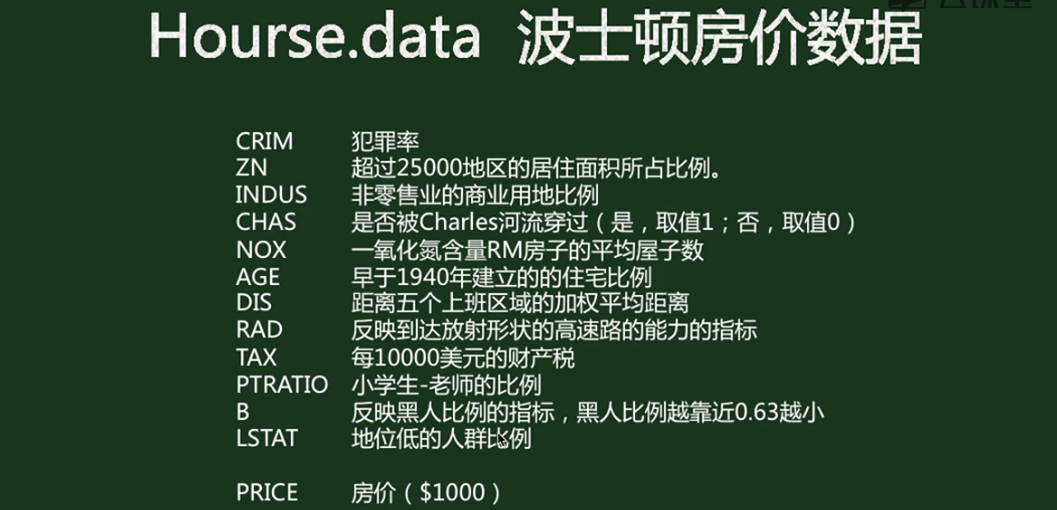
房价数据,506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
假如我们需要平方特征,只要修改get_data()中的data_original即可,在13列后添加平方项或者立方项等,由于我们不知道具体添加多少特征的组合更好,神经网络自动提取组合特征的功能就被很好的凸显出来了
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def get_data():
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') # 读取数据 scale_data = scale_n(data_original) # 归一化处理
np.random.shuffle(scale_data) # 打乱顺序
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) # 数组插入函数 train_X = data[:400, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:400, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[400:, :-1]
test_y = data[400:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y
其中:
np.loadtxt('housing.data') # 读取数据
# 本函数读取数据后自动转化为ndarray数组,可以自行设定分隔符delimiter=","
np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) # 数组插入函数
# 在数组中插入指定的行列,numpy.insert(arr, obj, values, axis=None)
# 和其他数组一样,axis不设定的话会把数组定为一维后插入,axis=0的话行扩展,axis=1的话列扩展
预处理
中心归零,标准差归一
def scale_n(x):
"""
减去平均值,除以标准差
"""
x = (x - np.mean(x,axis=0))/np.std(x,axis=0)
return x
线性回归类
class LinearModel():
def __init__(self,learn_rate=0.06,lamda=0.01,threhold=0.0000005):
"""
初始化一些参数
"""
self.learn_rate = learn_rate # 学习率
self.lamda = lamda # 正则化系数
self.threhold = threhold # 迭代阈值 def get_cost_grad(self,theta,X,y):
"""
计算代价cost和梯度grad
"""
y_pre = X.dot(theta)
cost = (y_pre-y).T.dot(y_pre-y) + self.lamda*theta.T.dot(theta)
grad = (2.0*X.T.dot(y_pre-y) + 2.0*self.lamda*theta)/X.shape[0] # 实际上是1个batch的梯度的累加值
return cost, grad def grad_check(self,X,y):
"""
梯度检查: 函数计算梯度 == L(theta+delta)-L(theta-delta) / 2delta
"""
m,n = X.shape
delta = 10**(-4)
sum_error = 0 for i in range(100):
theta = np.random.random((n,1))
j = np.random.randint(1,n) theta1,theta2 = theta.copy(),theta.copy()
theta1[j] += delta
theta2[j] -= delta cost1, grad1 = self.get_cost_grad(theta1, X, y)
cost2, grad2 = self.get_cost_grad(theta2, X, y)
cost, grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta , X, y) sum_error += np.abs(grad[j] - (cost1-cost2)/(delta*2))
print(sum_error/300.0) def train(self,X,y):
"""
初始化theta
训练后,将theta保存到实例变量里
"""
m,n = X.shape
theta = np.random.random((n,1)) prev_cost = None
for loop in range(1000):
cost,grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y)
theta -= self.learn_rate*grad
if prev_cost:
if prev_cost - cost < self.threhold:
break
prev_cost = cost
self.theta = theta
# print(theta,loop,cost) def predict(self,X):
"""
预测程序
"""
return X.dot(self.theta)
主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y = get_data() linear_model = LinearModel() linear_model.grad_check(train_X,train_y) linear_model.train(train_X,train_y) predict_train_y = linear_model.predict(train_X)
error = (predict_train_y - train_y)
rms_train = np.sqrt(np.mean(error ** 2,axis=0)) predict_test_y = linear_model.predict(test_X)
error = (predict_test_y - test_y)
rms_test = np.sqrt(np.mean(error ** 2,axis=0))
#
print(rms_train,rms_test)
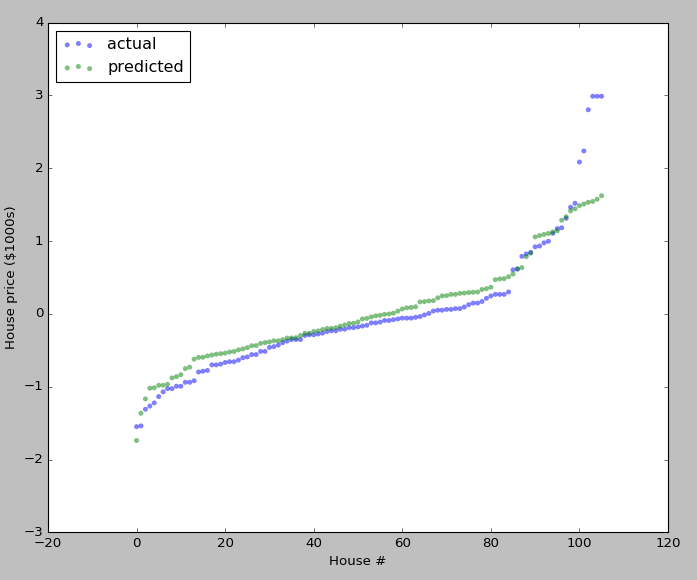
# [ 0.54031084] [ 0.60065021] plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size),sorted(test_y),c='b',edgecolor='None',alpha=0.5,label='actual')
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size),sorted(predict_test_y),c='g',edgecolor='None',alpha=0.5,label='predicted')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylabel('House price ($1000s)')
plt.xlabel('House #')
plt.show()
Logistic回归
数据获取&预处理
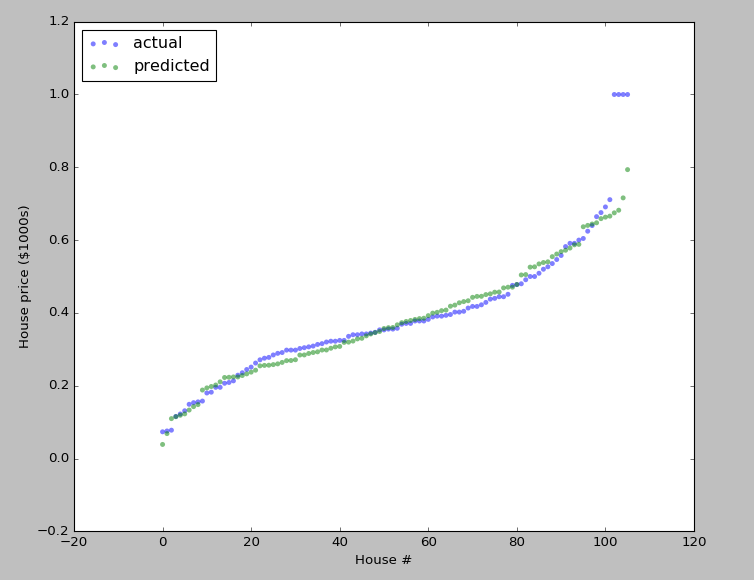
logistic回归输出值在0~1之间,所以数据预处理分两部分,前13列仍然是均值归零标准差归一,label列采取(x-x.min(axis=0))/(x.max(axis=0)-x.min(axis=0))的方式
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math def get_data(N=400):
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') scale_data = np.zeros(data_original.shape) scale_data[:,:13] = scale_n(data_original[:,:13])
scale_data[:,-1] = scale_max(data_original[:,-1]) np.random.shuffle(scale_data)
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) train_X = data[:N, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:N, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[N:, :-1]
test_y = data[N:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y def scale_n(x):
return (x-x.mean(axis=0))/x.std(axis=0)
def scale_max(x):
print (x.min(axis=0))
print (x.max(axis=0))
print (x.mean(axis=0))
print (x.std(axis=0)) return (x-x.min(axis=0))/(x.max(axis=0)-x.min(axis=0))
Logistic回归类
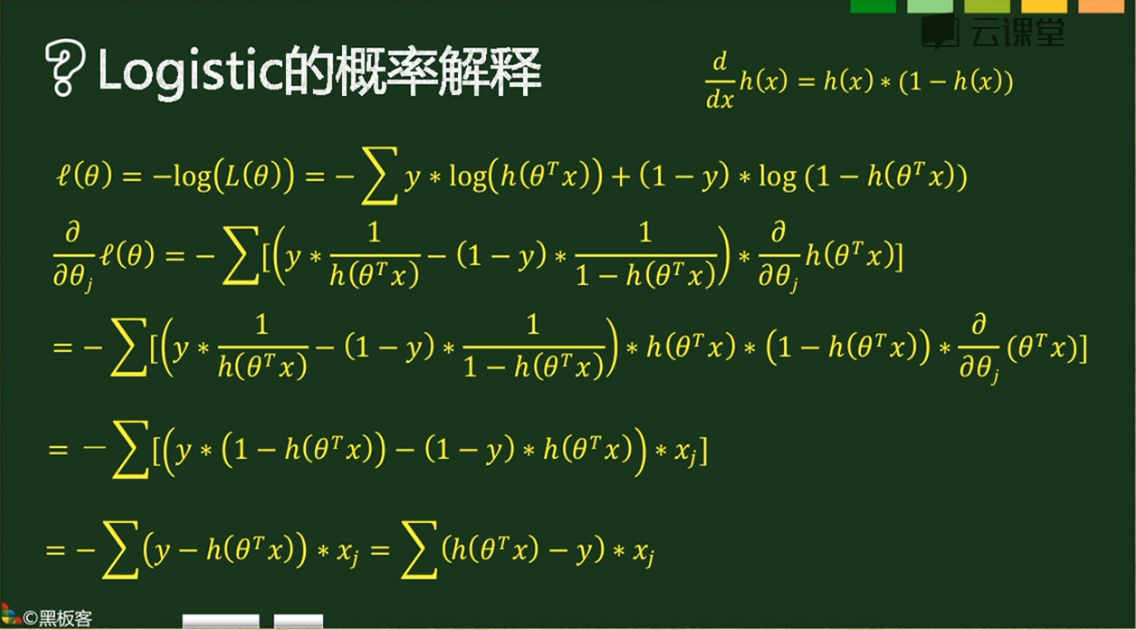
公式参考,
实际代码,
class LogisticModel(object):
def __init__(self,lamda=0.01, alpha=0.6,threhold=0.0000005):
self.alpha = alpha
self.threhold = threhold
self.lamda = lamda def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) def get_cost_grad(self,theta,X,y):
m, n = X.shape
y_dash = self.sigmoid(X.dot(theta))
error = np.sum((y * np.log(y_dash) + (1-y) * np.log(1-y_dash)),axis=1)
cost = -np.sum(error, axis=0)+self.lamda*theta.T.dot(theta)
grad = X.T.dot(y_dash-y)+2.0*self.lamda*theta return cost,grad/m def grad_check(self,X,y):
epsilon = 10**-4
m, n = X.shape sum_error=0 for i in range(300):
theta = np.random.random((n, 1))
j = np.random.randint(1,n)
theta1=theta.copy()
theta2=theta.copy()
theta1[j]+=epsilon
theta2[j]-=epsilon cost1,grad1 = self.get_cost_grad(theta1,X,y)
cost2,grad2 = self.get_cost_grad(theta2,X,y)
cost3,grad3 = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y) sum_error += np.abs(grad3[j]-(cost1-cost2)/float(2*epsilon)) def train(self,X,y):
m, n = X.shape # 400,15
theta = np.random.random((n, 1)) #[15,1]
#our intial prediction
prev_cost = None
loop_num = 0
while(True): #intial cost
cost,grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y) theta = theta- self.alpha * grad loop_num+=1
if loop_num%100==0:
print (cost,loop_num)
if prev_cost:
if prev_cost - cost <= self.threhold:
break
if loop_num>1000:
break prev_cost = cost self.theta = theta
print (theta,loop_num) def predict(self,X):
return self.sigmoid(X.dot(self.theta))
『科学计算』通过代码理解线性回归&Logistic回归模型的更多相关文章
- 『科学计算』通过代码理解SoftMax多分类
SoftMax实际上是Logistic的推广,当分类数为2的时候会退化为Logistic分类 其计算公式和损失函数如下, 梯度如下, 1{条件} 表示True为1,False为0,在下图中亦即对于每个 ...
- 『科学计算』L0、L1与L2范数_理解
『教程』L0.L1与L2范数 一.L0范数.L1范数.参数稀疏 L0范数是指向量中非0的元素的个数.如果我们用L0范数来规则化一个参数矩阵W的话,就是希望W的大部分元素都是0,换句话说,让参数W是稀 ...
- 『科学计算』可视化二元正态分布&3D科学可视化实战
二元正态分布可视化本体 由于近来一直再看kaggle的入门书(sklearn入门手册的感觉233),感觉对机器学习的理解加深了不少(实际上就只是调包能力加强了),联想到假期在python科学计算上也算 ...
- 『科学计算』科学绘图库matplotlib学习之绘制动画
基础 1.matplotlib绘图函数接收两个等长list,第一个作为集合x坐标,第二个作为集合y坐标 2.基本函数: animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update_poin ...
- 『科学计算』图像检测微型demo
这里是课上老师给出的一个示例程序,演示图像检测的过程,本来以为是传统的滑窗检测,但实际上引入了selectivesearch来选择候选窗,所以看思路应该是RCNN的范畴,蛮有意思的,由于老师的注释写的 ...
- 『科学计算』科学绘图库matplotlib练习
思想:万物皆对象 作业 第一题: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3, 1] y = [1, 3, 0, 1 ...
- 『TensorFlow』通过代码理解gan网络_中
『cs231n』通过代码理解gan网络&tensorflow共享变量机制_上 上篇是一个尝试生成minist手写体数据的简单GAN网络,之前有介绍过,图片维度是28*28*1,生成器的上采样使 ...
- 机器学习之线性回归---logistic回归---softmax回归
在本节中,我们介绍Softmax回归模型,该模型是logistic回归模型在多分类问题上的推广,在多分类问题中,类标签 可以取两个以上的值. Softmax回归模型对于诸如MNIST手写数字分类等问题 ...
- 『cs231n』通过代码理解gan网络&tensorflow共享变量机制_上
GAN网络架构分析 上图即为GAN的逻辑架构,其中的noise vector就是特征向量z,real images就是输入变量x,标签的标准比较简单(二分类么),real的就是tf.ones,fake ...
随机推荐
- python之路----面向对象进阶二
item系列 __getitem__\__setitem__\__delitem__ class Foo: def __init__(self,name,age,sex): self.name = n ...
- bzoj1638 / P2883 [USACO07MAR]牛交通Cow Traffic
P2883 [USACO07MAR]牛交通Cow Traffic 对于每一条边$(u,v)$ 设入度为0的点到$u$有$f[u]$种走法 点$n$到$v$(通过反向边)有$f2[v]$种走法 显然经过 ...
- 20145216史婧瑶《网络对抗》Web基础
20145216史婧瑶<网络对抗>Web基础 实验问题回答 (1)什么是表单 表单在网页中主要负责数据采集功能.一个表单有三个基本组成部分: 表单标签.表单域.表单按钮. (2)浏览器可以 ...
- 20145317《网络对抗》Exp4 恶意代码分析
20145317<网络对抗>Exp4 恶意代码分析 一.基础问题回答 (1)总结一下监控一个系统通常需要监控什么.用什么来监控. 通常监控以下几项信息: 注册表信息的增删添改 系统上各类程 ...
- Android实践项目汇报(一)
# 我要做的是Google天气客户端 一.Need(需求): 1. 功能性需求分析 天气预报客户端,顾名思义就是为用户提供实时准确的天气信息,方便用户出行生活.根据用户日常需求,软件实现后所达到的功能 ...
- Win32程序支持命令行参数的做法(转载)
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/lanzhi/p/6470406.html 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/kelsel/article/details/52759 ...
- C#工程详解
转:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoqingqing/p/5468072.html 前言 写这篇文章的目地是为了让更多的小伙伴对VS生成的工程有一个清晰的认识.在开发过程中,为 ...
- 【资源】分享一个最新版sublime 3143的注册码,亲测可用
注:请勿用作商业用途,有能力者请购买正版!!! —– BEGIN LICENSE —– TwitterInc 200 User License EA7E-890007 1D77F72E 390CDD9 ...
- openwrt的编译方法
1.获取最新包 ./scripts/feeds update -a 2.安装包 ./scripts/feeds install -a 3.配置 make menuconfig 4.编译 make -j ...
- C#创建继承的窗体
http://blog.csdn.net/chenyujing1234/article/details/7555369 关键技术 基窗体,实质上相当于面向对象编程中提到的基类,而继承窗体则是子类或派生 ...
