15天玩转redis —— 第五篇 集合对象类型
这篇我们来看看Redis五大类型中的第四大类型:“集合类型”,集合类型还是蛮有意思的,第一个是因为它算是只使用key的Dictionary简易版,
这样说来的话,它就比Dictionary节省很多内存消耗,第二个是因为它和C#中的HashSet是一个等同类型,废话不多说,先看redis手册,如下:

上面就是redis中的set类型使用到的所有方法,还是老话,常用的方法也就那么四个(CURD)。。。
一: 常用方法
1. SAdd
这个方法毫无疑问,就是向集合里面添加数据,比如下面这样,我往fruits集合里面添加喜爱的水果。
127.0.0.1:> sadd fruits apple
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> sadd fruits banana
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> smembers fruits
) "banana"
) "apple"
127.0.0.1:>
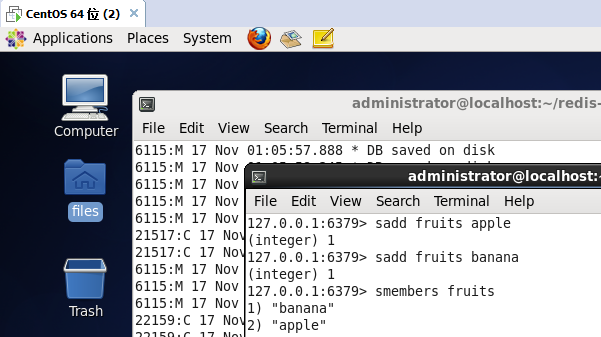
上面这个sadd你也看到了,我往集合里面成功添加了两个元素,现在你可能不满足这么简单的添加,你或许想知道set这个集合在redis底层是使用
什么来实现的,你可以用object encoding查看一下便知:
127.0.0.1:> object encoding fruits
"hashtable"
127.0.0.1:>
看到了吧,是hashtable这个吊毛,现在闭上眼睛都能想到,肯定就是只用key的dictionary啦,对不对,如果你还有疑问的话,我还可以找到底层
代码给你看,好不啦???
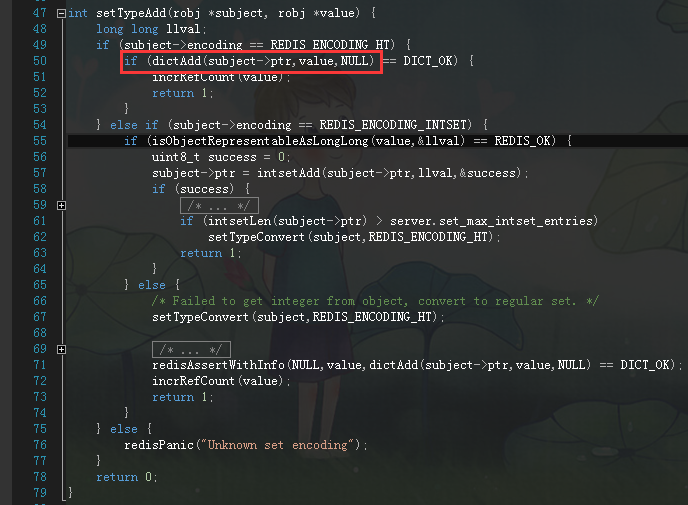
有没有看到dictAdd方法,而其中的第三个参数正好是Null。。。对应着*val形参,你看牛叉不牛叉。。。然后我再带你看看dictAdd方法的定义。
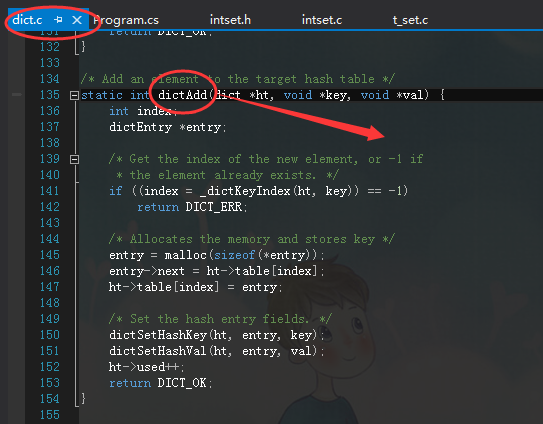
好了,关于hashtable的实现理论,我在上一篇文章中也已经说过了,这里就不再赘叙了。
2. SPOP,SMEMBERS
既然元素进来了,总不能不出来吧,这里的第一个SPOP:移除并返回集合中的一个随机元素,有一点奇怪的是,这种奇怪的方法其实在我们
C#中的HashSet并没有好办法解决,就比如”这个随机“就有点烦人了,下面这是我能想到的方法。
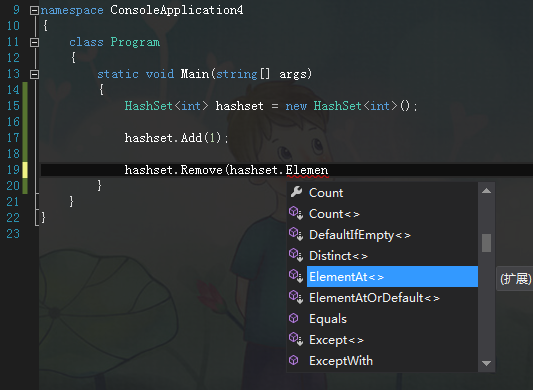
刚才随便插了一句话,下面我们继续SAdd,再SPop出来。
127.0.0.1:> sadd fruits pear
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> sadd fruits grape
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> sadd fruits chestnut
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> smembers fruits
) "grape"
) "pear"
) "banana"
) "apple"
) "chestnut"
127.0.0.1:> spop fruits
"apple"
127.0.0.1:> spop fruits
"chestnut"
127.0.0.1:> smembers fruits
) "grape"
) "pear"
) "banana"
127.0.0.1:>

这个方法确实还是蛮好的,起码它是原子性操作,如果要我自己实现的话,起码还是要10行左右代码的。
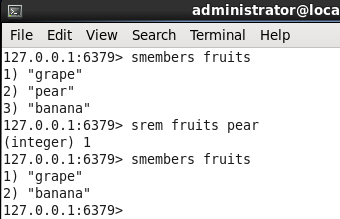
3. SREM
既然说到了CURD,那怎么能少了D呢,它的功能定义就是:移除集合 key 中的一个或多个 member 元素,不存在的 member 元素会被忽略,
下面我随便举个例子,删除fruits中的pear。
127.0.0.1:> smembers fruits
) "grape"
) "pear"
) "banana"
127.0.0.1:> srem fruits pear
(integer)
127.0.0.1:> smembers fruits
) "grape"
) "banana"
127.0.0.1:>
好了,常用的操作就那么几个,是不是觉得好傻瓜哦。。。傻瓜就对了,方法是简单的,关键你需要了解这个方法底层是如何实现的,这样才能做到
心里有数,就比如Set函数,它的源代码全部都在 “t.set.c” 中。
/*
* Copyright (c) 2009-2012, Salvatore Sanfilippo <antirez at gmail dot com>
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
*
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* * Neither the name of Redis nor the names of its contributors may be used
* to endorse or promote products derived from this software without
* specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/ #include "redis.h" /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Set Commands
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ void sunionDiffGenericCommand(redisClient *c, robj **setkeys, int setnum, robj *dstkey, int op); /* Factory method to return a set that *can* hold "value". When the object has
* an integer-encodable value, an intset will be returned. Otherwise a regular
* hash table. */
robj *setTypeCreate(robj *value) {
if (isObjectRepresentableAsLongLong(value,NULL) == REDIS_OK)
return createIntsetObject();
return createSetObject();
} int setTypeAdd(robj *subject, robj *value) {
long long llval;
if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
if (dictAdd(subject->ptr,value,NULL) == DICT_OK) {
incrRefCount(value);
return ;
}
} else if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isObjectRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == REDIS_OK) {
uint8_t success = ;
subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) {
/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains
* too many entries. */
if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > server.set_max_intset_entries)
setTypeConvert(subject,REDIS_ENCODING_HT);
return ;
}
} else {
/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */
setTypeConvert(subject,REDIS_ENCODING_HT); /* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer
* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */
redisAssertWithInfo(NULL,value,dictAdd(subject->ptr,value,NULL) == DICT_OK);
incrRefCount(value);
return ;
}
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return ;
} int setTypeRemove(robj *setobj, robj *value) {
long long llval;
if (setobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
if (dictDelete(setobj->ptr,value) == DICT_OK) {
if (htNeedsResize(setobj->ptr)) dictResize(setobj->ptr);
return ;
}
} else if (setobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isObjectRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == REDIS_OK) {
int success;
setobj->ptr = intsetRemove(setobj->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) return ;
}
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return ;
} int setTypeIsMember(robj *subject, robj *value) {
long long llval;
if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
return dictFind((dict*)subject->ptr,value) != NULL;
} else if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isObjectRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == REDIS_OK) {
return intsetFind((intset*)subject->ptr,llval);
}
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return ;
} setTypeIterator *setTypeInitIterator(robj *subject) {
setTypeIterator *si = zmalloc(sizeof(setTypeIterator));
si->subject = subject;
si->encoding = subject->encoding;
if (si->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
si->di = dictGetIterator(subject->ptr);
} else if (si->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
si->ii = ;
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return si;
} void setTypeReleaseIterator(setTypeIterator *si) {
if (si->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT)
dictReleaseIterator(si->di);
zfree(si);
} /* Move to the next entry in the set. Returns the object at the current
* position.
*
* Since set elements can be internally be stored as redis objects or
* simple arrays of integers, setTypeNext returns the encoding of the
* set object you are iterating, and will populate the appropriate pointer
* (eobj) or (llobj) accordingly.
*
* When there are no longer elements -1 is returned.
* Returned objects ref count is not incremented, so this function is
* copy on write friendly. */
int setTypeNext(setTypeIterator *si, robj **objele, int64_t *llele) {
if (si->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
dictEntry *de = dictNext(si->di);
if (de == NULL) return -;
*objele = dictGetKey(de);
} else if (si->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (!intsetGet(si->subject->ptr,si->ii++,llele))
return -;
}
return si->encoding;
} /* The not copy on write friendly version but easy to use version
* of setTypeNext() is setTypeNextObject(), returning new objects
* or incrementing the ref count of returned objects. So if you don't
* retain a pointer to this object you should call decrRefCount() against it.
*
* This function is the way to go for write operations where COW is not
* an issue as the result will be anyway of incrementing the ref count. */
robj *setTypeNextObject(setTypeIterator *si) {
int64_t intele;
robj *objele;
int encoding; encoding = setTypeNext(si,&objele,&intele);
switch(encoding) {
case -: return NULL;
case REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET:
return createStringObjectFromLongLong(intele);
case REDIS_ENCODING_HT:
incrRefCount(objele);
return objele;
default:
redisPanic("Unsupported encoding");
}
return NULL; /* just to suppress warnings */
} /* Return random element from a non empty set.
* The returned element can be a int64_t value if the set is encoded
* as an "intset" blob of integers, or a redis object if the set
* is a regular set.
*
* The caller provides both pointers to be populated with the right
* object. The return value of the function is the object->encoding
* field of the object and is used by the caller to check if the
* int64_t pointer or the redis object pointer was populated.
*
* When an object is returned (the set was a real set) the ref count
* of the object is not incremented so this function can be considered
* copy on write friendly. */
int setTypeRandomElement(robj *setobj, robj **objele, int64_t *llele) {
if (setobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
dictEntry *de = dictGetRandomKey(setobj->ptr);
*objele = dictGetKey(de);
} else if (setobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
*llele = intsetRandom(setobj->ptr);
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return setobj->encoding;
} unsigned long setTypeSize(robj *subject) {
if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
return dictSize((dict*)subject->ptr);
} else if (subject->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
return intsetLen((intset*)subject->ptr);
} else {
redisPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
} /* Convert the set to specified encoding. The resulting dict (when converting
* to a hash table) is presized to hold the number of elements in the original
* set. */
void setTypeConvert(robj *setobj, int enc) {
setTypeIterator *si;
redisAssertWithInfo(NULL,setobj,setobj->type == REDIS_SET &&
setobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET); if (enc == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
int64_t intele;
dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);
robj *element; /* Presize the dict to avoid rehashing */
dictExpand(d,intsetLen(setobj->ptr)); /* To add the elements we extract integers and create redis objects */
si = setTypeInitIterator(setobj);
while (setTypeNext(si,NULL,&intele) != -) {
element = createStringObjectFromLongLong(intele);
redisAssertWithInfo(NULL,element,dictAdd(d,element,NULL) == DICT_OK);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si); setobj->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_HT;
zfree(setobj->ptr);
setobj->ptr = d;
} else {
redisPanic("Unsupported set conversion");
}
} void saddCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set;
int j, added = ; set = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[]);
if (set == NULL) {
set = setTypeCreate(c->argv[]);
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[],set);
} else {
if (set->type != REDIS_SET) {
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
return;
}
} for (j = ; j < c->argc; j++) {
c->argv[j] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[j]);
if (setTypeAdd(set,c->argv[j])) added++;
}
if (added) {
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"sadd",c->argv[],c->db->id);
}
server.dirty += added;
addReplyLongLong(c,added);
} void sremCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set;
int j, deleted = , keyremoved = ; if ((set = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.czero)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return; for (j = ; j < c->argc; j++) {
if (setTypeRemove(set,c->argv[j])) {
deleted++;
if (setTypeSize(set) == ) {
dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[]);
keyremoved = ;
break;
}
}
}
if (deleted) {
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"srem",c->argv[],c->db->id);
if (keyremoved)
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[],
c->db->id);
server.dirty += deleted;
}
addReplyLongLong(c,deleted);
} void smoveCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *srcset, *dstset, *ele;
srcset = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[]);
dstset = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[]);
ele = c->argv[] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[]); /* If the source key does not exist return 0 */
if (srcset == NULL) {
addReply(c,shared.czero);
return;
} /* If the source key has the wrong type, or the destination key
* is set and has the wrong type, return with an error. */
if (checkType(c,srcset,REDIS_SET) ||
(dstset && checkType(c,dstset,REDIS_SET))) return; /* If srcset and dstset are equal, SMOVE is a no-op */
if (srcset == dstset) {
addReply(c,setTypeIsMember(srcset,ele) ? shared.cone : shared.czero);
return;
} /* If the element cannot be removed from the src set, return 0. */
if (!setTypeRemove(srcset,ele)) {
addReply(c,shared.czero);
return;
}
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"srem",c->argv[],c->db->id); /* Remove the src set from the database when empty */
if (setTypeSize(srcset) == ) {
dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[],c->db->id);
}
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
server.dirty++; /* Create the destination set when it doesn't exist */
if (!dstset) {
dstset = setTypeCreate(ele);
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[],dstset);
} /* An extra key has changed when ele was successfully added to dstset */
if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) {
server.dirty++;
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"sadd",c->argv[],c->db->id);
}
addReply(c,shared.cone);
} void sismemberCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set; if ((set = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.czero)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return; c->argv[] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[]);
if (setTypeIsMember(set,c->argv[]))
addReply(c,shared.cone);
else
addReply(c,shared.czero);
} void scardCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *o; if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.czero)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,o,REDIS_SET)) return; addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(o));
} void spopCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set, *ele, *aux;
int64_t llele;
int encoding; if ((set = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return; encoding = setTypeRandomElement(set,&ele,&llele);
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
ele = createStringObjectFromLongLong(llele);
set->ptr = intsetRemove(set->ptr,llele,NULL);
} else {
incrRefCount(ele);
setTypeRemove(set,ele);
}
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"spop",c->argv[],c->db->id); /* Replicate/AOF this command as an SREM operation */
aux = createStringObject("SREM",);
rewriteClientCommandVector(c,,aux,c->argv[],ele);
decrRefCount(ele);
decrRefCount(aux); addReplyBulk(c,ele);
if (setTypeSize(set) == ) {
dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[],c->db->id);
}
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
server.dirty++;
} /* handle the "SRANDMEMBER key <count>" variant. The normal version of the
* command is handled by the srandmemberCommand() function itself. */ /* How many times bigger should be the set compared to the requested size
* for us to don't use the "remove elements" strategy? Read later in the
* implementation for more info. */
#define SRANDMEMBER_SUB_STRATEGY_MUL 3 void srandmemberWithCountCommand(redisClient *c) {
long l;
unsigned long count, size;
int uniq = ;
robj *set, *ele;
int64_t llele;
int encoding; dict *d; if (getLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[],&l,NULL) != REDIS_OK) return;
if (l >= ) {
count = (unsigned) l;
} else {
/* A negative count means: return the same elements multiple times
* (i.e. don't remove the extracted element after every extraction). */
count = -l;
uniq = ;
} if ((set = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.emptymultibulk))
== NULL || checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return;
size = setTypeSize(set); /* If count is zero, serve it ASAP to avoid special cases later. */
if (count == ) {
addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk);
return;
} /* CASE 1: The count was negative, so the extraction method is just:
* "return N random elements" sampling the whole set every time.
* This case is trivial and can be served without auxiliary data
* structures. */
if (!uniq) {
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,count);
while(count--) {
encoding = setTypeRandomElement(set,&ele,&llele);
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,llele);
} else {
addReplyBulk(c,ele);
}
}
return;
} /* CASE 2:
* The number of requested elements is greater than the number of
* elements inside the set: simply return the whole set. */
if (count >= size) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,,NULL,REDIS_OP_UNION);
return;
} /* For CASE 3 and CASE 4 we need an auxiliary dictionary. */
d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL); /* CASE 3:
* The number of elements inside the set is not greater than
* SRANDMEMBER_SUB_STRATEGY_MUL times the number of requested elements.
* In this case we create a set from scratch with all the elements, and
* subtract random elements to reach the requested number of elements.
*
* This is done because if the number of requsted elements is just
* a bit less than the number of elements in the set, the natural approach
* used into CASE 3 is highly inefficient. */
if (count*SRANDMEMBER_SUB_STRATEGY_MUL > size) {
setTypeIterator *si; /* Add all the elements into the temporary dictionary. */
si = setTypeInitIterator(set);
while((encoding = setTypeNext(si,&ele,&llele)) != -) {
int retval = DICT_ERR; if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
retval = dictAdd(d,createStringObjectFromLongLong(llele),NULL);
} else {
retval = dictAdd(d,dupStringObject(ele),NULL);
}
redisAssert(retval == DICT_OK);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
redisAssert(dictSize(d) == size); /* Remove random elements to reach the right count. */
while(size > count) {
dictEntry *de; de = dictGetRandomKey(d);
dictDelete(d,dictGetKey(de));
size--;
}
} /* CASE 4: We have a big set compared to the requested number of elements.
* In this case we can simply get random elements from the set and add
* to the temporary set, trying to eventually get enough unique elements
* to reach the specified count. */
else {
unsigned long added = ; while(added < count) {
encoding = setTypeRandomElement(set,&ele,&llele);
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
ele = createStringObjectFromLongLong(llele);
} else {
ele = dupStringObject(ele);
}
/* Try to add the object to the dictionary. If it already exists
* free it, otherwise increment the number of objects we have
* in the result dictionary. */
if (dictAdd(d,ele,NULL) == DICT_OK)
added++;
else
decrRefCount(ele);
}
} /* CASE 3 & 4: send the result to the user. */
{
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de; addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,count);
di = dictGetIterator(d);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL)
addReplyBulk(c,dictGetKey(de));
dictReleaseIterator(di);
dictRelease(d);
}
} void srandmemberCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set, *ele;
int64_t llele;
int encoding; if (c->argc == ) {
srandmemberWithCountCommand(c);
return;
} else if (c->argc > ) {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
return;
} if ((set = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return; encoding = setTypeRandomElement(set,&ele,&llele);
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,llele);
} else {
addReplyBulk(c,ele);
}
} int qsortCompareSetsByCardinality(const void *s1, const void *s2) {
return setTypeSize(*(robj**)s1)-setTypeSize(*(robj**)s2);
} /* This is used by SDIFF and in this case we can receive NULL that should
* be handled as empty sets. */
int qsortCompareSetsByRevCardinality(const void *s1, const void *s2) {
robj *o1 = *(robj**)s1, *o2 = *(robj**)s2; return (o2 ? setTypeSize(o2) : ) - (o1 ? setTypeSize(o1) : );
} void sinterGenericCommand(redisClient *c, robj **setkeys, unsigned long setnum, robj *dstkey) {
robj **sets = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*setnum);
setTypeIterator *si;
robj *eleobj, *dstset = NULL;
int64_t intobj;
void *replylen = NULL;
unsigned long j, cardinality = ;
int encoding; for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
robj *setobj = dstkey ?
lookupKeyWrite(c->db,setkeys[j]) :
lookupKeyRead(c->db,setkeys[j]);
if (!setobj) {
zfree(sets);
if (dstkey) {
if (dbDelete(c->db,dstkey)) {
signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);
server.dirty++;
}
addReply(c,shared.czero);
} else {
addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk);
}
return;
}
if (checkType(c,setobj,REDIS_SET)) {
zfree(sets);
return;
}
sets[j] = setobj;
}
/* Sort sets from the smallest to largest, this will improve our
* algorithm's performance */
qsort(sets,setnum,sizeof(robj*),qsortCompareSetsByCardinality); /* The first thing we should output is the total number of elements...
* since this is a multi-bulk write, but at this stage we don't know
* the intersection set size, so we use a trick, append an empty object
* to the output list and save the pointer to later modify it with the
* right length */
if (!dstkey) {
replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);
} else {
/* If we have a target key where to store the resulting set
* create this key with an empty set inside */
dstset = createIntsetObject();
} /* Iterate all the elements of the first (smallest) set, and test
* the element against all the other sets, if at least one set does
* not include the element it is discarded */
si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[]);
while((encoding = setTypeNext(si,&eleobj,&intobj)) != -) {
for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
if (sets[j] == sets[]) continue;
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
/* intset with intset is simple... and fast */
if (sets[j]->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET &&
!intsetFind((intset*)sets[j]->ptr,intobj))
{
break;
/* in order to compare an integer with an object we
* have to use the generic function, creating an object
* for this */
} else if (sets[j]->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
eleobj = createStringObjectFromLongLong(intobj);
if (!setTypeIsMember(sets[j],eleobj)) {
decrRefCount(eleobj);
break;
}
decrRefCount(eleobj);
}
} else if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) {
/* Optimization... if the source object is integer
* encoded AND the target set is an intset, we can get
* a much faster path. */
if (eleobj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INT &&
sets[j]->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET &&
!intsetFind((intset*)sets[j]->ptr,(long)eleobj->ptr))
{
break;
/* else... object to object check is easy as we use the
* type agnostic API here. */
} else if (!setTypeIsMember(sets[j],eleobj)) {
break;
}
}
} /* Only take action when all sets contain the member */
if (j == setnum) {
if (!dstkey) {
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT)
addReplyBulk(c,eleobj);
else
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,intobj);
cardinality++;
} else {
if (encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET) {
eleobj = createStringObjectFromLongLong(intobj);
setTypeAdd(dstset,eleobj);
decrRefCount(eleobj);
} else {
setTypeAdd(dstset,eleobj);
}
}
}
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si); if (dstkey) {
/* Store the resulting set into the target, if the intersection
* is not an empty set. */
int deleted = dbDelete(c->db,dstkey);
if (setTypeSize(dstset) > ) {
dbAdd(c->db,dstkey,dstset);
addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(dstset));
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,"sinterstore",
dstkey,c->db->id);
} else {
decrRefCount(dstset);
addReply(c,shared.czero);
if (deleted)
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",
dstkey,c->db->id);
}
signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);
server.dirty++;
} else {
setDeferredMultiBulkLength(c,replylen,cardinality);
}
zfree(sets);
} void sinterCommand(redisClient *c) {
sinterGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,NULL);
} void sinterstoreCommand(redisClient *c) {
sinterGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,c->argv[]);
} #define REDIS_OP_UNION 0
#define REDIS_OP_DIFF 1
#define REDIS_OP_INTER 2 void sunionDiffGenericCommand(redisClient *c, robj **setkeys, int setnum, robj *dstkey, int op) {
robj **sets = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*setnum);
setTypeIterator *si;
robj *ele, *dstset = NULL;
int j, cardinality = ;
int diff_algo = ; for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
robj *setobj = dstkey ?
lookupKeyWrite(c->db,setkeys[j]) :
lookupKeyRead(c->db,setkeys[j]);
if (!setobj) {
sets[j] = NULL;
continue;
}
if (checkType(c,setobj,REDIS_SET)) {
zfree(sets);
return;
}
sets[j] = setobj;
} /* Select what DIFF algorithm to use.
*
* Algorithm 1 is O(N*M) where N is the size of the element first set
* and M the total number of sets.
*
* Algorithm 2 is O(N) where N is the total number of elements in all
* the sets.
*
* We compute what is the best bet with the current input here. */
if (op == REDIS_OP_DIFF && sets[]) {
long long algo_one_work = , algo_two_work = ; for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
if (sets[j] == NULL) continue; algo_one_work += setTypeSize(sets[]);
algo_two_work += setTypeSize(sets[j]);
} /* Algorithm 1 has better constant times and performs less operations
* if there are elements in common. Give it some advantage. */
algo_one_work /= ;
diff_algo = (algo_one_work <= algo_two_work) ? : ; if (diff_algo == && setnum > ) {
/* With algorithm 1 it is better to order the sets to subtract
* by decreasing size, so that we are more likely to find
* duplicated elements ASAP. */
qsort(sets+,setnum-,sizeof(robj*),
qsortCompareSetsByRevCardinality);
}
} /* We need a temp set object to store our union. If the dstkey
* is not NULL (that is, we are inside an SUNIONSTORE operation) then
* this set object will be the resulting object to set into the target key*/
dstset = createIntsetObject(); if (op == REDIS_OP_UNION) {
/* Union is trivial, just add every element of every set to the
* temporary set. */
for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */ si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;
decrRefCount(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
}
} else if (op == REDIS_OP_DIFF && sets[] && diff_algo == ) {
/* DIFF Algorithm 1:
*
* We perform the diff by iterating all the elements of the first set,
* and only adding it to the target set if the element does not exist
* into all the other sets.
*
* This way we perform at max N*M operations, where N is the size of
* the first set, and M the number of sets. */
si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[]);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* no key is an empty set. */
if (sets[j] == sets[]) break; /* same set! */
if (setTypeIsMember(sets[j],ele)) break;
}
if (j == setnum) {
/* There is no other set with this element. Add it. */
setTypeAdd(dstset,ele);
cardinality++;
}
decrRefCount(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
} else if (op == REDIS_OP_DIFF && sets[] && diff_algo == ) {
/* DIFF Algorithm 2:
*
* Add all the elements of the first set to the auxiliary set.
* Then remove all the elements of all the next sets from it.
*
* This is O(N) where N is the sum of all the elements in every
* set. */
for (j = ; j < setnum; j++) {
if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */ si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
if (j == ) {
if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;
} else {
if (setTypeRemove(dstset,ele)) cardinality--;
}
decrRefCount(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si); /* Exit if result set is empty as any additional removal
* of elements will have no effect. */
if (cardinality == ) break;
}
} /* Output the content of the resulting set, if not in STORE mode */
if (!dstkey) {
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,cardinality);
si = setTypeInitIterator(dstset);
while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {
addReplyBulk(c,ele);
decrRefCount(ele);
}
setTypeReleaseIterator(si);
decrRefCount(dstset);
} else {
/* If we have a target key where to store the resulting set
* create this key with the result set inside */
int deleted = dbDelete(c->db,dstkey);
if (setTypeSize(dstset) > ) {
dbAdd(c->db,dstkey,dstset);
addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(dstset));
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_SET,
op == REDIS_OP_UNION ? "sunionstore" : "sdiffstore",
dstkey,c->db->id);
} else {
decrRefCount(dstset);
addReply(c,shared.czero);
if (deleted)
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",
dstkey,c->db->id);
}
signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);
server.dirty++;
}
zfree(sets);
} void sunionCommand(redisClient *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,NULL,REDIS_OP_UNION);
} void sunionstoreCommand(redisClient *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,c->argv[],REDIS_OP_UNION);
} void sdiffCommand(redisClient *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,NULL,REDIS_OP_DIFF);
} void sdiffstoreCommand(redisClient *c) {
sunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+,c->argc-,c->argv[],REDIS_OP_DIFF);
} void sscanCommand(redisClient *c) {
robj *set;
unsigned long cursor; if (parseScanCursorOrReply(c,c->argv[],&cursor) == REDIS_ERR) return;
if ((set = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[],shared.emptyscan)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,set,REDIS_SET)) return;
scanGenericCommand(c,set,cursor);
}
15天玩转redis —— 第五篇 集合对象类型的更多相关文章
- 15天玩转redis —— 第四篇 哈希对象类型
redis中的hash也是我们使用中的高频数据结构,它的构造基本上和编程语言中的HashTable,Dictionary大同小异,如果大家往后有什么逻辑需要用 Dictionary存放的话,可以根据场 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第十一篇 让你彻底了解RDB存储结构
接着上一篇说,这里我们来继续分析一下RDB文件存储结构,首先大家都知道RDB文件是在redis的“快照”的模式下才会产生,那么如果 我们理解了RDB文件的结构,是不是让我们对“快照”模式能做到一个心中 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第十篇 对快照模式的深入分析
我们知道redis是带有持久化这个能力了,那到底持久化成到哪里,持久化成啥样呢???这篇我们一起来寻求答案. 一:快照模式 或许在用Redis之初的时候,就听说过redis有两种持久化模式,第一种是S ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第八篇 你不得不会的事务玩法
我们都知道redis追求的是简单,快速,高效,在这种情况下也就拒绝了支持window平台,学sqlserver的时候,我们知道事务还算是个比较复杂的东西, 所以这吊毛要是照搬到redis中去,理所当然 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第六篇 有序集合类型
今天我们说一下Redis中最后一个数据类型 “有序集合类型”,回首之前学过的几个数据结构,不知道你会不会由衷感叹,开源的世界真好,写这 些代码的好心人真的要一生平安哈,不管我们想没想的到的东西,在这个 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第三篇 无敌的列表类型
据说60%的人使用redis看重的是redis中的list类型,那这个list有什么用呢???不用我说大家都明白,做队列使用呗,为什么用它呢,很简单呗, 因为有了它我就不需要专门的MQ产品啦,比如说 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第七篇 同事的一次缓存操作引起对慢查询的认识
上个星期同事做一个业务模块,需要将一个80M的数据存入到redis缓存中,想法总是好的,真操作的时候遇到了HSet超时,我们使用的是C#的 StackExchange.Redis驱动. <red ...
- 从Redis中删除大集合对象的方法
Redis中的大集合对象,如set.zset等,如果有上千万个元素,一般是不能直接用del命令来删除的,因为del命令可能会耗时几秒钟,而redis本身是单线程的,在高并发的情况下会阻塞大量的请求,严 ...
- 15天玩转redis —— 第二篇 基础的字符串类型
我们都知道redis是采用C语言开发,那么在C语言中表示string都是采用char[]数组的,然后你可能会想,那还不简单,当我执行如下命令,肯定是直 接塞给char[]数组的. 如果你真的这么想的话 ...
随机推荐
- 第二章 深入 C# 数据类型
第二章 深入 C# 数据类型 1.封装又称信息隐藏,是指利用抽象数据类型将数据和数据的操作结合在一起,使其构成一个不可分割的独立实体,尽可能的隐藏内部的细节,只保留一些对外接口,使之于外部发生联系. ...
- 大叔也说Xamarin~Android篇~支付宝SDK的集成
回到目录 首先做为支付宝SDK它提供了多种平台,网页版,wap版,IOS版,android版等等,今天主要说一下在xamarin里使用android平台的sdk的方法,在网上介绍这块的文章不多,大叔本 ...
- 基础才是重中之重~Data层如何调用BLL层的方法,如果觉得奇怪请看本文章
回到目录 看似不伦不类 这个题目有点不伦不类,或者说有点伪模式了,不错,确实是这样,我们正确的开发思维是WEB层->BLL层->DATA层,每个层有对它下层的引用,下层不能引用上层,因为这 ...
- PDO事务处理
PDO事务处理 2014-9-3 10:44:19 By jiancaigege==================================== 概要:将多条sql操作(增删改)作为一个操作单 ...
- C#Color对象的使用介绍及颜色对照表
原文地址 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3e1177090101bzs3.html 今天用到了特转载 NET框架中的颜色基于4种成份,透明度,红,绿和蓝.每一种成份都 ...
- [javaweb]Java过滤器与包装设计模式的实用案例.
在filter中可以得到代表用户请求和响应的request.response对象,因此在编程中可以使用Decorator(装饰器)模式对request.response对象进行包装,再把包装对象传给目 ...
- Atitit cnchar simp best list 汉字简化方案 最简化汉字256个
Atitit cnchar simp best list 汉字简化方案 最简化汉字256个 1.1. 最简化发音1 1.2. 根据笔画密度,删除了密度高的字..1 1.3. 使用同发音的英文字母等代 ...
- vue.js学习之入门实例
之前一直看过vue.js官网api,但是很少实践,这里抽出时间谢了个入门级的demo,记录下一些知识点,防止后续踩坑,牵扯到的的知识点:vue.vue-cli.vue-router.webpack等. ...
- Mysql 事件(定时任务)
mysql 创建任务(事件) 1.检查数据库事件是否开启,如果 event_scheduler 等于 NO表示开启 SELECT @@event_scheduler; SHOW VARIABLES L ...
- js高程读书笔记(1-3章)
一.js简介 js是一种专为与网页交互而设计的脚本语言,由以下三个不同的部分组成: 1.ECMAScript,由ECMA-262(它规定了语言的这些组成部分:语法,类型,语句,关键字,保留字,操作符, ...
