Deep learning:四十九(RNN-RBM简单理解)
前言:
本文主要是bengio的deep learning tutorial教程主页中最后一个sample:rnn-rbm in polyphonic music. 即用RNN-RBM来model复调音乐,训练过程中采用的是midi格式的音频文件,接着用建好的model来产生复调音乐。对音乐建模的难点在与每首乐曲中帧间是高度时间相关的(这样样本的维度会很高),用普通的网络模型是不能搞定的(普通设计网络模型没有考虑时间维度,图模型中的HMM有这方面的能力),这种情况下可以采用RNN来处理,这里的RNN为recurrent neural network中文为循环神经网络,另外还有一种RNN为recursive neural network翻为递归神经网络。本文中指的是循环神经网络。
RNN简单介绍:
首先来看RNN和普通的feed-forward网络有什么不同。RNN的网络框架如下:
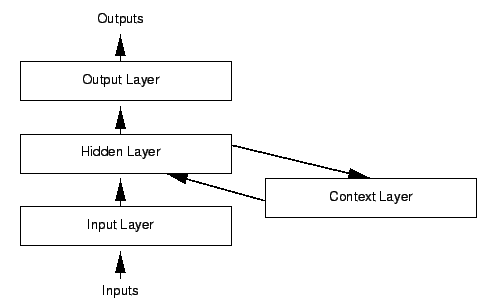
由结构图可以知道,RNN和feed-forward相比只是中间隐含层多了一个循环的圈而已,这个圈表示上一次隐含层的输出作为这一次隐含层的输入,当然此时的输入是需要乘以一个权值矩阵的,这样的话RNN模型参数只多了个权值矩阵。更形象的RNN图可以参考:

以及图:

按照上图所示,可知道RNN网络前向传播过程中满足下面的公式(参考文献Learning Recurrent Neural Networks with Hessian-Free Optimization):

其代价函数可以是重构的误差:
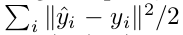
也可以是交叉熵:

相信熟悉普通深究网络的同学看懂这些应该不难。
RNN-RBM简单介绍:
RNN-RBM来自ICML2012的论文:Modeling Temporal Dependencies in High-Dimensional Sequences: Application to Polyphonic Music Generation and Transcription,它由一个单层的RBM网络和单层的RNN网络构成,且由RNN网络的输出作为最终网络的输出。RBM部分当生成模型的功能,比如这里的音乐生成,RNN部分当判别模型作用,比如它的输出当值可当做提取的特征。RNN-RBM模型的结构如下:
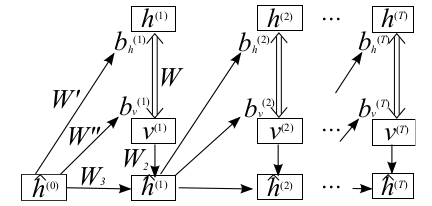
模型上面是RBM部分,下面是RNN部分,对应的公式可以参考论文。模型中一共有9个参数:

整个模型的代价函数为-P(v),其中:
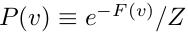
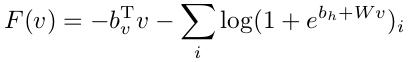
对该loss function求导,然后采用SGD算法就可以求出模型中的各个参数了。当然了,其中的RBM部分还需要用Gibbs采样完成CD-k算法。
实验结果:
实验部分参考http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rnnrbm.html,实验须用的数据和paper对应的见http://www-etud.iro.umontreal.ca/~boulanni/icml2012. 由于本人对乐理方面的知识不是很懂,很多实验代码细节没有去深究,只是看下算法的大概流程。由RNN-RBM生成的两个pinao roll数据如下(程序跑了20个小时左右):


迭代200次后的cost为:
......
Epoch 197/200 -4.7050858655
Epoch 198/200 -4.69198161366
Epoch 199/200 -4.66586797348
Epoch 200/200 -4.68651185036
代码如下:
# Author: Nicolas Boulanger-Lewandowski
# University of Montreal (2012)
# RNN-RBM deep learning tutorial
# More information at http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rnnrbm.html import glob
import os
import sys import numpy
try:
import pylab
except ImportError:
print "pylab isn't available, if you use their fonctionality, it will crash"
print "It can be installed with 'pip install -q Pillow'" from midi.utils import midiread, midiwrite
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.shared_randomstreams import RandomStreams #Don't use a python long as this don't work on 32 bits computers.
numpy.random.seed(0xbeef)
rng = RandomStreams(seed=numpy.random.randint(1 << 30))
theano.config.warn.subtensor_merge_bug = False #给定rbm的3个参数w,bv,bh,输入端数据v,以及gibbs采用长度k
#返回的tuple元素依次是:v_samples(k次gibbs采用得到的输入端数据,01化后的),cost(rbm模型中的-log(v)),monitor(监控用变量),
#updates(保留每次迭代的中间过程,如果是shared变量的话)
def build_rbm(v, W, bv, bh, k):
'''Construct a k-step Gibbs chain starting at v for an RBM. v : Theano vector or matrix
If a matrix, multiple chains will be run in parallel (batch).
W : Theano matrix
Weight matrix of the RBM.
bv : Theano vector
Visible bias vector of the RBM.
bh : Theano vector
Hidden bias vector of the RBM.
k : scalar or Theano scalar
Length of the Gibbs chain. Return a (v_sample, cost, monitor, updates) tuple: v_sample : Theano vector or matrix with the same shape as `v`
Corresponds to the generated sample(s).
cost : Theano scalar
Expression whose gradient with respect to W, bv, bh is the CD-k approximation
to the log-likelihood of `v` (training example) under the RBM.
The cost is averaged in the batch case.
monitor: Theano scalar
Pseudo log-likelihood (also averaged in the batch case).
updates: dictionary of Theano variable -> Theano variable
The `updates` object returned by scan.''' def gibbs_step(v): #该函数功能是一次gibbs采样后得到的mean_v,v
mean_h = T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(v, W) + bh)
h = rng.binomial(size=mean_h.shape, n=1, p=mean_h, #产生二项分布,隐含层节点01化
dtype=theano.config.floatX)
mean_v = T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(h, W.T) + bv)
v = rng.binomial(size=mean_v.shape, n=1, p=mean_v, #反向传播,输入层节点也01化
dtype=theano.config.floatX)
return mean_v, v #一次Gibbs采样后输入层01化前后的值
#输入的是v,输出的是每一次Gibbs采样后的v构成的list,一共进行k次Gibbs采样
chain, updates = theano.scan(lambda v: gibbs_step(v)[1], outputs_info=[v],
n_steps=k) #updates里面装的是每次的输入值
v_sample = chain[-1] #k次Gibbs采样后输入端的值(01化过后的) mean_v = gibbs_step(v_sample)[0] #再次Gibbs前进一次,得到没有01化的输入端数码,用于监控的变量
monitor = T.xlogx.xlogy0(v, mean_v) + T.xlogx.xlogy0(1 - v, 1 - mean_v)
monitor = monitor.sum() / v.shape[0] def free_energy(v): #公式4,能量的计算公式
return -(v * bv).sum() - T.log(1 + T.exp(T.dot(v, W) + bh)).sum()
cost = (free_energy(v) - free_energy(v_sample)) / v.shape[0] #代价函数 return v_sample, cost, monitor, updates def shared_normal(num_rows, num_cols, scale=1):
'''Initialize a matrix shared variable with normally distributed
elements.'''
return theano.shared(numpy.random.normal(
scale=scale, size=(num_rows, num_cols)).astype(theano.config.floatX)) def shared_zeros(*shape):
'''Initialize a vector shared variable with zero elements.'''
return theano.shared(numpy.zeros(shape, dtype=theano.config.floatX)) def build_rnnrbm(n_visible, n_hidden, n_hidden_recurrent):
'''Construct a symbolic RNN-RBM and initialize parameters. n_visible : integer
Number of visible units.
n_hidden : integer
Number of hidden units of the conditional RBMs.
n_hidden_recurrent : integer
Number of hidden units of the RNN. Return a (v, v_sample, cost, monitor, params, updates_train, v_t,
updates_generate) tuple: v : Theano matrix
Symbolic variable holding an input sequence (used during training)
v_sample : Theano matrix
Symbolic variable holding the negative particles for CD log-likelihood
gradient estimation (used during training)
cost : Theano scalar
Expression whose gradient (considering v_sample constant) corresponds to the
LL gradient of the RNN-RBM (used during training)
monitor : Theano scalar
Frame-level pseudo-likelihood (useful for monitoring during training)
params : tuple of Theano shared variables
The parameters of the model to be optimized during training.
updates_train : dictionary of Theano variable -> Theano variable
Update object that should be passed to theano.function when compiling the
training function.
v_t : Theano matrix
Symbolic variable holding a generated sequence (used during sampling)
updates_generate : dictionary of Theano variable -> Theano variable
Update object that should be passed to theano.function when compiling the
generation function.''' W = shared_normal(n_visible, n_hidden, 0.01)
bv = shared_zeros(n_visible)
bh = shared_zeros(n_hidden)
Wuh = shared_normal(n_hidden_recurrent, n_hidden, 0.0001)
Wuv = shared_normal(n_hidden_recurrent, n_visible, 0.0001)
Wvu = shared_normal(n_visible, n_hidden_recurrent, 0.0001)
Wuu = shared_normal(n_hidden_recurrent, n_hidden_recurrent, 0.0001)
bu = shared_zeros(n_hidden_recurrent) params = W, bv, bh, Wuh, Wuv, Wvu, Wuu, bu # learned parameters as shared
# variables v = T.matrix() # a training sequence
u0 = T.zeros((n_hidden_recurrent,)) # initial value for the RNN hidden
# units # If `v_t` is given, deterministic recurrence to compute the variable
# biases bv_t, bh_t at each time step. If `v_t` is None, same recurrence
# but with a separate Gibbs chain at each time step to sample (generate)
# from the RNN-RBM. The resulting sample v_t is returned in order to be
# passed down to the sequence history.
# 如果给定t时刻的v和t-1时刻的u,那么返回t时刻的u,bv,bh,含有25次Gibbs采样过程
# 如果只给定t-1时刻的u(即没有t时刻的v),则表示的是由rbm来产生v了,所以这时候返回的是t时刻的v和u,以及
# 迭代过程中输入端的变换过程updates
def recurrence(v_t, u_tm1):
bv_t = bv + T.dot(u_tm1, Wuv)
bh_t = bh + T.dot(u_tm1, Wuh)
generate = v_t is None
if generate:
v_t, _, _, updates = build_rbm(T.zeros((n_visible,)), W, bv_t, #第一个参数应该是v,因此这里的v是0
bh_t, k=25)
u_t = T.tanh(bu + T.dot(v_t, Wvu) + T.dot(u_tm1, Wuu))
return ([v_t, u_t], updates) if generate else [u_t, bv_t, bh_t] # For training, the deterministic recurrence is used to compute all the
# {bv_t, bh_t, 1 <= t <= T} given v. Conditional RBMs can then be trained
# in batches using those parameters.
(u_t, bv_t, bh_t), updates_train = theano.scan( #训练rbm过程的符号表达式(每次只包括25步的Gibbs采样)
lambda v_t, u_tm1, *_: recurrence(v_t, u_tm1),
sequences=v, outputs_info=[u0, None, None], non_sequences=params)
v_sample, cost, monitor, updates_rbm = build_rbm(v, W, bv_t[:], bh_t[:],
k=15)
updates_train.update(updates_rbm) # symbolic loop for sequence generation
(v_t, u_t), updates_generate = theano.scan(
lambda u_tm1, *_: recurrence(None, u_tm1),#进行generate产生过程的符号表达式,迭代200次
outputs_info=[None, u0], non_sequences=params, n_steps=200) return (v, v_sample, cost, monitor, params, updates_train, v_t, #cost在build_rbm()中产生
updates_generate) class RnnRbm: #两个功能,训练RNN-RBM模型和用训练好的RNN-RBM模型来产生样本
'''Simple class to train an RNN-RBM from MIDI files and to generate sample
sequences.''' def __init__(self, n_hidden=150, n_hidden_recurrent=100, lr=0.001,
r=(21, 109), dt=0.3):
'''Constructs and compiles Theano functions for training and sequence
generation. n_hidden : integer
Number of hidden units of the conditional RBMs.
n_hidden_recurrent : integer
Number of hidden units of the RNN.
lr : float
Learning rate
r : (integer, integer) tuple
Specifies the pitch range of the piano-roll in MIDI note numbers, including
r[0] but not r[1], such that r[1]-r[0] is the number of visible units of the
RBM at a given time step. The default (21, 109) corresponds to the full range
of piano (88 notes).
dt : float
Sampling period when converting the MIDI files into piano-rolls, or
equivalently the time difference between consecutive time steps.''' self.r = r
self.dt = dt
(v, v_sample, cost, monitor, params, updates_train, v_t,
updates_generate) = build_rnnrbm(r[1] - r[0], n_hidden, #在该函数里面有设置迭代次数等参数
n_hidden_recurrent) gradient = T.grad(cost, params, consider_constant=[v_sample])
updates_train.update(((p, p - lr * g) for p, g in zip(params,
gradient))) #sgd算法,利用公式4的cost公式搞定8个参数的更新
self.train_function = theano.function([v], monitor,
updates=updates_train)
self.generate_function = theano.function([], v_t, #updates_generate步骤在build_rnnrbm()中产生,音乐的产生主要在那函数中
updates=updates_generate) def train(self, files, batch_size=100, num_epochs=200):
'''Train the RNN-RBM via stochastic gradient descent (SGD) using MIDI
files converted to piano-rolls. files : list of strings
List of MIDI files that will be loaded as piano-rolls for training.
batch_size : integer
Training sequences will be split into subsequences of at most this size
before applying the SGD updates.
num_epochs : integer
Number of epochs (pass over the training set) performed. The user can
safely interrupt training with Ctrl+C at any time.''' assert len(files) > 0, 'Training set is empty!' \
' (did you download the data files?)'
dataset = [midiread(f, self.r,
self.dt).piano_roll.astype(theano.config.floatX)
for f in files] #读取midi文件 try:
for epoch in xrange(num_epochs): #训练200次
numpy.random.shuffle(dataset) #将训练样本打乱
costs = [] for s, sequence in enumerate(dataset): #返回的s是序号,sequence是dataset对应序号下的值
for i in xrange(0, len(sequence), batch_size):
cost = self.train_function(sequence[i:i + batch_size]) #train_function在init()函数中
costs.append(cost) print 'Epoch %i/%i' % (epoch + 1, num_epochs),
print numpy.mean(costs)
sys.stdout.flush() except KeyboardInterrupt:
print 'Interrupted by user.' def generate(self, filename, show=True):
'''Generate a sample sequence, plot the resulting piano-roll and save
it as a MIDI file. filename : string
A MIDI file will be created at this location.
show : boolean
If True, a piano-roll of the generated sequence will be shown.''' piano_roll = self.generate_function() #直接生成piano roll文件
midiwrite(filename, piano_roll, self.r, self.dt)#将piano_roll文件转换成midi文件并保存
if show:
extent = (0, self.dt * len(piano_roll)) + self.r
pylab.figure()
pylab.imshow(piano_roll.T, origin='lower', aspect='auto',
interpolation='nearest', cmap=pylab.cm.gray_r,
extent=extent)
pylab.xlabel('time (s)')
pylab.ylabel('MIDI note number')
pylab.title('generated piano-roll') def test_rnnrbm(batch_size=100, num_epochs=200):
model = RnnRbm()
#os.path.dirname(__file__)为获得当前文件的目录,os.path.split(path)是将path按照最后一个斜线分成父和子的部分
re = os.path.join(os.path.split(os.path.dirname(__file__))[0], #该代码完成的功能是,找到当前文件的上级目录下的/data/Nottinghan/train/*.mid文件
'data', 'Nottingham', 'train', '*.mid') #re得到该目录下的所有.mid文件
model.train(glob.glob(re),#glob.glob()只是将文件路径名等弄成linux的格式
batch_size=batch_size, num_epochs=num_epochs)
return model if __name__ == '__main__':
model = test_rnnrbm() #该函数主要用来训练RNN-RBM参数
model.generate('sample1.mid') #产生数据的v_t初始化都是0
model.generate('sample2.mid')
pylab.show()
实验总结:
关于bp算法:由于RNN-RBM中对loss函数求导用到了BPTT(back propgation through time)算法:BP算法加入了时间维度。为了加深对BP算法的理解,重新看了一遍推导过程。bp算法的推导过程是主要是由求导中的链式法则得到的。具体算法可参考Martin T.Hagan 的《神经网络设计》第11章(这本书写得不错,翻译得也还可以)。其思想大概为:损失函数F对第m层wij(连接第m层第i个节点和第m-1层第j个节点之间的权值)的导数等于F对第m层第i个节点输入值的导数,乘上该输入值对wij的导数(很容易知道这个导数等于第m-1层第j个节点的输出值)。而F对第m层第i个节点输入值的导数值又等于F对第m+1层输入值的导数(这时需要考虑第m+1中所有的节点)乘以第m+1层输入值对第m层第i个输入值的导数(这个导数值很容易由激发函数的导函数求得),并且我们通常说的bp算法是误差方向传播,这里的第m层误差指的就是F对第m层输入值的导数。由此可知,可以从最后一层依次往前求解,这就是bp算法的思想,本质上是高数里面的链式求导法则。
另外,实验中关于乐理对应的具体细节没有深究。
参考资料:
http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rnnrbm.html(教程主页)
《神经网络设计》,Martin T.Hagan.
http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~waleed/phd/html/node37.html(RNN图片来源1)
Recurrent Neural Networks in Ruby.(RNN图片来源2)
Learning Recurrent Neural Networks with Hessian-Free Optimization, James Martens,Ilya Sutskever.
Modeling Temporal Dependencies in High-Dimensional Sequences: Application to Polyphonic Music Generation and Transcription, Nicolas Boulanger-Lewandowski,Yoshua Bengio,Pascal Vincent.
http://www-etud.iro.umontreal.ca/~boulanni/icml2012(rnn-rbm项目主页)
Deep learning:四十九(RNN-RBM简单理解)的更多相关文章
- Deep learning:四十二(Denoise Autoencoder简单理解)
前言: 当采用无监督的方法分层预训练深度网络的权值时,为了学习到较鲁棒的特征,可以在网络的可视层(即数据的输入层)引入随机噪声,这种方法称为Denoise Autoencoder(简称dAE),由Be ...
- Deep learning:四十八(Contractive AutoEncoder简单理解)
Contractive autoencoder是autoencoder的一个变种,其实就是在autoencoder上加入了一个规则项,它简称CAE(对应中文翻译为?).通常情况下,对权值进行惩罚后的a ...
- Gradle 1.12用户指南翻译——第四十九章. Build Dashboard 插件
本文由CSDN博客貌似掉线翻译,其他章节的翻译请参见: http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/gradle-translation.html 翻译项目请关注Githu ...
- SQL注入之Sqli-labs系列第四十七关,第四十八关,第四十九关(ORDER BY注入)
0x1 源码区别点 将id变为字符型:$sql = "SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY '$id'"; 0x2实例测试 (1)and rand相结合的方式 ...
- m_Orchestrate learning system---二十九、什么情况下用数据库做配置字段,什么情况下用配置文件做配置
m_Orchestrate learning system---二十九.什么情况下用数据库做配置字段,什么情况下用配置文件做配置 一.总结 一句话总结: 配置文件 开发人员 重置 数据库 非开发人员 ...
- “全栈2019”Java第四十九章:重载与重写对比详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java第 ...
- 第四十九个知识点:描述在IPsec和TLS后的基本想法
第四十九个知识点:描述在IPsec和TLS后的基本想法 网络安全协议(Internet Protocol Security,IPsec)和安全传输层协议(Transport Layer Securit ...
- Deep learning for visual understanding: A review 视觉理解中的深度学习:回顾 之一
Deep learning for visual understanding: A review 视觉理解中的深度学习:回顾 ABSTRACT: Deep learning algorithms ar ...
- abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统——出库管理之一(四十九)
abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统目录 abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统——ABP总体介绍(一) abp(net core)+ ...
随机推荐
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7514017 更多请看专栏,地址 ...
- QQ在线客服设置
QQ在线客服设置 1.客户在添加QQ在线客服后,需要让用户在线不需要添加为好友就能在线对话,一般默认设置下会显示"您需要添加对方为好友+才能给对方发送会话消息",具体解决方法如下: ...
- Hadoop2.20集群搭建
hadoop2.0已经发布了稳定版本了,增加了很多特性,比如HDFS HA.YARN等. 注意:apache提供的hadoop-2.2.0的安装包是在32位操作系统编译的,因为hadoop依赖一些C+ ...
- Java中的受检异常
Java中的受检异常 Java提供了三种异常类型,受检异常(checked exception).运行时异常(runtime exception).错误(error).那么这受检异常在实际开发中又有什 ...
- EQueue - 详细谈一下消息持久化以及消息堆积的设计
前言 之前写了一篇文章,总体介绍了EQueue.在看这篇文章之前如果还没看过那篇文章,可能会看不懂这篇文章.所以建议没看过的朋友务必先看一下那篇文章中所提到的各种概念,这样才能更好的理解本文所说的内容 ...
- 超出TCP连接端口数限制(MaxUserPort)引起的服务器问题
昨天2台Windows Server 2012服务器出现奇怪的问题,自己竟然连不上自己的本机80端口,telnet 127.0.0.1 80也连不上,而更奇怪的是其它服务器可以连接到这2台服务器的80 ...
- js操作Dom的一些方法简化
众所周知JQ的选择符很强大,一些看起来很难实现的功能只要在$符号中传入简单的字符串就可以获取到各种层级关系的DOM,而却不用考虑浏览器的兼容性.但有时候在做小项目的时候并不需要引入JQ,而又不想频繁繁 ...
- dojo/query源码解析
dojo/query模块是dojo为开发者提供的dom查询接口.该模块的输出对象是一个使用css选择符来查询dom元素并返回NodeList对象的函数.同时,dojo/query模块也是一个插件,开发 ...
- .net开发笔记(十三) Winform常用开发模式第一篇
上一篇博客最后我提到“异步编程模型”(APM),之后本来打算整理一下这方面的材料然后总结一下写篇文章与诸位分享,后来在整理的过程中不断的延伸不断地扩展,发现完全偏离了“异步编程”这个概念,前前后后所有 ...
- html5 css3实现图中结构
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" > <head> <title>demo</title> ...
