入门到熟练-SpringBoot
Spring Boot概述
1.1. Spring Boot是什么
Spring Boot是一套基于Spring框架的微服务框架。
1.2. Spring Boot框架出现的背景
由于Spring是一个轻量级的企业开发框架,主要的功能就是用于整合和管理其他框架。
但随着整合的框架越来越多,Spring的整合配置也日益繁琐。在这个情况下,Spring团体有了一个想法:就是将平时主流使用的到的框架的整合配置预先写好,然后通过简单的几个参数就可以实现框架的快速整合。
这个想法催生Spring boot框架。
我们将这个实现了各种主流框架与Spring的自动整合的框架Spring boot称为Spring微服务框架:
1.3. Spring Boot的作用是什么
就是大大减少了Spring与其他框架整合的代码,也实现了Spring开发的Web应用的快速部署。
1.4. Spring Boot的特点
1.实现了各种主流的框架的快速整合
2.实现了Spring的应用的快速部署,使用Spring Boot的Web应用可以以Jar的方式部署。
1.5. Spring Boot学习的前提
1.由于Spring Boot的最小配置都是基于SpringMVC框架的,所以学习Spring Boot先要有Spring和SpringMVC框架的基础。
2.SpringBoot默认不支持JSP视图,官方推荐使用Thymeleaf或者Freemarker模板引擎。本文档没有对这两个模板引擎作详细介绍。
Spring Boot中可以使用Spring框架的所有注解。如果没有学过纯注解Spring框架配置,需要先学习Spring纯注解的配置。
所谓的纯注解:就是一个Spring配置文件都没有的配置。
涉及Spring框架的纯注解配置类常用注解如下:
|
注解名 |
说明 |
|
@Configuration |
声明一个配置类,配置类的功能等同spring的配置文件(重点) |
|
@Bean |
将没有声明 @Component/@Controller/@Serivce/@Repository的类加入到Spring容器 等同于Spring配置文件的<bean>标签 |
|
@PropertySource |
在Spring的配置里读取,增加的这个注解,可以使用@Value注解获得properties文件的内容 |
|
@Value |
获得上下文中,Properties文件的内容 等同与Spring配置文件的 ${key} |
|
@ComponentScan |
用于扫描类,创建对象到Spring容器中 等同Spring配置文件 <context:component-scan> |
|
@ConditionalOnMissingBean |
表示如果Spring容器已经有该类的对象就不执行创建对象的方法再创建一次了。 |
1.6. Spring Boot准备工具
学习Spring Boot建议使用Eclipse安装STS插件或者直接使用STS开发工具。
下载官网:https://spring.io/tools/sts
1.7. 参考资料
本文档编写参考了
1.Spring官方的示例代码,地址如下:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/tree/master/spring-boot-samples
2.SpringBoot官方参考文档,地址如下:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#getting-started
3.spring boot自动配置的框架,路径如下:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/tree/master/spring-boot-starters
2. Spring Boot的入门
2.1. 简单配置入门
2.1.1. 配置流程
1.新建一个maven项目
|
|
2.填写创建项目的信息,注意使用jar的方式创建项目就可以
|
|
3.到spring boot官方复制pom的依赖到pom.xml文件
网站地址为:http://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/
|
|
pom.xml文件内容如下:
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-demo-01</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> |
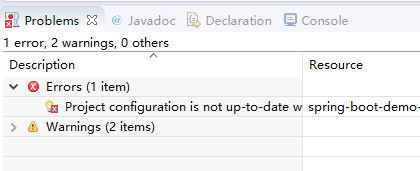
注意:如果复制spring boot依赖到pom.xml报以下错误
|
|
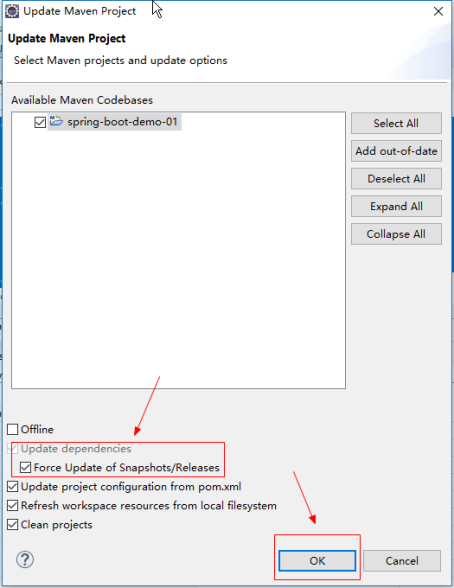
更新一下项目即可.如下图
|
|
4.编写一个简单的Java类
|
package hello; import org.springframework.boot.*; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.*; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; //声明@Controller存储类型注解,表示SampleController类启动是,对象会加载到Spring容器 @Controller //声明@EnableAutoConfiguration,表示程序使用Springboot默认的配置 @EnableAutoConfiguration public class SampleController { /** * 表示如果访问路径/,返回字符串Hello World! */ @RequestMapping("/") @ResponseBody String home() { return "Hello World!"; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //启动Spring Boot程序 SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args); } } |
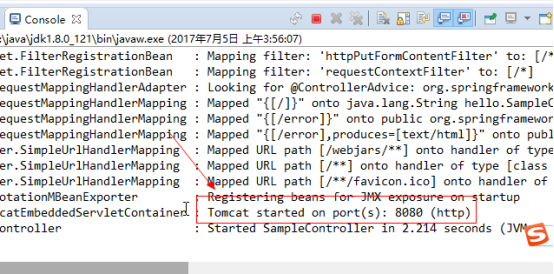
5.启动Spring Boot程序
|
|
6.启动成功,控制台提示我们使用8080端口访问
|
|
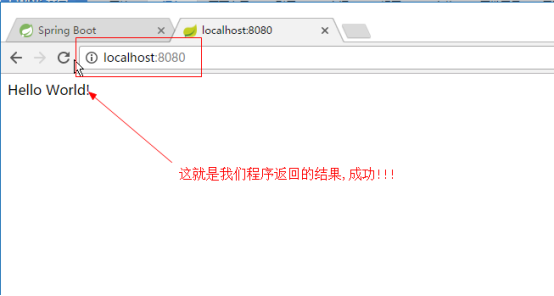
7.使用浏览器访问8080端口
|
|
2.1.2. 注意事项
maven是需要联网下载的jar包的。注意一下网络是否畅通。
2.2. 使用@SpringBootApplication注解配置
上面的示例有一个问题,代码如下:
|
SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args); |
启动的Controller只有一个,如果一个项目需要将多个类扫描到Spring的容器中如何解决呢?
答:使用@SpringBootApplication注解来配置。
入口类使用@SpringBootApplication注解,启动项目时,SpringBoot框架会扫描入口类的同级目录和子目录的类的对象到Spring容器。
2.2.1. 配置流程
1.创建一个Maven项目
|
|
2.将Spring boot的依赖复制到pom.xml文件
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-demo-02</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> |
3.将项目简单分层
|
|
4.在cn.itheima文件夹下创建一个入口类Application.java
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; //使用SpringBoot自动配置程序 @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //执行当前类,根据@SpringBootApplication的配置,启动SpringBoot程序 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
5.创建一个Controller,业务控制器
|
package cn.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller public class HelloController { @RequestMapping(value="/") @ResponseBody public String say(){ //返回字符串 return "HelloWorld!"; } } |
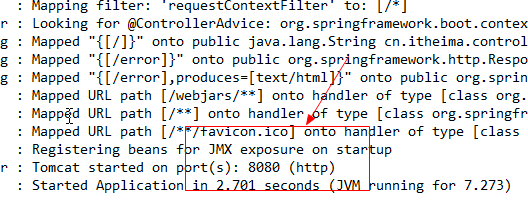
6.启动项目,控制台返回访问端口
|
|
7.使用浏览器访问
|
|
2.2.2. 注意事项
1.为什么放在cn.itheima包下呢?
答:@SpringBootApplication的配置默认根据入口类的所在位置扫描包以及入口类所在位置以及子包范围。
根据以上配置,使用@SpringBootApplication配置Spring boot项目。会自动扫描cn.itheima.*下面HelloController类。
从而可以得出使用@SpringBootApplication可以实现将多个类扫描到Spring容器里面。
2.3. 热启动
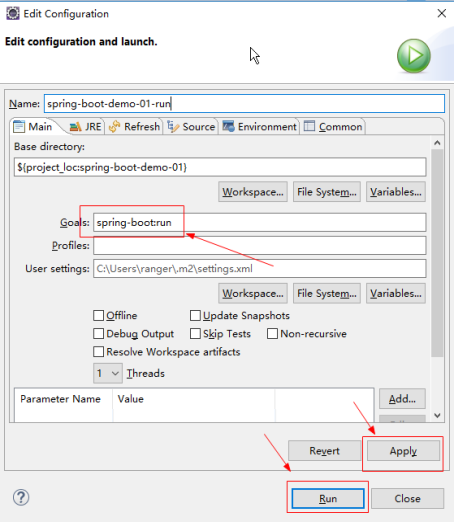
使用spring-boot:run命令启动项目,每次修改完成代码都要重新启动。是非常麻烦的。
我们就有那么一个想法,能不能修改完代码,程序不用重启直接自动编译了?
我们将修改完代码开发工具自动编译的过程称为,热启动。
Spring boot是支持热启动的。只有加入以下依赖就可以
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <!-- optional=true,依赖不会传递,该项目依赖devtools; 之后依赖该项目的项目如果想要使用devtools,需要重新引入 --> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> |
3. SpringBoot常见基础包说明
|
|
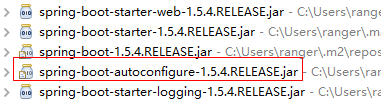
1.spring-boot-starter-web-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar:仅仅存放web项目需要的jar包的pom.xml
2.spring-boot-starter-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar:仅仅存放springboot最小核心需要的jar包的pom.xml
3.spring-boot-starter-logging-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar:仅仅存放日志输出需要的jar包的pom.xml
4.spring-boot-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar:springboot框架核心包
spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar:默认支持的自动配置的框架的配置包(重点)
重点是spring-boot-autoconfigure包,因为spring boot的所有内置的自动配置的类都在里面!
4. 常用API说明
4.1. SpringApplication类
4.1.1. 说明
作用:用于启动Spring Boot的程序,根据传入的类声明的注解来决定不同的启动方式。
4.1.2. 示例代码
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; //使用SpringBoot自动配置程序 @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //执行当前类,根据@SpringBootApplication的配置,启动SpringBoot程序 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
4.2. @EnableAutoConfiguration注解
4.2.1. 注解的声明
|
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; } |
4.2.2. 作用
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的作用是:启动程序时,告诉SpringApplication启动对象使用SpringBoot的默认配置。
只要在SpringBoot项目的入口类配置了@EnableAutoConfiguration,在SpringBoot框架启动是就会自动根据你导入的jar包来加载spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE-sources.jar中的xxxAutoconfiguration配置类,使用其默认配置。
|
|
4.2.3. 属性说明
exclude属性:使用Class格式的方式,排除默认自动启动中不需要的配置类
excludeName属性:使用类的限制名的方式,排序默认自动启动中不需要的配置类
4.3. @SpringBootApplication注解
4.3.1. 注解声明
|
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "exclude") Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "excludeName") String[] excludeName() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages") String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses") Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; } |
根据注解的声明可以得出:@SpringBootApplication注解也是启动Springboot的默认配置。只是在@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的基础上增加了扫描包@ComponentScan的这个注解。实现了并且扫描指定范围的类创建对象到容器里面。
4.3.2. 属性说明
1.basePackages属性
@SpringBootApplication默认扫描的范围是使用该注解的当前的类的包以及子包,如果要指定其他范围的包,可以是basePackages指定。
2.basePackageClasses属性
用于精确指定哪些类需要创建对象加载到Spring容器里面。
3.exclude属性
通过Class的方式排除不扫描的类,就是该类不创建对象。
4.excludeName属性
通过类的全限制名的方式,排除不扫描的类,指定的类不会在容器中创建对象。
4.4. @AutoConfigureBefore注解
4.4.1. 注解说明
指定在SpringBoot框架自动配置的配置类执行完成之前,执行指定的自定义的配置类。
如果放在Application入口类,表示在所有自动配置的配置类还没有可以就先加载自定义的配置类。
@AutoConfigureBefore注解属性:
value:使用类的方式指定自动配置类
name:使用类的全限制名(字符串)类指定配置类
4.4.2. 示例代码
1.创建一个普通的类,没有任何注解
|
package cn.itheima.utils; /** * 创建一个没有扫描注入容器注解的类 * @author ranger * */ public class TestUtils { /** * 返回测试信息 * @return */ public String test(){ return "-测试注入对象成功-"; } } |
2.创建一个自定义配置类,注入普通的类到Spring容器
|
package cn.itheima.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; package cn.itheima.config; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import cn.itheima.utils.TestUtils; /** * 创建一个自定义的配置类 * @author ranger * */ @Configuration public class MyConfiguration { /** * 返回一个对象到容器 * @return */ @Bean(name="testUtils") //表示如果Spring容器有TestUtils的对象就不执行这个方法在创建一次了。 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(TestUtils.class) public TestUtils getTestUtils(){ TestUtils testUtils=new TestUtils(); return testUtils; } } |
3.在入口类配置加入自定义配置类
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureBefore; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import cn.itheima.config.MyConfiguration; //使用SpringBoot自动配置程序 @SpringBootApplication //在自动配置的配置类之前启动自定义的配置类 @AutoConfigureBefore(value=MyConfiguration.class) public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //执行当前类,根据@SpringBootApplication的配置,启动SpringBoot程序 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
4.在Controller里面使用这个注入的对象
|
package cn.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import cn.itheima.utils.TestUtils; @Controller public class HelloController { @Autowired private TestUtils testUtils; @RequestMapping(value="/") @ResponseBody public String say(){ System.out.println(testUtils.test()); return testUtils.test(); } } |
5.测试,成功
|
|
4.5. @AutoConfigureAfter注解
指定在SpringBoot框架自动配置的配置类执行完成之后,然后执行指定的自定义的配置类。
4.6. @SpringBootTest注解
4.6.1. 注解说明
用于使用JUnit测试SpringBoot程序,启动SpringBoot框架。测试SpringBoot一定要加上。
4.6.2. 示例代码
|
package cn.itheima.test; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //如果不加该注解,无法启动SpringBoot @SpringBootTest public class DataSourceTest { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Test public void dataSource() { try { System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
5. SpringBoot配置流程(重点)
5.1. 概述
Spring Boot框架是一个将整合框架的整合代码都写好了的框架。所以我们要知道它的工作原理才能够,找到各种整合框架可以配置的属性,以及属性对应的属性名。
本章主要讲述如何在SpringBoot框架代码中找到application.properties配置文件的属性值。
5.2. 配置流程说明
1.SpringBoot的spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar中编写了所以内置支持的框架的自动整合代码
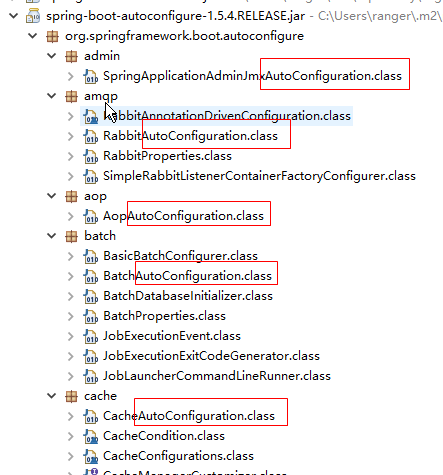
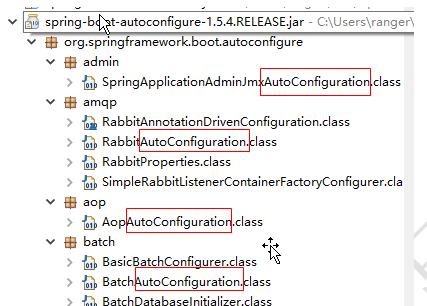
2.所以支持的框架根据功能类型来划分包,每个包都有一个XxxxAutoConfiguration配置类,都是一个基于纯注解的配置类,是各种框架整合的框架代码。如图所示:
|
|
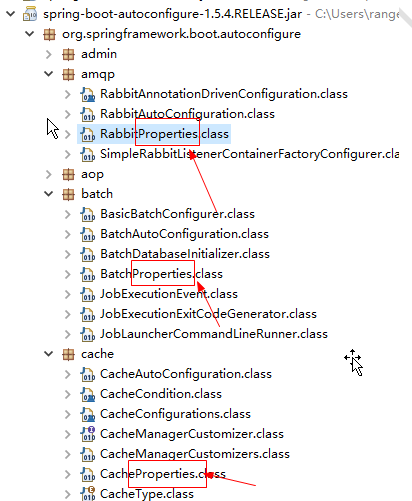
3.如果配置的框架有默认的配置参数,都放在一个命名为XxxxProperties的属性,如图所示
|
|
4.通过项目的resources下的application.properties文件可以修改每个整合框架的默认属性,从而实现了快速整合的目的。
|
|
5.3. 配置流程图
第一步:配置一个内置整合框架的参数,先到spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar找到对应的模块。
第二步:如果该框架有可以配置的参数,那么对应的整合模块中一定有一个XxxxProperties类,在里面可以找可以设置的参数。
第三部:在resources源目录下的application.properties文件里面可以修改XxxxProperties类中默认的参数。
配置流程如下:
|
|
6. 配置文件
Spring Boot的参数配置文件支持两种格式。分别为application.propertie,application.yml。
配置Spring Boot时可以二选一。
application.propertie:是键值对风格
application.yml:是层级键值对风格
6.1. application.propertie配置文件
6.1.1. application.propertie说明
默认情况下,Spring Boot会加载resources目录下的application.properties来获得配置的参数。
6.1.2. application.propertie多配置文件支持
1.在application.properties配置文件下,增加多个application-xxx.properties文件名的配置文件,其中xxx是一个任意的字符串。
例如:
|
application-database.properties application-mvc.properties application-freemarker.properties |
2.在application.properties总配置文件指定,加载的多个配置文件
例如:要同时使用,四个配置文件
|
application.properties、 application-databaseproperties application-mvc.properties application-freemarker.properties |
那么在application.properties其他配置文件指定为:
|
spring.profiles.active=database,mvc,freemarker |
6.2. application.yml配置文件
6.2.1. application.yml说明
SpringBoot支持一种由SpringBoot框架自制的配置文件格式。后缀为yml。yml后缀的配置文件的功能和properties后缀的配置文件的功能是一致的。配置时可以二选一。
例如:配置文件:application.properties
|
#配置数据源 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.type=org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource #spring-data-jpa配置 #显示SQL语句 spring.jpa.show-sql=true #表示是否需要根据view的生命周期来决定session是否关闭 spring.jpa.open-in-view=true |
可以修改为配置文件:application.yml,内容为:
|
#配置数据源 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 123456 #配置连接池 type: org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource #配置JPA的属性 jpa: show-sql: true open-in-view: true |
其实application.yml配置文件就是将原来application.properties使用(.)分割的方式,改为树状结构,使用(:)分割。
注意:最后key的字段与值之间的冒号(:)后面一定要有一个空格。
6.2.2. application.yml多配置文件支持
1.在application.yml配置文件下,增加多个application-xxx.yml文件名的配置文件,其中xxx是一个任意的字符串。
例如:
|
application-database.yml application-mvc.yml application-freemarker.yml |
2.在application.yml总配置文件指定,加载的多个配置文件
例如:要同时使用,四个配置文件
|
application.yml application-database.yml application-mvc.yml application-freemarker.yml |
那么在application.yml其他配置文件指定为:
|
spring: profiles: active: database,mvc,freemarker |
6.3. 配置示例-Spring数据源配置
配置Spring数据源,并支持DBCP2数据源
1.在pom.xml加入支持数据源的类库
|
<!-- 数据库驱动 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- dbcp2连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Springboot测试包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> |
2.找到数据源的配置类
|
|
3.数据源的配置类的属性如下
|
//注意这里 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware, InitializingBean { private ClassLoader classLoader; private Environment environment; private String name = "testdb"; private boolean generateUniqueName; //注意这里 private Class<? extends DataSource> type; private String driverClassName; private String url; private String username; private String password; private String jndiName; private boolean initialize = true; private String platform = "all"; private List<String> schema; private String schemaUsername; private String schemaPassword; private List<String> data; private String dataUsername; private String dataPassword; private boolean continueOnError = false; private String separator = ";"; private Charset sqlScriptEncoding; private EmbeddedDatabaseConnection embeddedDatabaseConnection = EmbeddedDatabaseConnection.NONE; private Xa xa = new Xa(); private String uniqueName; |
3.application.properties配置文件修改数据源参数:
|
#datasource spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 #support dbcp2 datasource spring.datasource.type=org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource |
1.spring.datasource这个前缀就是DataSourceProperties的@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")注解声明的前缀
2.属性就是DataSourceProperties对应的属性
4.测试代码
|
package cn.itheima.test; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //SpringBoot测试要加上这个注解 @SpringBootTest public class DataSourceTest { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Test public void dataSource() { try { System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
6.4. 获得自定义application.properties声明的属性值
使用@ConfigurationProperties注解可以直接获得application.properties配置的属性值。
@ConfigurationProperties属性说明:
prefix属性:表示获得application.properties时忽略的指定的前缀,如:
|
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false) |
ignoreUnknownFields属性:忽略未知的字段值。如果为true时,就是当application.properties设置的输入找不到对应的字段时,就忽略它。
@ConfigurationProperties的使用:
1.在pom.xml导入支持的依赖包
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> |
2.自定义一个TestProperties 属性类
|
package cn.itheima.utils; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="cn.itheima" ) public class TestProperties { private String path; public String getPath() { return path; } public void setPath(String path) { this.path = path; } } |
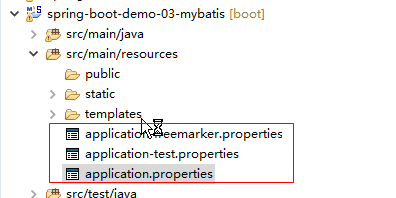
3.自定义一个application-test.properties文件
|
cn.itheima.path=demo-03 |
4.在application.properties指定application-test.properties配置文件
|
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.type=org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource spring.profiles.active=test |
5.启动支持TestProperties类自动配置
在入口类Application增加EnableConfigurationProperties注解支持
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import cn.itheima.utils.TestProperties; @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigurationProperties(value=TestProperties.class) public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
6.调用配置的属性path
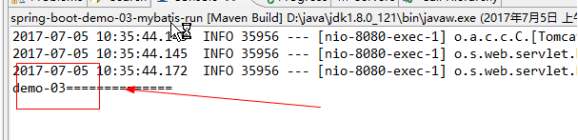
|
package cn.itheima.controller; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import cn.itheima.service.StudentService; import cn.itheima.utils.TestProperties; @Controller public class StudentController { @Autowired private TestProperties testProperties; @RequestMapping(value="/path") public String path(){ System.out.println(testProperties.getPath()+"=============="); return "index"; } } |
7.测试结果
|
|
7. Spring Boot视图
7.1. 视图概述
由于SpringBoot建议使用jar的方式发布web程序。所以不建议使用jsp视图,也不对jsp视图做默认的支持。
如果确实要使用JSP视图来说发布Spring Boot的应用,那么建议使用war的方式发布。
Spring Boot默认自动配置支持视图是以下的模板引擎:
7.2. FreeMarker模板引擎的配置
7.2.1. 配置流程
1.在pom.xml导入FreeMarker模板引擎依赖的包
|
<!-- freemarker支持包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId> </dependency> |
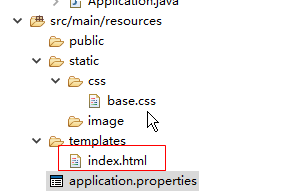
2.Spring Boot的模板引擎的默认路径是resources/templates,所以在resources下创建一个templates文件夹。将视图页面放在里面
|
|
3.这样Spring Boot直接就支持了返回freemarker的ftl视图了。
|
@RequestMapping(value="/index") public String index(Model model,HttpSession session){ System.out.println("-测试插入数据-"); Map<String, Object> entity=new HashMap<String, Object>(); //插入数据 entity.put("sname", "test3"); studentService.insert(entity); //返回index就会跳到index.ftl return "index"; } |
4.根据需要可以在resources的application.properties配置文件,修改freemarker视图的默认属性。
|
|
例如:
1.application.properties配置文件增加以下配置
|
#setting freemarker encoding spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8 |
7.2.2. 注意事项
注意Freemarker的自动配置的属性类为:spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar包的
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerProperties类。
freemarker视图的默认属性配置在里面
如下:
|
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.AbstractTemplateViewResolverProperties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.freemarker") public class FreeMarkerProperties extends AbstractTemplateViewResolverProperties { //默认的视图的存放路径 public static final String DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_LOADER_PATH = "classpath:/templates/"; //默认的前缀 public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = ""; //默认的后缀 public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".ftl"; private Map<String, String> settings = new HashMap<String, String>(); private String[] templateLoaderPath = new String[] { DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_LOADER_PATH }; private boolean preferFileSystemAccess = true; public FreeMarkerProperties() { super(DEFAULT_PREFIX, DEFAULT_SUFFIX); } public Map<String, String> getSettings() { return this.settings; } public void setSettings(Map<String, String> settings) { this.settings = settings; } public String[] getTemplateLoaderPath() { return this.templateLoaderPath; } public boolean isPreferFileSystemAccess() { return this.preferFileSystemAccess; } public void setPreferFileSystemAccess(boolean preferFileSystemAccess) { this.preferFileSystemAccess = preferFileSystemAccess; } public void setTemplateLoaderPath(String... templateLoaderPaths) { this.templateLoaderPath = templateLoaderPaths; } } |
2.查看Spring Boot内置的FreeMarkerProperties类的属性,发现application.properties里面可以设置的属性竟然比FreeMarkerProperties定义的属性多,为什么呢?
答:因为Spring Boot直接引用了FreeMarker框架原来内部定义的属性,只是在前面加一个前缀。
所以导致有一些没有默认值的属性不在FreeMarkerProperties类里面。
7.3. Thymeleaf模板引擎的配置
7.3.1. 配置流程
1.导入Thymeleaf的支持包
|
<!-- thymeleaf支持包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> |
2.Spring Boot的Thymeleaf模板引擎的默认路径是resources/templates,所以在resources下创建一个templates文件夹。将视图页面放在里面
内容为:
|
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <!-- 注意Thymeleaf模板引擎一定要引入xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"命名空间 --> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>hello</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <!-- ${name}用于获得Controller返回的Request的取值范围的值,${}一定要在th:开头的标签里才有效 --> <p th:text="'Hello!, ' + ${name} + '!'" >3333</p> </body> </html> |
3.这样Spring Boot直接就支持了返回Thymeleaf的html视图了。
|
@RequestMapping(value="/index") public String index(Model model){ System.out.println("-测试数据-"); model.addAttribute("name", "张三"); return "index"; } |
4.根据需要可以在resources的application.properties配置文件,增加Thymeleaf视图的默认属性。
|
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5 spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html #开发时关闭缓存,不然没法看到实时页面 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false |
7.3.2. 注意事项
具体的application-thymeleaf.properties配置文件能够配置的属性,根据自身实际的情况,可以查看spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar设置。
Thymeleaf的属性类为:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafProperties
|
|
7.4. JSP视图配置(极不推荐)
Spring Boot在默认自动配置已经不支持JSP视图。如果非要使用JSP视图。需要我们手工配置。
7.4.1. 配置流程
7.4.2. 注意事项
1.因为JSP是JavaWEB技术,依赖Servlet-API。所以如果使用jsp视图发布包格式为war包
2.也是因为JSP是依赖Servlet-API的,所以一定要实现一个SpringBootServletInitializer类的子类作为项目的入口,功能类似于web项目的web.xml
7.5. 默认读取的静态资源路径
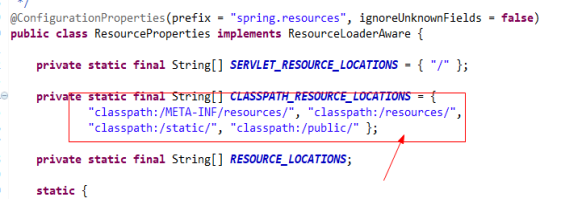
Spring Boot默认读取CSS、JavaScript、html、图片等静态资源的根目录为:
classpath:/META-INF/resources/
classpath:/resources
classpath:/static/
classpath:/public/
也就是说html使用到的CSS、image等静态资源可以放到以上目录文件夹
例如:
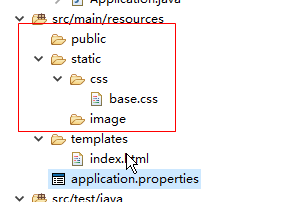
|
|
注意:具体查看org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ResourceProperties类的配置,如果要修改,在appplication.properties修改默认的路径。
|
|
8. SpringBoot整合
8.1. 使用的数据库SQL
框架整合统一使用一下SQL。
|
-- 导出 表 school.student 结构 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `SID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '编号', `SNAME` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `SEX` char(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别', `BIRTHDAY` date DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '生日', `AGE` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄', PRIMARY KEY (`SID`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='学生表'; -- 正在导出表 school.student 的数据:~5 rows (大约) DELETE FROM `student`; /*!40000 ALTER TABLE `student` DISABLE KEYS */; INSERT INTO `student` (`SID`, `SNAME`, `SEX`, `BIRTHDAY`, `AGE`) VALUES (1, '张三', '男', '1990-03-05', 27), (2, '李四', '男', '1993-10-13', 24), (3, '王五', '女', '1998-02-01', 19), (4, '赵六', '男', '2000-04-02', 17), (5, '陈七', '女', '1985-01-16', 32); |
8.2. SpringBoot整合Mybatis
8.2.1. 整合说明
Spring Boot默认没有对mybatis支持,而是Mybatis对springboot进行了支持。所以Spring Boot整合Mybatis的整合包要去Mybatis的的官方寻找。
路径为:https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter
Maven路径在:http://www.mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
8.2.2. 配置流程
1.创建一个Maven项目
|
|
2.在pom.xml导入需要的依赖包
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-demo-01</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <!-- freemarker支持包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- SpringBoot基础包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- dbcp2连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Springboot测试包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> |
3.创建包结果,并且创建三个类
|
|
4.编写Application.Java类的内容
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="cn.itheima") public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
5.编写配置文件application.properties
|
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 #dbcp2 datasource spring.datasource.type=org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource |
6.测试数据源
|
package cn.itheima.test; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class DataSourceTest { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Test public void dataSource() { try { System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
7.测试数据源正确后,编写StudentMapper.Java接口
|
package cn.itheima.mapper; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; //注意,使用的Mapper而不是@Repository @Mapper public interface StudentMapper { @Insert(value="INSERT INTO student (SNAME, SEX, BIRTHDAY, AGE) VALUES (#{sname}, #{sex},#{birthday}, #{age})") public int insert(Map<String,Object> entity); } |
8.编写一个Service类
|
package cn.itheima.service; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import cn.itheima.mapper.StudentMapper; @Service public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentMapper studentMapper; public int insert(Map<String,Object> entity){ return studentMapper.insert(entity); } } |
9.编写一个Controller类
|
package cn.itheima.controller; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import cn.itheima.service.StudentService; @Controller public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @RequestMapping(value="/index") public String index(Model model,HttpSession session){ System.out.println("-测试插入数据-"); Map<String, Object> entity=new HashMap<String, Object>(); //插入数据 entity.put("sname", "test3"); studentService.insert(entity); return "index"; } } |
10.启动程序测试
|
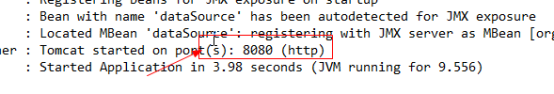
|
启动成功:提示使用8080端口访问。
|
|
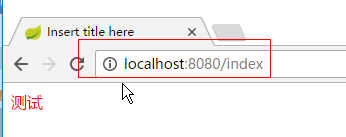
11.在浏览器执行访问
|
|
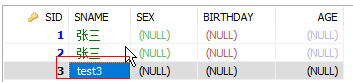
12.查看数据库结果,成功!
|
|
8.3. Spring Boot整合Spring-Data-JPA
8.3.1. 配置步骤
1.创建一个maven项目
|
|
2.复制依赖的包到pom.xml文件
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-demo-05-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 增加springboot 整合data-jpa的包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- dbcp2连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- SpringBoot测试包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> |
3.创建一个入口类,用于启动SpringBoot
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } } |
4.编写application.properties.注意文件名不要写错,配置数据源
|
#配置数据源 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.type=org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource #spring-data-jpa配置 #显示SQL语句 spring.jpa.show-sql=true #表示是否需要根据view的生命周期来决定session是否关闭 spring.jpa.open-in-view=true |
5.编写一个测试类测试数据源是否连接数据库成功
|
package cn.itheima.test; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class DataSourceTest { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Test public void dataSource(){ try { System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
如果出现以下信息表示测试成功
|
|
6.创建一个实体类
|
package cn.itheima.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="student") public class Student implements Serializable{ @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long sid;//BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, private String sname;//VARCHAR(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, private String sex;//VARCHAR(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL, private Integer age;//INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, private Date birthday;//DATETIME(6) NULL DEFAULT NULL, public Long getSid() { return sid; } public void setSid(Long sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } } |
7.创建一个操接口
|
package cn.itheima.repository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import cn.itheima.pojo.Student; @Repository public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> { } |
8.创建一个Service
|
package cn.itheima.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import cn.itheima.pojo.Student; import cn.itheima.repository.StudentRepository; @Service public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @Transactional public void save(Student entity){ studentRepository.save(entity); } } |
9.创建一个Controller
|
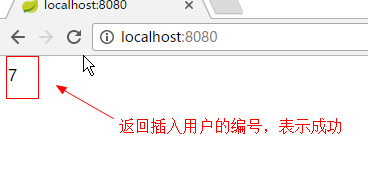
package cn.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import cn.itheima.pojo.Student; import cn.itheima.service.StudentService; @RestController public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @RequestMapping(value="/") public String save(){ Student entity=new Student(); entity.setSname("jpa用户"); studentService.save(entity); return entity.getSid().toString(); } } |
10.启动项目
|
|
启动成功信息,提示使用8080端口访问
|
|
成功信息
|
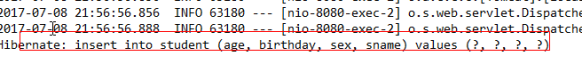
后台输出的语句
|
8.3.2. 注意事项
1.Spring-data-jpa只要Maven导入spring-boot-starter-data-jpa模块已经自动整合了。只要配置好Spring数据源就可以直接使用。如果需要连接池,可以再加一个连接池
|
<!-- 增加springboot 整合data-jpa的包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> |
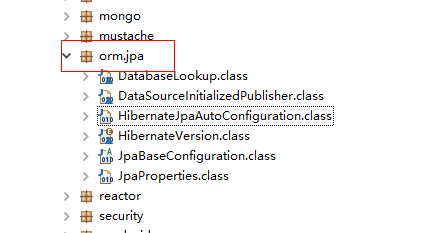
2.查看spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.4.RELEASE.jar可以获得整合的信息。
|
|
(1).可以配置的参数查看org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties类
(2).需要了解整合的代码查看
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration
9. 打包部署
SpringBoot支持使用Jar内嵌Web服务器(Tomcat)的方式发布,也支持生成war包放在外置的web服务器运行。
9.1. 使用jar发布应用
9.1.1. 配置步骤
1.pom.xml要显示加入插件org.springframework.boot,否则无法产生jar清单文件,导致打出来的jar无法使用命令运行。
|
<build> <plugins> <!-- 如果不配置全信息,打出来的包没有清单文件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> |
2.使用里面package打包
|
|
3.打包成功,产生spring-boot-demo-01-1.0.jar文件
|
|
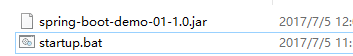
4.将spring-boot-demo-01-1.0.jar复制到一个文件夹下,在同一级目录编写一个bat文件。
|
|
内容格式:#java -jar <jar名>,如下:
|
java -jar spring-boot-demo-01-1.0.jar |
5.双击bat文件startup.bat
|
|
9.1.2. 修改内嵌Tomcat的参数
在application.properties设置相关参数即可,如:
|
#设置Tomcat端口 server.port=80 #设置Tomcat路径编码 server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8 #设置超时时间 server.connection-timeout=1000 |
9.2. 使用war发布应用
9.2.1. 配置流程
1.修改pom.xml文件去掉嵌入式的Tomcat服务器,以及增加serlvet-api依赖包
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- 移除嵌入式tomcat服务器 --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!-- 加入servlet-api的支持 --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> |
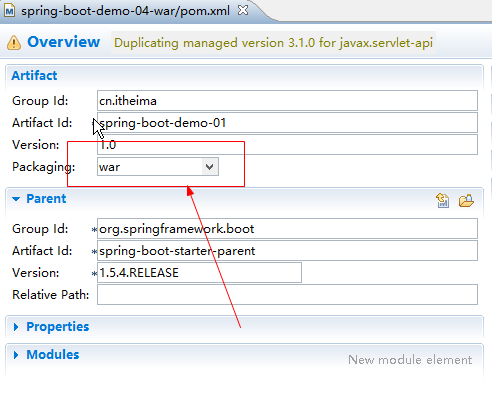
2.修改pom.xml文件的打包方式为war
|
|
3.增加一个web程序的WEB入口类要和Application同一级目录
|
package cn.itheima; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer; /** * 如果项目需要使用war发布,需要创建这个类,作为web程序的入口 * @author ranger * */ public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer { @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) { //表示获得web的请求时,调用Application类的实现 return builder.sources(Application.class); } } |
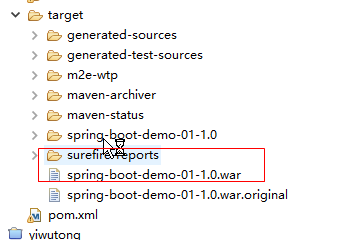
4.打包生成war文件
|
|
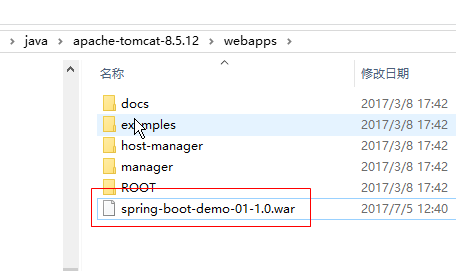
5.复制spring-boot-demo-01-1.0.war放在Tomcat的webapps下
|
|
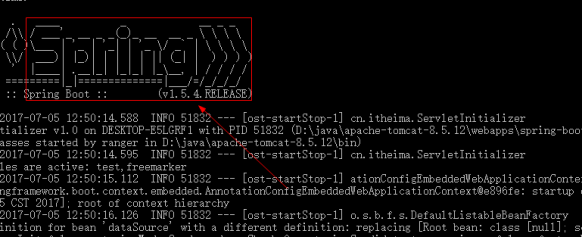
6.启动Tomcat,Tomcat控制台提示SpringBoot信息
|
|
7.浏览器访问,成功
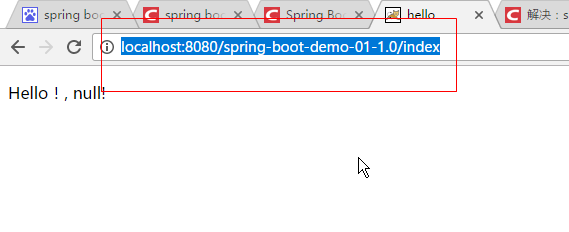
|
http://localhost:8080/spring-boot-demo-01-1.0/index
|
9.2.2. 注意事项
web网站入口类一定要继承SpringBootServletInitializer类,而且必须要给SpringBoot入口类Application同一级目录。
入门到熟练-SpringBoot的更多相关文章
- vue需要知道哪些才能算作入门以及熟练
前两天接到一个面试官问我vue什么程度才算作可以用于开发,以前从没遇到过类似问题.只能大致说了一些,事后觉得也应该总结一下,前端vue这么火热那究竟什么才算做入门什么才算做熟练,只是我个人观点,不代表 ...
- SLAM+语音机器人DIY系列:(二)ROS入门——9.熟练使用rviz
摘要 ROS机器人操作系统在机器人应用领域很流行,依托代码开源和模块间协作等特性,给机器人开发者带来了很大的方便.我们的机器人“miiboo”中的大部分程序也采用ROS进行开发,所以本文就重点对ROS ...
- 5.1 入门整合案例(SpringBoot+Spring-data-elasticsearch) ---- good
本节讲解SpringBoot与Spring-data-elasticsearch整合的入门案例. 一.环境搭建 新建maven项目,名字随意 pom.xml <parent> <gr ...
- git入门到熟练使用
最近以为接触ios开发,所以对git也产生了一点兴趣.所以在网上搜索资料开始学习,但大部分都是没用的copy的文章,有一个还不错的,推荐给大家 http://www.liaoxuefeng.com/w ...
- android入门到熟练(一)
1.andro系统架构:Linux内核层(提供驱动),系统运行库层和android运行时库(提供C/C++库的主要特性,如SQLite,OpenGL,Webkit等和Dalvik虚拟机),应用框架层, ...
- 入门到熟练-Eclipse开发工具
1. 概述 本文用于Eclipse说明开发功能的各种配置.希望可以帮助到对于Eclipse工具设置不同熟练的朋友,快速上手Eclipse开发工具. 2. Eclipse的配置 2.1. 设置Eclip ...
- ELK入门使用-与springboot集成
前言 ELK官方的中文文档写的已经挺好了,为啥还要记录本文?因为我发现,我如果不写下来,过几天就忘记了,而再次捡起来必然还要经历资料查找筛选测试的过程.虽然这个过程很有意义,但并不总是有那么多时间去做 ...
- SpringBoot无废话入门02:SpringBoot启动分析
1.核心注解 在上文中,我们讲到了@SpringBootApplication是SpringBoot的核心注解. 可以很方便的在idea中下载源码来查看该注解的源码,如下: 可以看到,该注解本身又被其 ...
- docker入门篇 部署springboot项目
安装docker Ubuntu16.04安装Docker 使用docker 注册docker服务 systemctl enable docker systemctl status docker 然后在 ...
随机推荐
- POJ(1195)(单点修改,区间查询)(二维)
题目大意 给定一个N*N的网格,刚开始每个网格的值都是0,接下来会对这些网格进行操作,有一下两种操作: 1."X Y A"对网格C[x][y]增加A 2."L B R T ...
- BZOJ-1010-[HNOI2008]玩具装箱toy(斜率优化)
Description P教授要去看奥运,但是他舍不下他的玩具,于是他决定把所有的玩具运到北京.他使用自己的压缩器进行压缩,其可以将任意物品变成一堆,再放到一种特殊的一维容器中.P教授有编号为1... ...
- vue传数据到模态框中
写一下我的做法 <a data-toggle="modal" data-target="#delete_tpl_modal" class="bt ...
- Struts2和SpringMVC的区别
简单谈一下Struts2和SpringMVC的区别,文章有所引用知乎所对应的答案数据,和所查看的其余资料数据,进行一个简单的汇总,后续查看时使用: 知乎解释链接为:https://www.zhihu. ...
- java 连接数据库测试类
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import ...
- cookie存储中文
写cookie Cookie chineseCookie = new Cookie( "chineseCookie ", URLEncoder. ...
- Myeclipse 配置Tomcat 出现 “Value must be an existing directory”错误
今天上午配了一下本机上的Myeclipse的tomcat,因为我本机上有两个版本的myeclipse,一个是用来公司开发的,一个是自己玩的,本机上装了两个版本jdk和两个版本的tomcat.配置自己玩 ...
- 从源码看 angular/material2 中 dialog模块 的实现
本文将探讨material2中popup弹窗即其Dialog模块的实现. 使用方法 引入弹窗模块 自己准备作为模板的弹窗内容组件 在需要使用的组件内注入 MatDialog 服务 调用 open 方法 ...
- Excel导出插件
前言 一个游戏通常需要10多个Excel表格或者更多来配置,一般会通过导出csv格式读取配置. 本文提供导出Excel直接生成c#文件,对应数据直接生成结构体和数组,方便开发排错和简化重复写每个表格的 ...
- 使用MVVM减少控制器代码实战(减少56%)
减少比例= (360(原来的行数)-159(瘦身后的行数))/360 = 56% 父类 MVC 和MVVM 前后基本不动 父类主要完成如下三个功能: 1)功能:MJRefrsh +上拉下拉没有更多数据 ...