算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
写在前面
整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
这一节内容可能会用到的库文件有 Sort 和 SortData,同样在 Github 上可以找到。
善用 Ctrl + F 查找题目。
习题&题解
2.1.1
题目
按照算法 2.1 所示轨迹的格式给出选择排序是如何将数组 E A S Y Q U E S T I O N 排序的。
解答
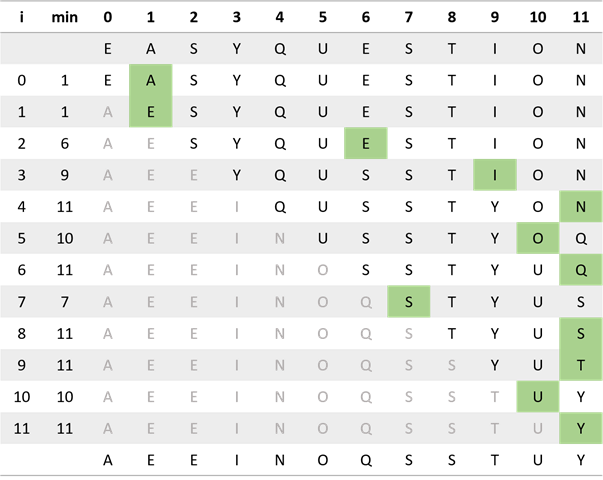
2.1.2
题目
在选择排序中,一个元素最多可能会被交换多少次?平均可能会被交换多少次?
解答
最多会被交换 n 次,只要将一个有序数列循环右移一位就可以构造这样的情况。
例如:
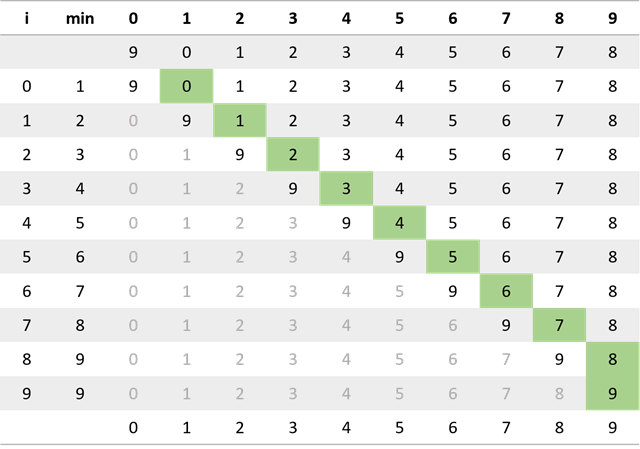
平均每个元素被交换了 N/N=1 次。(总共 N 个元素,总共发生了 N 次交换)
2.1.3
题目
构造一个含有 N 个元素的数组,使选择排序(算法 2.1)运行过程中 a[j] < a[min] (由此 min 会不断更新)成功的次数最大。
解答
你需要一个逆序的数组。
例如:9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
i=0 条件满足 8 次,1 和 9 交换,1 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 9。
i=1 条件满足 6 次,2 和 8 交换,1 2 7 6 5 4 3 8 9。
i=2 条件满足 4 次,3 和 7 交换,1 2 3 6 5 4 7 8 9。
i=3 条件满足 2 次,4 和 6 交换。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9。
一共满足了 8+6+4+2=20 次
2.1.4
题目
按照算法 2.2 所示轨迹的格式给出插入排序是如何将数组 E A S Y Q U E S T I O N 排序的。
解答
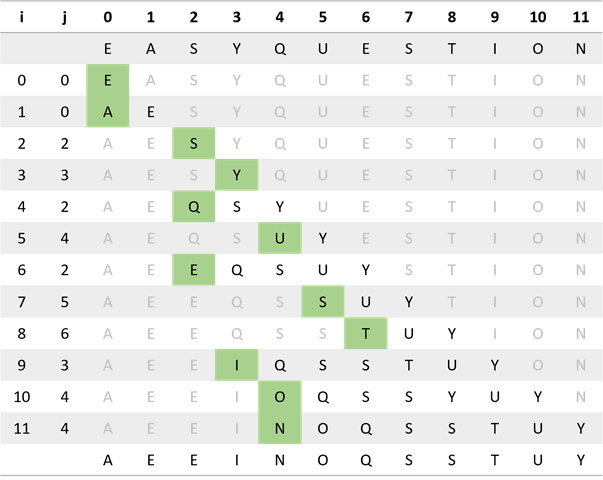
2.1.5
题目
构造一个含有 N 个元素的数组,使插入排序(算法 2.2)运行过程中内循环(for)的两个判断结果总是假。
解答
条件是:
j > 0 && less(a[j], a[j - 1])
第一个条件属于循环计数用的条件,与数组元素无关;
第二个条件当 a[j] 和 a[j - 1] 是一组逆序对时满足,因此这个条件总是为假 = 数组没有逆序对 = 数组有序。
因此只要输入已经排好序的数组即可。
逆序对:指序列中顺序相反的两个数,例如 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 8 9 中的 7 6。
2.1.6
题目
在所有主键都相同时,选择排序和插入排序谁更快?
解答
插入排序更快。
选择排序无论如何都需要 n + (n-1) + (n-2) + … + 1 = n^2/2 次比较。
插入排序在这种情况下只需要 n 次比较。(所有主键相同 = 数组已排序)
2.1.7
题目
对于逆序数组,选择排序和插入排序谁更快?
解答
假设比较的开销小于等于交换的开销,此时选择排序更快,具体比较见下表。
| 比较次数 | 交换次数 | |
| 插入排序 | ~N^2/2 | ~N^2/2 |
| 选择排序 | ~N^2/2 | N |
2.1.8
题目
假设元素只可能有三种值,使用插入排序处理这样一个随机数组的运行时间是线性的还是平方级别的?或是介于两者之间?
解答
平方级别。
如果数组中元素各不相同,那么这个结论很容易证明(一般的插入排序)。
接下来我们证明有重复元素的情况下,这个结论仍然成立:
首先对于插入排序过程中的某一时刻,我们有下图这样的一般情况:
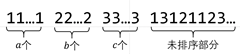
其中,1,2,3 分别代表三种不同的取值以及其先后顺序。
假设这是第 i 次插入前,如果第 i 次插入的是 1,我们需要交换 b+c 次,插入 2 则需要交换 c 次,插入 3 则不需要交换。
根据题意,这是一个随机数组,我们假设其为均匀分布,那么三种取值的出现几率相等。
第 i 次插入所需要的平均交换次数即为:
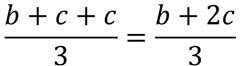
第 i 次插入后,b + 2c 视插入的元素不同会出现不同的变化:
如果插入的是 1,那么 b+2c 的值不会变化。
如果插入的是 2,那么 b+2c 的值增加 1。
如果插入的是 3,那么 b+2c 的值增加 2。
同样由于三种取值的概率相等,我们得出第 i + 1 次插入平均需要交换的次数为:
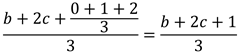
也就是说,平均每次插入都会使下一次插入的交换次数增加 1/3。
令 i=0,此时交换次数为 0,i+1 的交换次数即为 1/3,i+2 的交换次数即为 2/3,以此类推。
我们可以得出总交换次数:
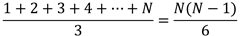
由此证明,在元素取值为 3 种且出现概率相等时,插入排序的交换开销时平方级别的。
比较开销和交换开销类似,一般情况下比较次数=交换次数+1,除非插入的数是已知最小的数(移动到最左侧),这个时候比较次数和交换次数相等。
因此比较次数=交换次数+N-e,e 是一个不大于 N 的数,代表插入的数是已知最小的数这种情况发生的次数。
根据上式可以得出结论:在元素取值为 3 种且出现概率相等时,插入排序的比较开销也是平方级别的。
综合两个结论即可证明插入排序的开销在题目描述的情况下是平方级别的。
证明完毕。
2.1.9
题目
按照算法 2.3 所示轨迹的格式给出希尔排序是如何将数组 E A S Y S H E L L S O R T Q U E S T I O N 排序的。
解答

2.1.10
题目
在希尔排序中为什么在实现 h 有序时不使用选择排序?
解答
对于部分有序的数组,插入排序比选择排序快。
这个结论可以在中文版 P158, 英文版 P252 找到。
2.1.11
题目
将希尔排序中实时计算递增序列改为预先计算并存储在一个数组中。
解答
希尔排序的官方实现:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/21elementary/Shell.java.html
只要稍作修改即可,详情见代码。
代码

/// <summary>
/// 利用希尔排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public override void Sort<T>(T[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int[] h = new int[2]; // 预先准备好的 h 值数组
int hTemp = 1;
int sequenceSize = 0;
for (sequenceSize = 0; hTemp < n; sequenceSize++)
{
if (sequenceSize >= h.Length) // 如果数组不够大则双倍扩容
{
int[] expand = new int[h.Length * 2];
for (int j = 0; j < h.Length; j++)
{
expand[j] = h[j];
}
h = expand;
}
h[sequenceSize] = hTemp;
hTemp = hTemp * 3 + 1;
}
for (int t = sequenceSize - 1; t >= 0; t--)
{
for (int i = h[t]; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= h[t] && Less(a[j], a[j - h[t]]); j -= h[t])
{
Exch(a, j, j - h[t]);
}
}
Debug.Assert(IsHSorted(a, h[t]));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}

2.1.12
题目
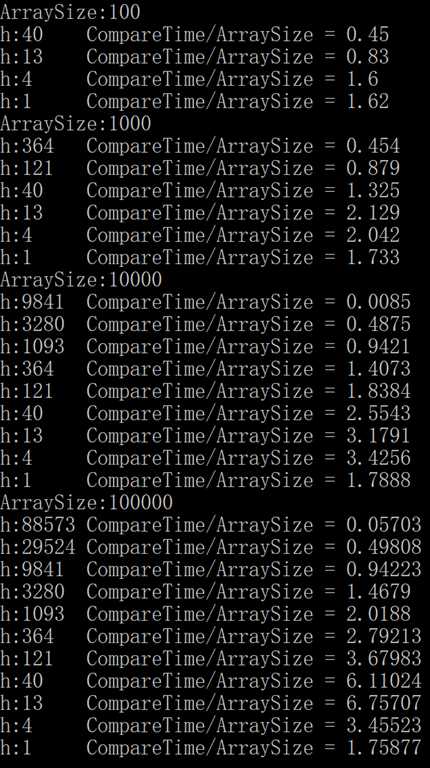
令希尔排序打印出递增序列的每个元素所带来的比较次数和数组大小的比值。
编写一个测试用例对随机 Double 数组进行希尔排序,验证该值是一个小常数,数组大小按照 10 的幂次递增,不小于 100。
解答
结果截图如下,同一个 h 值对应的比值在数组大小不同时保持为一个小常数:
代码

class Program
{
// 查看最后结果
// 可以发现相同的 h 在数组大小不同时所产生的比值十分接近。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Random random = new Random();
ShellSort sort = new ShellSort();
int size = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
double[] a = new double[size];
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
a[j] = random.NextDouble() * 100;
}
Console.WriteLine("ArraySize:" + size);
sort.Sort(a);
size *= 10;
}
}
}

2.1.13
题目
纸牌排序。
说说你会如何将一副扑克牌按花色排序(花色排序是黑桃、红桃、梅花和方片),
限制条件是所有牌都是背面朝上排成一列,而你一次只能翻看两张牌或者交换两张牌(保持背面朝上)。
解答
可以用冒泡排序做,具体方法如下:
翻一二两张,是逆序对就交换,否则什么也不做
翻二三两张,是逆序对就交换,否则什么也不做
一直到最后,可以保证最右侧的是最大花色的牌
然后不断重复上述过程,就可以完全排序
2.1.14
题目
出列顺序。
说说你会如何将一副扑克牌排序,
限制条件是只能查看最上面的两张牌,交换最上面的两张牌,或是将最上面的一张牌放到这摞牌的最下面。
解答
用一种类似于冒泡的方法做,具体步骤为:
重复以下步骤,直到全部完成一遍之后没有发生交换
重复以下步骤 n-1 次
如果顶端两张牌逆序,那么交换它们。
将第一张牌放到牌堆底部。
具体步骤图:

我们将牌排成一个环,用一支笔隔开,这里我们标记笔的左侧是牌堆顶部,右侧是牌堆底部。
那么我们能做的三个操作在这里即为:
查看最上面两张牌 = 从笔的位置开始,逆时针查看两张牌。
交换最上面两张牌 = 从笔的位置开始,逆时针选择两张牌并交换。
将最上面的一张牌放到最下面 = 将笔的位置逆时针移动一位。
下面我们开始执行开始说过的操作,目标顺序是自顶向下从小到大排列。
初始情况如图所示:

梅花7 和 红桃4 不是逆序对,直接将笔逆时针移动一位。

红桃4 和 黑桃6 不是逆序对,我们将笔逆时针移动一位。

再看 黑桃6 和 方片A,是逆序对,我们交换并将笔逆时针移动一位。

再看 黑桃6 和 红桃J,是逆序对,我们交换并将笔逆时针移动一位。

现在我们已经操作了 4 次,内部循环结束,我们将笔放回初始位置。

这样一次循环之后,我们就把最大的牌放在了最下面,依次类推即可完全排序。
2.1.15
题目
昂贵的交换。
一家货运公司的一位职工得到了一项任务,需要将若干大货箱按照发货时间摆放。
比较发货时间很容易(对照标签即可),但将两个货箱交换位置则很困难(移动麻烦)。
仓库已经快满了,只有一个空闲的仓位。这位职员应该使用哪种排序算法呢?
解答
选择排序
交换(也就是 Exch() 方法)需要一个额外空间,这里的条件满足。
现在我们应该使交换次数最少,选择排序只需要 N 次交换,比插入排序平均 N^2/4 少(N > 2)。
2.1.16
题目
验证。
编写一个 check() 方法,调用 sort() 对任意数组排序。
如果排序成功而且数组中的所有对象均没有被修改则返回 true,否则返回 false。
不要假设 sort() 只能通过 exch() 来移动数据,可以信任并使用 Array.sort()。
解答
如果移动数据时新建了对象,那么虽然值没有改变,但是数组中的对象被修改了。
代码
插入排序中的 Exch() 换成了如下方式:
string temp = new string(s[i].ToCharArray()); s[i] = s[min]; s[min] = temp;
全部程序代码如下:

using System;
namespace _2._1._16
{
/*
* 2.1.16
*
* 验证。
* 编写一个 check() 方法,
* 调用 sort() 对任意数组排序。
* 如果排序成功而且数组中的所有对象均没有被修改则返回 true,
* 否则返回 false。
* 不要假设 sort() 只能通过 exch() 来移动数据,
* 可以信任并使用 Array.sort()。
*
*/
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] test = new string[5] { "a", "b", "d", "c", "e" };
Console.WriteLine(CheckArraySort(test));
Console.WriteLine(CheckSelectionSort(test));
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试 Array.Sort() 方法。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">用于测试的数组。</param>
/// <returns>如果数组对象没有改变,返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
static bool CheckArraySort(string[] a)
{
string[] backup = new string[a.Length];
a.CopyTo(backup, 0);
Array.Sort(a);
foreach (string n in a)
{
bool isFind = false;
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (ReferenceEquals(n, backup[i]))
{
isFind = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isFind)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试选择排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">用于测试的数组。</param>
/// <returns>如果数组对象没有改变,返回 true,否则返回 false。</returns>
static bool CheckSelectionSort(string[] a)
{
string[] backup = new string[a.Length];
a.CopyTo(backup, 0);
SelectionSort(a);
foreach (string n in a)
{
bool isFind = false;
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (ReferenceEquals(n, backup[i]))
{
isFind = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isFind)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// 选择排序,其中的交换部分使用新建对象并复制的方法。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="s">用于排序的数组。</param>
public static void SelectionSort(string[] s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++)
{
int min = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < s.Length; j++)
{
if (s[j].CompareTo(s[min]) < 0)
{
min = j;
}
}
string temp = new string(s[i].ToCharArray());
s[i] = s[min];
s[min] = temp;
}
}
}
}

2.1.17
题目
动画。
修改插入排序和选择排序的代码,使之将数组内容绘制成正文中所示的棒状图。
在每一轮排序后重绘图片来产生动画效果,并以一张“有序”的图片作为结束,即所有的圆棒均已按照高度有序排列。
提示:使用类似于正文中的用例来随机生成 Double 值,在排序代码的适当位置调用 show() 方法,并在 show() 方法中清理画布并绘制棒状图。
解答
选择排序:
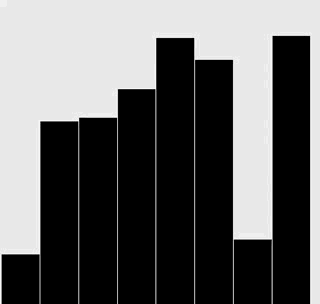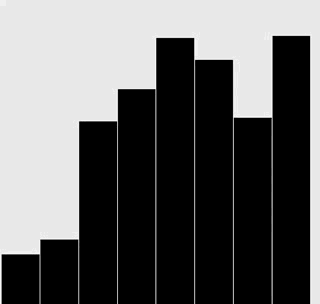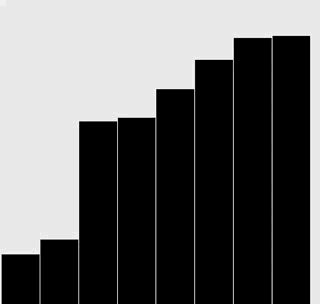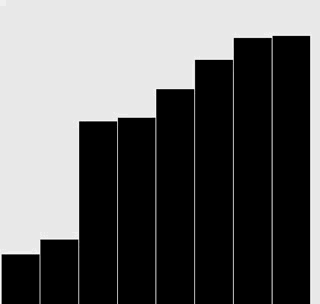
插入排序:
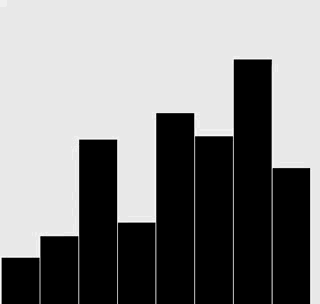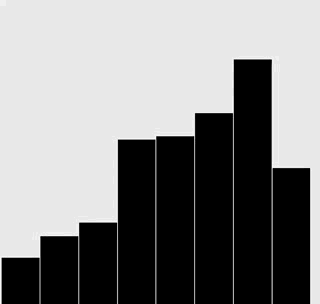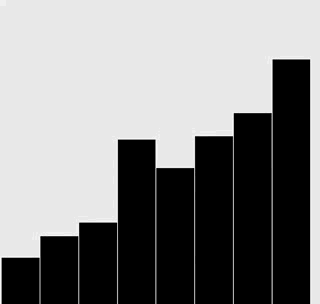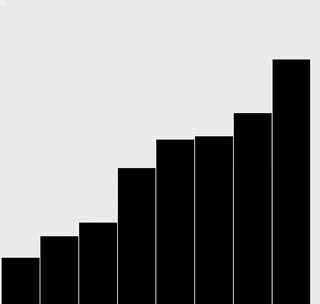
代码
使用一个 timer 按一定时间重绘数组,排序算法里面一次循环后等待一段时间再进行下一次循环。
这里排序算法是另开线程运行的,防止 Sleep 的时候让程序无响应。
选择排序:

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace _2._1._17
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
double[] randomDoubles;
public Form2(int N)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.randomDoubles = new double[N];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
this.randomDoubles[i] = random.NextDouble() * 0.8 + 0.2;
}
drawPanel();
this.timer1.Interval = 60;
this.timer1.Start();
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.SelectionSort));
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 选择排序。
/// </summary>
private void SelectionSort()
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
int min = i;
for (int j = i; j < this.randomDoubles.Length; j++)
{
if (this.randomDoubles[min] > this.randomDoubles[j])
{
min = j;
}
}
double temp = this.randomDoubles[i];
this.randomDoubles[i] = this.randomDoubles[min];
this.randomDoubles[min] = temp;
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 在屏幕上用柱形图绘制数组。
/// </summary>
private void drawPanel()
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.Clear(this.BackColor);
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
Rectangle clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle drawRect = new Rectangle(clientRect.X + 10, clientRect.Y + 10, clientRect.Width - 10, clientRect.Height - 10);
PointF[] barX = new PointF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
float unitX = (float)drawRect.Width / this.randomDoubles.Length;
unitX -= 4;
barX[0] = new PointF(4, drawRect.Top);
for (int i = 1; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
barX[i] = new PointF(2 + unitX + barX[i - 1].X, drawRect.Top);
}
RectangleF[] bars = new RectangleF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
SizeF size = new SizeF(unitX, (float)this.randomDoubles[i] * drawRect.Height);
bars[i] = new RectangleF(barX[i], size);
}
graphics.FillRectangles(Brushes.Black, bars);
graphics.Dispose();
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
drawPanel();
}
}
}

插入排序:

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace _2._1._17
{
public partial class Form3 : Form
{
double[] randomDoubles;
public Form3(int N)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.randomDoubles = new double[N];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
this.randomDoubles[i] = random.NextDouble() * 0.8 + 0.2;
}
drawPanel();
this.timer1.Interval = 60;
this.timer1.Start();
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.InsertionSort));
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入排序。
/// </summary>
private void InsertionSort()
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j > 0 && this.randomDoubles[j] < this.randomDoubles[j - 1]; j--)
{
double temp = this.randomDoubles[j];
this.randomDoubles[j] = this.randomDoubles[j - 1];
this.randomDoubles[j - 1] = temp;
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 在屏幕上用柱形图绘制数组。
/// </summary>
private void drawPanel()
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.Clear(this.BackColor);
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
Rectangle clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle drawRect = new Rectangle(clientRect.X + 10, clientRect.Y + 10, clientRect.Width - 10, clientRect.Height - 10);
PointF[] barX = new PointF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
float unitX = (float)drawRect.Width / this.randomDoubles.Length;
unitX -= 4;
barX[0] = new PointF(4, drawRect.Top);
for (int i = 1; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
barX[i] = new PointF(2 + unitX + barX[i - 1].X, drawRect.Top);
}
RectangleF[] bars = new RectangleF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
SizeF size = new SizeF(unitX, (float)this.randomDoubles[i] * drawRect.Height);
bars[i] = new RectangleF(barX[i], size);
}
graphics.FillRectangles(Brushes.Black, bars);
graphics.Dispose();
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
drawPanel();
}
}
}

2.1.18
题目
可视轨迹。
修改你为上一题给出的解答,为插入排序和选择排序生成和正文中类似的可视轨迹。
提示:使用 setYscale() 函数是一个明智的选择。
附加题:添加必要的代码,与正文中的图片一样用红色和灰色强调不同角色的元素。
解答
选择排序
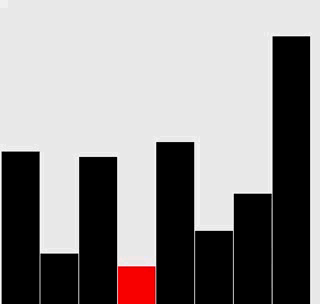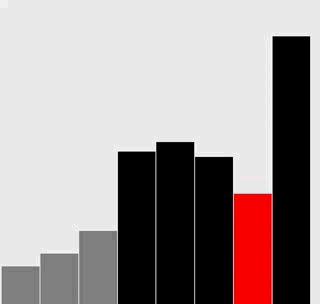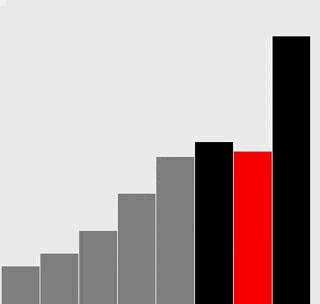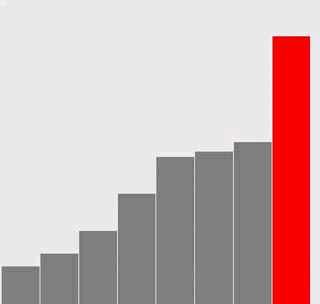
插入排序
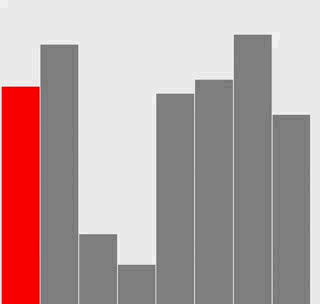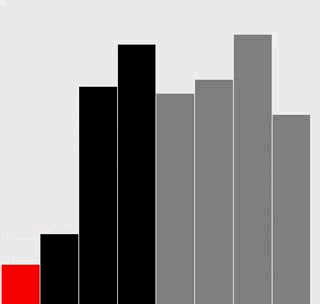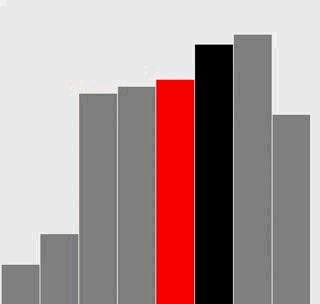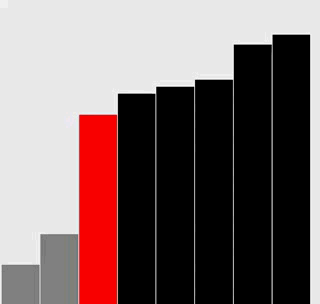
代码
与上题类似,但要特别标出移动的元素。
选择排序:

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace _2._1._18
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
double[] randomDoubles;
int sortI;
int sortJ;
int sortMin;
public Form2(int N)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.randomDoubles = new double[N];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
this.randomDoubles[i] = random.NextDouble() * 0.8 + 0.2;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 选择排序。
/// </summary>
private void SelectionSort()
{
for (this.sortI = 0; this.sortI < this.randomDoubles.Length; this.sortI++)
{
this.sortMin = this.sortI;
for (this.sortJ = this.sortI; this.sortJ < this.randomDoubles.Length; this.sortJ++)
{
if (this.randomDoubles[this.sortMin] > this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ])
{
this.sortMin = this.sortJ;
}
}
drawPanel();
double temp = this.randomDoubles[this.sortI];
this.randomDoubles[this.sortI] = this.randomDoubles[this.sortMin];
this.randomDoubles[this.sortMin] = temp;
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 绘制柱形图。
/// </summary>
private void drawPanel()
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.Clear(this.BackColor);
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
Rectangle clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle drawRect = new Rectangle(clientRect.X + 10, clientRect.Y + 10, clientRect.Width - 10, clientRect.Height - 10);
PointF[] barX = new PointF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
float unitX = (float)drawRect.Width / this.randomDoubles.Length;
unitX -= 4;
barX[0] = new PointF(4, drawRect.Top);
for (int i = 1; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
barX[i] = new PointF(2 + unitX + barX[i - 1].X, drawRect.Top);
}
RectangleF[] bars = new RectangleF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
SizeF size = new SizeF(unitX, (float)this.randomDoubles[i] * drawRect.Height);
bars[i] = new RectangleF(barX[i], size);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bars.Length; i++)
{
if (i == this.sortMin)
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Red, bars[i]);
}
else if (i < this.sortI)
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Gray, bars[i]);
}
else
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Black, bars[i]);
}
}
graphics.Dispose();
}
private void Form2_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SelectionSort();
}
}
}

插入排序

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace _2._1._18
{
public partial class Form3 : Form
{
double[] randomDoubles;
int sortI;
int sortJ;
int n = 0;
public Form3(int N)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.randomDoubles = new double[N];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
this.randomDoubles[i] = random.NextDouble() * 0.8 + 0.2;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入排序。
/// </summary>
private void InsertionSort()
{
for (this.sortI = 0; this.sortI < this.randomDoubles.Length; this.sortI++)
{
for (this.sortJ = this.sortI; this.sortJ > 0 && this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ] < this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ - 1]; this.sortJ--)
{
double temp = this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ];
this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ] = this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ - 1];
this.randomDoubles[this.sortJ - 1] = temp;
}
drawPanel();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 绘制柱形图。
/// </summary>
private void drawPanel()
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.Clear(this.BackColor);
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
Rectangle clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle drawRect = new Rectangle(clientRect.X + 10, clientRect.Y + 10, clientRect.Width - 10, clientRect.Height - 10);
PointF[] barX = new PointF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
float unitX = (float)drawRect.Width / this.randomDoubles.Length;
unitX -= 4;
barX[0] = new PointF(4, drawRect.Top);
for (int i = 1; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
barX[i] = new PointF(2 + unitX + barX[i - 1].X, drawRect.Top);
}
RectangleF[] bars = new RectangleF[this.randomDoubles.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.randomDoubles.Length; i++)
{
SizeF size = new SizeF(unitX, (float)this.randomDoubles[i] * drawRect.Height);
bars[i] = new RectangleF(barX[i], size);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bars.Length; i++)
{
if (i == this.sortJ)
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Red, bars[i]);
}
else if (i <= this.sortI && i > this.sortJ)
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Black, bars[i]);
}
else
{
graphics.FillRectangle(Brushes.Gray, bars[i]);
}
}
graphics.Dispose();
}
private void Form3_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InsertionSort();
}
}
}

2.1.19
题目
希尔排序的最坏情况。
用 1 到 100 构造一个含有 100 个元素的数组并用希尔排序和递增序列 1 4 13 40 对其排序,使比较次数尽可能多。
解答
不得不说这道题意外的难。
放上论文链接:Shellsort and Sorting Networks (Outstanding Dissertations in the Computer Sciences)
这篇论文的第二章给出了一种构造最坏序列的方法,当然理想最坏(n^(3/2))是达不到的了。
最后结果是 793 次。
代码
构造最坏情况的类

namespace _2._1._19
{
class ShellSortWorstCase
{
/// <summary>
/// 获得最坏情况的数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组大小。</param>
/// <returns>希尔排序最坏情况的数组。</returns>
public static int[] GetWorst(int n)
{
int l = 0;
int?[] a = new int?[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
a[i] = null;
}
int P = 40;
int PAddition = P;
for (int i = 0; l < 100; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[j] == null && IsVisible(j, P))
{
l++;
a[j] = l;
}
}
P += PAddition;
}
int[] b = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
b[i] = (int)a[i + 1];
}
return b;
}
/// <summary>
/// 确认 j - i 是不是在排序样板(Sorting Template)上。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="i"></param>
/// <param name="j"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool IsVisible(int i, int j)
{
int k = 0;
while (k <= 100)
{
if (j - i >= k * 40 && j - i <= k * 41)
return true;
k++;
}
return false;
}
}
}

会显示比较次数的 ShellSort 类

using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._19
{
public class ShellSort : BaseSort
{
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数。
/// </summary>
public ShellSort() { }
/// <summary>
/// 利用希尔排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public override void Sort<T>(T[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int compareTime = 0;
int h = 1;
while (h < n / 3)
{
h = 3 * h + 1;
}
while (h >= 1)
{
for (int i = h; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= h && Less(a[j], a[j - h]); j -= h)
{
Exch(a, j, j - h);
compareTime++;
}
compareTime++;
}
Debug.Assert(IsHSorted(a, h));
h /= 3;
}
Console.WriteLine("CompareTime:" + compareTime);
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查一次希尔排序后的子数组是否有序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">排序后的数组。</param>
/// <param name="h">子数组间隔。</param>
/// <returns>是否有序。</returns>
private bool IsHSorted<T>(T[] a, int h) where T : IComparable<T>
{
for (int i = h; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - h]))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}

Main 方法

using System;
namespace _2._1._19
{
/*
* 2.1.19
*
* 希尔排序的最坏情况。
* 用 1 到 100 构造一个含有 100 个元素的数组并用希尔排序和
* 递增序列 1 4 13 40 对其排序,
* 使比较次数尽可能多。
*
*/
class Program
{
// 开放题,没有标准答案
// 共参考的最差情况为 n^(3/2)
// 本例共 793 次
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] b;
ShellSort sort = new ShellSort();
b = ShellSortWorstCase.GetWorst(100);
for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(b[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
sort.Sort(b);
}
}
}

2.1.20
题目
希尔排序的最好情况。最好情况是什么?证明你的结论。
解答
由于每次 h 排序都是插入排序,希尔排序最好情况就是插入排序的最好情况,也就是已排序的数组。
2.1.21
题目
可比较的交易。
用我们的 Date 类(请见 2.1.1.4 节)作为模板扩展你的 Transaction 类(请见练习 1.2.13),
实现 Comparable 接口,使交易能够按照金额排序。
解答
事实上官方给出来的 Date 类以及 Transaction 类都已经实现了这些接口。
Date 类:Date.java
Transaction 类:Transaction.java
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._21
{
/*
* 2.1.21
*
* 可比较的交易。
* 用我们的 Date 类(请见 2.1.1.4 节)
* 作为模板扩展你的 Transaction 类(请见练习 1.2.13),
* 实现 Comparable 接口,使交易能够按照金额排序。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Transaction[] a = new Transaction[4];
a[0] = new Transaction("Turing 6/17/1990 644.08");
a[1] = new Transaction("Tarjan 3/26/2002 4121.85");
a[2] = new Transaction("Knuth 6/14/1999 288.34");
a[3] = new Transaction("Dijkstra 8/22/2007 2678.40");
Console.WriteLine("Unsorted");
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Sort by amount");
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
insertionSort.Sort(a, new Transaction.HowMuchOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}

2.1.22
题目
交易排序测试用例。
编写一个 SortTransaction 类,在静态方法 main() 中从标准输入读取一系列交易,将它们排序并在标准输出中打印结果。
解答
和上题类似,只要传入事先写好的比较器就可以了。
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._22
{
/*
* 2.1.22
*
* 交易排序测试用例。
* 编写一个 SortTransaction 类,
* 在静态方法 main() 中从标准输入读取一系列交易,
* 将它们排序并在标准输出中打印结果。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Transaction[] a = new Transaction[4];
// 样例输入
// Turing 6/17/1990 644.08
// Tarjan 3/26/2002 4121.85
// Knuth 6/14/1999 288.34
// Dijkstra 8/22/2007 2678.40
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
string input = Console.ReadLine();
a[i] = new Transaction(input);
}
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
Console.WriteLine("Unsorted");
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Sort by date");
insertionSort.Sort(a, new Transaction.WhenOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Sort by customer");
insertionSort.Sort(a, new Transaction.WhoOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Sort by amount");
insertionSort.Sort(a, new Transaction.HowMuchOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}

2.1.23
题目
纸牌排序。
请几位朋友分别将一副扑克牌排序(见练习2.1.13)。
仔细观察并记录他们所使用的方法。
解答
方法多种多样。
首先是冒泡,见习题 2.1.13
插入排序也可以,如下:
从前往后不断翻牌,
对于翻到的每张牌,一直和之前的牌交换,
直至前面的牌比它小或者它已经是第一张了。
也可以用基数排序
从前向后依次翻开牌,
按照花色分成四堆,
然后按花色从大到小重新排列。
比较符合直觉的是选择排序
寻找最小的牌并放到第一位,
寻找范围向右缩减一位,重复上一步,直到最后一张。
还有其他方法,这里不再赘述。
2.1.24
题目
插入排序的哨兵。
在插入排序的实现中先找出最小的元素并将其置于数组的最左边,这样就能去掉内循环的判断条件 j>0。
使用 SortCompare 来评估这种做法的效果。
注意:这是一种常见的规避边界测试的方法,能够省略判断条件的元素通常称为哨兵。
解答
如果使用官方的实现(InsertionX.java),最后结果可能会比一般插入排序慢,因为它是用冒泡的方法找最小值的。
一般做法是在待排序数组的最前端插入一个很小的值(比如 int.MinValue),然后对 a[1]~a[n] 排序。
代码
参考官方实现的插入排序:

using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._24
{
/// <summary>
/// 插入排序类。
/// </summary>
public class InsertionSort : BaseSort
{
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数。
/// </summary>
public InsertionSort() { }
/// <summary>
/// 利用插入排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public override void Sort<T>(T[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int exchanges = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
{
Exch(a, i, i - 1);
exchanges++;
}
}
if (exchanges == 0)
return;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; Less(a[j], a[j - 1]); --j)
{
Exch(a, j, j - 1);
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, 0, i));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}
/// <summary>
/// 利用插入排序将数组排序。(使用指定比较器)
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">数组元素类型。</typeparam>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
/// <param name="c">比较器。</param>
public void Sort<T>(T[] a, IComparer<T> c)
{
int n = a.Length;
int exchanges = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - 1], c))
{
Exch(a, i, i - 1);
exchanges++;
}
}
if (exchanges == 0)
return;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; Less(a[j], a[j - 1], c); --j)
{
Exch(a, j, j - 1);
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, 0, i, c));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, c));
}
}
}

2.1.25
题目
不需要交换的插入排序。
在插入排序的实现中使较大元素右移一位只需要访问一次数组(而不用使用 exch())。
使用 SortCompare 来评估这种做法的效果。
解答
使用依次赋值的方式腾出空间,到达指定位置之后再把元素插入。
看代码会方便理解一点。
官方实现:InsertionX.java。
代码

using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._25
{
/// <summary>
/// 插入排序类。
/// </summary>
public class InsertionSort : BaseSort
{
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数。
/// </summary>
public InsertionSort() { }
/// <summary>
/// 利用插入排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public override void Sort<T>(T[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int exchanges = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0 ; i--)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
{
Exch(a, i, i - 1);
exchanges++;
}
}
if (exchanges == 0)
return;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
int j = i;
T v = a[i];
while (Less(v, a[j - 1]))
{
a[j] = a[j - 1];
j--;
}
a[j] = v;
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, 0, i));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}
/// <summary>
/// 利用插入排序将数组排序。(使用指定比较器)
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">数组元素类型。</typeparam>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
/// <param name="c">比较器。</param>
public void Sort<T>(T[] a, IComparer<T> c)
{
int n = a.Length;
int exchanges = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - 1], c))
{
Exch(a, i, i - 1);
exchanges++;
}
}
if (exchanges == 0)
return;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
int j = i;
T v = a[i];
while (Less(v, a[j - 1], c))
{
a[j] = a[j - 1];
j--;
}
a[j] = v;
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, 0, i, c));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a, c));
}
}
}

2.1.26
题目
原始数据类型。
编写一个能够处理 int 值的插入排序的新版本,
比较它和正文中所给出的实现(能够隐式地用自动装箱和拆箱转换 Integer 值并排序)的性能。
解答
直接针对特殊值的话显然会快很多。

代码
直接把泛型改成 int 即可。

namespace _2._1._26
{
/// <summary>
/// 插入排序类。
/// </summary>
public class InsertionSort
{
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数。
/// </summary>
public InsertionSort() { }
/// <summary>
/// 利用插入排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public void Sort(int[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j > 0 && a[j] < a[j - 1]; --j)
{
int t = a[j];
a[j] = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = t;
}
}
}
}
}

2.1.27
题目
希尔排序的用时是次平方级的。
在你的计算机上用 SortCompare 比较希尔排序和插入排序以及选择排序。
测试数组的大小按照 2 的幂次递增,从 128 开始。
解答
数据比较大的时候会比较明显。
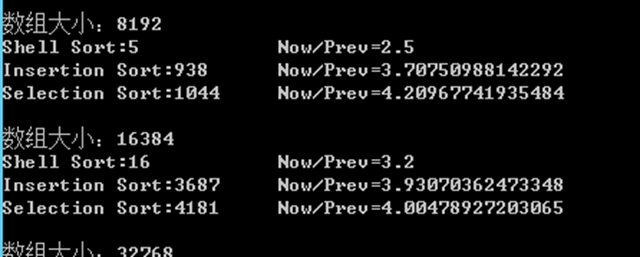
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._27
{
/*
* 2.1.27
*
* 希尔排序的用时是次平方级的。
* 在你的计算机上用 SortCompare 比较希尔排序和插入排序以及选择排序。
* 测试数组的大小按照 2 的幂次递增,从 128 开始。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 128;
Random random = new Random();
double shellPrev = 1;
double insertionPrev = 1;
double selectionPrev = 1;
while (n < 65538)
{
int[] testShell = new int[n];
int[] testInsertion = new int[n];
int[] testSelection = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
testShell[i] = random.Next();
testInsertion[i] = testShell[i];
testSelection[i] = testShell[i];
}
Console.WriteLine("数组大小:" + n);
Console.Write("Shell Sort:");
double shellNow = SortCompare.Time(new ShellSort(), testShell);
Console.WriteLine(shellNow + "\t\tNow/Prev=" + shellNow / shellPrev);
Console.Write("Insertion Sort:");
double insertionNow = SortCompare.Time(new InsertionSort(), testInsertion);
Console.WriteLine(insertionNow + "\tNow/Prev=" + insertionNow / insertionPrev);
Console.Write("Selection Sort:");
double selectionNow = SortCompare.Time(new SelectionSort(), testSelection);
Console.WriteLine(selectionNow + "\tNow/Prev=" + selectionNow / selectionPrev);
Console.WriteLine();
shellPrev = shellNow;
insertionPrev = insertionNow;
selectionPrev = selectionNow;
n *= 2;
}
}
}
}

2.1.28
题目
相等的主键。
对于主键仅可能取两种值的数组,评估和验证插入排序和选择排序的性能,假设两种主键值出现的概率相同。
解答
插入排序会比选择排序快上许多,当然增长级别不变。
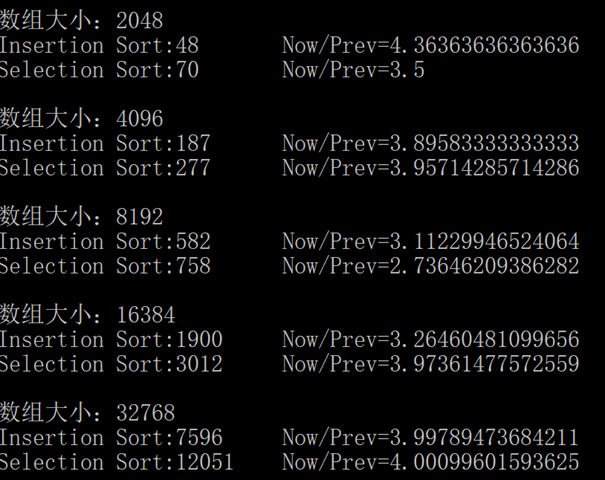
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._28
{
/*
* 2.1.28
*
* 相等的主键。
* 对于主键仅可能取两种值的数组,
* 评估和验证插入排序和选择排序的性能,
* 假设两种主键值出现的概率相同。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 1024;
Random random = new Random();
double insertionPrev = 1;
double selectionPrev = 1;
while (n < 65538)
{
int[] testInsertion = new int[n];
int[] testSelection = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
testInsertion[i] = random.Next(2);
testSelection[i] = testInsertion[i];
}
Console.WriteLine("数组大小:" + n);
Console.Write("Insertion Sort:");
double insertionNow = SortCompare.Time(new InsertionSort(), testInsertion);
Console.WriteLine(insertionNow + "\tNow/Prev=" + insertionNow / insertionPrev);
Console.Write("Selection Sort:");
double selectionNow = SortCompare.Time(new SelectionSort(), testSelection);
Console.WriteLine(selectionNow + "\tNow/Prev=" + selectionNow / selectionPrev);
Console.WriteLine();
insertionPrev = insertionNow;
selectionPrev = selectionNow;
n *= 2;
}
}
}
}

2.1.29
题目
希尔排序的递增序列。
通过实验比较算法 2.3 中所使用的递增序列和递增序列 1, 5, 19, 41, 109, 209, 505, 929, 2161, 3905, 8929, 16001, 36289, 64769, 146305, 260609
(这是通过序列 9×4^(k)-9×2^(k)+1 和 4^(k)-3×2^(k)+1 综合得到的)。
可以参考练习 2.1.11。
解答
当然是题目给出的递增序列更快啦,因为这个序列就是作者提出来的嘛。
(论文链接: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0196677486900015)
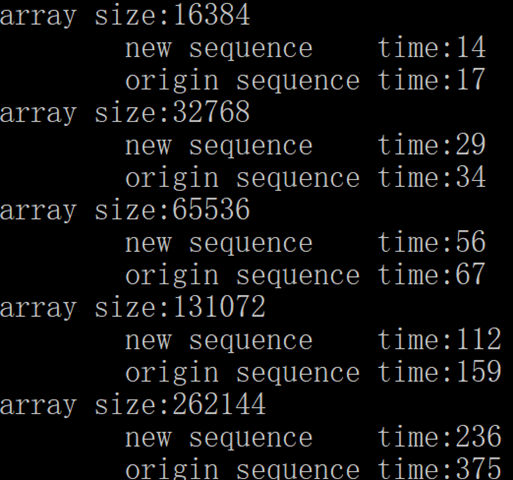
代码
修改了一下 shellsort,让它按照给定的 h 序列排序。

using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._29
{
public class ShellSort : BaseSort
{
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数。
/// </summary>
public ShellSort() { }
/// <summary>
/// 利用希尔排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">待排序的元素类型。</typeparam>
/// <param name="a">待排序的数组。</param>
/// <param name="h">需要使用的递增序列。</param>
public void Sort<T>(T[] a, int[] h) where T : IComparable<T>
{
int n = a.Length;
int t = 0;
while (h[t] < a.Length)
{
t++;
if (t >= h.Length)
break;
}
t--;
for ( ; t >= 0; t--)
{
for (int i = h[t]; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= h[t] && Less(a[j], a[j - h[t]]); j -= h[t])
{
Exch(a, j, j - h[t]);
}
}
Debug.Assert(IsHSorted(a, h[t]));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}
/// <summary>
/// 利用希尔排序将数组按升序排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>
public override void Sort<T>(T[] a)
{
int n = a.Length;
int[] h = new int[2]; // 预先准备好的 h 值数组
int hTemp = 1;
int sequenceSize = 0;
for (sequenceSize = 0; hTemp < n; sequenceSize++)
{
if (sequenceSize >= h.Length) // 如果数组不够大则双倍扩容
{
int[] expand = new int[h.Length * 2];
for (int j = 0; j < h.Length; j++)
{
expand[j] = h[j];
}
h = expand;
}
h[sequenceSize] = hTemp;
hTemp = hTemp * 3 + 1;
}
for (int t = sequenceSize - 1; t >= 0; t--)
{
for (int i = h[t]; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= h[t] && Less(a[j], a[j - h[t]]); j -= h[t])
{
Exch(a, j, j - h[t]);
}
}
Debug.Assert(IsHSorted(a, h[t]));
}
Debug.Assert(IsSorted(a));
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查一次希尔排序后的子数组是否有序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">排序后的数组。</param>
/// <param name="h">子数组间隔。</param>
/// <returns>是否有序。</returns>
private bool IsHSorted<T>(T[] a, int h) where T : IComparable<T>
{
for (int i = h; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (Less(a[i], a[i - h]))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}

2.1.30
题目
几何级数递增序列。
通过实验找到一个 t,使得对于大小为 N=10^6 的任意随机数组,使用递增序列 1, [t], [t^2], [t^3], [t^4], ... 的希尔排序的运行时间最短。
给出你能找到的三个最佳 t 值以及相应的递增序列。
以下练习描述的是各种用于评估排序算法的测试用例。
它们的作用是用随机数据帮助你增进对性能特性的理解。
随着命令行指定的实验测试的增大,可以和 SortCompare 一样在它们中使用 time() 函数来得到更精确的结果。
在以后的几节中我们会使用这些练习来评估更为复杂的算法。
解答
2,3,4
t 越大的话,按照这个递增序列,10^6 次能够满足的 h 也就越少。
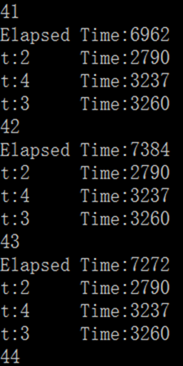
代码

using System;
using Sort;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace _2._1._30
{
/*
* 2.1.30
*
* 几何级数递增序列。
* 通过实验找到一个 t,使得对于大小为 N=10^6 的任意随机数组,
* 使用递增序列 1, [t], [t^2], [t^3], [t^4], ... 的希尔排序的运行时间最短。
* 给出你能找到的三个最佳 t 值以及相应的递增序列。
* 以下练习描述的是各种用于评估排序算法的测试用例。
* 它们的作用是用随机数据帮助你增进对性能特性的理解。
* 随着命令行指定的实验测试的增大,
* 可以和 SortCompare 一样在它们中使用 time() 函数来得到更精确的结果。
* 在以后的几节中我们会使用这些练习来评估更为复杂的算法。
*
*/
class Program
{
// t = 2, 3, 4
// t 大于 10 之后,由于每次排序 h 缩减的太快,
// 时间会越来越近似于直接插入排序。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = SortCompare.GetRandomArrayInt(1000000);
int[] array2 = new int[array.Length];
array.CopyTo(array2, 0);
Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
long[] bestTimes = new long[3];
long[] bestTs = new long[3];
for (int i = 0; i < bestTimes.Length; i++)
{
bestTimes[i] = long.MaxValue;
bestTs[i] = int.MaxValue;
}
long nowTime = 0;
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
for (int t = 2; t <= 1000000; t++)
{
Console.WriteLine(t);
timer.Restart();
shellSort.Sort(array, t);
nowTime = timer.ElapsedMilliseconds;
timer.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("Elapsed Time:" + nowTime);
for (int i = 0; i < bestTimes.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("t:" + bestTs[i]);
Console.WriteLine("\tTime:" + bestTimes[i]);
}
if (bestTimes[2] > nowTime)
{
bestTimes[2] = nowTime;
bestTs[2] = t;
Array.Sort(bestTimes, bestTs);
}
array2.CopyTo(array, 0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bestTimes.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("t:" + bestTs[i]);
Console.Write("\tTime:" + bestTimes[i]);
}
}
}
}

2.1.31
题目
双倍测试。
编写一个能够对排序算法进行双倍测试的用例。
数组规模 N 的起始值为 1000,排序后打印 N、估计排序用时、实际排序用时以及在 N 倍增之后两次用时的比例。
用这段程序验证在随机输入模型下插入排序和选择排序的运行时间都是平方级别的。
对希尔排序的性能做出猜想并验证你的猜想。
解答
这里截取数据量比较大的时候的数据。
插入排序和选择排序显然都是平方级别的。
希尔排序猜测是线性的,实际上要比线性大一点(次平方级)。
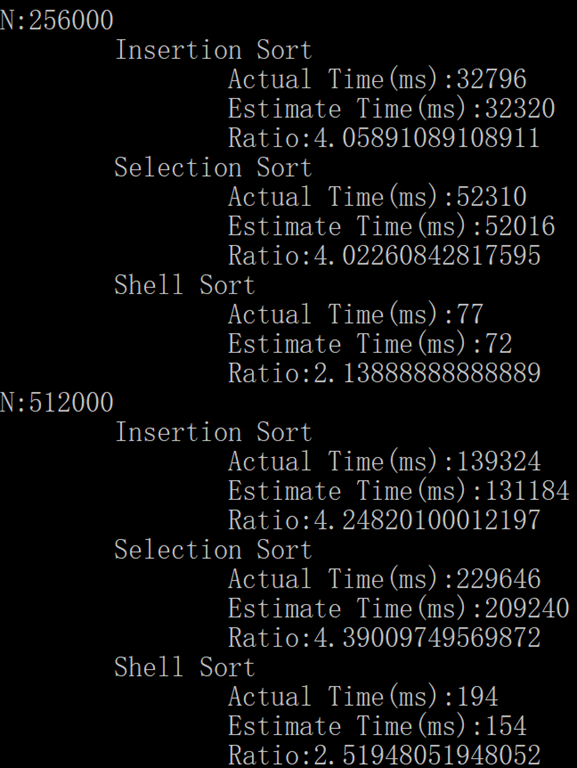
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._31
{
/*
* 2.1.31
*
* 双倍测试。
* 编写一个能够对排序算法进行双倍测试的用例。
* 数组规模 N 的起始值为 1000,
* 排序后打印 N、估计排序用时、实际排序用时以及在 N 倍增之后两次用时的比例。
* 用这段程序验证在随机输入模型下插入排序和选择排序的运行时间都是平方级别的。
* 对希尔排序的性能做出猜想并验证你的猜想。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = 1000;
InsertionSort insertion = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selection = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shell = new ShellSort();
double prevInsertion = 0;
double prevSelection = 0;
double prevShell = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("N:" + N);
int[] array = SortCompare.GetRandomArrayInt(N);
int[] arrayBak = new int[N];
array.CopyTo(arrayBak, 0);
Console.WriteLine("\tInsertion Sort");
double now = SortCompare.Time(insertion, array);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tActual Time(ms):" + now);
if (i != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t\tEstimate Time(ms):" + prevInsertion * 4);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tRatio:" + now / prevInsertion);
}
prevInsertion = now;
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
Console.WriteLine("\tSelection Sort");
now = SortCompare.Time(selection, array);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tActual Time(ms):" + now);
if (i != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t\tEstimate Time(ms):" + prevSelection * 4);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tRatio:" + now / prevSelection);
}
prevSelection = now;
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
Console.WriteLine("\tShell Sort");
now = SortCompare.Time(shell, array);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tActual Time(ms):" + now);
if (i != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t\tEstimate Time(ms):" + prevShell * 2);
Console.WriteLine("\t\tRatio:" + now / prevShell);
}
prevShell = now;
N *= 2;
}
}
}
}

2.1.32
题目
运行时间曲线图。
编写一个测试用例,使用 StdDraw 在各种不同规模的随机输入下将算法的平均运行时间绘制成一张曲线图。
可能需要添加一两个命令行参数,请尽量设计一个实用的工具。
解答
基本上都是这么个样子:

代码

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._32
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
BaseSort sort;
int n;
double[] result;
/// <summary>
/// 构造一个绘图结果窗口。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">用于做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <param name="n">用于测试的初始数据量。</param>
public Form2(BaseSort sort, int n)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.sort = sort;
this.n = n;
this.result = Test(n);
this.timer1.Interval = 1000;
this.timer1.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 执行八次耗时测试,每次数据量翻倍。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">初始数据量。</param>
/// <returns>测试结果数据。</returns>
public double[] Test(int n)
{
double[] result = new double[8];
for (int i = 0; i < result.Length; i++)
{
result[i] = SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(this.sort, n, 3);
n *= 2;
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 绘制曲线图。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="result">结果数组。</param>
public void DrawPanel(double[] result)
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.ClientRectangle.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
Rectangle clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
Rectangle drawRect = new Rectangle(clientRect.X + 10, clientRect.Y + 10, clientRect.Width - 10, clientRect.Height - 10);
PointF[] dataPoints = new PointF[result.Length];
float unitX = (float)drawRect.Width / result.Length;
float unitY = (float)(drawRect.Height / result.Max());
SizeF pointSize = new SizeF(8, 8);
for (int i = 0; i < result.Length; i++)
{
dataPoints[i] = new PointF(drawRect.Left + unitX * i, (float)(unitY * result[i]));
graphics.FillEllipse(Brushes.Black, new RectangleF(dataPoints[i], pointSize));
}
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DrawPanel(this.result);
this.timer1.Stop();
}
}
}

2.1.33
题目
分布图。
对于你为练习 2.1.33 给出的测试用例,
在一个无穷循环中调用 sort() 方法将由第三个命令行参数指定大小的数组排序,
记录每次排序的用时并使用 StdDraw 在图上画出所有平均运行时间,应该能够得到一张运行时间的分布图。
解答
这里每次结果的 Y 轴位置都是随机生成的,这样图像会好看点。
X 轴代表消耗的时间。
选择排序:
插入排序:
希尔排序:
代码

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._33
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
List<double> resultList;
List<float> resultYList;
Rectangle clientRect;
Rectangle drawRect;
BaseSort sort;
int n;
/// <summary>
/// 构造一个绘制结果窗口。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">用于测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <param name="n">测试算法是生成的数据量。</param>
public Form2(BaseSort sort, int n)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.resultList = new List<double>();
this.resultYList = new List<float>();
this.clientRect = this.ClientRectangle;
this.drawRect = new Rectangle(this.clientRect.X + 10, this.clientRect.Y + 10, this.clientRect.Width - 10, this.clientRect.Height - 10);
this.sort = sort;
this.n = n;
this.timer1.Interval = 500;
this.timer1.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 执行一次测试并绘制图像。
/// </summary>
public void Test()
{
Random random = new Random();
double[] array = SortCompare.GetRandomArrayDouble(this.n);
double time = SortCompare.Time(this.sort, array);
this.resultList.Add(time);
this.resultYList.Add((float)(random.NextDouble() * this.drawRect.Height));
DrawPanel(this.resultList.ToArray(), this.resultYList.ToArray());
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据已有的数据绘制图像。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="result">耗时数据(X 轴)</param>
/// <param name="resultY">Y 轴数据</param>
public void DrawPanel(double[] result, float[] resultY)
{
Graphics graphics = this.CreateGraphics();
graphics.Clear(this.BackColor);
graphics.TranslateTransform(0, this.ClientRectangle.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(1, -1);
PointF[] dataPoints = new PointF[result.Length];
float unitX = (float)(this.drawRect.Width / (result.Max() - result.Min()));
double min = result.Min();
SizeF pointSize = new SizeF(8, 8);
for (int i = 0; i < result.Length; i++)
{
dataPoints[i] = new PointF((float)(unitX * (result[i] - min)), resultY[i]);
graphics.FillEllipse(Brushes.Black, new RectangleF(dataPoints[i], pointSize));
}
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Test();
}
}
}

2.1.34
题目
罕见情况。
编写一个测试用例,调用 sort() 方法对实际应用中可能出现困难或极端情况的数组进行排序。
比如,数组可能已经是有序的,或是逆序的,数组中的所有主键相同,数组的主键只有两种值,大小是 0 或 1的数组。
解答
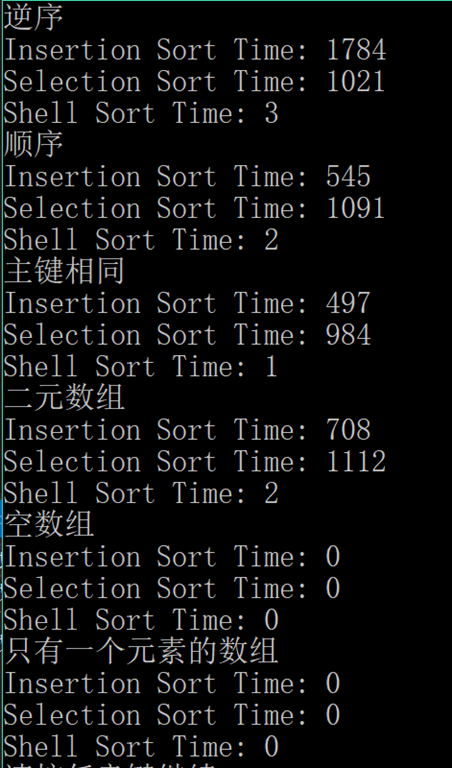
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._34
{
/*
* 2.1.34
*
* 罕见情况。
* 编写一个测试用例,
* 调用 sort() 方法对实际应用中可能出现困难或极端情况的数组进行排序。
* 比如,数组可能已经是有序的,
* 或是逆序的,
* 数组中的所有主键相同,
* 数组的主键只有两种值,
* 大小是 0 或 1 的数组。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
// 逆序
Console.WriteLine("逆序");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + ReverseSortTest(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + ReverseSortTest(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + ReverseSortTest(shellSort));
// 顺序
Console.WriteLine("顺序");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + SortedSortTest(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + SortedSortTest(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + SortedSortTest(shellSort));
// 主键相同
Console.WriteLine("主键相同");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + EqualSortTest(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + EqualSortTest(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + EqualSortTest(shellSort));
// 二元数组
Console.WriteLine("二元数组");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + BinarySortTest(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + BinarySortTest(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + BinarySortTest(shellSort));
// 空数组
Console.WriteLine("空数组");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + ZeroArraySizeSort(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + ZeroArraySizeSort(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + ZeroArraySizeSort(shellSort));
// 只有一个元素的数组
Console.WriteLine("只有一个元素的数组");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort Time: " + OneArraySizeSort(insertionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort Time: " + OneArraySizeSort(selectionSort));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort Time: " + OneArraySizeSort(shellSort));
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造逆序数组并用其对指定输入算法进行测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的算法。</param>
/// <returns>算法耗时。</returns>
static double ReverseSortTest(BaseSort sort)
{
int[] array = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
array[i] = array.Length - i;
}
return SortCompare.Time(sort, array);
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造已排序的数组并用其对指定排序算法测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <returns>算法的耗时。</returns>
static double SortedSortTest(BaseSort sort)
{
return SortCompare.TimeSortedInput(sort, 10000, 1);
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造只有一个值的数组并用其对指定排序算法做测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <returns>算法的耗时。</returns>
static double EqualSortTest(BaseSort sort)
{
int[] array = new int[10000];
Random random = new Random();
int num = random.Next();
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
array[i] = num;
}
return SortCompare.Time(sort, array);
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造只有两种取值的数组并用其对指定排序算法做测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <returns>排序算法的耗时。</returns>
static double BinarySortTest(BaseSort sort)
{
int[] array = new int[10000];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
array[i] = random.Next(2);
}
return SortCompare.Time(sort, array);
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造空数组并用其对指定排序算法做测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <returns>排序算法的耗时。</returns>
static double ZeroArraySizeSort(BaseSort sort)
{
int[] array = new int[0];
return SortCompare.Time(sort, array);
}
/// <summary>
/// 构造只有一个元素的数组并用其对指定排序算法做测试。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sort">需要做测试的排序算法。</param>
/// <returns>排序算法的耗时。</returns>
static double OneArraySizeSort(BaseSort sort)
{
int[] array = new int[1];
Random random = new Random();
array[0] = random.Next();
return SortCompare.Time(sort, array);
}
}
}

2.1.35
题目
不均匀的概率分布。编写一个测试用例,使用非均匀分布的概率来生成随机排列的数据,包括:
- 高斯分布
- 泊松分布
- 几何分布
- 离散分布(一种特殊情况见练习 2.1.28)。
评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的影响。
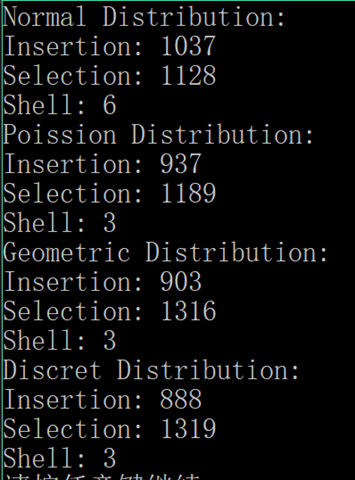
解答
难点是如何生成符合这些分布的随机数。
Java 的话官方给的 stdRandom 里面都有相应的实现。
结果:
代码
几种随机数的实现:

using System;
namespace Sort
{
/// <summary>
/// 静态类,包含用于生成排序算法测试数据的方法。
/// </summary>
public static class SortUtil
{
public static Random UniformGenerator = new Random();
/// <summary>
/// 产生符合正态分布的随机数。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="average">正态分布的期望值 μ。</param>
/// <param name="standardDeviation">正态分布的标准差 σ。</param>
/// <returns>符合正态分布的随机数。</returns>
public static double Normal(double average, double standardDeviation)
{
double u1 = UniformGenerator.NextDouble();
double u2 = UniformGenerator.NextDouble();
double z0 = Math.Sqrt(-2.0 * Math.Log(u1)) * Math.Cos(Math.PI * 2 * u2);
return z0 * standardDeviation + average;
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成符合泊松分布的随机数。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="average">泊松分布的期望值 λ。</param>
/// <returns>一个符合泊松分布的随机数。</returns>
public static double Poission(double average)
{
double x = 0;
double p = Math.Pow(Math.E, -average);
double s = p;
double u = UniformGenerator.NextDouble();
do
{
x++;
p *= average / x;
s += p;
} while (u > s);
return x;
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成符合几何分布的随机数。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="p">几何分布的概率 p,这应该是一个小于 1 的非负数。</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentOutOfRangeException">概率不能大于 1.</exception>
/// <returns>符合几何分布的随机数。</returns>
public static double Geometry(double p)
{
if (p > 1)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("p", "概率不能大于 1");
}
double result;
result = Math.Ceiling(Math.Log(1 - UniformGenerator.NextDouble()) / Math.Log(1 - p));
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据指定的几率数组产生符合离散分布的随机数。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="probabilities">各取值的可能性。</param>
/// <returns>符合随机分布的随机整数。</returns>
public static double Discrete(double[] probabilities)
{
if (probabilities == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Argument array is null");
}
double EPSION = 1E-14;
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.Length; i++)
{
if (probabilities[i] <= 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException("array entry " + i + " must be nonnegative:" + probabilities[i]);
}
sum += probabilities[i];
}
if (sum > 1.0 + EPSION || sum < 1.0 - EPSION)
{
throw new ArgumentException("sum of array entries does not equal 1.0:" + sum);
}
while (true)
{
double r = UniformGenerator.NextDouble();
sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.Length; i++)
{
sum += probabilities[i];
if (sum > r)
{
return i;
}
}
}
}
}
}

Main 方法:

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._35
{
/*
* 2.1.35
*
* 不均匀的概率分布。编写一个测试用例,使用非均匀分布的概率来生成随机排列的数据,包括:
* 高斯分布
* 泊松分布
* 几何分布
* 离散分布(一种特殊情况见练习 2.1.28)。
* 评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的影响。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
int n = 10000;
// 高斯分布(正态分布)
double[] arrayInsertion = SortCompare.GetNormalDistributionArray(n);
double[] arraySelection = new double[n];
double[] arrayShell = new double[n];
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Normal Distribution:");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion: " + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection: " + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell: " + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
// 泊松分布
arrayInsertion = SortCompare.GetPossionDistributionArray(n);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Poission Distribution:");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion: " + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection: " + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell: " + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
// 几何分布
arrayInsertion = SortCompare.GetGeometricDistributionArray(n, 0.3);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Geometric Distribution:");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion: " + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection: " + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell: " + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
// 离散分布
arrayInsertion = SortCompare.GetDiscretDistributionArray(n, new double[] { 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1 });
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("Discret Distribution:");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion: " + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection: " + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell: " + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
}
}
}

2.1.36
题目
不均匀的数据。编写一个测试用例,生成不均匀的测试数据,包括:
- 一半数据是 0,一半数据是 1
- 一半数据是 0,1/4 是 1,1/4 是 2,以此类推
- 一半数据是 0,一半是随机 int 值。
评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
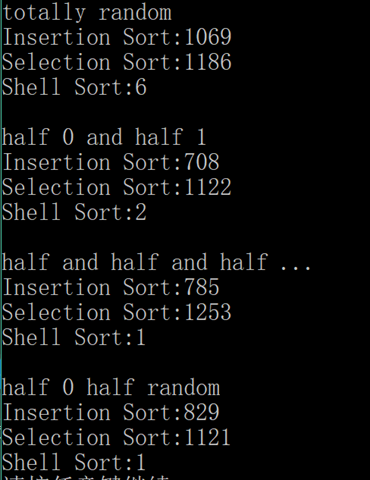
解答
最后结果:
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._36
{
/*
* 2.1.36
*
* 不均匀的数据。
* 编写一个测试用例,
* 生成不均匀的测试数据,包括:
* 一半数据是 0,一半数据是 1
* 一半数据是 0,1/4 是 1,1/4 是 2,以此类推
* 一半数据是 0,一半是随机 int 值。
* 评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
*
*/
class Program
{
// 选择排序的耗时与输入值的内容无关,不受影响。
// 对于插入排序,以上几种情况都是重复值较多的情况,插入排序的速度会加快。
// 希尔排序本质上也是插入排序,因此也会更快一些。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 10000;
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
int[] arrayInsertion = new int[n];
int[] arraySelection = new int[n];
int[] arrayShell = new int[n];
// 对照,完全随机
arrayInsertion = HalfZeroHalfOne(n);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("totally random");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(insertionSort, n, 1));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(selectionSort, n, 1));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(shellSort, n, 1));
Console.WriteLine();
// 一半是 0 一半是 1
arrayInsertion = HalfZeroHalfOne(n);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("half 0 and half 1");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
Console.WriteLine();
// 一半是 0, 1/4 是 1, 1/8 是 2……
arrayInsertion = HalfAndHalf(n);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayShell.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("half and half and half ...");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
Console.WriteLine();
// 一半是 0,一半是随机 int 值
arrayInsertion = HalfZeroHalfRandom(n);
arrayInsertion.CopyTo(arraySelection, 0);
arrayShell.CopyTo(arrayShell, 0);
Console.WriteLine("half 0 half random");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, arrayInsertion));
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, arraySelection));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, arrayShell));
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取一半是 0 一半是 1 的随机 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组大小。</param>
/// <returns>一半是 0 一半是 1 的 <see cref="int"/>数组。</returns>
static int[] HalfZeroHalfOne(int n)
{
int[] result = new int[n];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (random.NextDouble() >= 0.5)
{
result[i] = 0;
}
else
{
result[i] = 1;
}
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成 1/2 为 0, 1/4 为 1, 1/8 为 2 …… 的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组长度。</param>
/// <returns>1/2 为 0, 1/4 为 1, 1/8 为 2 …… 的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。</returns>
static int[] HalfAndHalf(int n)
{
int[] array = new int[n];
HalfIt(0, 0, n / 2, array);
Shuffle(array);
return array;
}
/// <summary>
/// 递归生成 1/2 为 0, 1/4 为 1, 1/8 为 2 …… 的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="start">填充起点。</param>
/// <param name="number">起始编号。</param>
/// <param name="length">填充长度</param>
/// <param name="array">用于填充的数组。</param>
/// <returns>一个 <see cref="int"/> 数组。</returns>
static int[] HalfIt(int start, int number, int length, int[] array)
{
if (length == 0)
return array;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
array[start + i] = number;
}
return HalfIt(start + length, number + 1, length / 2, array);
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成一半是 0 一半是随机整数的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组大小。</param>
/// <returns>生成一半是 0 一半是随机整数的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。</returns>
static int[] HalfZeroHalfRandom(int n)
{
int[] array = new int[n];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
array[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = n / 2; i < n; i++)
{
array[i] = random.Next();
}
Shuffle(array);
return array;
}
/// <summary>
/// 打乱数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要打乱的数组。</param>
static void Shuffle(int[] a)
{
int N = a.Length;
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int r = i + random.Next(N - i);// 等于StdRandom.uniform(N-i)
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
}
}
}

2.1.37
题目
部分有序。编写一个测试用例,生成部分有序数组,包括:
- 95% 有序,其余部分为随机值。
- 所有元素和它们的正确位置的距离都不超过 10。
- 5% 的元素随机分布在整个数组中,剩下的数据都是有序的。
评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
解答
主要说一下第二个的实现,把一个数组循环左移/右移几位即可。
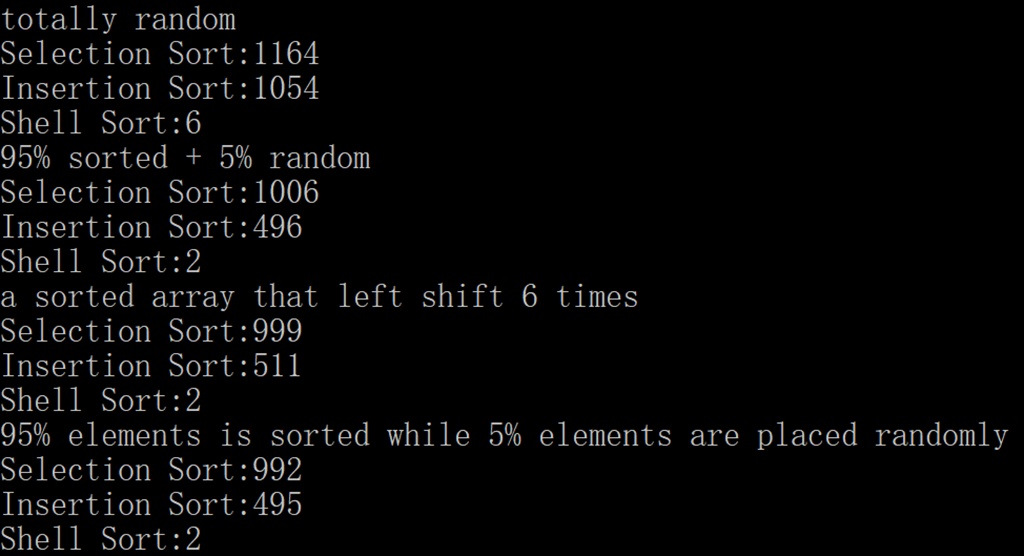
代码

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._37
{
/*
* 2.1.37
*
* 部分有序。
* 编写一个测试用例,生成部分有序数组,包括:
* 95% 有序,其余部分为随机值。
* 所有元素和它们的正确位置的距离都不超过 10。
* 5% 的元素随机分布在整个数组中,剩下的数据都是有序的。
* 评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
*
*/
class Program
{
// 选择排序的性能只与数组大小有关,以上三种情况耗时都是近似的。
// 插入排序的性能与逆序对数量有关,部分有序的情况下耗时会小于完全随机。
// 希尔排序与插入排序类似。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
int n = 10000;
int[] selectionArray = new int[n];
int[] insertionArray = new int[n];
int[] shellArray = new int[n];
// 完全随机的对照
Console.WriteLine("totally random");
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(selectionSort, n, 1));
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(insertionSort, n, 1));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.TimeRandomInput(shellSort, n, 1));
// 95% 有序,其余部分为随机值。
selectionArray = Sorted95Random5(n);
selectionArray.CopyTo(insertionArray, 0);
selectionArray.CopyTo(shellArray, 0);
Console.WriteLine("95% sorted + 5% random");
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, selectionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, insertionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, shellArray));
// 所有元素和它们的正确位置的距离都不超过 10。
selectionArray = RandomIn10(n);
selectionArray.CopyTo(insertionArray, 0);
selectionArray.CopyTo(shellArray, 0);
Console.WriteLine("a sorted array that left shift 6 times");
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, selectionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, insertionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, shellArray));
// 5% 的元素随机分布在整个数组中,剩下的数据都是有序的。
selectionArray = RandomIn10(n);
selectionArray.CopyTo(insertionArray, 0);
selectionArray.CopyTo(shellArray, 0);
Console.WriteLine("95% elements is sorted while 5% elements are placed randomly");
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, selectionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, insertionArray));
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + SortCompare.Time(shellSort, shellArray));
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成 95% 有序,最后 5% 随机的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组的大小。</param>
/// <returns>95% 有序,最后 5% 随机的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。</returns>
static int[] Sorted95Random5(int n)
{
int[] array = new int[n];
int randomStart = (int)(n * 0.05);
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n - randomStart; i++)
{
array[i] = i;
}
for (int i = n - randomStart; i < n; i++)
{
array[i] = random.Next();
}
return array;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回一个 <see cref="int"/> 数组,其中的每个元素和它的正确位置的距离都不超过 10。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">数组大小。</param>
/// <returns>一个 <see cref="int"/> 数组,其中的每个元素和它的正确位置的距离都不超过 10。</returns>
static int[] RandomIn10(int n)
{
Queue<int> array = new Queue<int>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
array.Enqueue(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
array.Enqueue(array.Dequeue());
}
return array.ToArray();
}
/// <summary>
/// 生成 5% 元素随机分布,剩余有序的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">需要生成的数组大小。</param>
/// <returns>5% 元素随机分布,剩余有序的 <see cref="int"/> 数组。</returns>
static int[] Shuffle5Percent(int n)
{
Random random = new Random();
int percent5 = (int)(n * 0.05);
int[] randomIndex = new int[percent5];
for (int i = 0; i < percent5; i++)
{
randomIndex[i] = random.Next(percent5);
}
int[] randomValue = new int[percent5];
for (int i = 0; i < percent5; i++)
{
randomValue[i] = randomIndex[i];
}
Shuffle(randomValue);
int[] array = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
array[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < percent5; i++)
{
array[randomIndex[i]] = randomValue[i];
}
return array;
}
/// <summary>
/// 打乱数组。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要打乱的数组。</param>
static void Shuffle(int[] a)
{
int N = a.Length;
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int r = i + random.Next(N - i);// 等于StdRandom.uniform(N-i)
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
}
}
}

2.1.38
题目
不同类型的元素。编写一个测试用例,生成由多种数据类型元素组成的数组,元素的主键值随机,包括:
- 每个元素的主键均为 String 类型(至少长 10 个字符),并含有一个 double 值。
- 每个元素的主键均为 double 类型,并含有 10 个 String 值(每个都至少长 10 个字符)。
- 每个元素的主键均为 int 类型,并含有一个 int[20] 值。
评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
解答
这里实现了一个 Pair 类,用来排序。
每一个元素都有相应的 key 值和 value 值,排序时只使用 key 值进行排序。
代码

using System;
using Sort;
namespace _2._1._38
{
/*
* 2.1.38
*
* 不同类型的元素。
* 编写一个测试用例,生成由多种数据类型元素组成的数组,元素的主键值随机,包括:
* 每个元素的主键均为 String 类型(至少长 10 个字符),并含有一个 double 值。
* 每个元素的主键均为 double 类型,并含有 10 个 String 值(每个都至少长 10 个字符)。
* 每个元素的主键均为 int 类型,并含有一个 int[20] 值。
* 评估并验证这些输入数据对本节讨论的算法的性能的影响。
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 10000;
double[] results = TestA(n);
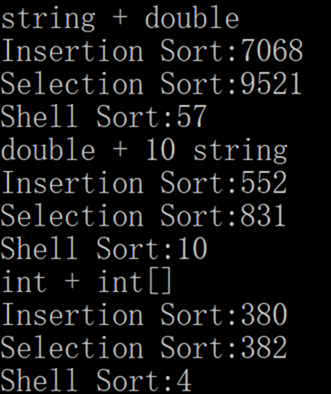
Console.WriteLine("string + double");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + results[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + results[1]);
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + results[2]);
results = TestB(n);
Console.WriteLine("double + 10 string");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + results[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + results[1]);
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + results[2]);
results = TestC(n);
Console.WriteLine("int + int[]");
Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort:" + results[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort:" + results[1]);
Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort:" + results[2]);
}
/// <summary>
/// 第一个测试,测试结果按照 Insertion, Selection, Shell 排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">测试的数组长度。</param>
/// <returns>测试结果。</returns>
static double[] TestA(int n)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
Random random = new Random();
// 每个元素的主键均为 String 类型(至少长 10 个字符),并含有一个 double 值。
Pair<string, double>[] array = new Pair<string, double>[n];
Pair<string, double>[] arrayBak = new Pair<string, double>[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
array[i] = new Pair<string, double>(RandomString(20, random), random.NextDouble());
}
array.CopyTo(arrayBak, 0);
double[] results = new double[3];
results[0] = SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[1] = SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[2] = SortCompare.Time(shellSort, array);
return results;
}
/// <summary>
/// 第二个测试,测试结果按照 Insertion, Selection, Shell 排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">测试的数组长度。</param>
/// <returns>测试结果。</returns>
static double[] TestB(int n)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
Random random = new Random();
// 每个元素的主键均为 double 类型,并含有 10 个 String 值(每个都至少长 10 个字符)。
Pair<double, string[]>[] array = new Pair<double, string[]>[n];
Pair<double, string[]>[] arrayBak = new Pair<double, string[]>[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string[] temp = new string[10];
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
temp[j] = RandomString(12, random);
}
array[i] = new Pair<double, string[]>(random.NextDouble(), temp);
}
array.CopyTo(arrayBak, 0);
double[] results = new double[3];
results[0] = SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[1] = SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[2] = SortCompare.Time(shellSort, array);
return results;
}
/// <summary>
/// 第三个测试,测试结果按照 Insertion, Selection, Shell 排序。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">测试的数组长度。</param>
/// <returns>测试结果。</returns>
static double[] TestC(int n)
{
InsertionSort insertionSort = new InsertionSort();
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
ShellSort shellSort = new ShellSort();
Random random = new Random();
// 每个元素的主键均为 int 类型,并含有一个 int[20] 值。
Pair<int, int[]>[] array = new Pair<int, int[]>[n];
Pair<int, int[]>[] arrayBak = new Pair<int, int[]>[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int[] temp = new int[20];
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++)
{
temp[j] = random.Next();
}
array[i] = new Pair<int, int[]>(random.Next(), temp);
}
array.CopyTo(arrayBak, 0);
double[] results = new double[3];
results[0] = SortCompare.Time(insertionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[1] = SortCompare.Time(selectionSort, array);
arrayBak.CopyTo(array, 0);
results[2] = SortCompare.Time(shellSort, array);
return results;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取一个随机 <see cref="string"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"><see cref="string"/> 的长度。</param>
/// <param name="random">随机数生成器。</param>
/// <returns>获取一个随机 <see cref="string"/>。</returns>
static string RandomString(int n, Random random)
{
char[] value = new char[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
value[i] = (char)random.Next(char.MinValue + 10, char.MaxValue - 10);
}
return new string(value);
}
}
}

算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1的更多相关文章
- 算法第四版 在Eclipse中调用Algs4库
首先下载Eclipse,我选择的是Eclipse IDE for Java Developers64位版本,下载下来之后解压缩到喜欢的位置然后双击Eclipse.exe启动 然后开始新建项目,File ...
- 算法第四版jar包下载地址
算法第四版jar包下载地址:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/
- 算法第四版-文字版-下载地址-Robert Sedgewick
下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/moshenglv/10777447 算法第四版,文字版,可复制,方便copy代码 目录: 第1章 基 础 ...... ...
- 二项分布。计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数(算法第四版1.1.27)
算法第四版35页问题1.1.27,估计用一下代码计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数: public static double binomial(int n,int ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之优先队列--Priority Queues
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.4优先队列(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:API 与初级实现 2:堆得定义 3:堆排序 4:事件驱动的仿真 优先队列最重要的操作就是删 ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之快速排序 QuickSort
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.3快速排序(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:快速排序 2:
- 算法第四版 coursera公开课 普林斯顿算法 ⅠⅡ部分 Robert Sedgewick主讲《Algorithms》
这是我在网上找到的资源,下载之后上传到我的百度网盘了. 包含两部分:1:算法视频的种子 2:字幕 下载之后,请用迅雷播放器打开,因为迅雷可以直接在线搜索字幕. 如果以下链接失效,请在下边留言,我再更新 ...
- 相似度分析,循环读入文件(加入了HanLP,算法第四版的库)
相似度分析的,其中的分词可以采用HanLP即可: http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1421978002609.htm /****************** ...
- 算法第四版 用eclipse实现书中UnionFind例子
一 安装环境 直接下载algs4.exe 下载完成后C:\Users\zle 下面会有algs4 文件夹 原文: Our installer downloads, installs, and conf ...
- 配置《算法 第四版》的Eclipse开发环境
1. 安装JAVA JAVA网址:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html 配置环境变量(我把JAVA安装在 ...
随机推荐
- 实验四 Android程序设计-5
点击button按钮,进入下一活动,"the third activity"
- java面试笔试总结(一)--亲生经历的面试题
说明:本文只是自己的一些心得体会,答案也是自己写的,正确与否,还需考证 java笔试题 1java笔试题1 启动3个线程打印递增的数字, 线程1先打印1,2,3,4,5, 然后是线程2打印6,7 ...
- Codeforces Gym 100269K Kids in a Friendly Class 构造题
Kids in a Friendly Class 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/gym/100269/attachments Description Kevin resemb ...
- 在iOS项目中使用截图
最近项目中要求将个人的信息生成一张图片,以名片的方式分享出去.由此就需要使用截图功能.需求如图: 代码如下:
- JS操作小数运算,结果莫名其妙出现多位小数问题
Number类型: Number类型是ECMAScript中最常用和最令人关注的类型了:这种类型使用IEEE754格式来表示整数和浮点数值(浮点数值在某些语言中也被成为双精度数值),为支持各种数据类型 ...
- FIREDAC用于LINUX报头文件FireDAC.VCLUI.Wait找不到
FIREDAC用于LINUX报头文件FireDAC.VCLUI.Wait找不到 FIREDAC LINUX下面,此控件 此属性 必须设为CONSOLE. 默认值只能用于WINDOWS操作系统.
- 使用Apache POI导出Excel小结--导出XLS格式文档
使用Apache POI导出Excel小结 关于使用Apache POI导出Excel我大概会分三篇文章去写 使用Apache POI导出Excel小结--导出XLS格式文档 使用Apache POI ...
- .NET Oracle Developer的福音——ODP.NET Managed正式推出
.NET Oracle Developer的福音--ODP.NET Managed正式推出 在.NET平台下开发Oracle应用的小伙伴们肯定都知道一方面做Oracle开发和实施相比SqlServ ...
- [转]How to solve SSIS error code 0xC020801C/0xC004700C/0xC0047017
本文转自:http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/534651/HowplustoplussolveplusSSISpluserrorpluscodeplus0xC B ...
- JSP和Servlet中的几个编码的作用及原理
首先,说说JSP和Servlet中的几个编码的作用. 在JSP和Servlet中主要有以下几个地方可以设置编码,pageEncoding="UTF-8".contentType=& ...
