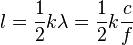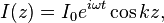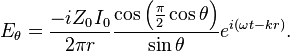Half Wavelength Dipole Antenna
Reference :
1. wikipedia
The dipole antenna is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna.It consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods, which are usually bilaterally symmetrical.Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors.
Dipoles are resonant antennas, meaning that the elements serve as resonators, with standing waves of radio current flowing back and forth between their ends. So the length of the dipole elements is determined by the wavelength of the radio waves used. The most common form is the half-wave dipole, in which each of the two rod elements is approximately 1/4 wavelength long, so the whole antenna is a half-wavelength long. The radiation pattern of a vertical dipole is omnidirectional; it radiates equal power in allazimuthal directions perpendicular to the axis of the antenna. For a half-wave dipole the radiation is maximum, 2.15 dBi perpendicular to the antenna axis, falling monotonically with elevation angle to zero on the axis, off the ends of the antenna.
Several different variations of the dipole are also used, such as thefolded dipole, short dipole, cage dipole, bow-tie, and batwing antenna. Dipoles may be used as standalone antennas themselves, but they are also employed as feed antennas (driven elements) in many more complex antenna types, such as the Yagi antenna, parabolic antenna, reflective array, turnstile antenna, log periodic antenna, and phased array.
Dipole characteristics

1. Impedance
The feedpoint impedance of a dipole antenna is very sensitive to its electrical length. Therefore, a dipole will generally only perform optimally over a rather narrow bandwidth, beyond which its impedance will become a poor match for the transmitter or receiver (and transmission line). The real (resistive) and imaginary (reactive) components of that impedance, as a function of electrical length, are shown in the accompanying graph.

A true half-wave dipole is one half of the wavelength λ in length, where λ=c/f in free space. Such a dipole has a feedpoint impedance consisting of 73Ω resistance and +43Ω reactance, thus presenting a slightly inductive reactance. In order to cancel that reactance, and present a pure resistance to the feedline, the element is shortened by the factor k for a net length of:
The adjustment factor k, in order for the reactance to be cancelled, depends on the diameter of the conductor. For thin wires (diameter= 0.00001 wavelengths), k is approximately 0.98; for thick conductors (diameter= 0.008 wavelengths), k drops to about 0.94. This is because the effect of antenna length on reactance is much greater for thinner conductors. For the same reason, antennas with thicker conductors have a wider operating bandwidth over which they attain an acceptablestanding wave ratio.

Dipole antennas of lengths approximately equal to any odd multiple of λ/2 are also resonant, presenting a small reactance (which can be cancelled by a small length adjustment). However these are rarely used. One size that is more practical though is a dipole with a length of 5/4 wavelengths. Not being close to 3/2 wavelengths, this antenna's impedance has a large (negative) reactance and can only be used with an impedance matching network (or "antenna tuner"). It is a desirable length because such an antenna has the highest gain for any dipole which isn't a great deal longer.
2. Radiation pattern and gain
Neglecting electrical inefficiency, the antenna gain is equal to the directive gain, which is 1.5 or 1.76 dBi for a short dipole, increasing to 1.64 or 2.15 dBi for a half-wave dipole. For a 5/4 wave dipole the gain further increases to about 5.2 dBi, making this length desirable for that reason even though the antenna is then off-resonance. Longer dipoles than that have radiation patterns that are multi-lobed, with poorer gain (unless they are much longer) even along the strongest lobe.

3. Feeding a dipole antenna
Ideally, a half-wave dipole should be fed using a balanced transmission line matching its typical 65 - 70Ω input impedance. Twin lead with a similar impedance is available but seldom used.
Many types of coaxial cable have a characteristic impedance of 75Ω, which would therefore be a good match for a half-wave dipole, however coax is an unbalanced transmission line (with one terminal at ground potential) whereas a dipole antenna presents a balanced input (both terminals have an equal but opposite voltage with respect to ground). When a balanced antenna is fed with a single-ended line, common mode currents can cause the coax line to radiate in addition to the antenna itself, distorting the radiation pattern and changing the impedance seen by the line. The dipole can be properly fed, and retain its expected characteristics, by using a balun in between the coaxial feedline and the antenna terminals. Connection of coax to a dipole antenna using a balun is plot below.




Another solution, especially for receiving antennas, is to use common 300 ohm twin lead in conjunction with a folded dipole. The folded dipole is similar to the simple half-wave dipole but with the feedpoint impedance multiplied by 4, thus closely matching that 300 ohm impedance. This is the most common household antenna for fixed FM broadcast band tuners, which usually include balanced 300 ohm antenna input terminals.
4. detailed calculation
The current distribution is that of a standing wave, approximately sinusoidal along the length of the dipole, with a node at each end and an antinode (peak current) at the center (feedpoint):

where k = 2π/λ and z runs from −L /2 to L /2.
In the far field, this produces a radiation pattern whose electric field is given by
A numerical integration of this integral over all solid angle, as we did for the short dipole, supplies a value for the radiation resistance: 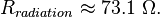 Using the induced EMF method, the real part of the driving point impedance can also be written in terms of the cosine integral:
Using the induced EMF method, the real part of the driving point impedance can also be written in terms of the cosine integral:

5 simlation result

Half Wavelength Dipole Antenna的更多相关文章
- Dipole Antenna : 2
Characteristics of dipole antenna. %% % characteristics of dipole antenna % author : Leon % email:ya ...
- dipole antenna simulation by FEKO
新建变量 建立模型 设置频率 馈电设置为wire port ,Edge 选中振子,从中心馈电. 设置输入信号 Mesh. run solver.在post feko中查看相关结果
- dipole antenna simulation by HFSS
工作频点为1GHz,新建工程,添加新设计,编辑添加下面的变量 建立天线模型,即两个金属圆柱.编辑完一个振子后,另一半可以用镜像命令产生参数如下设置 ,材料为PEC 两个圆柱间建立一个矩形片,连接两个圆 ...
- dipole antenna simulation by CST
CST偶极子天线仿真,半波振子天线 一.本文使用CST仿真频率为1GHz的偶极子天线,使用2013版本.仿真的步骤为 1.选择一个CST的天线工程模板 2.设置好默认的单位 3.设置背景的材料(空气腔 ...
- Radio Basics for RFID
Radio Basics for RFID The following is excerpted from Chapter 3: Radio Basics for UHF RFID from the ...
- 由浅入深学习PBR的原理和实现
目录 一. 前言 1.1 本文动机 1.2 PBR知识体系 1.3 本文内容及特点 二. 初阶:PBR基本认知和应用 2.1 PBR的基本介绍 2.1.1 PBR概念 2.1.2 与物理渲染的差别 2 ...
- RFID 读写器 Reader Writer Cloner
RFID读写器的工作原理 RFID的数据采集以读写器为主导,RFID读写器是一种通过无线通信,实现对标签识别和内存数据的读出和写入操作的装置. 读写器又称为阅读器或读头(Reader).查询器(Int ...
- 802.11 wireless 三
802.11 wireless 3watts,milliwatts,and Decibels瓦特(功率单位)的定义是1焦耳/秒微波炉1000瓦特,手机100-200毫瓦 decibels(分贝:比较能 ...
- POJ 3020 Antenna Placement
Antenna Placement Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 5645 Accepted: 2825 Des ...
随机推荐
- 重新想象 Windows 8 Store Apps (42) - 多线程之线程池: 延迟执行, 周期执行, 在线程池中找一个线程去执行指定的方法
[源码下载] 重新想象 Windows 8 Store Apps (42) - 多线程之线程池: 延迟执行, 周期执行, 在线程池中找一个线程去执行指定的方法 作者:webabcd 介绍重新想象 Wi ...
- csharp: MVC Controls
http://mvccontrolstoolkit.codeplex.com/ MVC Controls Toolkit http://mvcjquerycontrols.codeplex.com/ ...
- gene框架文档 - 路由类 gene_router
路由类 Gene\Router 介绍 Gene\Router 是gene框架的核心类之一,本框架区别于其他常见框架的最大地方就是独特.强大.简单的路由定义等.路由强大灵活,支持回调.类方法:支持res ...
- python3学习笔记目录
目录: Python基础(一),Day1 python基础(二),Day2 python函数和常用模块(一),Day3 python函数和常用模块(二),Day4 python函数和常用模块(三),D ...
- PHP json编码遇到的问题
今天遇到了json编码解码之后中文消失的问题,一探究竟,写下这篇文章 PHP中提供了json_encode 和json_decode 这对函数 将PHP中 值转化成 字符串,但是遇到中文的时候,很容 ...
- mysql oom之后的page 447 log sequence number 292344272 is in the future
mysql oom之后,重启时发生130517 16:00:10 InnoDB: Error: page 447 log sequence number 292344272InnoDB: is in ...
- Webform(内置对象-Response与Redirect、QueryString传值、Repeater删改)
一.内置对象(一)Response - 响应请求对象1.定义:Response对象用于动态响应客户端请示,控制发送给用户的信息,并将动态生成响应.Response对象只提供了一个数据集合cookie, ...
- PlayFramework 1 自定义标签 -- FastTags http://unmi.cc/category/javajee/playframework/
最早是用 HTML 来自定义标签,现在觉得 HTML 写有关逻辑的代码就有点不伦不类了,HTML 里着重是显示代码.前有一篇 PlayFramework 1 模板应用 -- Java 对象扩展 学习 ...
- javascript --- 词法分析
JavaScript代码自上而下执行,但是在js代码执行前,会首先进行词法分析,所以事实上,js运行要分为词法分析和执行两个阶段. 词法分析主要分为三步: 第一步: 分析形参: 第二步: 分析变量声明 ...
- 回车键和button按钮都绑定同一个事件,如何避免按回车的时候button重复点击
保存一个全局变量,用来记录Button的焦点状态 <button onclick="login();" onfocus="window.buttonIsFocuse ...