【Oracle】常用的SQL语句
抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/qiu18359243869/p/9474515.html
提示:dual是一个虚拟表,用来构成select的语法规则,oracle保证dual里面永远只有一条记录。
一、基本操作
--新建表:
create table table1( id varchar(300) primary key, name varchar(200) not null); --插入数据
insert into table1 (id,name) values ('aa','bb'); --更新数据
update table1 set id = 'bb' where id='cc'; --删除数据
delete from table1 where id ='cc'; --清空表数据
--是DDL操作,不产生rollback,速度快,delete操作在删除大数据量时会很慢
truncate table table1; --删除表
drop table table1; --修改表名:
alter table table1 rename to table2; --添加新字段
--alter table 表名 add(字段名 字段类型 默认值 是否为空);
alter table user add(age number(6));
alter table user add (course varchar2(30) default '空' not null); --修改字段
--alter table 表名 modify (字段名 字段类型 默认值 是否为空);
alter table user modify((age number(8)); --修改字段名
--alter table 表名 rename column 列名 to 新列名;
alter table user rename column course to newcourse; -- 删除字段
--alter table 表名 drop column 字段名;
alter table user drop column course; --表数据复制:
insert into table1 (select * from table2); --复制表结构:
create table table1 select * from table2 where 1>1; --复制表结构和数据:
create table table1 select * from table2; --复制指定字段:
create table table1 as select id, name from table2 where 1>1; --条件查询:
select id,name (case gender when 0 then '男' when 1 then ‘女’ end ) gender from table1
--添加主键
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ADD CONSTRAINT PK_NAME PRIMARY KEY(COLUMN_NAME); --添加外键
--有三种形式的外键约束:
--1.普通外键约束(如果存在子表引用父表主键,则无法删除父表记录)
--2.级联外键约束(可删除存在引用的父表记录,而且同时把所有有引用的子表记录也删除)
--3.置空外键约束(可删除存在引用的父表记录,同时将子表中引用该父表主键的外键字段自动设为NULL,但该字段应允许空值) --普通外键
ALTER TABLE T_INVOICE_DETAIL ADD CONSTRAINT FK_INVOICE_ID FOREIGN KEY(INVOICE_ID ) REFERENCES T_INVOICE(ID);
--级联外键
ALTER TABLE T_INVOICE_DETAIL ADD CONSTRAINT FK_INVOICE_ID FOREIGN KEY(INVOICE_ID ) REFERENCES T_INVOICE(ID) ON DELETE CASCADE;
--置空外键
ALTER TABLE T_INVOICE_DETAIL ADD CONSTRAINT FK_INVOICE_ID FOREIGN KEY(INVOICE_ID ) REFERENCES T_INVOICE(ID) ON DELETE SET NULL; --删除主键/外键
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME DROP CONSTRAINT PK_NAME ; --创建序列
create sequence sequence_name
minvalue 1 --最小值
nomaxvalue --不设置最大值(由机器决定),或 根据表字段的值范围设置 maxvalue
maxvalue 999 -- 最大值
start with 1 --从1开始计数,数值可变
increment by 1 --每次加1,数值可变
nocycle --一直累加,不循环;cycle:达到最大值后,将从头开始累加
nocache; --不建缓冲区。 如果建立cache那么系统将自动读取cache值个seq,这样会加快运行速度;如果在单机中使用cache,或者oracle死了,那么下次读取的seq值将不连贯,所以不建议使用cache。 --修改序列
alter sequence sequence_name-- 序列名 也可以更改
minvalue 1
maxvalue 99999999
start with 10
increment by 1
cycle -- 到10000后,从头开始
nocache; --删除序列
drop sequence sequence_name --查询数据库的所有序列
select * from all_sequences; --查询序列的下一个值
SELECT SEQ_NAME.NEXTVAL FROM dual; --修改序列的下个值
----X为正数负数都可以
alter sequence SEQ_NAME increment BY X; --重新将序列的值的增长值设为1
alter sequence SEQ_NAME increment BY 1; --创建索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名1,列名2,......); --删除索引
drop index 索引名; --在数据库中查找表名
select * from user_tables where table_name like 'tablename%'; --查看表的所有索引
select * from all_indexes where table_name = 'tablename'; --查看表的所有索引列
select* from all_ind_columns where table_name = 'tablename';
二、数学函数
--绝对值:abs()
select abs(-2) value from dual; --(2) --取整函数(大):ceil()
select ceil(-2.001) value from dual; --(-2) --取整函数(小):floor()
select floor(-2.001) value from dual; --(-3) --取整函数(截取):trunc()
select trunc(-2.001) value from dual; -- (-2) --四舍五入:round()
select round(1.234564,4) value from dual; --(1.2346) --取平方:Power(m,n)
select power(4,2) value from dual; --(16) --取平方根:SQRT()
select sqrt(16) value from dual; --(4) --取随机数:dbms_random(minvalue,maxvalue)
select dbms_random.value() from dual; (默认是0到1之间)
select dbms_random.value(2,4) value from dual; (2-4之间随机数) --取符号:Sign()
select sign(-3) value from dual; --(-1)
select sign(3) value from dual; --(1) --取集合的最大值:greatest(value)
select greatest(-1,3,5,7,9) value from dual; --(9) --取集合的最小值:least(value)
select least(-1,3,5,7,9) value from dual; --(-1) --处理Null值:nvl(空值,代替值)
select nvl(null,10) value from dual; --(10)
select nvl(score,10) score from student;
三、rownum相关
--rownum小于某个数时可以直接作为查询条件(注意oracle不支持select top)
select * from student where rownum <3; --查询rownum大于某个数值,需要使用子查询,并且rownum需要有别名
select * from(select rownum rn ,id,name from student) where rn>2;
select * from (select rownum rn, student.* from student) where rn >3; --区间查询
select * from (select rownum rn, student.* from student) where rn >3 and rn<6; --排序+前n条
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRUVER d order by drivernumber)t )p where p.rn<10; --排序+区间查询1
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn<9 and p.rn>6; --排序+区间查询2
select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t where rownum<9 )p where p.rn>6;--效率远高于方式一
四、分页查询
假设每页显示10条
1. 不包含排序
--效率低 select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d )p where p.rn<=20 and p.rn>=10; select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d )p where p.rn between 10 and 20; --效率高 select * from (select rownum rn, d.* from DJDRIVER d where rownum<=20 )p where p.rn>=10;
2. 包含排序
--排序+区间查询1(效率低) select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn<=20 and p.rn>=10; select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t )p where p.rn between 10 and 20; --排序+区间查询2(效率高) select * from (select rownum rn, t.* from ( select d.* from DJDRIVER d order by DJDRIVER_DRIVERTIMES)t where rownum<=20 )p where p.rn>=10;
五、时间处理
1. to_char和to_date基本使用
--日期
--年 yyyy yyy yy year
--月 month mm mon month
--日+星期 dd ddd(一年中第几天) dy day
--小时 hh hh24
--分 mi
--秒 ss
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')currenttime,
to_char(sysdate,'yyyy') year,
to_char(sysdate,'mm') month,
to_char(sysdate,'dd') day,
to_char(sysdate,'day') week,
to_char(sysdate,'hh24')hour,
to_char(sysdate,'mi') minute,
to_char(sysdate,'ss') second
from dual;
select to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')currenttime,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'yyyy')year,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'mm')month,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'dd') day,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'day') week,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'day','NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE=American') week, --设置语言
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'hh24')hour,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'mi') minute,
to_char(to_date('2009-07-04 05:02:01','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),'ss') second
from dual;
2. months_between
select months_between(to_date('03-31-2014','MM-DD-YYYY'),to_date('12-31-2013','MM-DD-YYYY')) "MONTHS"
FROM DUAL;
3. next_day
select sysdate today, next_day(sysdate,6) nextweek from dual;
4. 时间区间
-- borrow 为具体的表名
select cardid, borrowdate from borrow where to_date(borrowdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') between
to_date('2014-02-01 00:00:00','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') and
to_date('2014-05-01 00:00:00','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss');
5. interval
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') currenttime,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' year,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalyear,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' month,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalMonth,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' day,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalday,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' hour,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalHour,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' minute,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalMinute,
to_char(sysdate - interval '' second,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') intervalSecond
from dual;
6. add_months
select add_months(sysdate,12) newtime from dual;
7. extract
select extract(month from sysdate) "This Month",
extract(year from add_months(sysdate,36)) " Years" from dual;
六、字符函数
--字符函数
select substr('abcdefg',1,5)substr, --字符串截取
instr('abcdefg','bc') instr, --查找子串 'Hello'||'World' concat, --连接 trim(' wish ') trim, --去前后空格
rtrim('wish ') rtrim, --去后面空格
ltrim(' wish') ltrim, --去前面空格 trim(leading 'w' from 'wish') deleteprefix, --去前缀
trim(trailing 'h' from 'wish') deletetrailing, --去后缀
trim('w' from 'wish') trim1, ascii('A') A1,
ascii('a') A2, --ascii(转换为对应的十进制数)
chr(65) C1,
chr(97) C2, --chr(十进制转对应字符) length('abcdefg') len, --length lower('WISH')lower,
upper('wish')upper,
initcap('wish')initcap, --大小写变换 replace('wish1','','youhappy') replace, --替换 translate('wish1','','y')translate, --转换,对应一位(前面的位数大于等于后面的位数)
translate('wish1','sh1','hy')translate1, concat('','') concat --连接 from dual;
七、to_number
--to_number(expr)
--to_number(expr,format)
--to_number(expr,format,'nls-param') select to_number('')number1, --converts a string to number
trunc(to_number('0123.123'),2) number2,
to_number('120.11','999.99') number3,
to_number('0a','xx') number4, --converts a hex number to decimal
to_number(100000,'xxxxxx') number5 from dual;
八、聚合函数
student表如下:
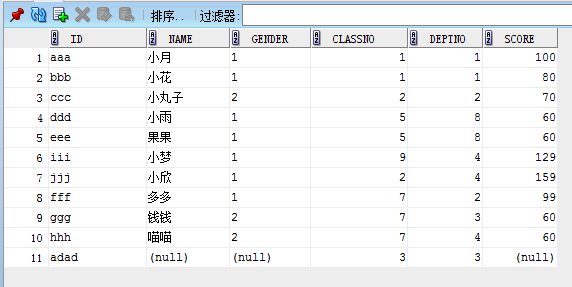
1.count
--count (distinct|all)
select count(1) as count from student;--效率最高
select count(*) as count from student;
select count(distinct score) from student;
2. avg
--avg (distinct|all)
select avg(score) score from student;
select avg(distinct score) from student;
select classno,avg(score) score from student group by classno;
3. max
--max (distinct|all)
select max(score) from student;
select classno, max(score) score from student group by classno;
4. min
--min (distinct|all)
select min(score) from student;
select classno, min(score) score from student group by classno;
5. stddev(standard deviation)标准差
--stddev
select stddev(score) from student;
select classno, stddev(score) score from student group by classno;
6. sum
--sum
select sum(score) from student;
select classno, sum(score) score from student group by classno;
7. median--中位数
--median
select median(score) from student;
select classno, median(score) score from student group by classno;
九、案例演示
【Oracle】常用的SQL语句的更多相关文章
- oracle常用的SQL语句
一些常用的SQL语句: --建表 create table adolph (id number(10,0), name varchar2(20), ...
- oracle 常用select sql语句
本人认为很实用的几条语句 1)select ... from ...into... 2)insert into ...select ... 3)select ...from ...left join ...
- Oracle数据库常用的Sql语句整理
Oracle数据库常用的Sql语句整理 查看当前用户的缺省表空间 : select username,default_tablespace from user_users; 2.查看用户下所有的表 : ...
- 经典SQL语句大全以及50个常用的sql语句
经典SQL语句大全 一.基础 1.说明:创建数据库CREATE DATABASE database-name 2.说明:删除数据库drop database dbname3.说明:备份sql serv ...
- 常用经典SQL语句大全完整版--详解+实例 (存)
常用经典SQL语句大全完整版--详解+实例 转 傻豆儿的博客 http://blog.sina.com.cn/shadou2012 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_84 ...
- 经典SQL语句大全、50个常用的sql语句
50个常用的sql语句 Student(S#,Sname,Sage,Ssex) 学生表 Course(C#,Cname,T#) 课程表 SC(S#,C#,score) 成绩表 Teacher(T#,T ...
- 常用经典SQL语句大全完整版--详解+实例 《来自网络,很全没整理,寄存与此》
常用经典SQL语句大全完整版--详解+实例 下列语句部分是Mssql语句,不可以在access中使用. SQL分类: DDL—数据定义语言(CREATE,ALTER,DROP,DECLARE) DML ...
- MySQL 常用的sql语句小结(待续)
mysql 常用的sql语句 1.查看数据库各个表中的记录数 USE information_schema; SELECT table_name,table_rows FROM tables WHER ...
- SQL Server中常用的SQL语句(转):
SQL Server中常用的SQL语句 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/rainman/archive/2013/05/04/3060428.html 1.概述 名词 笛卡尔积.主 ...
- 说说oracle分页的sql语句
说说oracle分页的sql语句,分排序和不排序两种. 当结果集不需要进行排序时,每页显示条数为:rowPerPage,当前页数为:currentPage. 1. 相对来说,这种查询速度会快一些,因为 ...
随机推荐
- ArcGIS API for JavaScript小白入门
简单理解就是:通过js调用arcgis相关的方法和通过html引入css等资源来展示地图,代码如下: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> & ...
- FAQ: Oracle Flex ASM 12c / 12.1 (Doc ID 1573137.1)
FAQ: Oracle Flex ASM 12c / 12.1 (Doc ID 1573137.1) APPLIES TO: Oracle Database - Enterprise Edition ...
- django之跨站请求伪造csrf
目录 跨站请求伪造 csrf 钓鱼网站 模拟实现 针对form表单 ajax请求 csrf相关的两个装饰器 跨站请求伪造 csrf 钓鱼网站 就类似于你搭建了一个跟银行一模一样的web页面 , 用户在 ...
- 【转载】解决:'webpack-dev-server' 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序 或批处理文件。
注:网上能搜到的常规解决办法我都试了不好用,这个是最快的解决办法. 以下是转载的解决办法: ****************************************************** ...
- CG-CTF SQL注入
SQL注入1 题目 访问题目网址 先查看一下源码 仔细分析一下核心源码 <?php if($_POST[user] && $_POST[pass]) { //判断user和pas ...
- RabbitMQ基础理解
RabbitMQ基本理解 MQ是消息中间件,常见的有RabbitMQ,Kafka,RocketMQ,activeMQ 等,用于分布式系统中.作用有三点 解耦 异步 削峰 RabbitMQ 整体上是一个 ...
- cordova+vue混合式开发App
应要求第一次使用cordova打包了一下vue写的app项目,期间遇到了不少问题,整理一下流程并记录一下常见问题吧. cordova打包项目需要的环境配置啥的就不具体讲啦,百度一下很多教 ...
- mysql5.7中timestam默认值'0000-00-00 00:00:00'报错
在mysql5.7中设置 timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00'会报错: 解决办法: mysql> set sql_mode='NO_A ...
- Think in Java 笔记(chapter1-7)
Content Chapter 1:对象导论 Chapter 2:一切都是对象 Chapter 3:操作符 Chapter 4:控制执行流程 Chapter 5:初始化与清理 Chapter 6:访问 ...
- java之Set接口(单列集合)
Set接口概述 java.util.Set 接口和 java.util.List 接口一样,同样继承自 Collection 接口,它与 Collection 接口中的方法基本一致,并没有对 Coll ...
