Word List 1
前言
图片均来源网络
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.1 Super computer
- 1.2 Mainframe
- 1.3 Server
- 1.4 Desktop PC
- 1.5 Notebook or Laptop PC
- 1.6 Game device
- 1.7 Smart Phone
- 1.8 Terminal
- 2.1 Cluster
- 2.2 Load balancing
- 2.3 Cache
- 2.4 BIOS
- 2.5 System Bus
- 3.1 GPU
- 3.2 CPU
- 3.3 System or Mother Board
- 3.4 Power supply
- 3.5 SDRAM
- 3.6 Hard Drive
- 3.7 Solid State Drive
- 3.8 Computer Case
- 3.9 Optical Disks
- 3.9. 1 CD
- 3.9.2 DVD
- 3.9.3 Blu-ray
- 4.1 Mega, Giga, Tera, Peta, ExaByte
- 4.2 Mega, Giga, TeraHertz
- 4.3 R.P.M. (Hard drive)
- 5.1 USB
- 5.2 Firewire
- 5.3 Thunderbolt
- 5.4 HDMI
- 5.5 DisplayPort
- 6.1 Mouse
- 6.2 Monitor
- 6.3 Touch Screen
- 6.4 Keyboard
- 参考资料
1.1 Super computer
超级计算机

- the world’s largest and fastest computers;
- used for complex scientific calculations, provide researchers with insight into phenomena to observe in laboratories;
- compare to a desktop computer: they both contain hard drives, memory, and processors. But their speed and memory sizes are different;
- large number of processors, enormous disk storage, and substantial memory;
- powerful and high speed.
1.2 Mainframe
服务器,主机

- Prior to the advent of the personal computer or PC, the minicomputer, and the microcomputer, the term “computer” simply referred to mainframes.
- a large powerful and high-speed computer;
- the centre of a network.
- the central processing unit and primary memory of a computer.
- supporting numerous workstations or peripherals(shared by many users or can be used by many people at the same time or thousands of individual users can log in simultaneously from a variety of sources or control many tasks being run by many users simultaneously);
- can do very large or complicated tasks;
- What differentiates the modern mainframe from these other classes of computers is the scope of the processing taking place. The typical mainframe today serves tens of thousands of users processing thousands of transactions every second while maintaining centralized terabyte -size databases. Even the mighty supercomputer, although unquestionably faster doing one thing at a time, is not up to this task.
1.3 Server
服务器

- A system on a network that provides a service to other systems connected to the network.
- The term was originally restricted to the case where both the server and the systems it served were on the same local area network, and where the server was likely to be expensive in comparison with the systems it served.
- The term is now used much more generally, applying to systems where the server and the system to which it provides a service (the client) may be linked by a metropolitan area network or wide area network, and where the server may be much less costly than the client.
1.4 Desktop PC
台式电脑

- An entire computer that sits on a desk or table.
- It usually consists of: a display, either color or monochrome; a system box containing the processor, memory, disk drives, power supply, and communication interfaces; a keyboard; a pointing device, often a mouse.
- Although the desktop computer is relatively cumbersome compared with a notebook computer of equivalent power, it currently has a significantly better power/performance ratio.
- Part of a graphical user interface which invites the user to imagine that some or all of the screen is an actual desktop on which actions analogous to those occurring on a physical desktop can be carried out. These include the opening and closing of folders, the entry and modification of text, the disposal of unwanted material into a wastebasket, and the use of communication systems analogous to telephones and mailboxes. The analogy is supposed to make life easier for office workers unused to computers.
1.5 Notebook or Laptop PC
笔记本电脑

- A computer about the size of a piece of A4 paper and a few cm thick with a hinge along the long side.
- When opened up, a full-sized keyboard and monochrome or color LCD screen are revealed. Notebooks can have all the processing power and features of desktop computers.
- To increase their flexibility the pointing device is often a trackerball embedded in the keyboard rather than a mouse, which requires a hard flat surface to operate successfully.
1.6 Game device
游戏设备

1.7 Smart Phone
智能手机

- A smart phone is a type of mobile phone that can perform many of the operations that a computer does, such as accessing the Internet.
1.8 Terminal
终端

Generally, a terminal is a combination of keyboard and display screen.
A device that enables you to communicate with a computer.
In networking, a terminal is a personal computer or workstation
connected to a mainframe. The personal computer usually runs terminal
emulation software that makes the mainframe think it is like any other
mainframe terminal.
In VoIP terminology, a network endpoint which may provide audio only,
audio and video, audio and data, or audio, video, and data
communications with another terminal. The most common VoIP terminal is a
phone.
2.1 Cluster
簇,集群
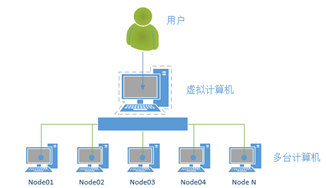
文件占用磁盘空间,基本单位不是字节而是簇。一般情况下,软盘每簇是1个扇区(扇区sector),硬盘每簇的扇区数与硬盘的总容量大小有关。
计算机集群Cluster,可以把多台计算机连接在一起使用,平分资源或互为保障。一个计算机集群是指一组连接起来的电脑,它们共同工作对外界来说就像一个电脑一样。集群一般由局域网连接,但也有例外。
集群一般用于单个电脑无法完成的高性能计算,拥有较高的性价比。集群就是由一些互相连接在一起的计算机构成的一个并行或分布式系统,从外部来看,它们仅仅是一个系统,对外提供统一的服务。
2.2 Load balancing
负载均衡
For larger number of users, load balancing and server clustering techniques are unavoidable.
对于更大数量的用户,负载均衡和服务器集群技术就在所难免了。
Acceleration: Understand the different load balancing algorithm options and content caching.
加速:理解不同的负载平衡算法选项和内容缓存。
The pattern also includes policies for configuring dynamically scaled server provisioning, load balancing, and caching.
该模式还包括对动态缩放的服务器配置、负载均衡和缓存进行配置的策略。
2.3 Cache
高速缓冲存储器
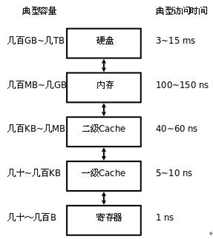
通常由SRAM组成
- a part of a computer’s memory that stores copies of data that is often needed while a program is running;
- used for temporary storage of data;
- can be accessed more quickly than the main memory.
2.4 BIOS
基本输入输出系统 Basic Input Output System
- BIOS is an acronym for basic input/output system(responsible for performing input and output operations when so directed)
- the built-in software(firmware permanently resident in microcomputer systems)
- determines what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk
- an important part of any computer system
- On personal computers (PCs), the BIOS contains all the code required
to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial
communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions. - The BIOS is typically placed in a ROM chip that comes with the computer (it is often called a ROM BIOS).
- This ensures that the BIOS will always be available and will not be damaged by disk failures.
- It also makes it possible for a computer to boot itself.
- RAM is faster than ROM, though, many computer manufacturers design
systems so that the BIOS is copied from ROM to RAM each time the
computer is booted. This is known as shadowing. - The BIOS is usually called from the operating system, but can be
called directly from applications. Calling the BIOS directly can result
in performance gains and loss of portability. - BIOS is typically stored in a flash memory device on the system’s
motherboard. Most new computers have a BIOS that allows you to boot the
machine using a DHCP server.
Many modern PCs have a flash BIOS, which means that the BIOS has been
recorded on a flash memory chip, which can be updated if necessary.
2.5 System Bus
系统总线
- works by combining the functions of the three main buses: namely,
the data, address and control buses. Each of the three buses has its
separate characteristics and responsibilities; - a pathway composed of cables and connectors used to carry data between a computer microprocessor and the main memory;
- provides a communication path for the data and control signals moving between the major components of the computer system.
3.1 GPU
图形处理器 Graphics Processing Unit

图形处理器(英语:Graphics Processing Unit,缩写:GPU),又称显示核心、视觉处理器、显示芯片,是显卡的处理器,是一种专门在个人电脑、工作站、游戏机和一些移动设备(如平板电脑、智能手机等)上图像运算工作的微处理器。
用途是将计算机系统所需要的显示信息进行转换驱动,并向显示器提供行扫描信号,控制显示器的正确显示,是连接显示器和个人电脑主板的重要元件,也是“人机对话”的重要设备之一。显卡作为电脑主机里的一个重要组成部分,承担输出显示图形的任务,对于从事专业图形设计的人来说显卡非常重要。
3.2 CPU
中央处理器central processing unit
- the part of a computer that controls all the other parts of the system;
- processes all the data and makes the computer work.
3.3 System or Mother Board
系统板,主板

- a piece of computer hardware
- the “backbone” of the PC(the “mother” that holds all the pieces
together or serves to connect all of the parts of a computer together) - The CPU, memory, hard drives, and other ports and expansion cards all connect to the motherboard directly or via cables.
3.4 Power supply
电源

- Also called a power supply unit or PSU;
- the component that supplies power to a computer.
3.5 SDRAM
同步动态随机存取内存 synchronous dynamic random-access memory

A type of DRAM that can run at much higher clock speeds than conventional memory.
SDRAM actually synchronizes itself with the CPU’s bus and is capable
of running about three times faster than conventional FPM RAM, and about
twice as fast EDO DRAM and BEDO DRAM. SDRAM is replacing EDO DRAM in
many newer computers.SDRAM是有一个同步接口的动态随机存取内存。通常DRAM是有一个异步接口的,这样它可以随时响应控制输入的变化。而SDRAM有一个同步接口,在响应控制输入前会等待一个时钟信号,这样就能和计算机的系统总线同步。时钟被用来驱动一个有限状态机,对进入的指令进行管线(Pipeline)操作。
DRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory),即动态随机存取存储器,最为常见的系统内存。DRAM
只能将数据保持很短的时间。为了保持数据,DRAM使用电容存储,所以必须隔一段时间刷新(refresh)一次,如果存储单元没有被刷新,存储的信息就会丢失。
(关机就会丢失数据)RAM系统内存。是随机存取存储器 (random-access memory) 的缩写,它是系统临时存储程序指令和数据的主要区域。ram 中的每个位置均由一个称为内存地址的号码标识。关闭系统后,ram 中保存的任何数据均会丢失。
3.6 Hard Drive
硬盘驱动器 hard disk drive,HDD

- A part of a computer
- Reads data on a hard disk where you can store your entire CD collection.
- Hard disk:
- Rigid magnetic disk for storing computer programs and data. A
built-in hard disk drive in a typical personal computer consists of a
number of hard platters, coated with a magnetic material set on a common
spindle. They are housed inside a sealed container, with a motor to
spin the stack of platters, a head to write (record) and read (replay)
each side of each platter, and associated electronic circuits. Hard disk
capacity is continually being increased.
- Rigid magnetic disk for storing computer programs and data. A
3.7 Solid State Drive
固态驱动器,固态硬盘

Comparison of the inside of a hard disk drive (HDD) versus a solid-state
drive (SSD), which has no moving parts for quieter and more reliable
operation.
3.8 Computer Case
机箱

3.9 Optical Disks
光盘(CD,DVD, Blu-ray)
- A storage medium from which data is read and to which it is written by lasers.
- Optical disks can store much more data than most portable magnetic media, such as floppies.
- There are three basic types of optical disks:CD-ROM /WORM
/erasable.These three technologies are not compatible with one another;
each requires a different type of disk drive and disk. Even within one
category, there are many competing formats, although CD-ROMs are
relatively standardized.
3.9. 1 CD

3.9.2 DVD

3.9.3 Blu-ray
蓝光格式的光驱
- An HD-DVD format that uses blue-violet laser technology.
- The rewritable Blu-ray disc, with a data transfer rate of 36Mbps,
can hold up to 27GBof data on a single-sided single layer disc (compared
to the traditional DVD 4.7GB capacity), which amounts to about 12 hours
of standard video or more than 2 hours of high-definition video.
4.1 Mega, Giga, Tera, Peta, ExaByte
Mega 兆
In binary systems, mega stands for 2 to the 20th power, or 1,048,576.
One megabyte, therefore, is 1,048,576 bytes(this is equivalent to 1,024K)
Giga 千兆
When applied to computers, which use the binary notation system, giga
represents 2 to the 30th power, which is 1,073,741,824, a little more
than 1 billion. A gigabyte, therefore, is about 1.073 billion bytes.
terabyte兆兆字节
2 to the 40th power (1,099,511,627,776) bytes. This is approximately 1 trillion bytes. Terabyte is abbreviated as TB.
petabyte
Enterprise storage systems are starting to leave the terabyte behind,
moving into petabytes and toward the exabyte stage. A petabyte (PB) is
1015 bytes of data, 1,000 terabytes (TB) or 1,000,000 gigabytes (GB).
4.2 Mega, Giga, TeraHertz
Mega 兆
In decimal systems, the prefix mega means one million
One megabyte, therefore, is 1,000,000
Giga 千兆
When decimal notation is used, giga stands for 10 to the 9th power. For example, a gigavolt is 1,000,000,000 volts.
TeraHertz 兆赫
4.3 R.P.M. (Hard drive)
每分钟转数
5.1 USB
Universal Serial Bus

- An external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps.
- A single USB port can be used to connect peripheral devices, such as mice, modems, and keyboards.
- USB also supports Plug-and-Play installation and hot plugging.
5.2 Firewire
火线

- Known as IEEE1394 and, on computers produced by Sony, as iLink.
- A high-speed, general purpose serial bus supporting a chain of up to 63 devices.
- Operating at a speed of up to 400Mbps it has, to a large degree, been overtaken by USB, which can operate at up to 480 Mbps.
- Still the main system used for transfer of video between computers
and digital camcorders and some external disk drives also use this
interface.
5.3 Thunderbolt
雷电接口

- Designed to connect high-performance peripherals and HD video
displays via a single port using two communications methods, or
protocols, PCI Express for data transfer and DisplayPort for displays. - Data transfer rates provided by thunderbolt is 20 times faster than the USB 2.0 standard and 12 times faster than FireWire 800.
- With Thunderbolt, you can also daisy-chain up to six devices,
including a display, without the need for a hub, and also provides 10
watts of power to peripherals.
5.4 HDMI
高清多媒体接口 High-Definition Multimedia Interface

- The first industry-supported uncompressed, all-digital audio/video proprietary interface.
- It is a single cable and user-friendly connector that replaces the maze of cabling behind the home entertainment center.
- Provides an interface between any audio/video source, such as a
set-top box, DVD player, or A/V receiver and an audio and/or video
monitor, such as a digital television (DTV), over a single cable. - HDMI supports standard, enhanced, or high-definition video, plus multi-channel digital audio on a single cable.
- It transmits all ATSC HDTV standards and supports 8-channel digital
audio with bandwidth to spare to accommodate future enhancements and
requirements. - HDMI was defined to carry 8 channels, of 192kHz, 24-bit uncompressed audio, which exceeds all current consumer media formats.
- HDMI can carry any flavor of compressed audio format such as Dolby or DTS.
- HDMI has the capacity to support existing high-definition video
formats such as 720p, 1080i, and 1080p, along with support of enhanced
definition formats like 480p, as well as standard definition formats
such as NTSC or PAL.
5.5 DisplayPort
显示端口

- DisplayPort (DP) is an audio/video (A/V) display interface used to connect a video source to a display device.
- You can connect a computer monitor to the PC using the DisplayPort.
- DisplayPort primarily replaces older interface technologies, including VGA and DVI.
- The interface is typically found on tablets, notebooks, and desktop
computers and monitors. The display interface is also included on some
digital televisions but is more often associated with devices related to
computing and digital consumer electronics (CE).
6.1 Mouse
鼠标

- A device that controls the movement of the cursor or pointer on a display screen.
- A small object you can roll along a hard, flat surface. Its name is
derived from its shape, which looks a bit like a mouse, its connecting
wire that one can imagine to be the mouse’s tail, and the fact that one
must make it scurry along a surface. As you move the mouse, the pointer
on the display screen moves in the same direction.
6.2 Monitor
显示屏

a television screen used to show particular kinds of information; a screen that shows information from a computer。
6.3 Touch Screen
触摸屏

a computer screen which allows you to give instructions to the computer by touching areas on it.
6.4 Keyboard
键盘

A keyboard is defined as the
set of typewriter-like keys that enables you to enter data into a
computer or other devices. Computer keyboards are similar to
electric-typewriters but contain additional typing keys.
参考资料
柯林斯词典
牛津词典
ENCYCLopedia.com[https://www.encyclopedia.com/science-and-technology/computers-and-electrical-engineering/computers-and-computing]
webopedia.com[https://www.webopedia.com/TERM]
techopedia.com[https://www.techopedia.com/definition/2307]
Word List 1的更多相关文章
- Word/Excel 在线预览
前言 近日项目中做到一个功能,需要上传附件后能够在线预览.之前也没做过这类似的,于是乎就查找了相关资料,.net实现Office文件预览大概有这几种方式: ① 使用Microsoft的Office组件 ...
- C#中5步完成word文档打印的方法
在日常工作中,我们可能常常需要打印各种文件资料,比如word文档.对于编程员,应用程序中文档的打印是一项非常重要的功能,也一直是一个非常复杂的工作.特别是提到Web打印,这的确会很棘手.一般如果要想选 ...
- C# 给word文档添加水印
和PDF一样,在word中,水印也分为图片水印和文本水印,给文档添加图片水印可以使文档变得更为美观,更具有吸引力.文本水印则可以保护文档,提醒别人该文档是受版权保护的,不能随意抄袭.前面我分享了如何给 ...
- 获取打开的Word文档
using Word = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word; int _getApplicationErrorCount=0; bool _isMsOffice = true ...
- How to accept Track changes in Microsoft Word 2010?
"Track changes" is wonderful and remarkable tool of Microsoft Word 2010. The feature allow ...
- C#将Word转换成PDF方法总结(基于Office和WPS两种方案)
有时候,我们需要在线上预览word文档,当然我们可以用NPOI抽出Word中的文字和表格,然后显示到网页上面,但是这样会丢失掉Word中原有的格式和图片.一个比较好的办法就是将word转换成pdf,然 ...
- 开源Word读写组件DocX 的深入研究和问题总结
一. 前言 前两天看到了asxinyu大神的[原创]开源Word读写组件DocX介绍与入门,正好我也有类似的自动生成word文档得需求,于是便仔细的研究了这个DocX. 我也把它融入到我的项目当中并进 ...
- [.NET] 开头不讲"Hello Word",读尽诗书也枉然 : Word 操作组件介绍 - Spire.Doc
开头不讲"Hello Word",读尽诗书也枉然 : Word 操作组件介绍 - Spire.Doc [博主]反骨仔 [原文地址]http://www.cnblogs.com/li ...
- C# Word中设置/更改文本方向
C# Word中设置/更改文本方向 一般情况下在Word中输入的文字都是横向的,今天给大家分享两种方法来设置/更改一个section内的所有文本的方向及部分文本的方向,有兴趣的朋友可以试下. 首先,从 ...
- C# 合并及拆分Word文档
本文简要分析一下如何如何使用C#简单实现合并和拆分word文档.平时我们在处理多个word文档时,可能会想要将两个文档合并为一个,或者是将某个文档的一部分添加到另一个文档中,有的时候也会想要将文档拆分 ...
随机推荐
- PMBOK 指南 第二章 项目运行环境
2.1概述 事业环境因素(EEF)源于项目外部(往往企业外部) 组织过程资产(OPA)源于企业内部 2.2 事业环境因素 项目团队不能控制 2.2.1 组织内部的事业环境因素 组织文化.结构和治理 设 ...
- python-基础r/R、b、u/U含义
1.r/R,代表非转义的原始字符串,一般使用在正则表达式和win目录上 2.b“” 代表b后面的内容为bytes类型 3.u/U 表示对字符串进行unicode编码,一般使用在有中午的地方,防止乱码.
- UE4入门学习笔记开篇
做了3年的Unity, 现在开始转入到做UE4,一来就进入一个超大项目组中学习,度过了最初2个月的生涩和紧张后,现在准备开始慢慢总结,慢慢学习,逐步深入理解和研究UE. 做了3年的游戏开发后,个人感悟 ...
- 【zabbix部署】基于linux安装zabbix监控服务和被监控服务
环境配置 zabbix_server:10.0.0.1 zabbix_agentd:10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2(暂定) 操作系统:centos7.6 安装环境配置 1. LNMP环境 zabb ...
- 使用vue脚手架快速创建vue项目(入门)
1.安装环境 为了方便,以下操作大多数中命令行中运行,window可以用cmd,powershell,gitbash等. 安装node.js 打开它的官网,或者中文网站,然后直接下载就可以了,然后跟安 ...
- 如何判断IE OCX插件正常安装?
项目中用到了一个第三方的ie ocx控件,而经常遇到客户和测试小伙伴反馈相关功能无法正常使用,也没有友好提示.考虑到这个问题,必须要有一个ie ocx控件的检查机制. 检查原理 创建ActiveXOb ...
- Redisson基本用法
1. Redisson Redisson是Redis官方推荐的Java版的Redis客户端.它提供的功能非常多,也非常强大,此处我们只用它的分布式锁功能. https://github.com/re ...
- node.js安装本地模块遇到的目录锁定问题【新手问题】
昨天发过文字版的,后来以为问题没解决就删除,今天偷个懒,直接上图. 被书中的介绍给误导了,虽然和书中不一样,但实际上自己练习写的模块已经是可用了.也犯了个常识性的错误:Warn一般不会有太大的影响.
- Larave中CSRF攻击
1.什么是CSRF攻击? CSRF是跨站请求伪造(Cross-site request forgery)的英文缩写\ Laravel框架中避免CSRF攻击很简单 ...
- vmware vsphere client 虚拟机动态添加磁盘
0x00 事件 为了在虚拟机添加了磁盘之后,不重启机器加载新磁盘. 如上图,添加了一块 10G 的磁盘之后. 在虚拟机中是看不到新添加的磁盘: 0x01 解决 运行如下命令,通过重新扫描 SCSI ( ...
