什么是pytorch(3神经网络)(翻译)
神经网络
torch.nn 包可以用来构建神经网络。
前面介绍了 autograd包, nn 依赖于 autograd 用于定义和求导模型。 nn.Module 包括layers(神经网络层), 以及forward函数 forward(input),其返回结果 output.
例如我们来看一个手写数字的网络:
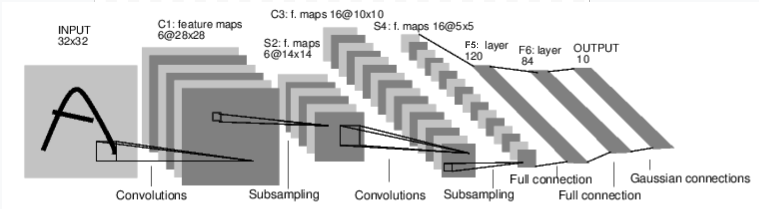
卷积神经网络
这是一个简单的前馈神经网络。接受输入,向前传几层,然后输出结果。
一个神经网络训练的简单过程是:
- 定义一个具有可学习参数的神经网络。
- 输入数据集迭代
- 网络运算数据输入的计算结果
- 计算损失 (how far is the output from being correct)
- 传播梯度
- 跟新权值,通常可以简单的使用梯度下降:
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
定义网络
先来顶一个网络:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution
# kernel
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) def forward(self, x):
# Max pooling over a (2, 2) window
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# If the size is a square you can only specify a single number
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:] # all dimensions except the batch dimension
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features net = Net()
print(net)
Out:
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
你只需要定义前向传播函数 forward , 后向传播函数 backward (梯度的计算) 就会使用autograd自动定义。你可以在forward函数里使用任何Tensor的运算。
网络的学习到的参数可以通过net.parameters()获取。
params = list(net.parameters())
print(len(params))
print(params[0].size()) # conv1's .weight
输出:
10
torch.Size([6, 1, 5, 5])
让我们随机输入一个 32x32 的数据。Note: Expected input size to this net(LeNet) is 32x32.
要把MNIST dataset作为该网络的数据集,需要把数据 resize到32x32.
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32)
out = net(input)
print(out)
输出:
tensor([[ 0.1246, -0.0511, 0.0235, 0.1766, -0.0359, -0.0334, 0.1161, 0.0534,
0.0282, -0.0202]], grad_fn=<ThAddmmBackward>)
使所有参数的梯度恢复为0,然后使用随机梯度后向传播:
net.zero_grad()
out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10))
注意:
torch.nn 只支持mini-batches. 整个 torch.nn 包只接受批样本,不接受单个样本。
例如, nn.Conv2d 接受一个4D的张量形如: nSamples x nChannels x Height x Width.
如果你只有一个样本,那就使用 input.unsqueeze(0) 创造一个假的mini-batch。
在进一步之前,我们来回顾目前你所见到的所有类。
- 回顾:
-
torch.Tensor- 一个多维度的数组,支持自动梯度backward()。其梯度任然保存在张量里。nn.Module- 神经网络模型。方便的封装参数,可以导出模型到GPU,加载模型,导出模型等。nn.Parameter- 一种张量, 自动注册为paramter当赋给Module作为属性。autograd.Function- 实现 forward and backward 的定义,包括autograd. EveryTensoroperation, creates at least a singleFunctionnode, that connects to functions that created aTensorand encodes its history.
- 到此, 我们覆盖了:
-
- 定义一个网络
- 处理输入和反向传播。
- 剩余的内容:
-
- 计算损失
- 更新网络的参数
损失函数
一个损失函数接受(output,targe)对作为输入,计算output和target相差的程度。
nn包里有多种不同的 loss functions 。最简单的损失函数是: nn.MSELoss ,计算(output,target)间的均方误差损失函数。
For example:
output = net(input)
target = torch.randn(10) # a dummy target, for example
target = target.view(1, -1) # make it the same shape as output
criterion = nn.MSELoss() loss = criterion(output, target)
print(loss)
输出:
tensor(1.3638, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
Now, if you follow loss in the backward direction, using its .grad_fn attribute, you will see a graph of computations that looks like this:
input -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d
-> view -> linear -> relu -> linear -> relu -> linear
-> MSELoss
-> loss
现在我们使用 loss.backward(),就会被 loss所微分, 所有计算图里参数属性为 requires_grad=True 将会使 .grad Tensor 和gradient累加起来。
For illustration, let us follow a few steps backward:
print(loss.grad_fn) # MSELoss
print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0]) # Linear
print(loss.grad_fn.next_functions[0][0].next_functions[0][0]) # ReLU
Out:
<MseLossBackward object at 0x7f0e86396a90>
<ThAddmmBackward object at 0x7f0e863967b8>
<ExpandBackward object at 0x7f0e863967b8>
反向传播
为了反向传播误差,我们必须使用loss.backward(). 首先需要清除已存在的梯度,然后把梯度累加起来。
现在我们就可以调用:loss.backward(), 我们来看看 conv1’s bias gradients 在反向传播前后。
net.zero_grad() # zeroes the gradient buffers of all parameters
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
loss.backward()
print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')
print(net.conv1.bias.grad)
输出:
conv1.bias.grad before backward
tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
conv1.bias.grad after backward
tensor([ 0.0181, -0.0048, -0.0229, -0.0138, -0.0088, -0.0107])
现在,我们来看如何使用损失函数。
进一步阅读:
nn包包括了各种类型的模型和损失函数,可以用来构建深度神经网络的block,详细参阅nn的文档:here.
最后一步需要学习的是:
- 跟新网络的参数
跟新权重Update the weights
最简单方式就是使用随机梯度下降(SGD):
weight = weight - learning_rate * gradient
可以使用以下代码:
learning_rate = 0.01
for f in net.parameters():
f.data.sub_(f.grad.data * learning_rate)
神经网络里可以使用各种跟新权重的方法, 比如:SGD, Nesterov-SGD, Adam, RMSProp, etc等,为了使用这些方法,有一个小包 : torch.optim 实现了这些方法。
用起来非常的容易:
import torch.optim as optim # create your optimizer
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) # in your training loop:
optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers
output = net(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() # Does the update
注意:
使用optimizer.zero_grad()把网络的参数梯度手动设置为0.前面在Backprop说了,梯度会累加起来的。
什么是pytorch(3神经网络)(翻译)的更多相关文章
- 使用pytorch构建神经网络的流程以及一些问题
使用PyTorch构建神经网络十分的简单,下面是我总结的PyTorch构建神经网络的一般过程以及我在学习当中遇到的一些问题,期望对你有所帮助. PyTorch构建神经网络的一般过程 下面的程序是PyT ...
- 使用PyTorch构建神经网络以及反向传播计算
使用PyTorch构建神经网络以及反向传播计算 前一段时间南京出现了疫情,大概原因是因为境外飞机清洁处理不恰当,导致清理人员感染.话说国外一天不消停,国内就得一直严防死守.沈阳出现了一例感染人员,我在 ...
- 基于 PyTorch 和神经网络给 GirlFriend 制作漫画风头像
摘要:本文中我们介绍的 AnimeGAN 就是 GitHub 上一款爆火的二次元漫画风格迁移工具,可以实现快速的动画风格迁移. 本文分享自华为云社区<AnimeGANv2 照片动漫化:如何基于 ...
- Pytorch循环神经网络LSTM时间序列预测风速
#时间序列预测分析就是利用过去一段时间内某事件时间的特征来预测未来一段时间内该事件的特征.这是一类相对比较复杂的预测建模问题,和回归分析模型的预测不同,时间序列模型是依赖于事件发生的先后顺序的,同样大 ...
- Pytorch卷积神经网络识别手写数字集
卷积神经网络目前被广泛地用在图片识别上, 已经有层出不穷的应用, 如果你对卷积神经网络充满好奇心,这里为你带来pytorch实现cnn一些入门的教程代码 #首先导入包 import torchfrom ...
- 基于PyTorch的Seq2Seq翻译模型详细注释介绍(一)
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明.本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qysh123/article/detai ...
- pytorch 孪生神经网络DNN
代码内容请见: https://github.com/LiuXinyu12378/DNN-network
- 什么是pytorch(2Autograd:自动求导)(翻译)
Autograd: 自动求导 pyTorch里神经网络能够训练就是靠autograd包.我们来看下这个包,然后我们使用它来训练我们的第一个神经网络. autograd 包提供了对张量的所有运算自动求导 ...
- python日记:用pytorch搭建一个简单的神经网络
最近在学习pytorch框架,给大家分享一个最最最最基本的用pytorch搭建神经网络并且训练的方法.本人是第一次写这种分享文章,希望对初学pytorch的朋友有所帮助! 一.任务 首先说下我们要搭建 ...
- PyTorch 1.4 中文文档校对活动正式启动 | ApacheCN
一如既往,PyTorch 1.4 中文文档校对活动启动了! 认领须知 请您勇敢地去翻译和改进翻译.虽然我们追求卓越,但我们并不要求您做到十全十美,因此请不要担心因为翻译上犯错--在大部分情况下,我们的 ...
随机推荐
- 个人爱好:idea 项目结构呈现风格
- ARM内核版本号和SOC版本号
原博:https://blog.csdn.net/wxywxywxy110/article/details/78764988 内核版本号 SoC版本号 ...
- angular 2 animation 结构笔记 version 4.2.2
import { Component, Input, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { trigger, state, style, animate, t ...
- laravel 实现增 与查
//调用模型层 <?phpnamespace App;use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Mod ...
- 多线程thread的使用
1.thread是多线程,凡是thread的子类都是一个线程. 2.thread必须调用start方法进开启线程,不能直接调用Runnable中的run方法,因为直接调用run方法没有创建新的线程,就 ...
- systemctl用法及其语法
1.确定是否安装systemd及其版本 # systemctl –version 2.确定systemd和systemctl的二进制文件和库文件的安装位置 # whereis systemd # wh ...
- 【转】react入门实例教程
作者: 阮一峰 日期: 2015年3月31日 写在前面:原文链接http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/03/react.html github地址https:/ ...
- Samba服务与Nginx服务
Samba服务: 1 准备环境 =====>part1: iptables -F 清楚防火墙配置 #systemctl disable firewalld #开机默认关闭 #systemctl ...
- vue-vuex状态管理-1
export default vuex.Store{ State, //数据库. getters,// 是我们从数据库里取数据的 API,getters 得是一个”纯函数“ actions,//处理数 ...
- js--------1.时间
//获取当前时间 yyyy-MM-dd function getNowFormatDate() { var date = new Date(); var seperator1 = "-&qu ...
