算法练习LeetCode初级算法之链表
删除链表中的节点

|
/** |
|
* Definition for singly-linked list. |
|
* public class ListNode { |
|
* int val; |
|
* ListNode next; |
|
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; } |
|
* } |
|
*/ |
|
class Solution { |
|
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) { |
|
node.val=node.next.val; |
|
node.next=node.next.next; |
|
} |
|
} |
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
两次遍历算法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy.next=head;
int length=0;
ListNode p=head;
while (p!=null) {
length++;
p=p.next;
}
ListNode first=dummy;
length-=n;
while (length>0) {
length--;
first=first.next;
}
first.next=first.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
一次遍历算法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = dummy;
ListNode second = dummy;
// Advances first pointer so that the gap between first and second is n nodes apart
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
first = first.next;
}
// Move first to the end, maintaining the gap
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
反转链表
我的解法:利用Linklist比较好理解,有点投机取巧,面试不一定可以得吧!!!哈哈哈,但是测试通过了
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
x.val=list.removeLast();
}
return head;
}
}
迭代法,一开始不好理解,仔细琢磨后还是很好理解的
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=null;
while (head!=null) {
ListNode temp=head.next;//先把后面的数据储存到temp
head.next=newHead;//把head添加到newHead
newHead=head;//把head添加到newHead,newHead重新作为新的头指针
head=temp;//让头指针指向下一个数据,已保存在temp里
}
return newHead;
}
}
递归法,仔细研究后还是可以理解的
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return newHead(head);
}
public ListNode newHead(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=newHead(head.next);
head.next.next=head;//反转链表,把把下一个数连接到newHead上
head.next=null;//指向空,防止再次递归导致覆盖后面的内容。
return newHead;
}
}
以上两种方法,通过从网站学习理解,必须站在巨人的肩膀上,哈哈哈!
注明学习网址:https://blog.csdn.net/fx677588/article/details/72357389,虽然不是转载,但有借鉴。
合并两个有序链表
我的解法:很好实现,思路简单,但耗时长一点
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=l1;x!=null;x=x.next)
{
list.add(x.val);
}
for(ListNode x=l2;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
Collections.sort(list);
ListNode head=null;
for (int i = list.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ListNode n=new ListNode(list.get(i));
n.next=head;
head=n;
}
return head;
}
}
大神一解法,递归解法,代码简洁
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode rspHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode rsp=rspHead;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
rspHead.next=l1;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l1=l1.next;
}else{
rspHead.next=l2;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(l1==null){
rspHead.next=l2;
}else{
rspHead.next=l1;
}
return rsp.next;
}
}
大神二解法,利用双指针,现将带头链表头指针用rsp保存,最后返回rsp.next
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode rspHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode rsp=rspHead;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
rspHead.next=l1;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l1=l1.next;
}else{
rspHead.next=l2;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(l1==null){
rspHead.next=l2;
}else{
rspHead.next=l1;
}
return rsp.next;
}
}
回文链表
我的解法:感觉已经脱离了链表,不行,不好,时间太长!
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size()/2; i++) {
if (list.get(i).compareTo(list.get(list.size()-i-1))!=0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
大神解法:挺好!先找链表中点,然后再反转后半部分,最后再分别遍历比较,直到后半部分遍历完!
class Solution {
ListNode node1=new ListNode(0);
ListNode node2=new ListNode(0);
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while (fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
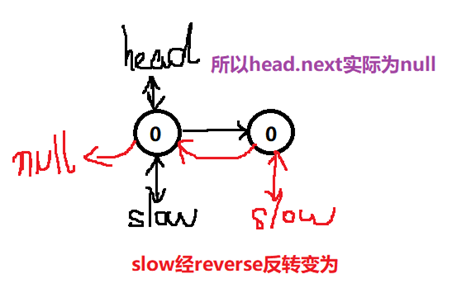
slow=reverse(slow.next);//此处如果是show的话,将从中点的前一个匹配,比较难理解,后面附图说明
while (slow!=null) {
if (head.val!=slow.val) {//到这里,head短的话会成为空指针而报错!!!
return false;
}
head=head.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=reverse(head.next);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=null;
return newHead;
}
}
说明:如果测试样例输入0,0的话,黄色标记为什么会报错!
环形链表
我的解法:利用hashset
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return false;
}
Set<ListNode> set=new HashSet<>();
int n=0;
ListNode x=head;
while (set.size()>=n) {
set.add(x);
x=x.next;
n++;
if (x==null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
大神解法:
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null) {
return false;
}
ListNode l1=head,l2=head.next;
while (l1!=null&&l2!=null&&l2.next!=null) {
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next.next;
if (l1==l2) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
递归解法,更为简洁
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return false;
if(head.next==head)return true;
ListNode l=head.next;
head.next=head;
boolean isCycle=hasCycle(l);
return isCycle;
}
}
算法练习LeetCode初级算法之链表的更多相关文章
- 【LeetCode算法】LeetCode初级算法——字符串
在LeetCode初级算法的字符串专题中,共给出了九道题目,分别为:反转字符串,整数反转,字符串中的第一个唯一字符,有效的字母异位词,验证回文字符串,字符串转换整数,实现strStr(),报数,最 ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之字符串
反转字符串 我的解法比较low,利用集合的工具类Collections.reverse反转,用时过长 class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之数组
删除数组中的重复项 官方解答: 旋转数组 存在重复元素 只出现一次的数 官方解答: 同一个字符进行两次异或运算就会回到原来的值 两个数组的交集 II import java.util.Arr ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之其他
位1的个数 解法一: class Solution { // you need to treat n as an unsigned value public int hammingWeight(int ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之数学
Fizz Buzz class Solution { public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) { List<String> list=new L ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之设计问题
打乱数组 不断的让第一个与后面随机选择的数交换 class Solution { private int[] nums; private int[] initnums; public Solution ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之动态规划
爬楼梯:斐波那契数列 假设你正在爬楼梯.需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶. 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶.你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢? 注意:给定 n 是一个正整数. 非递归解法 class S ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之排序和搜索
合并两个有序数组 class Solution { public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) { System.arrayco ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之树
二叉树的前序遍历 我的解法:利用递归,自底向下逐步添加到list,返回最终的前序遍历list class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderT ...
随机推荐
- Java基础之枚举类型
枚举 为什么需要枚举 在Java开发过程中,有时需要定义一系列有限的数据,如:月份.星期等.<br> java1.5之前,主要通过定义一系列静态常量完成. class Genders{ p ...
- crontab 相关
修改编辑器 select-editor 查看服务状态 service cron status (linux下为crond ,ubuntu为cron) 1-59/2 1,10,12 * * * ...
- PythonStudy——列表的常用操作 List of common operations
# 1.索引取值: 列表名[index] s1 = [1, 3, 2] print(s1[0]) print(s1[-1]) # 2.列表运算: 得到的是新list s2 = [1, 2, 3] pr ...
- Java_IO异常处理方式_入门小笔记
package IO; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; /** * IO异常处理方式 */ class FileWrite ...
- Office常用技巧
文章目录 大小写切换 把word里的自动编号转换为真实的文本 大小写切换 word中修改单词/句子的大小写:选中文字,按shift+F3,可在全大写.全小写.首字符大写间切换. 把word里的自动编号 ...
- jQeury 批量删除
/*批量删除*/ function datadel(){ var ids = new Array(); $("input[name='batch']:checked").each( ...
- 1.2.1 Excel如何从身份证号中提取日期
在对应的单元格中我们输入公式: =MID(B3,7,4)&"年"&MID(B3,11,2)&"月"&MID(B3,13,2)&a ...
- Linux打开文件设置
在某些情况下会要求增加Linux的文件打开数,以增加服务器到处理效率,在Linux下查看最多能打开的文件数量为: cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 然后设置ulimit -n 文件数 ...
- 入坑docker
入坑docker docker入门指南 docker入门指南 docker基础概念 docker分 server/client. server后台管理着所有的images/instances. 用户通 ...
- 将json转换为数据结构体
主要用到的依赖:(划重点:这个依赖需要加jdk版本号,不加的话用不了,且目前最高是jdk15) (ps: 用于json与其他类型格式转换,JSONObject, JSONArray等来自这个包) &l ...
