python入门 -- 学习笔记2
习题11:提问
-- 接受键盘的输入 raw_input
input() 和 raw_input() 有何不同?
input() 函数会把你输入的东西当做 Python 代码进行处理,这么做会有安全问题,你应该避开
这个函数。
代码:
print "how old are you?",
age = raw_input()
print "How tail are you?",
height = raw_input()
print "how much do you weight?",
weight = raw_input()
print "So, you're %r old, %r tall and %r heavy." % (
age, height, weight)
结果:

习题12:提示别人
代码:
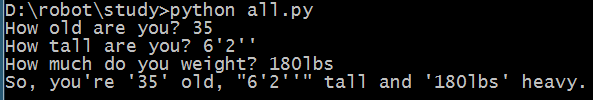
age = raw_input("How old are you? ")
height = raw_input("How tall are you? ")
weight = raw_input("How much do you weight? ")
print "So, you're %r old, %r tall and %r heavy." % (age, height, weight)
结果:
习题13:参数、解包、变量
-- 将变量传递给脚本的方法(所谓脚本,就是你写的 .py 程序),涉及“参数”
-- import 将python已有的功能引入脚本直接使用
-- argv:参数变量
-- 解包:script, first, second, third = argv 把argv中的东西解包,将所有的参数一次赋予左边的变量名
-- argv 和 raw_input() 有什么不同?
不同点在于用户输入的时机。如果参数是在用户执行命令时就要输入,那就是 argv,如果是在脚本运行过程中需要用户输入,那就使用 raw_input()。
代码:
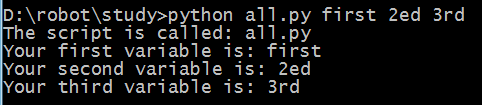
from sys import argv
script, first, second, third = argv
print "The script is called:", script
print "Your first variable is:", first
print "Your second variable is:", second
print "Your third variable is:", third
结果:
习题14:提示与传递
代码:
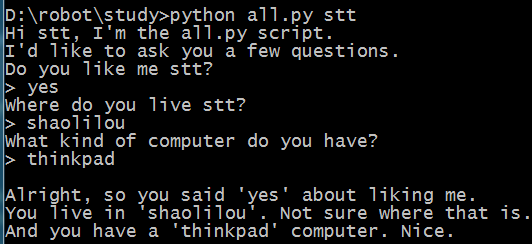
from sys import argv
script, user_name = argv
prompt = '> '
print "Hi %s, I'm the %s script." % (user_name, script)
print "I'd like to ask you a few questions."
print "Do you like me %s?" % user_name
likes = raw_input(prompt)
print "Where do you live %s?" % user_name
lives = raw_input(prompt)
print "What kind of computer do you have?"
computer = raw_input(prompt)
print '''
Alright, so you said %r about liking me.
You live in %r. Not sure where that is.
And you have a %r computer. Nice.
''' % (likes, lives, computer)
结果:
习题15:读取文件
-- 涉及两个文件,一个脚本文件.py文件,另一个是ex15_sample.txt
第二个文件内容:
This is stuff I typed into a file.
It is really cool stuff.
Lots and lots of fun to have in here.
-- open() 打开文件 返回的是一个“file object”
-- read() 读取文件内容
代码:
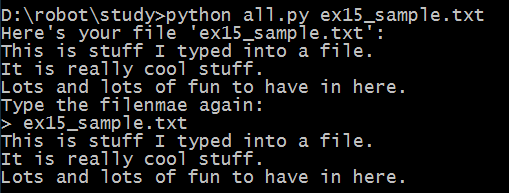
from sys import argv
script, filename = argv
txt = open(filename)
print "Here's your file %r:" % filename
print txt.read()
print "Type the filenmae again:"
file_again = raw_input("> ")
txt_again = open(file_again)
print txt_again.read()
结果:
习题16:读写文件
-- close 关闭文件
-- read 读取文件内容
-- readline 读取文本文件中的一行
-- write(stuff) 将stuff写入文件
代码:
from sys import argv
script, filename = argv
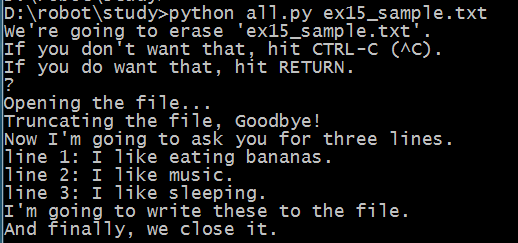
print "We're going to erase %r." % filename
print "If you don't want that, hit CTRL-C (^C)."
print "If you do want that, hit RETURN."
raw_input("?")
print "Opening the file..."
target = open(filename, 'w')
print "Truncating the file, Goodbye!"
target.truncate()
print "Now I'm going to ask you for three lines."
line1 = raw_input("line 1: ")
line2 = raw_input("line 2: ")
line3 = raw_input("line 3: ")
print "I'm going to write these to the file."
target.write(line1)
target.write('\n')
target.write(line2)
target.write('\n')
target.write(line3)
target.write('\n')
print "And finally, we close it."
target.close()
结果:
习题17:更多文件操作
-- exists() 判断文件是否存在,存在,继续执行;不存在,新建文件再继续执行
代码:
from sys import argv
from os.path import exists
script, from_file, to_file = argv
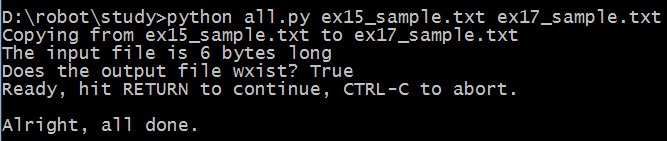
print "Copying from %s to %s" % (from_file, to_file)
#we could do these two on one line too, how?
in_file = open(from_file)
indata = in_file.read()
print "The input file is %d bytes long" % len(indata)
print "Does the output file wxist? %r" % exists(to_file)
print "Ready, hit RETURN to continue, CTRL-C to abort."
raw_input()
out_file = open(to_file, 'w')
out_file.write(indata)
print "Alright, all done."
out_file.close()
in_file.close()
结果:
习题18:命名、变量、代码、函数
函数可做三洋事情:
1、给代码片段命名,就跟“变量”给字符串和数字命名一样
2、可以接受参数,就跟脚本接受argv一样
3、通过使用#1和#2,可以创建“微型脚本”或者“小命令”
介绍:
def:定义
函数名:可以随意取,最好能体现出函数的功能来,注意命名规范!不可重复
参数:放在圆括号内
格式:def 函数名称 (参数-多个参数以“,”隔开):
函数内容 开始编写前缩进4个空格
函数可以接收参数,也可以不接收参数
运行/调用函数,函数名后紧跟(参数-可有可无,可多个)
代码:
# this one is like your scripts with argv
def print_two(*args):
arg1, arg2 = args
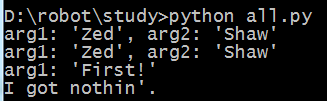
print "arg1: %r, arg2: %r" % (arg1, arg2)
# ok, that *args is actually pointless, we can just do this
def print_two_again(arg1, arg2):
print "arg1: %r, arg2: %r" % (arg1, arg2)
# this just takes one argument
def print_one(arg1):
print "arg1: %r" % arg1
# this one takes no arguments
def print_none():
print "I got nothin'."
print_two("Zed", "Shaw")
print_two_again("Zed", "Shaw")
print_one("First!")
print_none()
结果:
习题19:函数和变量
代码:
def cheese_and_crackers(cheese_count, boxes_of_crackers):
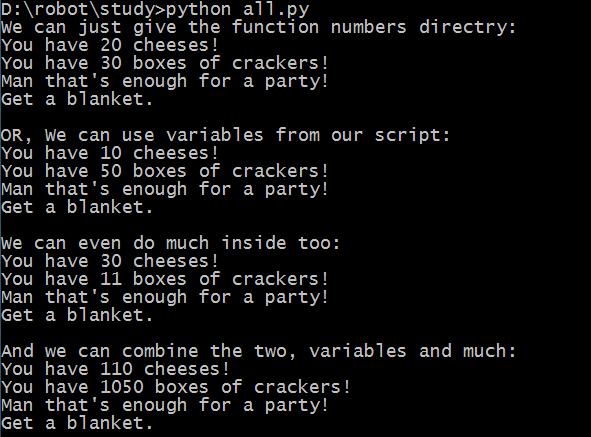
print "You have %d cheeses!" % cheese_count
print "You have %d boxes of crackers!" % boxes_of_crackers
print "Man that's enough for a party!"
print "Get a blanket.\n"
print "We can just give the function numbers directry:"
cheese_and_crackers(20, 30)
print "OR, We can use variables from our script:"
amount_of_cheese = 10
amount_of_crackers = 50
cheese_and_crackers(amount_of_cheese, amount_of_crackers)
print "We can even do much inside too:"
cheese_and_crackers(10 + 20, 5 + 6)
print "And we can combine the two, variables and much:"
cheese_and_crackers(amount_of_cheese + 100, amount_of_crackers + 1000)
结果:
习题20:函数和文件
-- 更多文件操作 seek() readline()
代码:
from sys import argv
script, input_file = argv
def print_all(f):
print f.read()
def rewind(f):
f.seek(0)
def print_a_line(line_count, f):
print line_count, f.readline()
current_file = open(input_file)
print "First let's print the whole file:\n"
print_all(current_file)
print "Now let's rewind, kind of like a tape."
rewind(current_file)
print "Let's print three lines:"
current_line = 1
print_a_line(current_line, current_file)
current_line = current_line + 1
print_a_line(current_line, current_file)
current_line = current_line + 1
print_a_line(current_line, current_file)
结果:

python入门 -- 学习笔记2的更多相关文章
- Python入门学习笔记4:他人的博客及他人的学习思路
看其他人的学习笔记,可以保证自己不走弯路.并且一举两得,即学知识又学方法! 廖雪峰:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958 ...
- Python入门学习笔记
了解 一下Python中的基本语法,发现挺不适应的,例如变量经常想去指定类型或者if加个括号之类的.这是在MOOC中学习到的知识中一点简单的笔记. Python的变量和数据类型: 1.Python这种 ...
- python入门学习笔记(三)
10.函数 求绝对值的函数 abs(x) 也可以在交互式命令行通过 help(abs) 查看abs函数的帮助信息.调用 abs 函数:>>> abs(100)100>>& ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (二)
今天学习了一些简单的语法规则,话不多说,开始了: 二.数据类型 常用数据类型中的整形和浮点型就不多说了. 1.字符串 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记1
学习资料:笨方法学Python 准备: 安装环境----请自行网络搜索(Windows安装很简单,和其他安装程序一样) 找一个自己习惯的编辑器(比如:sublime text 3) 创建一个专门的目录 ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (一)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lujianwenance/p/5939786.html 说到学习一门语言第一步就是先选定使用的工具(环境).因为本人是个小白,所以征求了一下同 ...
- python入门学习笔记(二)
6.6替换元素 7.tuple类型 7.1创建tuple 7.2创建单元素tuple 7.3"可变"的tuple 8.条件判断和循环 8.1,if语句 8.2,if... ...
- python入门学习笔记(一)
写在开头: A:python的交互式环境 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记4
习题38:列表的操作 当你看到像 mystuff.append('hello') 这样的代码时,你事实上已经在 Python 内部激发了一个连锁反应.以下是它的工作原理: 1. Python 看到你用 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记3
习题21:函数可以返回东西 过程解析: 1.定义函数:如def add(形参)函数 2.调用函数: add(实参) 别忘记加() 3.在函数调用的时候将实参的值传给形参,代入到函数中进行计算,r ...
随机推荐
- Js/使用js来改变图片的url
1.使用js的方式来改变url地址: $('#a1').attr("src","test1.jpg");这种方式来改变图片的url地址: 而不是采用$('#a1 ...
- Bootstrap如何禁止响应式布局 不适配
Bootstrap 会自动帮你针对不同的屏幕尺寸调整你的页面,使其在各个尺寸的屏幕上表现良好.下面我们列出了如何禁用这一特性,就像这个非响应式布局实例页面一样. 禁止响应式布局有如下几步: 移除 此 ...
- switch留个爪,之后还需要再研究下
public class SwitchDemo { public static void main (String [] args) { for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) ...
- python 的 format 函数
python的格式化字符串方法之一------------format 函数 它通过{}和:来代替%. 数字 格式 输出 描述 3.1415926 {:.2f} 3.14 保留小数点后两位 3.141 ...
- Django 小饭桌项目实战笔记
gulp-sass安装 安装报错,原因未设置全局镜像源npm config set sass_binary_site https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node-sass/ ...
- java 原子性 可见性 有序性
原子性 原子性是指一个操作或多个操作要么全部执行完成且执行过程不被中断,要么就不执行. 如向变量x赋值操作 x = 10 是原子性的,就不会出现赋值操作进行到一半(x的低16位赋值成功,高16位没有赋 ...
- vld for memory leak detector (release version)
有没有这样的情况,无法静态的通过启动和退出来查找内存泄露,比如网络游戏,你总不能直接关游戏那玩家怎么办? 现在vld支持release,我们可以动态的找. 1.在release版本使用vld了.< ...
- JVM内部细节之一:synchronized关键字及实现细节(轻量级锁Lightweight Locking)
在C程序代码中我们可以利用操作系统提供的互斥锁来实现同步块的互斥访问及线程的阻塞及唤醒等工作.然而在Java中除了提供Lock API外还在语法层面上提供了synchronized关键字来实现互斥同步 ...
- Git从远程clone项目报错cannot open git-upload-pack,将http.sslVerify设为false即可
通过HTTPS访问Git远程仓库,如果服务器的SSL证书未经过第三方机构签署,那么Git就会报错 通过https访问Git远程仓库,如果服务器的SSL证书没有经过第三方机构签署,就会出现cannot ...
- Android ScrollView嵌套Recyclerview滑动卡顿,松手即停问题解决;
假如你的布局类似这样的: <ScrollView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height=&quo ...
