sklearn 可视化模型的训练测试收敛情况和特征重要性
show the code:
# Plot training deviance
def plot_training_deviance(clf, n_estimators, X_test, y_test):
# compute test set deviance
test_score = np.zeros((n_estimators,), dtype=np.float64)
for i, y_pred in enumerate(clf.staged_predict(X_test)):
test_score[i] = clf.loss_(y_test, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Deviance')
train_score = clf.train_score_
logging.info("len(train_score): %s" % len(train_score))
logging.info(train_score)
logging.info("len(test_score): %s" % len(test_score))
logging.info(test_score)
plt.plot(np.arange(n_estimators) + 1, train_score, 'b-',
label='Training Set Deviance')
plt.plot(np.arange(n_estimators) + 1, test_score, 'r*', label='Test Set Deviance')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel('Boosting Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Deviance')
plt.show() # Plot feature importance
def plot_feature_importance(clf, feature_names):
feature_importance = clf.feature_importances_
# make importances relative to max importance
feature_importance = 100.0 * (feature_importance / feature_importance.max())
sorted_idx = np.argsort(feature_importance)
pos = np.arange(sorted_idx.shape[0]) + .5
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.barh(pos, feature_importance[sorted_idx], align='center')
# plt.yticks(pos, feature_names[sorted_idx])
plt.yticks(pos, [feature_names[idx] for idx in sorted_idx])
plt.xlabel('Relative Importance')
plt.title('Variable Importance')
plt.show() class Train(object):
def __init__(self, data_file):
self.data_file = data_file
self.x_fields = ["xxx", "xxx", "xxx"]
self.x_features, self.y_labels = self.load_data() def load_data(self):
x_features, y_labels = [], []
# ......
return x_features, y_labels def train_model(self):
model = GradientBoostingRegressor(random_state=42)
model.fit(self.x_features, self.y_labels)
y_pred = model.predict(self.x_features)
logging.info("mean_squared_error: %.6f" % mean_squared_error(self.y_labels, y_pred))
logging.info("mean_squared_log_error: %.6f" % mean_squared_log_error(self.y_labels, y_pred)) plot_training_deviance(clf=model, n_estimators=model.get_params()["n_estimators"], X_test=self.x_features, y_test=self.y_labels) # 输出feature重要性
logging.info("feature_importances_: %s" % model.feature_importances_)
plot_feature_importance(clf=model, feature_names=self.x_fields)
参考的是sklearn中的样例: Gradient Boosting regression — scikit-learn 0.19.2 documentation
画出的图如下所示:
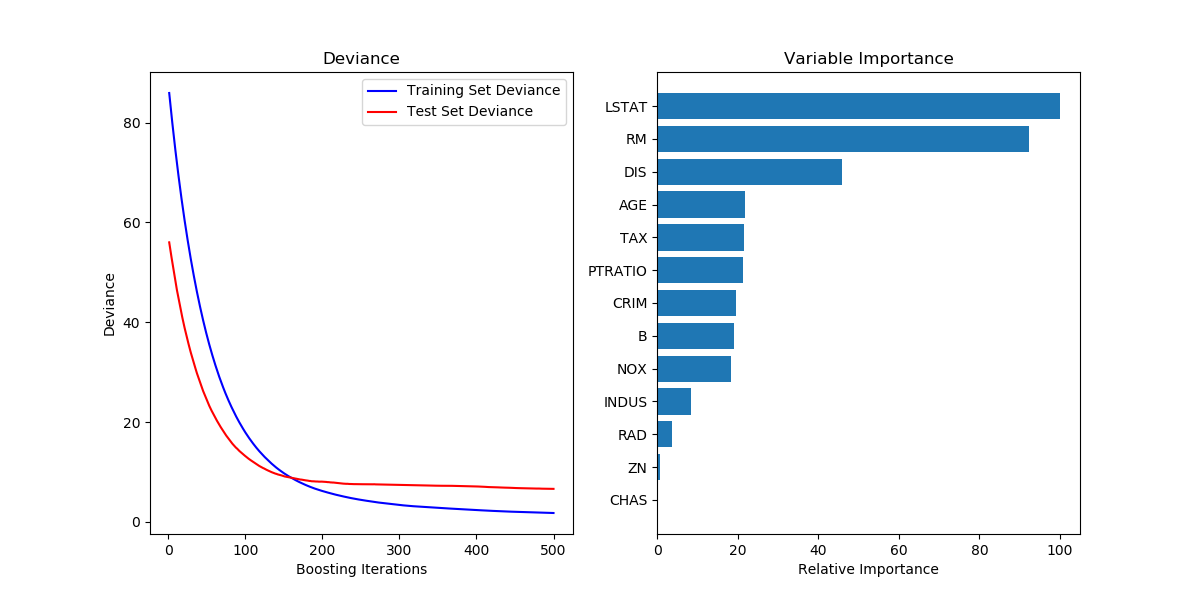
sklearn 可视化模型的训练测试收敛情况和特征重要性的更多相关文章
- 【集成学习】sklearn中xgboost模块中plot_importance函数(绘图--特征重要性)
直接上代码,简单 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ ################################################ ...
- 使用 TensorBoard 可视化模型、数据和训练
使用 TensorBoard 可视化模型.数据和训练 在 60 Minutes Blitz 中,我们展示了如何加载数据,并把数据送到我们继承 nn.Module 类的模型,在训练数据上训练模型,并在测 ...
- sklearn——train_test_split 随机划分训练集和测试集
sklearn——train_test_split 随机划分训练集和测试集 sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split随机划分训练集和测试集 官网文档:http: ...
- 机器学习使用sklearn进行模型训练、预测和评价
cross_val_score(model_name, x_samples, y_labels, cv=k) 作用:验证某个模型在某个训练集上的稳定性,输出k个预测精度. K折交叉验证(k-fold) ...
- pytorch seq2seq模型训练测试
num_sequence.py """ 数字序列化方法 """ class NumSequence: """ ...
- 学习笔记TF016:CNN实现、数据集、TFRecord、加载图像、模型、训练、调试
AlexNet(Alex Krizhevsky,ILSVRC2012冠军)适合做图像分类.层自左向右.自上向下读取,关联层分为一组,高度.宽度减小,深度增加.深度增加减少网络计算量. 训练模型数据集 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测
0.引言 利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,给一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑: 使用的数据集中69张没笑脸,65张有笑脸,训练结果识别精度在95%附近: 效果: 图1 示例效果 工程利用pytho ...
- sklearn保存模型的两种方式
sklearn 中模型保存的两种方法 一. sklearn中提供了高效的模型持久化模块joblib,将模型保存至硬盘. from sklearn.externals import joblib # ...
- sklearn保存模型-【老鱼学sklearn】
训练好了一个Model 以后总需要保存和再次预测, 所以保存和读取我们的sklearn model也是同样重要的一步. 比如,我们根据房源样本数据训练了一下房价模型,当用户输入自己的房子后,我们就需要 ...
随机推荐
- [css]网站骨架布局作业
实现效果图: 代码实现 第一次写的时候不知道如何下手, 后来摸清规律了,由大到小. 由全局到局部 第一次还遇到区块命名问题, 和哪个该怎么划分问题 第一次还遇到由于划分不规整,所以有些代码没达到预期的 ...
- Hadoop mapreduce自定义分组RawComparator
本文发表于本人博客. 今天接着上次[Hadoop mapreduce自定义排序WritableComparable]文章写,按照顺序那么这次应该是讲解自定义分组如何实现,关于操作顺序在这里不多说了,需 ...
- Struts2中struts.multipart.maxSize配置
今天使用Struts2的文件上传控件时,在struts.xml中,将处理上传的action中的fileUpload拦截器的maximumSize参数设置为5000000,上传了一个3M的文件后发现控制 ...
- Android查缺补漏(IPC篇)-- 进程间通讯之AIDL详解
本文作者:CodingBlock 文章链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/codingblock/p/8436529.html 进程间通讯篇系列文章目录: Android查缺补漏(IP ...
- 20145204 《Java程序设计》第1周学习总结
20145204 <Java程序设计>第1周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 本周经过不断的钻研课本,及看一些老师的视频,我对Java有了一个全新的认知.是的,Java和C都是一种语言,但是Ja ...
- duilib : 滑动显示的窗口实现以及 悬浮窗 (转载)
1. vc 判断窗口是否显示 BOOL IsWindowVisible(HWND hWnd); 2.悬浮窗 http://blog.csdn.net/lincyang/article/details ...
- 在pom.xml中使用distributionManagement将项目打包上传到nexus私服
本文介绍 如何在pom.xml中使用distributionManagement将项目打包上传到nexus私服 1.pom.xml文件添加distributionManagement节点 <!- ...
- 学习Zookeeper之第3章Zookeeper内部原理
第 3 章 Zookeeper 内部原理 3.1 选举机制 3.2 节点类型 3.3 stat 结构体 3.4 监听器原理 1)监听原理详解 2)常见的监听 3.5 写数据流程 第 3 章 Z ...
- supervisor安装与问题
[转]安装supervisor以及可能碰到的问题 单击此处查看原文 supervisor作为一个进程管理的python软件非常的给力 但是一不小心就会遇到一些问题 就比如下面这个: unix:///v ...
- CSU 1963 Feed the rabbit(斜率优化dp)
http://acm.csu.edu.cn/csuoj/problemset/problem?pid=1963 题意:有m个坑,每只兔子会在ti时刻回到坑中,现在有n个人,每个人都可以从任意时间(&l ...
