简单主机批量管理工具(这里实现了paramiko 用su切换到root用户)
项目名:简单主机批量管理工具
一、需求
1、主机分组
2、可批量执行命令、发送文件,结果实时返回,执行格式如下
batch_run -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_clusters,db_servers -cmd "df -h"
batch_scp -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_clusters,db_servers -action put -local test.py -remote /tmp/
3、主机用户名密码、端口可以不同
二、设计表结构(model原型)

三、代码结构
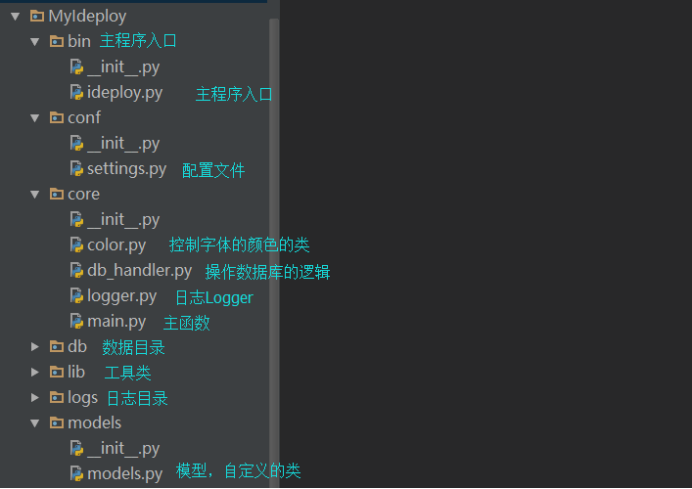
model.py 表结构(model)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from lib import commons
from multiprocessing import Lock class Host(object):
MUTEX = Lock() def __init__(self, host, port, user, password):
self.MUTEX.acquire()
self.hostId = commons.create_id('host')
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.user = user
self.password = password
self.MUTEX.release() def __eq__(self, other):
res = False
if type(other) == type(self):
if self.host == other.host:
res = True
return res def __str__(self):
return 'hostId:%s host:%s' % (self.hostId, self.host) class Group(object):
MUTEX = Lock() def __init__(self, groupName):
self.MUTEX.acquire()
self.groupId = commons.create_id('group')
self.groupName = groupName
self.MUTEX.release() def __eq__(self, other):
res = False
if type(other) == type(self):
if self.groupName == other.groupName:
res = True
return res def __str__(self):
return 'groupId:%s group:%s' % (self.groupId, self.groupName) class Group2Host(object):
MUTEX = Lock() def __init__(self, hostId, groupId):
self.MUTEX.acquire()
self.g2hId = commons.create_id('group2Host')
self.hostId = hostId
self.groupId = groupId
self.MUTEX.release() def __eq__(self, other):
res = False
if type(other) == type(self):
if self.hostId == other.hostId and self.groupId == other.groupId:
res = True
return res def __str__(self):
return 'g2hId:%s group2Host:%s' % (self.g2hId, (self.hostId, self.groupId),)
model.py
main.py(这里实现了paramiko 用su - root 切换到root用户,再继续执行命令)
# Author:ton
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import paramiko
import os
import threading
import shelve
import re
import time
import xlrd
import xlwt
import json
from conf import settings
from models import models
from core.db_handler import Db_handler
from core.color import Colors
from core import logger
from threading import Thread # paramiko.util.log_to_file(os.path.join(settings.LOG_PATH, 'paramiko.log'))
class Ideploy(object):
def __init__(self):
self.initDb()
self.logger = logger.logger('MyIdeploy.log')
self.host_db = shelve.open(os.path.join(settings.HOST_TABLE_PATH, 'host'))
self.group_db = shelve.open(os.path.join(settings.GROUP_TABLE_PATH, 'group'))
self.g2h_db = shelve.open(os.path.join(settings.G2H_TABLE_PATH, 'group2Host'))
# 默认有default主机组
self.default_group_obj = Db_handler.getGroupObjByGroupName(self.group_db, 'default')
if not self.default_group_obj:
self.default_group_obj = models.Group('default')
Db_handler.insert_group(self.group_db, self.default_group_obj)
self.thread_list = []
self.instructions()
self.run()
self.host_db.close()
self.group_db.close()
self.g2h_db.close() @staticmethod
def exit():
exit('Bye') @staticmethod
def instructions():
"""使用说明"""
msg = """
1、在conf/setttings下配置好需要暴力尝试密码的password_list和host_list
2、在Terminal终端运行工具:python bin/ideploy.py -t start
3、输入violentCipher,回车,完成后提示"暴力尝试密码完毕!"
4、输入manageHosts,回车,可以查看管理暴力尝试密码成功的主机列表,记住默认主机组(default)的groupId为1,输入b,退出
5、输入executeCommand,回车,输入批量执行命令:batch_run -g 1 -cmd "hostname",该hostname命令执行的主机对象为默认主机组(default)下的所有主机
6、输入show_task,回车,可以看到批量执行命令的结果
7、继续输入批量执行命令:batch_scp -g 1 -action put -local __init__.py -remote /tmp/target.py,把本地文件__init__.py上传至远端/tmp/下,并取名为target.py
8、输入show_task,回车,可以看到批量执行上传文件的结果
9、输入q,退出批量执行命令的界面,输入exit,退出程序
"""
print(msg) @staticmethod
def initDb():
"""初始化数据库、日志目录"""
# 初始化各表目录及其自增长ID记录文件
for table_name in settings.TABLE_LIST:
table_path = os.path.join(settings.DATABASE_PATH, table_name)
table_id_file = os.path.join(table_path, 'countId')
if not os.path.isdir(table_path): # 创建数据文件路径
os.mkdir(table_path)
if not os.path.isfile('%s.dat' % table_id_file): # 创建自增长ID记录文件
data_dic = shelve.open(table_id_file)
data_dic['id'] = ''
data_dic.close()
# 初始化日志目录
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'logs')):
os.mkdir(os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'logs')) def run(self):
while True:
print("欢迎来到Ideploy".center(45, '-'))
msg = """
violentCipher暴力尝试密码
createGroups创建主机组
manageHosts管理主机
executeCommand批量执行命令
exportHostToExcel导出主机信息到excel表
importHostFromExcel从excel表导入主机信息
exit退出
"""
print(Colors(msg))
print('thread number:%s' % threading.active_count())
print("".center(50, '-'))
choice = input('输入命令>>').strip()
if hasattr(self, choice):
getattr(self, choice)() def violentCipher(self):
"""为每个主机分配线程尝试ssh密码"""
for host in settings.host_list:
# 多线程尝试ssh密码
t = Thread(target=self.tryPasswordForHost, args=(host, settings.port, settings.user))
t.setDaemon(True)
self.thread_list.append(t)
# 单线程尝试ssh密码
# self.try_password_for_host(ip, settings.port, settings.user)
for t in self.thread_list:
t.start()
for t in self.thread_list:
t.join()
self.thread_list = []
print(Colors('暴力尝试密码完毕!输入"manageHosts"可以管理主机', 'green')) def tryPasswordForHost(self, host, port, user):
"""循环ssh密码列表尝试密码,并把正确密码保存文件"""
password_list = settings.password_list
for passwd in password_list:
try:
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(hostname=host, port=port, username=user, password=passwd, timeout=3)
msg = 'correct ip:%s user:%s password:%s' % (host, user, passwd)
print(Colors(msg, 'green'))
# 更新host、g2h表
host_obj = models.Host(host, port, user, passwd)
Db_handler.update_host(self.host_db, host_obj)
return_host_obj = Db_handler.check_unique_host(self.host_db, host_obj)
if return_host_obj:
host_obj = return_host_obj
Db_handler.insert_g2h(self.g2h_db, host_obj, self.default_group_obj)
break
except KeyError as e:
raise e # 调试
except Exception as e:
print(Colors(str(e), 'red'))
msg = 'wrong ip:%s user:%s password:%s' % (host, user, passwd)
print(Colors(msg, 'red'))
finally:
ssh.close() def checkPassword(self):
"""检查ssh密码和root密码的有效性"""
pass def exportHostToExcel(self):
"""从数据库导出所有主机信息到excel表里"""
# 创建workbook和sheet对象
workbook = xlwt.Workbook() # 注意Workbook的开头W要大写
sheet1 = workbook.add_sheet('sheet1', cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 向sheet页中写入列名数据
column_names = ['host', 'groupName', 'user', 'password', 'port']
for index, col in enumerate(column_names):
sheet1.write(0, index, col)
# 读取数据库,按group读取host
group_list = []
for key in self.group_db:
group_list.append(self.group_db[key])
group_list.sort(key=lambda group_obj: group_obj.groupId, reverse=False) # 根据groupId排序
for g_obj in group_list:
# 根据主机组Id,获取该主机组所有主机Obj列表
host_list = Db_handler.getHostObjListByGroupId(self.host_db, self.g2h_db, g_obj.groupId)
host_list.sort(key=lambda obj: obj.host, reverse=False) # 根据主机的ip排序
# 向sheet页中写入host数据
for row_num, host_obj in enumerate(host_list, 1):
col_values = [host_obj.host, g_obj.groupName, host_obj.user, host_obj.password, host_obj.port]
for col_num, col_val in enumerate(col_values):
sheet1.write(row_num, col_num, col_val)
workbook.save(os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'hosts.xls'))
print(Colors('导出成功!导出文件:%s' % os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'hosts.xls'), 'green')) def importHostFromExcel(self):
"""从excel表中导入主机信息并存入数据库"""
# 打开一个workbook
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'hosts.xls'))
# 定位到sheet1
sheet1 = workbook.sheets()[0]
# 遍历sheet1中所有行row
num_rows = sheet1.nrows
for row_num in range(1, num_rows):
row_val = sheet1.row_values(row_num)
group_obj = Db_handler.getGroupObjByGroupName(self.group_db, row_val[1])
if group_obj:
host_obj = models.Host(row_val[0], int(row_val[4]), row_val[2], row_val[3])
Db_handler.update_host(self.host_db, host_obj)
return_host_obj = Db_handler.check_unique_host(self.host_db, host_obj)
if return_host_obj:
host_obj = return_host_obj
Db_handler.insert_g2h(self.g2h_db, host_obj, group_obj)
else:
print(Colors('没有该主机组名[%s]' % row_val[1], 'red'))
else:
print(Colors("导入成功!请输入'manageHosts'查看导入的主机", 'green')) def createGroups(self):
while True:
create_groupName = input('请输入需要创建的主机组名(b退出):').strip()
if not create_groupName: continue
if create_groupName == 'b': break
create_group = models.Group(create_groupName)
result_code = Db_handler.insert_group(self.group_db, create_group)
if result_code:
print(Colors('创建主机组成功', 'green'))
else:
print(Colors('该主机组已存在', 'red')) def manageHosts(self):
"""分配主机到主机组"""
# 解析分配的hostId和groupId,判断是否存在
while True:
print('所有主机信息如下:')
self.displayHosts()
choice_action = input('请输入要对主机组执行的操作(add添加,del删除,b退出):').strip()
if choice_action == 'b':
break
elif choice_action != 'add' and choice_action != 'del':
continue
quit_flag = True
while quit_flag:
choice_hostIds = input('请输入hostId(用空格隔开)(b退出):').strip()
if not choice_hostIds: continue
if choice_hostIds == 'b': break
hostId_list = choice_hostIds.split()
exist_flag = True
for hostId in hostId_list:
if hostId not in self.host_db:
exist_flag = False
print(Colors('输入要操作的hostId:%s 不存在' % hostId, 'red'))
if not exist_flag: continue
while quit_flag:
choice_groupId = input('请输入要操作的groupId(b退出):').strip()
if not choice_groupId: continue
if choice_groupId == 'b': break
if choice_groupId not in self.group_db:
print(Colors('输入的groupId:%s 不存在' % choice_groupId, 'red'))
continue
# 开始更新g2h表
for hostId in hostId_list:
if choice_action == 'add':
Db_handler.insert_g2h(self.g2h_db, self.host_db[hostId], self.group_db[choice_groupId])
else:
Db_handler.delete_g2h(self.g2h_db, self.host_db[hostId], self.group_db[choice_groupId])
print(Colors('配置成功', 'green'))
quit_flag = False def displayHosts(self):
"""展示管理的主机"""
group_list = []
for key in self.group_db:
group_list.append(self.group_db[key])
group_list.sort(key=lambda group_obj: group_obj.groupId, reverse=False) # 根据groupId排序
for g_obj in group_list:
# 根据主机组Id,获取该主机组所有主机Obj列表
host_list = Db_handler.getHostObjListByGroupId(self.host_db, self.g2h_db, g_obj.groupId)
print(Colors(
'Group:%s[%d](groupId:%s)' % (g_obj.groupName, len(host_list), g_obj.groupId), 'cyan'))
host_list.sort(key=lambda obj: obj.host, reverse=False) # 根据主机的ip排序
for host_obj in host_list:
print('\t%s' % host_obj) def executeCommand(self):
"""批量执行ssh命令"""
SSHClient(self) class TaskList(list):
def __init__(self, item=()):
super().__init__(item)
self.logger = logger.logger('task_list') def append(self, p_object):
if not isinstance(p_object, dict):
raise TypeError
super().append(p_object)
# with open(os.path.join(settings.BASE_PATH, 'task_list'), 'a') as f:
# f.write(json.dumps(p_object) + '\n')
self.logger.info(json.dumps(p_object)) class SSHClient(object):
def __init__(self, ideploy_obj):
self.ideploy_obj = ideploy_obj
self.task_list = TaskList()
self.interactive() @staticmethod
def help_msg():
"""ssh命令帮助信息"""
msg = """注意:-h 后为hostId,-g 后为groupId
batch_run -h 1,2,3 -g 1,2 -cmd "df -h"
batch_scp -h 1,2,3 -g 1,2 -action put -local test.py -remote /tmp/
show_task 查看ssh命令结果
"""
print(msg) def interactive(self):
while True:
print('\n thread number:%s' % threading.active_count())
cmd = input(Colors('批量执行命令>>', 'cyan')).strip()
if not cmd: continue
if cmd == 'q': break
if hasattr(self, cmd[:9]):
getattr(self, cmd[:9])(cmd[9:].strip())
else:
self.help_msg() @staticmethod
def create_task_dic(hostId, host, command, result, date):
task_dic = {
'hostId': hostId,
'host': host,
'command': command,
'result': result,
'date': date,
}
return task_dic def show_task(self, cmd):
for task_dic in self.task_list:
print(
'\033[36m(hostId:%s)host:\033[0m%s \033[36mcommand:\033[0m%s \033[36mresult:\033[0m\n%s \033[36mdate:\033[0m%s' % (
task_dic['hostId'], task_dic['host'], task_dic['command'], task_dic['result'], task_dic['date'])) def batch_run(self, cmd):
"""批量执行batch_run命令"""
argv_dic = self.parse_run_command(cmd)
if argv_dic['cmd']:
self.batch('batch_run', argv_dic)
else:
self.help_msg() def connect_batch_run(self, host_obj, argv_dic):
"""与ssh服务端通讯执行远程ssh命令"""
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
try:
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(hostname=host_obj.host, port=host_obj.port, username=host_obj.user, password=host_obj.password,
timeout=5)
channel = ssh.invoke_shell()
result = ''
if host_obj.user != 'root':
# channel.send("sudo su - \n")
channel.send("su - \n")
# 下面几行代码是发送 su - root命令时所需要输入的root密码,配置了/etc/sudoers NOPASSWD就不用密码了
while not re.search(r'(P|p)assword: $', result):
result += channel.recv(8196).decode('utf-8')
self.ideploy_obj.logger.info(b"++" + result.encode('utf-8') + b'++')
result = ''
channel.send('%s\n' % settings.root_pwd)
while not re.search(r'#[^#]{0,13}$', result):
result += channel.recv(8196).decode('utf-8')
self.ideploy_obj.logger.info(b"++" + result.encode('utf-8') + b'++')
result = ''
channel.send('%s\n' % argv_dic['cmd'])
while not re.search(r'#[^#]{0,13}$', result):
result += channel.recv(8196).decode('utf-8')
self.ideploy_obj.logger.info(b"++" + result.encode('utf-8') + b'++')
result_list = re.findall(r".*\n", result)[1:]
result = ''.join(result_list)
channel.close()
self.task_list.append(self.create_task_dic(host_obj.hostId, host_obj.host,
argv_dic['cmd'], result,
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())))
except Exception as e:
self.task_list.append(
self.create_task_dic(host_obj.hostId, host_obj.host, argv_dic['cmd'], str(e),
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())))
finally:
ssh.close() def connect_batch_scp(self, host_obj, argv_dic):
"""与ssh服务端建立sftp通道执行远程scp命令"""
try:
transport = paramiko.Transport((host_obj.host, host_obj.port))
transport.connect(username=host_obj.user, password=host_obj.password, )
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
if argv_dic['action'] == 'put':
# 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py
sftp.put(argv_dic['local'], argv_dic['remote'])
else:
# 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path
sftp.get(argv_dic['remote'], argv_dic['local'])
self.task_list.append(
self.create_task_dic(host_obj.hostId, host_obj.host,
'action[%s] local[%s] remote[%s]' % (
argv_dic['action'], argv_dic['local'], argv_dic['remote']), 'OK',
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())))
except Exception as e:
self.task_list.append(
self.create_task_dic(host_obj.hostId, host_obj.host,
'action[%s] local[%s] remote[%s]' % (
argv_dic['action'], argv_dic['local'], argv_dic['remote']), str(e),
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())))
finally:
try:
transport.close()
except UnboundLocalError:
pass def batch(self, batch_type, argv_dic):
"""为每个host分配一个线程去连接ssh服务端批量执行batch_run或batch_scp命令"""
finished_hostId_list = []
batch_type_func = 'connect_%s' % batch_type
if argv_dic.get('group_list'):
for groupId in argv_dic['group_list']:
if groupId in self.ideploy_obj.group_db:
host_list = Db_handler.getHostObjListByGroupId(self.ideploy_obj.host_db, self.ideploy_obj.g2h_db,
groupId)
for host_obj in host_list:
t = Thread(target=getattr(self, batch_type_func), args=(host_obj, argv_dic))
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
finished_hostId_list.append(host_obj.hostId)
else:
self.task_list.append(self.create_task_dic("groupId[%s]" % groupId, None,
None, "groupId[%s] is not exist" % groupId,
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())))
if argv_dic.get('host_list'):
for hostId in argv_dic['host_list']:
if hostId in self.ideploy_obj.host_db:
if hostId not in finished_hostId_list:
t = Thread(target=getattr(self, batch_type_func),
args=(self.ideploy_obj.host_db[hostId], argv_dic))
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
else:
self.task_list.append(self.create_task_dic(hostId, None,
None, "hostId[%s] is not exist" % hostId,
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))) def batch_scp(self, cmd):
"""批量执行batch_scp命令"""
argv_dic = self.parse_scp_command(cmd)
if argv_dic['action'] and argv_dic['local'] and argv_dic['remote']:
self.batch('batch_scp', argv_dic)
else:
self.help_msg() @staticmethod
def parse_target(cmd): # -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_clusters,db_servers -cmd "df -h"
"""解析-h、-g参数,获取主机、主机组列表"""
host_str = re.match(r"-h[ ]+[^-]+", cmd)
host_list = host_str.group().strip()[2:].strip().replace(r" ", "").split(",") if host_str else None
group_str = re.search(r"-g[ ]+[^-]+", cmd)
group_list = group_str.group().strip()[2:].strip().replace(r" ", "").split(",") if group_str else None
return host_list, group_list def parse_run_command(self, cmd): # -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_clusters,db_servers -cmd "df -h"
"""解析batch_run命令参数"""
host_list, group_list = self.parse_target(cmd)
real_cmd_str = re.search(r"-cmd[ ]+(\'|\")(?P<cmd>.*)(\'|\")", cmd)
if real_cmd_str:
real_cmd_dic = real_cmd_str.groupdict()
real_cmd_str = real_cmd_dic['cmd'].strip()
else:
real_cmd_str = None
argv_dic = {
'host_list': host_list,
'group_list': group_list,
'cmd': real_cmd_str
}
return argv_dic def parse_scp_command(self, cmd): # -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_clusters,db_servers -action put -local test.py -remote /tmp/
"""解析batch_scp命令参数"""
host_list, group_list = self.parse_target(cmd)
action_str = re.search(r"-action[ ]+[^-]+", cmd)
action_str = action_str.group().strip()[7:].strip() if action_str else None
local_str = re.search(r"-local[ ]+[^-]+", cmd)
local_str = local_str.group().strip()[6:].strip() if local_str else None
remote_str = re.search(r"-remote[ ]+[^-]+", cmd)
remote_str = remote_str.group().strip()[7:].strip() if remote_str else None
argv_dic = {
'host_list': host_list,
'group_list': group_list,
'action': action_str,
'local': local_str,
'remote': remote_str
}
return argv_dic
mian.py
db_handler.py
import shelve
from models import models
from core.color import Colors
from multiprocessing import Lock class Db_handler(object):
HOST_MUTEX = Lock()
GROUP_MUTEX = Lock()
G2H_MUTEX = Lock() @staticmethod
# 根据主机组名称,获取该主机组Obj
def getGroupObjByGroupName(group_db, groupName):
for key in group_db:
if group_db[key].groupName == groupName:
return group_db[key]
return @staticmethod
# 根据主机组Id,获取该主机组所有主机Obj列表
def getHostObjListByGroupId(host_db, g2h_db, groupId):
host_list = []
for key in g2h_db:
if g2h_db[key].groupId == groupId:
host_list.append(host_db[g2h_db[key].hostId])
return host_list # 检查主机表唯一性(host字段唯一)(判断一个host对象是否存在)
@classmethod
def check_unique_host(cls, host_db, host_obj):
for key in host_db:
if host_db[key] == host_obj:
# print('存在host:%s'%host_db[key])
return host_db[key]
return # 检查主机组表唯一性(groupName字段唯一)(判断一个group对象是否存在)
@classmethod
def check_unique_group(cls, group_db, group_obj):
for key in group_db:
if group_db[key] == group_obj:
# print('存在group:%s'%group_db[key])
return group_db[key]
return # 检查主机组-主机表唯一性(记录中存在重复的hostId和groupId)(判断一个group2Host对象是否存在)
@classmethod
def check_unique_g2h(cls, g2h_db, g2h_obj):
for key in g2h_db:
if g2h_db[key] == g2h_obj:
# print('存在g2h:%s'%g2h_db[key])
return g2h_db[key]
return # update host table
@classmethod
def update_host(cls, host_db, host_obj):
cls.HOST_MUTEX.acquire()
return_host_obj = cls.check_unique_host(host_db, host_obj)
if not return_host_obj:
host_db[host_obj.hostId] = host_obj
print(Colors('insert host table 1 row', bcolor='green'))
else:
host_obj.hostId = return_host_obj.hostId
host_db[return_host_obj.hostId] = host_obj
print(Colors('update host table 1 row', bcolor='cyan'))
cls.HOST_MUTEX.release() # insert group table
@classmethod
def insert_group(cls, group_db, group_obj):
result_code = False
cls.GROUP_MUTEX.acquire()
if not cls.check_unique_group(group_db, group_obj):
group_db[group_obj.groupId] = group_obj
result_code = True
print(Colors('insert group table 1 row', bcolor='green'))
cls.GROUP_MUTEX.release()
return result_code # insert g2h table
@classmethod
def insert_g2h(cls, g2h_db, host_obj, group_obj):
result_code = False
cls.G2H_MUTEX.acquire()
g2h_obj = models.Group2Host(host_obj.hostId, group_obj.groupId)
if not cls.check_unique_g2h(g2h_db, g2h_obj):
g2h_db[g2h_obj.g2hId] = g2h_obj
result_code = True
print(Colors('insert g2h table 1 row', bcolor='green'))
cls.G2H_MUTEX.release()
return result_code # delete g2h table
@classmethod
def delete_g2h(cls, g2h_db, host_obj, group_obj):
result_code = False
cls.G2H_MUTEX.acquire()
for key in g2h_db:
if g2h_db[key].hostId == host_obj.hostId and g2h_db[key].groupId == group_obj.groupId:
g2h_db.pop(key)
result_code = True
print(Colors('delete g2h table 1 row', bcolor='yellow'))
cls.G2H_MUTEX.release()
return result_code
db_handler.py
logger.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import os
from logging import handlers
from conf import settings def logger(log_file):
log_level = settings.log_level
if log_level == 'debug':
log_level = logging.DEBUG
elif log_level == 'info':
log_level = logging.INFO
elif log_level == 'warning':
log_level = logging.WARNING
elif log_level == 'error':
log_level = logging.ERROR
else:
log_level = logging.CRITICAL
# 1.生成logger对象
logger = logging.getLogger(log_file)
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# 2.生成handler对象
fh = handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename=os.path.join(settings.LOG_PATH, log_file),
when='D', interval=1, backupCount=3)
fh.setLevel(log_level)
# 2.1 把handler对象绑定到logger
if not logger.handlers:
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 3.生成formatter对象
f = logging.Formatter(fmt='%(asctime)s %(name)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', datefmt=None)
# 3.1 把formatter对象绑定到handler
fh.setFormatter(f)
return logger
logger.py
color.py
def Colors(text, fcolor=None, bcolor=None, style=None):
"""自定义字体样式及颜色"""
# 字体颜色
fg = {
'black': '\033[30m', # 字体黑
'red': '\033[31m', # 字体红
'green': '\033[32m', # 字体绿
'yellow': '\033[33m', # 字体黄
'blue': '\033[34m', # 字体蓝
'magenta': '\033[35m', # 字体紫
'cyan': '\033[36m', # 字体青
'white': '\033[37m', # 字体白
'end': '\033[0m' # 默认色
}
# 背景颜色
bg = {
'black': '\033[40m', # 背景黑
'red': '\033[41m', # 背景红
'green': '\033[42m', # 背景绿
'yellow': '\033[43m', # 背景黄
'blue': '\033[44m', # 背景蓝
'magenta': '\033[45m', # 背景紫
'cyan': '\033[46m', # 背景青
'white': '\033[47m', # 背景白
}
# 内容样式
st = {
'bold': '\033[1m', # 高亮
'url': '\033[4m', # 下划线
'blink': '\033[5m', # 闪烁
'seleted': '\033[7m', # 反显
} if fcolor in fg:
text = fg[fcolor] + text + fg['end']
if bcolor in bg:
text = bg[bcolor] + text + fg['end']
if style in st:
text = st[style] + text + fg['end']
return text
color.py
settings.py
# Author:ton
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os BASE_PATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
LOG_PATH = os.path.join(BASE_PATH, 'logs')
DATABASE_PATH = os.path.join(BASE_PATH, 'db')
HOST_TABLE_PATH = os.path.join(DATABASE_PATH, 'host')
GROUP_TABLE_PATH = os.path.join(DATABASE_PATH, 'group')
G2H_TABLE_PATH = os.path.join(DATABASE_PATH, 'group2Host')
TABLE_LIST = ['host', 'group', 'group2Host'] # 暴力破解配置项
user = 'sshusr'
password_list = ['', 'sshusr123', '', ]
host_list = ['10.0.0.11', '10.0.0.12', '10.0.0.13', '10.0.0.14']
port = 22
root_pwd = '' # 日志记录配置项
log_level = 'debug'
settings.py
四、使用说明
1、在conf/setttings下配置好需要暴力尝试密码的password_list和host_list
2、在Terminal终端运行工具:python bin/ideploy.py -t start
3、输入violentCipher,回车,完成后提示"暴力尝试密码完毕!"
4、输入manageHosts,回车,可以查看管理暴力尝试密码成功的主机列表,记住默认主机组(default)的groupId为1,输入b,退出
5、输入executeCommand,回车,输入批量执行命令:batch_run -g 1 -cmd "hostname",该hostname命令执行的主机对象为默认主机组(default)下的所有主机
6、输入show_task,回车,可以看到批量执行命令的结果
7、继续输入批量执行命令:batch_scp -g 1 -action put -local __init__.py -remote /tmp/target.py,把本地文件__init__.py上传至远端/tmp/下,并取名为target.py
8、输入show_task,回车,可以看到批量执行上传文件的结果
9、输入q,退出批量执行命令的界面,输入exit,退出程序 截图:
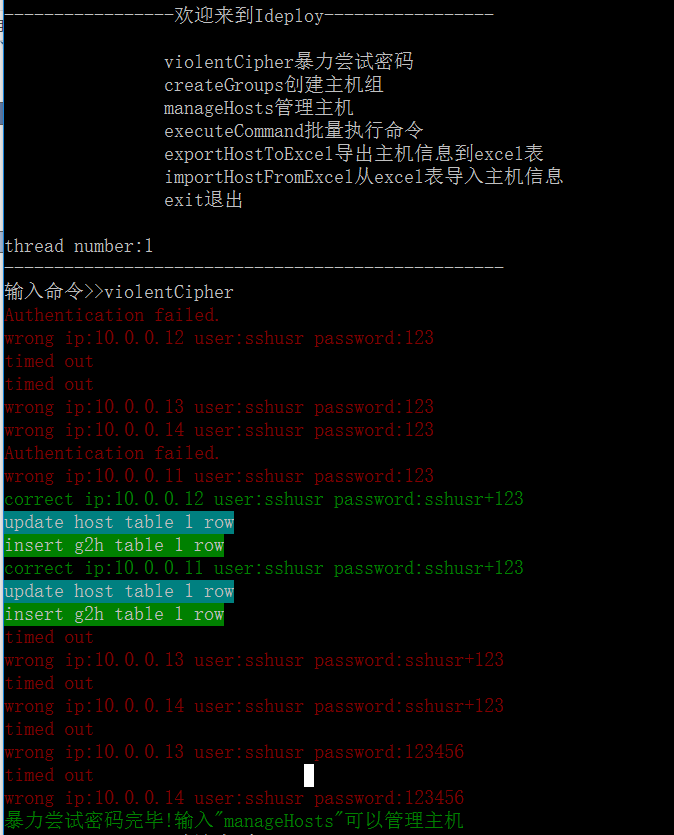



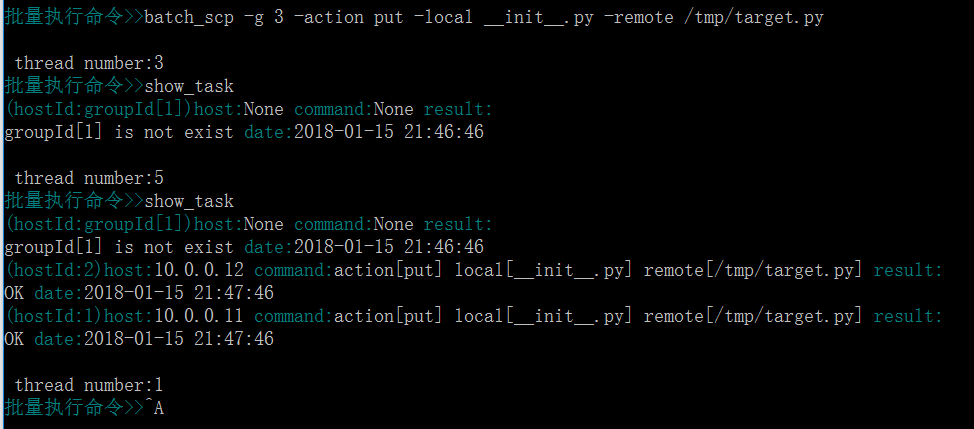
PS:任务列表(show_task)会同时记录到logs/task_list文件,永久保存

简单主机批量管理工具(这里实现了paramiko 用su切换到root用户)的更多相关文章
- Python开发程序:简单主机批量管理工具
题目:简单主机批量管理工具 需求: 主机分组 登录后显示主机分组,选择分组后查看主机列表 可批量执行命令.发送文件,结果实时返回 主机用户名密码可以不同 流程图: 说明: ### 作者介绍: * au ...
- Python简单主机批量管理工具
一.程序介绍 需求: 简单主机批量管理工具 需求: 1.主机分组 2.主机信息使用配置文件 3.可批量执行命令.发送文件,结果实时返回 4.主机用户名密码.端口可以不同 5.执行远程命令使用param ...
- python之简单主机批量管理工具
今天做了一个很简单的小项目,感受到paramiko模块的强大. 一.需求 二.简单需求分析及流程图 需求很少,我就简单地说下: 1. 主机分组可以配置文件实现(我用字典存数据的). 2. 登陆功能不做 ...
- python 简单主机批量管理工具
需求: 主机分组 主机信息配置文件用configparser解析 可批量执行命令.发送文件,结果实时返回,执行格式如下 batch_run -h h1,h2,h3 -g web_cluster ...
- 【Python之旅】第六篇(七):开发简易主机批量管理工具
[Python之旅]第六篇(七):开发简易主机批量管理工具 python 软件开发 Paramiko模块 批量主机管理 摘要: 通过前面对Paramiko模块的学习与使用,以及Python中多线程与多 ...
- Linux系统——Ansible批量管理工具
批量管理工具: (1)ansible 操作简单(适用于500台以下服务器) (2)saltstack 比较复杂(一般适用于1000-4w台服务器) (3)puppet超级复杂 systemctl(统一 ...
- 轻量级批量管理工具pssh
pssh工具 pssh工具是个轻量级的批量管理工具,相比同类型的开源工具 Ansible,Saltstack,他比较轻量级,需要对管理的主机做秘钥认证 Ansible是可以做秘钥认证,也可以通过配置文 ...
- Linux下批量管理工具pssh安装和使用
Linux下批量管理工具pssh安装和使用 pssh工具包 安装:yum -y install pssh pssh:在多个主机上并行地运行命令 pscp:把文件并行地复制到多个主机上 prsync:通 ...
- windows下运行的linux服务器批量管理工具(带UI界面)
产生背景: 由于做服务器运维方面的工作,需要一人对近千台LINUX服务器进行统一集中的管理,如同时批量对LINUX服务器执行相关的指令.同时批量对LINUX服务器upload程序包.同时批量对LINU ...
随机推荐
- Vue如何循环渲染图片
Vue如何把服务器返回的图片数据渲染出来 首先,一般来说,当请求图片的接口时,会返回一个数组,这个数组里会是一些图片的名字,比如1.jpg,2.jpg. 我的做法是先在data里定义一个数组,来存储服 ...
- javascript知识点杂记
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++) { setTimeout(function() { console.log(i); //输出10个10,因为setTimeout方法是异步 ...
- PhpStorm 查看当前类中所有的方法
展示当前类中的所有方法 Ctrl + F12 方法之间移动 alt + 向上箭头/向下箭头
- ElasticSearch 安装root用户启动失败问题解决
1. 下载ElasticSearch 2.3.3 2. 安装JDK 1.8.0以上版本 3. ElasticSearch 安装时会出现 Exception in thread "main ...
- Learning notes | Data Analysis: 1.1 data evaluation
| Data Evaluation | - Use Shift + Enter or Shift + Return to run the upper box so as to make it disp ...
- leetcode记录-组合两个表
表1: Person +-------------+---------+ | 列名 | 类型 | +-------------+---------+ | PersonId | int | | Firs ...
- 推荐一个学习Flex chart的好网站
推荐一个学习Flex chart的好网站 2013-03-04 14:16:56| 分类: Flex | 标签: |字号大中小 订阅 推荐一个学习Flex chart的好网站 最近在做一个 ...
- 20155230 实验四《android程序设计》实验报告
20155230 实验四<Android程序设计>实验报告 一.安装Android Stuidio 二.从一个活动启动另一个活动 在启动活动的活动里添加如下语句即可 Intent inte ...
- 20155338 2006-2007-2 《Java程序设计》第2周学习总结
20155338 2006-2007-2 <Java程序设计>第2周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 本周学习了教材的第三章内容,大体上都较好理解,有很多内容基本上都跟C语言的知识类似,学习的内 ...
- Potree学习总结
一. 简介 基于Web端的三维模型展示,这里仅介绍Three.js和Potree. Three.js 是一款基于WebGL的运行在浏览器中的 3D 开源引擎,用它创建各种三维场景.它类似于M ...
