hdu 1979 DFS + 字典树剪枝
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1979
Fill the blanks
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 373 Accepted Submission(s): 155
And there is a blank line between the every two matrixs.
1009
9221
3191
1021
9029
3911
……
1559
3821
3391
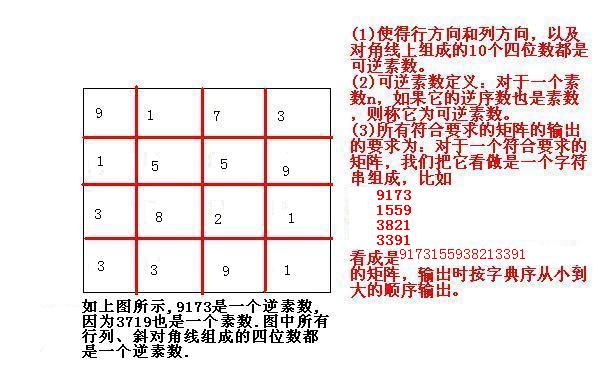
1000 --- 9999中有204个顺着和倒着读都是素数的数。
考虑的就是暴力dfs,然后最后再判断?超时。可以打表。
可以用字典树维护前缀,
每次都维护主对角线和副对角线的数字,还有四条列。然后如果不存在这样的前缀,直接剪掉就好。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
#define MY "H:/CodeBlocks/project/CompareTwoFile/DataMy.txt", "w", stdout
#define ANS "H:/CodeBlocks/project/CompareTwoFile/DataAns.txt", "w", stdout #include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
const int maxn=1e5+;
bool prime[maxn];//这个用bool就够了,
bool check[maxn];
int goodprime[maxn];
char strprime[ + ][];
int lenprime = ;
struct node {
int cnt;
struct node * pNext[];
} tree[maxn], *T;
int num;
struct node * create() {
struct node * p = &tree[num++];
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i) {
p->pNext[i] = NULL;
}
p->cnt = ;
return p;
}
void insert(struct node **T, int val) {
struct node *p = *T;
if (p == NULL) {
*T = p = create();
}
char str[] = {};
int lenstr = ;
while (val / > ) {
str[++lenstr] = val % + '';
val /= ;
}
str[++lenstr] = val + '';
str[lenstr + ] = '\0';
strcpy(strprime[lenprime] + , str + );
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) {
int id = str[i] - '';
if (p->pNext[id]) {
p->pNext[id]->cnt++;
} else p->pNext[id] = create();
p = p->pNext[id];
}
return;
}
int find(struct node *T, int val) {
struct node *p = T;
if (!p) return ;
char str[] = {};
int lenstr = ;
while (val / > ) {
str[++lenstr] = val % + '';
val /= ;
}
str[++lenstr] = val + '';
str[lenstr + ] = '\0';
reverse(str + , str + + lenstr);
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) {
int id = str[i] - '';
if (!p->pNext[id]) return ;
p = p->pNext[id];
}
return p->cnt;
}
void init_prime() {
for (int i = ; i <= maxn - ; i++) {
if (!check[i]) { //说明i是质数
prime[i] = true;
for (int j = * i; j <= maxn - ; j += i) { //筛掉i的倍数
check[j] = true; //那么j就没可能是质数了
//book[j]=i; //表示j的最大质因数是i,不断更新。后面的质因数更大
//用这个的时候,需要把2*i变成i,否则book[2]不行。
}
}
}
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i) {
int t = ;
int h = i;
if (!prime[i]) continue;
while (h / > ) {
t = t * + h % ;
h /= ;
}
t = t * + h;
if (prime[t]) {
goodprime[++lenprime] = i;
insert(&T, t);
}
}
return ;
}
int f[];
bool book[ + ];
int ans;
bool tocheck(int toval[]) {
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i) {
if (!find(T, toval[i])) return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int cur, int valmain, int valother, int toval[]) {
if (cur == ) {
++ans;
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i) {
printf("%d\n", goodprime[f[i]]);
}
if (ans != ) printf("\n");
// while(1);
return;
}
for (int i = ; i <= lenprime; ++i) {
f[cur] = i;
if (cur == ) {
valmain = valmain * + strprime[i][] - '';
valother = valother * + strprime[i][] - '';
} else if (cur == ) {
valmain = valmain * + strprime[i][] - '';
valother = valother * + strprime[i][] - '';
} else if (cur == ) {
valmain = valmain * + strprime[i][] - '';
valother = valother * + strprime[i][] - '';
} else {
valmain = valmain * + strprime[i][] - '';
valother = valother * + strprime[i][] - '';
}
for (int j = ; j <= ; ++j) {
toval[j] = toval[j] * + strprime[i][j] - '';
}
if (!find(T, valmain) || !find(T, valother) || !tocheck(toval)) {
valmain /= ;
valother /= ;
for (int j = ; j <= ; ++j) {
toval[j] /= ;
}
continue;
}
// printf("%d\n", ++ans);
dfs(cur + , valmain, valother, toval);
valmain /= ;
valother /= ;
for (int j = ; j <= ; ++j) {
toval[j] /= ;
}
}
}
void work() {
// printf("%d\n", prime[9029]);
// printf("%d\n", find(T, 9209));
int toval[] = {};
dfs(, , , toval);
// cout << ans << endl;
} int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
init_prime();
work();
return ;
}
hdu 1979 DFS + 字典树剪枝的更多相关文章
- HDU 1298 T9 字典树+DFS
必须要批评下自己了,首先就是这个题目的迟疑不定,去年做字典树的时候就碰到这个题目了,当时没什么好的想法,就暂时搁置了,其实想法应该有很多,只是居然没想到. 同样都是对单词进行建树,并插入可能值,但是拨 ...
- HDU 5877 dfs+ 线段树(或+树状树组)
1.HDU 5877 Weak Pair 2.总结:有多种做法,这里写了dfs+线段树(或+树状树组),还可用主席树或平衡树,但还不会这两个 3.思路:利用dfs遍历子节点,同时对于每个子节点au, ...
- POJ 3764 - The xor-longest Path - [DFS+字典树变形]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3764 Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Description In an edge-w ...
- hdu 2846(字典树)
Repository Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- HDU 2846 Repository (字典树 后缀建树)
Repository Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Total ...
- HDU 1671 (字典树统计是否有前缀)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1671 Problem Description Given a list of phone number ...
- three arrays HDU - 6625 (字典树)
three arrays \[ Time Limit: 2500 ms \quad Memory Limit: 262144 kB \] 题意 给出 \(a\),\(b\) 数组,定义数组 \(c[i ...
- HDU 1298 T9 ( 字典树 )
题意 : 给你 w 个单词以及他们的频率,现在给出模拟 9 键打字的一串数字,要你在其模拟打字的过程中给出不同长度的提示词,出现的提示词应当是之前频率最高的,当然提示词不需要完整的,也可以是 w 个单 ...
- GCPC 2013_A Boggle DFS+字典树 CSU 1457
上周比赛的题目,由于那个B题被神编译器的优化功能给卡了,就没动过这个题,其实就是个字典树嘛.当然,由于要在Boggle矩阵里得到初始序列,我还一度有点虚,不知道是用BFS还是DFS,最后发现DFS要好 ...
随机推荐
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(十五)Html基础积累总结(下)
本文来自:曹胜欢博客专栏.转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/csh624366188 一:表格 1.表格的基本语法 <table>...</table> ...
- 20170301 Excel 导出函数XXL_SIMPLE_API
* XMPLT_V-COL_NO = . * XMPLT_V-COL_NAME = '物料号码'. * APPEND XMPLT_V. * * XMPLT_V-COL_NO = . * XMPLT_V ...
- HDU 5438 Ponds
Ponds Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)Total Sub ...
- 基于Delphi7 WebService 在Apache发布及Apache使用说明
基于Delphi7 WebService 在Apache 发布及Apache 使用说明 qq:394251165 前段时间,需要将基于Delphi7 WebService 发布在Apache, 很是苦 ...
- js 中call,apply,bind的区别
call.apply.bind方法的共同点与区别: apply.call.bind 三者都是用来改变函数的this对象的指向: apply.call.bind 三者都可以利用后续参数传参: bind ...
- MYSQL初级学习笔记七:MySQL中使用正则表达式!(视频序号:初级_44)
知识点九:MySQL中使用正则表达式(44) (1):REGEXP‘匹配方式’: (2):常用匹配方式: 模式字符 ^ 匹配字符开始的部分 $ 匹配字符串结尾的部分 . 代表字符串中的任意一个字符,包 ...
- jsp的4大作用域
jsp的4大作用域 首先要声明一点,所谓“作用域”就是“信息共享的范围”,也就是说一个信息能够在多大的范围内有效.4个JSP内置对象的作用域分别为:application.session.reques ...
- 深入理解WeakHashmap
转自:http://mikewang.blog.51cto.com/3826268/880775 (一) 查看API文档,WeakHashmap要点如下: 1. 以弱键 实现的基于哈希表的 Map.在 ...
- hdu-5120 Intersection(计算几何)
题目链接: Intersection Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Ot ...
- Opencv函数setMouseCallback鼠标事件响应
用户通过鼠标对图像视窗最常见的操作有: 1. 左键单击按下 2. 左键单击抬起 3. 左键按下拖动 4. 鼠标指针位置移动 单次单击操作响应事件及顺序 Opencv中setMouseCallback( ...