【传智播客】Libevent学习笔记(三):事件循环
00. 目录
声明: 该博客来源于传智播客C++学院相关培训参考手册
01. event_base_loop函数
一旦有了一个已经注册了某些事件的event_base(关于如何创建和注册事件请看笔记四),就需要让libevent等待事件并且通知事件的发生。
event_base_loop函数
/**
Wait for events to become active, and run their callbacks.
This is a more flexible version of event_base_dispatch().
By default, this loop will run the event base until either there are no more
pending or active events, or until something calls event_base_loopbreak() or
event_base_loopexit(). You can override this behavior with the 'flags'
argument.
@param eb the event_base structure returned by event_base_new() or
event_base_new_with_config()
@param flags any combination of EVLOOP_ONCE | EVLOOP_NONBLOCK
@return 0 if successful, -1 if an error occurred, or 1 if we exited because
no events were pending or active.
@see event_base_loopexit(), event_base_dispatch(), EVLOOP_ONCE,
EVLOOP_NONBLOCK
*/
int event_base_loop(struct event_base *base, int flag); //while(1) { .... }
功能:
等待事件被触发, 然后执行对应的回调函数
参数:
base: event_base_new的返回值
flag: 标志
返回值:
成功: 0成功 1表示没有事件触发
失败: -1
循环相关标志:
/** @name Loop flags
These flags control the behavior of event_base_loop().
*/
/**@{*/
/** Block until we have an active event, then exit once all active events
* have had their callbacks run. */
#define EVLOOP_ONCE 0x01
/** Do not block: see which events are ready now, run the callbacks
* of the highest-priority ones, then exit. */
#define EVLOOP_NONBLOCK 0x02
/**@}*/
默认情况下,event_base_loop()函数运行event_base直到其中没有已经注册的事件为止。执行循环的时候,函数重复地检查是否有任何已经注册的事件被触发(比如说,读事件的文件描述符已经就绪,可以读取了;或者超时事件的超时时间即将到达)。如果有事件被触发,函数标记被触发的事件为“激活的”,并且执行这些事件。
在flags参数中设置一个或者多个标志就可以改变event_base_loop()的行为。如果设置了EVLOOP_ONCE,循环将等待某些事件成为激活的,执行激活的事件直到没有更多的事件可以执行,然会返回。如果设置了EVLOOP_NONBLOCK,循环不会等待事件被触发:循环将仅仅检测是否有事件已经就绪,可以立即触发,如果有,则执行事件的回调。
完成工作后,如果正常退出,event_base_loop()返回0;如果因为后端中的某些未处理错误而退出,则返回-1。
为帮助大家理解,这里给出event_base_loop()的算法概要:
while (any events are registered with the loop) {
if (EVLOOP_NONBLOCK was set, or any events are already active)
If any registered events have triggered, mark them active.
else
Wait until at least one event has triggered, and mark it active.
for (p = 0; p < n_priorities; ++p {
if (any event with priority of p is active) {
Run all active events with priority of p.
break; /* Do not run any events of a less important priority */
}
}
if (EVLOOP_ONCE was set or EVLOOP_NONBLOCK was set)
break;
}
02. event_base_dispatch函数
event_base_dispatch()等同于没有设置标志的event_base_loop()。所以,event_base_dispatch()将一直运行,直到没有已经注册的事件了,或者调用了event_base_loopbreak()或者event_base_loopexit()为止。
/**
Event dispatching loop
This loop will run the event base until either there are no more pending or
active, or until something calls event_base_loopbreak() or
event_base_loopexit().
@param base the event_base structure returned by event_base_new() or
event_base_new_with_config()
@return 0 if successful, -1 if an error occurred, or 1 if we exited because
no events were pending or active.
@see event_base_loop()
*/
int event_base_dispatch(struct event_base *base);
等价于没有设置标志的 event_base_loop函数
event_base_dispatch()将一直运行,直到没有已经注册的事件了,或者调用了event_base_loopbreak()或者event_base_loopexit()为止。
这些函数定义在<event2/event.h>中,从libevent 1.0版就存在了。
03. event_base_loopexit函数
/**
Exit the event loop after the specified time
The next event_base_loop() iteration after the given timer expires will
complete normally (handling all queued events) then exit without
blocking for events again.
Subsequent invocations of event_base_loop() will proceed normally.
@param eb the event_base structure returned by event_init()
@param tv the amount of time after which the loop should terminate,
or NULL to exit after running all currently active events.
@return 0 if successful, or -1 if an error occurred
@see event_base_loopbreak()
*/
int event_base_loopexit(struct event_base *base, const struct timeval *tv);
功能:
让event_base在给定时间之后停止循环。
参数:
base event_base_new的返回值
tv 表示延时的时间,如果为NULL 立即停止循环,没有延时
返回值:
成功: 0成功
失败: -1
注意:
如果event_base当前正在执行任何激活事件的回调,则回调会继续运行,直到运行完所有激活事件的回调之才退出。
04. event_base_loopbreak函数
/**
Abort the active event_base_loop() immediately.
event_base_loop() will abort the loop after the next event is completed;
event_base_loopbreak() is typically invoked from this event's callback.
This behavior is analogous to the "break;" statement.
Subsequent invocations of event_loop() will proceed normally.
@param eb the event_base structure returned by event_init()
@return 0 if successful, or -1 if an error occurred
@see event_base_loopexit()
*/
int event_base_loopbreak(struct event_base *base);
功能:
让event_base立即停止循环。
参数:
base event_base_new的返回值
返回值:
成功: 0成功
失败: -1
这些函数声明在<event2/event.h>中。event_break_loopexit()函数首次在libevent 1.0c版本中实现;event_break_loopbreak()首次在libevent 1.4.3版本中实现。
注意:
event_base_loopbreak()让event_base立即退出循环。它与event_base_loopexit(base,NULL)的不同在于,如果event_base当前正在执行激活事件的回调,它将在执行完当前正在处理的事件后立即退出。
event_base_loopexit(base,NULL)和event_base_loopbreak(base)在事件循环没有运行时的行为不同:前者安排下一次事件循环在下一轮回调完成后立即停止(就好像带EVLOOP_ONCE标志调用一样);后者却仅仅停止当前正在运行的循环,如果事件循环没有运行,则没有任何效果。
官方参考示例一: 立即退出循环
#include <event2/event.h>
/* Here's a callback function that calls loopbreak */
void cb(int sock, short what, void *arg)
{
struct event_base *base = arg;
event_base_loopbreak(base);
}
void main_loop(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t watchdog_fd)
{
struct event *watchdog_event;
/* Construct a new event to trigger whenever there are any bytes to
read from a watchdog socket. When that happens, we'll call the
cb function, which will make the loop exit immediately without
running any other active events at all.
*/
watchdog_event = event_new(base, watchdog_fd, EV_READ, cb, base);
event_add(watchdog_event, NULL);
event_base_dispatch(base);
}
官方参考示例二: 执行事件循环10秒,然后退出
#include <event2/event.h>
void run_base_with_ticks(struct event_base *base)
{
struct timeval ten_sec;
ten_sec.tv_sec = 10;
ten_sec.tv_usec = 0;
/* Now we run the event_base for a series of 10-second intervals, printing
"Tick" after each. For a much better way to implement a 10-second
timer, see the section below about persistent timer events. */
while (1) {
/* This schedules an exit ten seconds from now. */
event_base_loopexit(base, &ten_sec);
event_base_dispatch(base);
puts("Tick");
}
}
测试代码: 每隔3秒钟输出一个字符串
#include <stdio.h>
#include <event.h>
int main(void)
{
struct event_base *base = NULL;
struct timeval tmo = {3, 0};
base = event_base_new();
if (NULL == base)
{
printf("event_base_new failded...\n");
return 1;
}
while(1)
{
//设置三秒钟退出事件循环
event_base_loopexit(base, &tmo);
//进入事件循环
event_base_dispatch(base);
printf("hello itcast\n");
}
event_base_free(base);
return 0;
}
05. event_base_got_exit函数
有时候需要知道对event_base_dispatch()或者event_base_loop()的调用是正常退出的,还是因为调用event_base_loopexit()或者event_base_break()而退出的。可以调用下述函数来确定是否调用了loopexit或者break函数。
/**
Checks if the event loop was told to exit by event_loopexit().
This function will return true for an event_base at every point after
event_loopexit() is called, until the event loop is next entered.
@param eb the event_base structure returned by event_init()
@return true if event_base_loopexit() was called on this event base,
or 0 otherwise
@see event_base_loopexit()
@see event_base_got_break()
*/
int event_base_got_exit(struct event_base *base);
功能:
判断循环是否因为调用event_base_loopexit()或者event_base_break()而退出的时候返回true,否则返回false。下次启动事件循环的时候,这些值会被重设。
参数:
base event_base_new的返回值
返回值:
true 循环是因为调用对应的函数而退出
0 其它情况
参考示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <event.h>
int main(void)
{
struct event_base *base = NULL;
struct timeval tmo = {3, 0};
base = event_base_new();
if (NULL == base)
{
printf("event_base_new failded...\n");
return 1;
}
while(1)
{
event_base_loopexit(base, &tmo);
event_base_dispatch(base);
printf("hello itcast\n");
//如果事件循环因为event_base_loopexit而退出 返回true
if (event_base_got_exit(base))
{
printf("event_base_got_exit return true\n");
}
}
event_base_free(base);
return 0;
}
06. event_base_got_break函数
有时候需要知道对event_base_dispatch()或者event_base_loop()的调用是正常退出的,还是因为调用event_base_loopexit()或者event_base_break()而退出的。可以调用下述函数来确定是否调用了loopexit或者break函数。
/**
Checks if the event loop was told to abort immediately by event_loopbreak().
This function will return true for an event_base at every point after
event_loopbreak() is called, until the event loop is next entered.
@param eb the event_base structure returned by event_init()
@return true if event_base_loopbreak() was called on this event base,
or 0 otherwise
@see event_base_loopbreak()
@see event_base_got_exit()
*/
int event_base_got_break(struct event_base *base);
功能:
判断循环是否因为调用event_base_loopexit()或者event_base_break()而退出的时候返回true,否则返回false。下次启动事件循环的时候,这些值会被重设。
参数:
base event_base_new的返回值
返回值:
true 循环是因为调用对应的函数而退出
0 其它情况
07. event_base_dump_events函数
有时候需要在事件回调中获取当前时间的近似视图,但不想调用gettimeofday()(可能是因为OS将gettimeofday()作为系统调用实现,而你试图避免系统调用的开销)。
在回调中,可以请求libevent开始本轮回调时的当前时间视图。
void event_base_dump_events(struct event_base *, FILE *);
/** Sets 'tv' to the current time (as returned by gettimeofday()),
looking at the cached value in 'base' if possible, and calling
gettimeofday() or clock_gettime() as appropriate if there is no
cached time.
Generally, this value will only be cached while actually
processing event callbacks, and may be very inaccuate if your
callbacks take a long time to execute.
Returns 0 on success, negative on failure.
*/
int event_base_gettimeofday_cached(struct event_base *base,
struct timeval *tv);
如果event_base当前正在执行回调,event_base_gettimeofday_cached()函数设置tv_out参数的值为缓存的时间。否则,函数调用evutil_gettimeofday()获取真正的当前时间。成功时函数返回0,失败时返回负数。
返回值:
成功 0
失败 负数
注意:
注意,因为libevent在开始执行回调的时候时间值会被缓存,所以这个值至少是有一点不精确。如果回调执行很长时间,这个值将非常不精确。
这个函数是libevent 2.0.4-alpha新引入的。
08. event_base_dump_events函数
为帮助调试程序(或者调试libevent),有时候可能需要已经加入到event_base的所有事件及其状态的完整列表。调用event_base_dump_events()可以将这个列表输出到指定的文件中。
这个列表是人可读的,未来版本的libevent将会改变其格式。
void event_base_dump_events(struct event_base *base, FILE *file);
功能:
转储event_base的状态到文件中。
参数:
base event_base_new的返回值
file FILE类型指针
返回值:
无
这个函数在libevent 2.0.1-alpha版本中引入。
09. 废弃的事件循环函数
前面已经讨论过,老版本的libevent 具有“当前”event_base的概念。
本文讨论的某些事件循环函数具有操作当前event_base的变体。除了没有base参数外,这些函数跟当前新版本函数的行为相同。
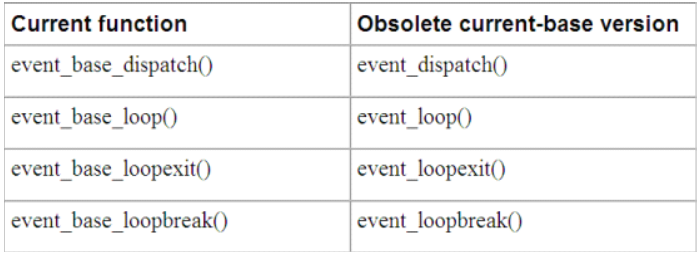
2.0版本之前的event_base是不支持锁的,所以这些函数并不是完全线程安全的:不允许在执行事件循环的线程之外的其他线程中调用_loopbreak()或者_loopexit()函数。
10.参考
相关书籍: http://www.wangafu.net/~nickm/libevent-book/Ref2_eventbase.html
官方参考网站: https://www.monkey.org/~provos/libevent/doxygen-2.0.1/index.html
【传智播客】Libevent学习笔记(三):事件循环的更多相关文章
- 传智播客Springmvc_mybatis学习笔记
文件地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_26078953/10614459
- 传智播客JavaWeb day02笔记
2015年1月21日 今天的主要内容:介绍了几款常用Javaweb服务器,重点介绍了tomcat以及tomcat的安装和怎么样检测安装成功 1.JavaWeb常见服务器 Tomcat(免费但是只支持部 ...
- 传智播客成都校园php纪律指控
继传智播客成都校区php第一期班圆满开班,说明php的火爆一点儿也不亚于java! 经传智播客商讨决定,传智播客成都校区php学科收费标准例如以下: 採用下面不论什么一种方式都能够享受优惠价: 一.自 ...
- 【传智播客】Libevent学习笔记(五):基本类型和函数
目录 00. 目录 01. 基本类型 1.1 evutil_socket_t类型 1.2 标准类型 1.3 各种兼容性类型 02. 可移植的定时器函数 03. 套接字API兼容性 04. 可移植的字符 ...
- 【传智播客】Libevent学习笔记(四):事件event
目录 00. 目录 01. 事件概述 02. 创建事件 03. 事件的标志 04. 事件持久性 05. 超时事件 06. 信号事件 07. 设置不使用堆分配的事件 08. 事件的未决和非未决 09. ...
- 【传智播客】Libevent学习笔记(二):创建event_base
目录 00. 目录 01. 简介 02. 创建默认的event_base 03. 创建复杂的event_base 3.1 event_config_new函数 3.2 event_base_new_w ...
- 传智播客.NET视频学习课件
传智播客.NET视频学习课件访问.NET网站了解更多课程详情http://net.itcast.cn(小提示:为什么本书中超链接打不开?)此套课件是伴随 传智播客.net实况教学视频 (小提示:为什么 ...
- 传智播客学习之Android运行原理 (转)
传智播客学习之Android运行原理 (2010-03-20 22:45:15) 转载▼ 今天终于忙里偷闲,和大家探讨一下android技术,第一次听到3G应该追溯到大学三年级的时候了,记得当时现代通 ...
- 传智播客C语言视频第二季(第一季基础上增加诸多C语言案例讲解,有效下载期为10.5-10.10关闭)
卷 backup 的文件夹 PATH 列表卷序列号为 00000025 D4A8:14B0J:.│ 1.txt│ c语言经典案例效果图示.doc│ ├─1传智播客_尹成_C语言从菜鸟到高手_第一 ...
随机推荐
- Collection View Programming Guide for iOS---(一)----About iOS Collection Views
Next About iOS Collection Views 关于iOS Collection Views A collection view is a way to present an orde ...
- 用Xtrabackup实现MySQL全库备份与恢复
xtrabackup包含两个主要的工具,即xtrabackup和innobackupex,二者区别如下: (1)xtrabackup只能备份innodb和xtradb两种引擎的表,而不能备份myisa ...
- Nginx: 统计PV、UV、独立IP
1.概念: UV(Unique Visitor):独立访客,将每个独立上网电脑(以cookie为依据)视为一位访客,一天之内(00:00-24:00),访问您网站的访客数量.一天之内相同cookie的 ...
- P5165 xtq的棋盘
传送门 设\(f[i]\)为\(i\)位置向左走一步的期望时间,那么答案就是\(\sum_{i=1}^mf[i]\) 首先\(f[n]=1\),设\(p\)为向左的概率,对于\(i<n\)的位置 ...
- Django学习:模板继承和配置静态文件
一.模板继承 目的是:减少代码的冗余 语法: {% block classinfo %} {% endblock %} 具体步骤: 1.创建一个base.html文件,2.把要显示的页面的内容写在这里 ...
- C#大话设计模式学习总结
如有雷同,不胜荣欣,如转载,请注明 C#大话设计模式学习总结 一.工厂模式 面向对象的三个特性:封装,继承和多态 1.封装 Class Operate { privatedouble _numberA ...
- iOS Swift3 用全局“宏”时要注意的问题
当你需要定义一个APP全局“宏”来调用 UserDefaults.standard里存储的值的时候, 一定要将这个“宏”定义为计算属性,否则你得到的值只会在APP启动的时候计算一次. 示例如下: va ...
- iOS NavigationBar 导航栏自定义
1. 设置导航栏NavigationBar的背景颜色: a) setBarTintColor : 设置NagivationBar的颜色 也可以用 : [[UINavigationBar appear ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 011 F - Train Service Planning
题目传送门:https://agc011.contest.atcoder.jp/tasks/agc011_f 题目大意: 现有一条铁路,铁路分为\(1\sim n\)个区间和\(0\sim n\)个站 ...
- Codeforces Round #395 (Div. 2) D
Description One of Timofey's birthday presents is a colourbook in a shape of an infinite plane. On t ...
