zookeeper【5】分布式锁
我们常说的锁是单进程多线程锁,在多线程并发编程中,用于线程之间的数据同步,保护共享资源的访问。而分布式锁,指在分布式环境下,保护跨进程、跨主机、跨网络的共享资源,实现互斥访问,保证一致性。
架构图:
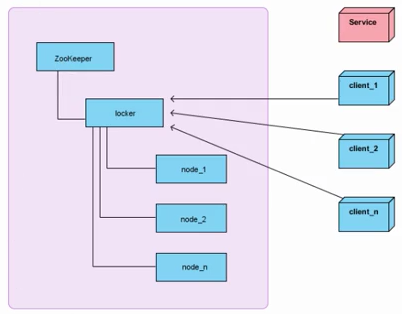
分布式锁获取思路
a、在获取分布式锁的时候在locker节点下创建临时顺序节点,释放锁的时候删除该临时节点。
b、客户端调用createNode方法在locker下创建临时顺序节点,然后调用getChildren(“locker”)来获取locker下面的所有子节点,注意此时不用设置任何Watcher。
c、客户端获取到所有的子节点path之后,如果发现自己创建的子节点序号最小,那么就认为该客户端获取到了锁。
d、如果发现自己创建的节点并非locker所有子节点中最小的,说明自己还没有获取到锁,此时客户端需要找到比自己小的那个节点,然后对其调用exist()方法,同时对其注册事件监听器。
e、之后,让这个被关注的节点删除,则客户端的Watcher会收到相应通知,此时再次判断自己创建的节点是否是locker子节点中序号最小的,如果是则获取到了锁,如果不是则重复以上步骤继续获取到比自己小的一个节点并注册监听。
实现代码:
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.IZkDataListener;
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.ZkClient;
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.exception.ZkNoNodeException; import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class BaseDistributedLock { private final ZkClientExt client;
private final String path;
private final String basePath;
private final String lockName;
private static final Integer MAX_RETRY_COUNT = 10; public BaseDistributedLock(ZkClientExt client, String path, String lockName){ this.client = client;
this.basePath = path;
this.path = path.concat("/").concat(lockName);
this.lockName = lockName; } // 删除成功获取锁之后所创建的那个顺序节点
private void deleteOurPath(String ourPath) throws Exception{
client.delete(ourPath);
} // 创建临时顺序节点
private String createLockNode(ZkClient client, String path) throws Exception{
return client.createEphemeralSequential(path, null);
} // 等待比自己次小的顺序节点的删除
private boolean waitToLock(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception{ boolean haveTheLock = false;
boolean doDelete = false; try { while ( !haveTheLock ) {
// 获取/locker下的经过排序的子节点列表
List<String> children = getSortedChildren(); // 获取刚才自己创建的那个顺序节点名
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length()+1); // 判断自己排第几个
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
if (ourIndex < 0){ // 网络抖动,获取到的子节点列表里可能已经没有自己了
throw new ZkNoNodeException("节点没有找到: " + sequenceNodeName);
} // 如果是第一个,代表自己已经获得了锁
boolean isGetTheLock = ourIndex == 0; // 如果自己没有获得锁,则要watch比我们次小的那个节点
String pathToWatch = isGetTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - 1); if ( isGetTheLock ){
haveTheLock = true; } else { // 订阅比自己次小顺序节点的删除事件
String previousSequencePath = basePath .concat( "/" ) .concat( pathToWatch );
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
final IZkDataListener previousListener = new IZkDataListener() { public void handleDataDeleted(String dataPath) throws Exception {
latch.countDown(); // 删除后结束latch上的await
} public void handleDataChange(String dataPath, Object data) throws Exception {
// ignore
}
}; try {
//订阅次小顺序节点的删除事件,如果节点不存在会出现异常
client.subscribeDataChanges(previousSequencePath, previousListener); if ( millisToWait != null ) {
millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ( millisToWait <= 0 ) {
doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node
break;
} latch.await(millisToWait, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS); // 在latch上await
} else {
latch.await(); // 在latch上await
} // 结束latch上的等待后,继续while重新来过判断自己是否第一个顺序节点
}
catch ( ZkNoNodeException e ) {
//ignore
} finally {
client.unsubscribeDataChanges(previousSequencePath, previousListener);
} }
}
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
//发生异常需要删除节点
doDelete = true;
throw e;
} finally {
//如果需要删除节点
if ( doDelete ) {
deleteOurPath(ourPath);
}
}
return haveTheLock;
} private String getLockNodeNumber(String str, String lockName) {
int index = str.lastIndexOf(lockName);
if ( index >= 0 ) {
index += lockName.length();
return index <= str.length() ? str.substring(index) : "";
}
return str;
} // 获取/locker下的经过排序的子节点列表
List<String> getSortedChildren() throws Exception {
try{ List<String> children = client.getChildren(basePath);
Collections.sort(
children, new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String lhs, String rhs) {
return getLockNodeNumber(lhs, lockName).compareTo(getLockNodeNumber(rhs, lockName));
}
}
);
return children; } catch (ZkNoNodeException e){
client.createPersistent(basePath, true);
return getSortedChildren();
}
} protected void releaseLock(String lockPath) throws Exception{
deleteOurPath(lockPath);
} protected String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null; String ourPath = null;
boolean hasTheLock = false;
boolean isDone = false;
int retryCount = 0; //网络闪断需要重试一试
while ( !isDone ) {
isDone = true; try {
// 在/locker下创建临时的顺序节点
ourPath = createLockNode(client, path);
// 判断自己是否获得了锁,如果没有获得那么等待直到获得锁或者超时
hasTheLock = waitToLock(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
} catch ( ZkNoNodeException e ) { // 捕获这个异常
if ( retryCount++ < MAX_RETRY_COUNT ) { // 重试指定次数
isDone = false;
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
if ( hasTheLock ) {
return ourPath;
} return null;
} }
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public interface DistributedLock {
/*
* 获取锁,如果没有得到就等待
*/
public void acquire() throws Exception;
/*
* 获取锁,直到超时
*/
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception;
/*
* 释放锁
*/
public void release() throws Exception;
}
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class SimpleDistributedLockMutex extends BaseDistributedLock implements
DistributedLock { //锁名称前缀,成功创建的顺序节点如lock-0000000000,lock-0000000001,...
private static final String LOCK_NAME = "lock-"; // zookeeper中locker节点的路径
private final String basePath; // 获取锁以后自己创建的那个顺序节点的路径
private String ourLockPath; private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { ourLockPath = attemptLock(time, unit);
return ourLockPath != null; } public SimpleDistributedLockMutex(ZkClientExt client, String basePath){ super(client,basePath,LOCK_NAME);
this.basePath = basePath; } // 获取锁
public void acquire() throws Exception {
if ( !internalLock(-1, null) ) {
throw new IOException("连接丢失!在路径:'"+basePath+"'下不能获取锁!");
}
} // 获取锁,可以超时
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { return internalLock(time, unit);
} // 释放锁
public void release() throws Exception { releaseLock(ourLockPath);
} }
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.serialize.BytesPushThroughSerializer;
public class TestDistributedLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ZkClientExt zkClientExt1 = new ZkClientExt("192.168.1.105:2181", 5000, 5000, new BytesPushThroughSerializer());
final SimpleDistributedLockMutex mutex1 = new SimpleDistributedLockMutex(zkClientExt1, "/Mutex");
final ZkClientExt zkClientExt2 = new ZkClientExt("192.168.1.105:2181", 5000, 5000, new BytesPushThroughSerializer());
final SimpleDistributedLockMutex mutex2 = new SimpleDistributedLockMutex(zkClientExt2, "/Mutex");
try {
mutex1.acquire();
System.out.println("Client1 locked");
Thread client2Thd = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
mutex2.acquire();
System.out.println("Client2 locked");
mutex2.release();
System.out.println("Client2 released lock");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
client2Thd.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
mutex1.release();
System.out.println("Client1 released lock");
client2Thd.join();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.ZkClient;
import org.I0Itec.zkclient.serialize.ZkSerializer;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; public class ZkClientExt extends ZkClient { public ZkClientExt(String zkServers, int sessionTimeout, int connectionTimeout, ZkSerializer zkSerializer) {
super(zkServers, sessionTimeout, connectionTimeout, zkSerializer);
} @Override
public void watchForData(final String path) {
retryUntilConnected(new Callable<Object>() { public Object call() throws Exception {
Stat stat = new Stat();
_connection.readData(path, stat, true);
return null;
} });
} }
zookeeper【5】分布式锁的更多相关文章
- zookeeper实现分布式锁服务
A distributed lock base on zookeeper. zookeeper是hadoop下面的一个子项目, 用来协调跟hadoop相关的一些分布式的框架, 如hadoop, hiv ...
- [ZooKeeper.net] 3 ZooKeeper的分布式锁
基于ZooKeeper的分布式锁 ZooKeeper 里实现分布式锁的基本逻辑: 1.zookeeper中创建一个根节点(Locks),用于后续各个客户端的锁操作. 2.想要获取锁的client都在L ...
- 基于 Zookeeper 的分布式锁实现
1. 背景 最近在学习 Zookeeper,在刚开始接触 Zookeeper 的时候,完全不知道 Zookeeper 有什么用.且很多资料都是将 Zookeeper 描述成一个“类 Unix/Linu ...
- zookeeper的分布式锁
实现分布式锁目前有三种流行方案,分别为基于数据库.Redis.Zookeeper的方案,其中前两种方案网络上有很多资料可以参考,本文不做展开.我们来看下使用Zookeeper如何实现分布式锁. 什么是 ...
- zookeeper 实现分布式锁安全用法
zookeeper 实现分布式锁安全用法 标签: zookeeper sessionExpire connectionLoss 分布式锁 背景 ConnectionLoss 链接丢失 SessionE ...
- 基于Zookeeper的分布式锁
实现分布式锁目前有三种流行方案,分别为基于数据库.Redis.Zookeeper的方案,其中前两种方案网络上有很多资料可以参考,本文不做展开.我们来看下使用Zookeeper如何实现分布式锁. 什么是 ...
- 转载 [ZooKeeper.net] 3 ZooKeeper的分布式锁
[ZooKeeper.net] 3 ZooKeeper的分布式锁 基于ZooKeeper的分布式锁 源码分享:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1miQCDKk ZooKeeper ...
- Redis与Zookeeper实现分布式锁的区别
Redis实现分布式锁 1.根据lockKey区进行setnx(set not exist,如果key值为空,则正常设置,返回1,否则不会进行设置并返回0)操作,如果设置成功,表示已经获得锁,否则并没 ...
- Zookeeper系列四:Zookeeper实现分布式锁、Zookeeper实现配置中心
一.Zookeeper实现分布式锁 分布式锁主要用于在分布式环境中保证数据的一致性. 包括跨进程.跨机器.跨网络导致共享资源不一致的问题. 1. 分布式锁的实现思路 说明: 这种实现会有一个缺点,即当 ...
- 10分钟看懂!基于Zookeeper的分布式锁
实现分布式锁目前有三种流行方案,分别为基于数据库.Redis.Zookeeper的方案,其中前两种方案网络上有很多资料可以参考,本文不做展开.我们来看下使用Zookeeper如何实现分布式锁. 什么是 ...
随机推荐
- Perl6 必应抓取(2):最终版
use HTTP::UserAgent; use URI::Encode; Firefox/52.0>); my $bing_url = 'http://cn.bing.com/search?q ...
- git忽略特殊文件或文件夹
1.在项目目录中添加“.gitignore”文件,项目目录就是你存放git工程的目录就是有“.git”目录的目录 vi .gitignore 2.在文件中添加如下内容,其中“/runtime/”是忽略 ...
- mac idea内存溢出
VM options: -mx2048m -XX:MaxPermSize=2048m -Drebel.spring_plugin=true -Drebel.hibernate_plugin=true
- 最后一面《HR面》------十大经典提问
1.HR:你希望通过这份工作获得什么? 1).自杀式回答:我希望自己为之工作的企业能够重视质量,而且会给做得好的员工予以奖励.我希望通过这份工作锻炼自己,提升自己的能力,能让公司更加重视我. a.“我 ...
- Tomcat 上传war包后 会自动部署
- 20165203《Java程序设计》第五周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 第七章 内部类 注意内部类和外嵌类的关系: 外嵌类的成员变量和方法在内部类有效 内部类的类体不可以声明static变量和方法.外嵌类的类体可以用内部类声明对象. 内部类仅供它的外嵌类 ...
- Python创建ES索引
# pip install elasticsearch from datetime import datetime from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch es ...
- GUC-6 Callable 接口
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.ut ...
- Asp.net Vnext TagHelpers
概述 本文已经同步到<Asp.net Vnext 系列教程 >中] TagHelpers 是vnext中引入的新功能之一.TagHelper 的作用是类似于发挥在以前版本的 ASP.NET ...
- Hive(三)Hive元数据信息对应MySQL数据库表
概述 Hive 的元数据信息通常存储在关系型数据库中,常用MySQL数据库作为元数据库管理.上一篇hive的安装也是将元数据信息存放在MySQL数据库中. Hive的元数据信息在MySQL数据中有57 ...
