Java基础学习篇---------多线程
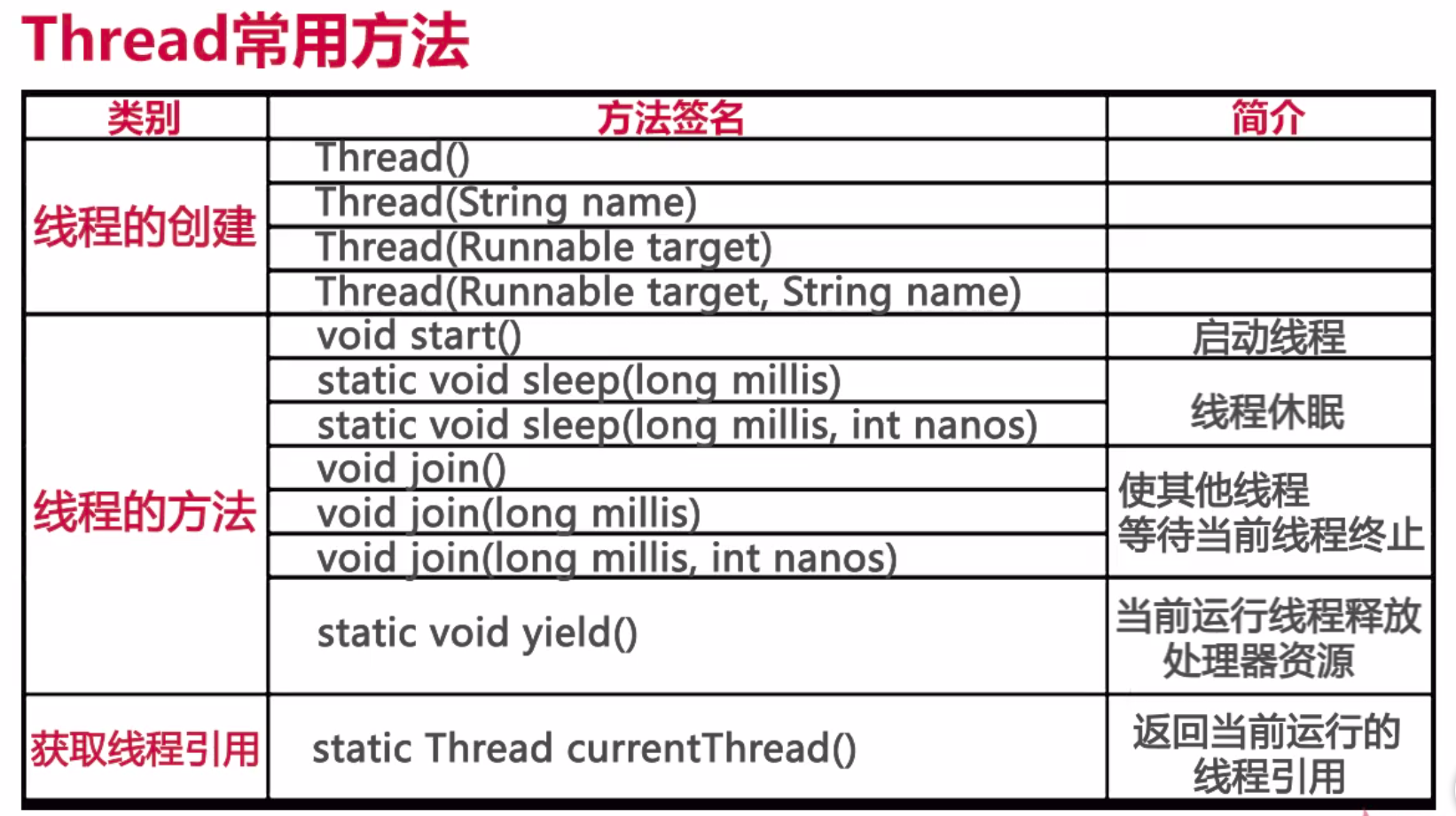
一.编写两种多线程的方法
(1).Thread(它是继承Runnable的子类)
class MyThread extends Thread{
private int ticket = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0 ; i<20;i++){
if(this.ticket>0)
System.out.println("卖出的票数为" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyThread().start();
new MyThread().start();
new MyThread().start();
}
}
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为1
(2).继承Runnable接口的实现
class MyThread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0 ; i<20;i++){
if(this.ticket>0)
System.out.println("卖出的票数为" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
new Thread(myThread).start();
new Thread(myThread).start();
new Thread(myThread).start();
//myThread.start();
//myThread1.start();
//myThread2.start();
}
}
卖出的票数为4
卖出的票数为5
卖出的票数为2
卖出的票数为3
卖出的票数为1
二、两种线程的区别
Thread的方法:会受到单继承的局限性,且不方便表示出数据共享的概念
Runnable的方法 : 不会受到单继承的局限性,可以方便表示出数据共享的概念
它们最终都会调用Thread().start的方法。
三、常见的线程的编写
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.printf("这是hello world");
}
}).start(); 四、线程的同步和死锁
1.线程同步的方法 : 同步代码块、同步方法
(1).同步代码的关键字 : synchronized
class Mythread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 8 ;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<20; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("剩余的票数" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mythread = new Mythread();
new Thread(mythread,"A").start();
new Thread(mythread,"B").start();
new Thread(mythread,"C").start();
new Thread(mythread,"D").start();
new Thread(mythread,"E").start();
}
}
(2).代码的同步的方法:在方法上面加synchronized的关键字
class Mythread implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 8 ;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i<20; i++) {
this.sale();
}
}
public synchronized void sale(){
if (this.ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("剩余的票数" + this.ticket--);
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mythread = new Mythread();
new Thread(mythread,"A").start();
new Thread(mythread,"B").start();
new Thread(mythread,"C").start();
new Thread(mythread,"D").start();
new Thread(mythread,"E").start();
}
}
五、线程的优先级
Thread.setPriority(int num) : 设置线程的优先级
六、生产者和消费者
1.解决重复的操作必须使用等待和唤醒的功能
Object类中含有使用的关键函数
1.等待的使用: wait()
2.唤醒第一个: notify()
3.唤醒全部 : notifyAll() : 谁的优先级高先执行谁
2.生产者消费者的代码
class Message{
private String name;
private String context;
private Boolean flag = true;
public synchronized void setName(String name , String context) {
if (this.flag == false){
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.name = name;
this.context = context;
this.flag = false;
super.notify();
}
public synchronized void getName() {
if(this.flag == true){
try {
super.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(this.name + ":"+ context);
this.flag = true;
super.notify();
}
}
class Product implements Runnable{
private Message message;
public Product(Message msg){
this.message = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
if(i % 2 == 0 ) {
message.setName("想成为","诗人");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
message.setName("不想成为","囚犯");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class Custor implements Runnable{
private Message message;
public Custor(Message msg){
this.message = msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
message.getName();
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
// 测试静态内部类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Message message = new Message();
// Product product = new Product(message);
// Custor custor = new Custor(message);
// Thread thread1 = new Thread(product);
// Thread thread2 = new Thread(custor);
// thread1.start();
// thread2.start();
new Thread(new Product(message)).start();
new Thread(new Custor(message)).start();
}
}
七、sleep()和wait()的区别
1.sleep() : 它是Thread的内部定义的,可以自动唤醒
2.wait() : 它是Object的内部定义的,需要手工用notify或notifyAll唤醒
Java基础学习篇---------多线程的更多相关文章
- Java基础学习总结 -- 多线程的实现
目录: 继承Thread类 start()方法实现多线程的原理 实现Runnable接口 Thread类 与 Runnable接口 的联系与区别 多线程的实现方法: 继承Thread类 实现Runna ...
- Java基础学习篇---------继承
一.覆写(重写) 1.含义:子类的定义方法.属性和父类的定义方法.属性相同时候 方法名称相同,参数相同以及参数的个数也相同,此时为覆写(重写) 扩充知识点: 覆盖:只有属性名字和方法名字相同,类型.个 ...
- Java基础学习(八) - 多线程
理解线程 进程是指一个内存中运行的应用程序,系统运行一个程序即是一个进程从创建,运行,结束的过程. 线程是进程中的一个执行单元,负责当前进程中程序的执行,一个进程中至少有一个线程. 多线程的特点是并发 ...
- Java基础学习篇---------this、object的学习
一.this的学习方法 1.使用this调用构造方法市一定放在构造方法的首行 2.使用this调用构造方法时一定流出调用的出口 public class MyClass { public MyClas ...
- Java基础学习篇---------String、集合的学习
一.String常用的方法: 1. == 实质比较两个对象的地址数值 String a = "hello" (hello为匿名对象) String a1 = "hell ...
- Java基础学习篇---------封装
一.类和对象分配内存 二.Java中的内部类 : 可以直接去访问外部类的所有属性(包括私有成员) 1.Java中成员内部类 (1).内部类的方法可以直接访问外部类的类中的所有成员变量 (2).外部类 ...
- Java基础学习篇---------static
一.static的使用 1.使用static定义的属性往往通过类名直接调用,它的属性(方法)不属于某一个的对象的.所以对象没有创建之前就可以对static的属性的调用,方法亦如此. 2.static ...
- Java基础学习篇---------多态
一.多态性的理解 1.向上转型:子类为父类对象实例化,调用的一定是子类覆写的方法,他们之间找的是共性 2.向下转型:子类扩充了父类的某些功能,而父类中没有该功能,他们之间找的是特性 案例: Numbe ...
- Java基础学习-- 继承 的简单总结
代码参考:Java基础学习小记--多态 为什么要引入继承? 还是做一个媒体库,里面可以放CD,可以放DVD.如果把CD和DVD做成两个没有联系的类的话,那么在管理这个媒体库的时候,要单独做一个添加CD ...
随机推荐
- AdmBaseController 判断是否登录
代码 using Service.IService; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using ...
- 源代码安装grub-customizer
wget https://launchpad.net/grub-customizer/5.0/5.0.6/+download/grub-customizer_5.0.6.tar.gztar zxvf ...
- 挪过来的spring mvc 的入门 介绍
目录 一.前言二.spring mvc 核心类与接口三.spring mvc 核心流程图 四.spring mvc DispatcherServlet说明 五.spring mvc 父子上下文的说明 ...
- lnmp vhost 虚拟目录配置
以前常用Windows 很熟悉,lnmp 配置虚拟目录也很简单. 安装完lnmp环境之后,在nginx的配置文件夹下,我采用的方法是复制default.conf 然后重命名为vhost_a.conf ...
- oracle执行多个pl/sql块
DECLARE V_SQL_DROP_TABLE VARCHAR2(50) := 'DROP TABLE MY_TEST2'; V_SQL_CREATE_TABLE VARCHAR2( ...
- 想到的regular方法果然已经被sklearn实现了就是L1和L2组合rugular
- Tomcat中的Web.xml和servlet.xml的学习
Web.xml文件使用总结 作用: 存储项目相关的配置信息,保护servlet.解耦一些数据对程序的依赖 使用位置: 每个web项目中 Tomcat服务器中(在服务器目录conf目录中) 区别: We ...
- Django模型层(2)
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/8963244.html from django.db import models class Author(m ...
- BZOJ 1008 [HNOI2008]越狱 (简单排列组合 + 快速幂)
1008: [HNOI2008]越狱 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 10503 Solved: 4558[Submit][Status ...
- Java 注解概要
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2013/04/24/3036689.html(Java注解就跟C#的特性是一样的) 要深入学习注解,我们就必须能定 ...
