二叉查找树(BST)的实现
一、二叉树介绍
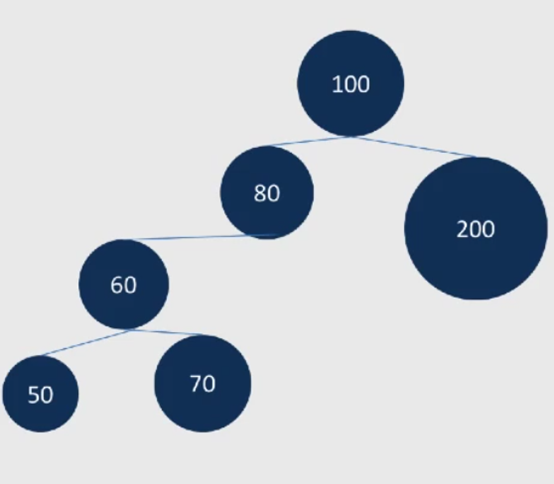
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree,BST),又称二叉排序树,也称二叉搜索树,它或者是一颗空树,或者具有如下性质的树:若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值;若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值。它的左右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
结论:中序遍历一颗二叉查找树可以得到一个按关键字递增的有序序列。简单来说,比根小的往左边放 比根大的往右边放。
二、代码实现
1、BST结点类:
public class BSTNode<K, V> {
public K key;
public V value;
public BSTNode<K, V> left;
public BSTNode<K, V> right;
public BSTNode<K, V> parent;
public boolean isLeftChild;
public int height;
public int num;
public boolean isRed = true; // 后面才学习的红黑树
public BSTNode() {
}
public BSTNode(K key, V value, BSTNode<K, V> left, BSTNode<K, V> right, BSTNode<K, V> parent) {
super();
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.parent = parent;
}
public boolean isLeft() {
return isLeftChild;
}
public boolean isRight() {
return !isLeftChild;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (isRed ? "红色" : "黑色") + " [" + key + "]<-" + (parent == null ? "" : parent.key);
}
}
2、BST接口:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer; public interface IBinarySearchTree<K, V> {
/**
* 新增节点
* @param k 关键字
* @param v 值
*/
BSTNode<K, V> insert(K k, V v); /**
* 中序遍历
* @param con 处理中序遍历的每个元素的函数
*/
void inorder(Consumer<K> con); /**
* 查找元素
* @param key
* @return
*/
V lookupValue(K key); /**
* 获取最小关键字
* @return
*/
K min(); /**
* 获取最大关键字
* @return
*/
K max(); /**
* 移除关键字对应的节点
* @param key
*/
void remove(K key); /**
* x的后继——比x大的第一个元素 1、是其右子树的最小值
* 2、没有右子树,则向上追溯,直到某个祖先节点是左孩子,返回这个祖先节点的父节点,它就是x的后继
*
* @param x
* @return
*/
K successor(K x); /**
* 前驱
* @param x 关键字
* @return
*/
K predecessor(K x); boolean isBalance(); /**
* 返回节点数
* @return
*/
int getSize(); /**
* 高度
* @return
*/
int getHeight(); List<List<BSTNode<K, V>>> levelOrder();
}
3、BST实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.function.Consumer; /**
* 二叉搜索树
*
*/
public class BinarySearchTree<K, V> implements IBinarySearchTree<K, V> {
/**
* 根节点
*/
protected BSTNode root;
/**
* 元素个数
*/
protected int size;
private Comparator comparator; public BinarySearchTree() {
} public BinarySearchTree(Comparator comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
} // parent curr 双指针
@Override
public BSTNode<K, V> insert(K key, V value) {
if (!(key instanceof Comparable)) {
throw new ClassCastException();
} BSTNode<K, V> parent = null;
BSTNode<K, V> curr = root;
while (curr != null) {
parent = curr;
if (compare(key, curr.key) < 0) {
curr = curr.left;
} else if (compare(key, curr.key) > 0) {
curr = curr.right;
} else {
curr.value = value;
return curr;
}
}
curr = new BSTNode(key, value, null, null, null);
//link current to parent
curr.parent = parent;
if (parent == null) {
root = curr;
} else if (compare(key, parent.key) < 0) {
parent.left = curr;
curr.isLeftChild = true;
} else {
parent.right = curr;
curr.isLeftChild = false;
} size++;
updateHeight(curr);
return curr;
} private void updateHeight(BSTNode<K, V> curr) {
if (curr.parent == null) return;//util root BSTNode<K, V> p = curr.parent;
if (p.height == curr.height) {
p.height++;
updateHeight(p);//递归
}
} @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private int compare(K key1, K key2) {
if (null == comparator) {
return ((Comparable) key1).compareTo((Comparable) key2);
} else {
return comparator.compare(key1, key2);
}
} /**
* 中序遍历
* @param con 处理中序遍历的每个元素的函数
*/
@Override
public void inorder(Consumer<K> con) {
if (root != null)
// inorder2(root, con);
inorder(root, con);
} /* 递归形式 */
private void inorder(BSTNode<K, V> p, Consumer<K> con) {
if (p != null) {
inorder(p.left, con);
con.accept(p.key);
inorder(p.right, con);
}
} /*迭代形式*/
private void inorder2(BSTNode<K, V> p, Consumer<K> con) {
Stack<BSTNode<K, V>> stack = new Stack<>();
BSTNode<K, V> curr = p;
//curr不为空或者栈不为空,都可以继续处理
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {//没有生产也没有消费,就退出循环了
//沿左支线一撸到底,全部入栈
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
//处理栈顶
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
BSTNode<K, V> pop = stack.pop();
con.accept(pop.key);
// curr指向pop的右子树,继续外层循环
curr = pop.right;//有可能为空,为空,只消费栈中内容,不为空,就要向栈中生产若干内容
}
}
} // 二叉查找树查找之所以快 每次丢弃一半 lgn
@Override
public V lookupValue(K key) {
BSTNode<K, V> lookupNode = lookupNode(key);
return lookupNode == null ? null : lookupNode.value;
} protected BSTNode<K, V> lookupNode(K key) {
BSTNode<K, V> p = root;
//只要p不为空,并且没找到
while (p != null && compare(key, p.key) != 0) {
if (compare(key, p.key) < 0)
p = p.left;
else
p = p.right;
}
return p;
} // 最左边的结点
@Override
public K min() {
return minNode(root).key;
} protected BSTNode<K, V> minNode(BSTNode p) {
while (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p;
} // 最右边的结点
@Override
public K max() {
return maxNode(root).key;
} protected BSTNode<K, V> maxNode(BSTNode p) {
while (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
return p;
} /*右单旋
* p
* q
* */
protected void rightRotate(BSTNode p, BSTNode q) {
boolean pIsLeft = p.isLeft();
BSTNode pp = p.parent; BSTNode x = q.right;
p.left = x;
if (x != null) {
x.parent = p;
x.isLeftChild = true;
}
q.right = p;
p.parent = q;
p.isLeftChild = false; //设定p和gg的关系
q.parent = pp;
if (pp == null) {
root = q;
return;
}
if (pIsLeft) {
pp.left = q;
q.isLeftChild = true;
} else {
pp.right = q;
q.isLeftChild = false;
}
} /*左单旋*/
protected void leftRotate(BSTNode p, BSTNode q) {
boolean pIsLeft = p.isLeft();
BSTNode pp = p.parent;
//p和q的左子——B的关系
BSTNode B = q.left;
p.right = B;
if (B != null) {
B.parent = p;
B.isLeftChild = false;
} //p,q的关系
q.left = p;
p.parent = q;
p.isLeftChild = true; //p和pp的关系
q.parent = pp;
//p是根节点
if (pp == null) {
root = q;
return;
} if (pIsLeft) {
pp.left = q;
q.isLeftChild = true;
} else {
pp.right = q;
q.isLeftChild = false;
}
} @Override
public void remove(K key) {
removeNode(lookupNode(key));
size--;// 记得减少元素个数
} protected void removeNode(BSTNode<K, V> x) {
if (x != null) {
if (x.left == null && x.right == null) {// leaf node. 第一种情况 没有子节点
if (x.parent == null) {
root = null;
return;
}
if (x.isLeftChild) {
x.parent.left = null;
} else {
x.parent.right = null;
}
x.parent = null;
x = null;
} else if (x.left == null) {// 第二种情况 有子节点,但左子为空,有右孩子
if (x.isLeftChild) {
BSTNode<K, V> c = x.right;
BSTNode<K, V> parent = x.parent;
parent.left = c;
c.isLeftChild = true;
c.parent = parent;
} else {
if (x.parent != null) {
x.parent.right = x.right;
x.right.parent = x.parent;
} else {// 根节点
root = x.right;
}
}
x = null;
} else if (x.right == null) {// 第三种情况 有子节点,但右子为空,有左孩子
if (x.isLeftChild) {
x.parent.left = x.left;
x.left.parent = x.parent;
} else {
if (x.parent != null) {
x.parent.right = x.left;
x.left.isLeftChild = false;
x.left.parent = x.parent;
} else { // 根节点
root = x.left;
}
}
x = null;
} else { // 第四种情况 都不为空
BSTNode<K, V> minOfRight = minNode(x.right);
x.key = minOfRight.key;// 更换x的内容
removeNode(minOfRight); // 删掉右子树种最小的元素
}
}
} // 有右子树 ,则后继为右子树最小
// 否则往上回溯,找到一个是左结点的祖先,则后继是该结点的父亲
@Override
public K successor(K x) {
BSTNode<K, V> xNode = lookupNode(x);
if (xNode == null) {
return null;
}
BSTNode<K, V> yNode = successor(xNode);
return yNode == null ? null : yNode.key; } protected BSTNode<K, V> successor(BSTNode<K, V> xNode) {
if (xNode == null) {
return null;
}
if (xNode.right != null) {
return minNode(xNode.right);
}
BSTNode<K, V> yNode = xNode.parent;
while (yNode != null && xNode == yNode.right) {
xNode = yNode;
yNode = yNode.parent;
}
return yNode;
} // 与找后继结点对称
@Override
public K predecessor(K x) {
BSTNode<K, V> xNode = lookupNode(x);
if (xNode == null) {
return null;
}
if (xNode.left != null) {
return maxNode(xNode.left).key;
}
BSTNode<K, V> yNode = xNode.parent;
while (yNode != null && xNode.isLeftChild) {
xNode = yNode;
yNode = yNode.parent;
}
return yNode == null ? null : yNode.key;
} @Override
public boolean isBalance() {
return !unBalance(root);
} protected boolean unBalance(BSTNode g) {
if (g == null) return false;
int minus = getHeight(g.left) - getHeight(g.right);
return Math.abs(minus) > 1
|| unBalance(g.right)
|| unBalance(g.left);
} /**
* 获取树的节点数
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
} @Override
public int getHeight() {
return getHeight(root);
} protected int getHeight(BSTNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
int l = getHeight(node.left);
int r = getHeight(node.right);
return 1 + Math.max(l, r);
} public List<List<BSTNode<K, V>>> levelOrder(BSTNode<K, V> x) {
// int num=x.num;//累进的编号
List<List<BSTNode<K, V>>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<BSTNode<K, V>> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(x);
BSTNode<K, V> last = x;
BSTNode<K, V> nLast = null;
List<BSTNode<K, V>> l = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(l);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
BSTNode<K, V> peek = q.peek();
//把即将弹出的节点的子节点加入队列
if (peek.left != null) {
peek.left.num = peek.num * 2;
q.add(peek.left);
nLast = peek.left;
}
if (peek.right != null) {
peek.right.num = peek.num * 2 + 1;
q.add(peek.right);
nLast = peek.right;
} l.add(q.poll());//弹出,加入到当前层列表
if (peek == last && !q.isEmpty()) {//如果现在弹出的节点是之前标记的最后节点,就要换列表
l = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(l);
last = nLast;
}
}
return res;
} // 层次遍历
@Override
public List<List<BSTNode<K, V>>> levelOrder() {
root.num = 1;
return levelOrder(root);
} // 按照格式打印
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
List<List<BSTNode<K, V>>> lists = levelOrder();
int level = 1;
int height = getHeight();
for (List<BSTNode<K, V>> l :
lists) {
int gap = ex(2, height - level) - 1;//gap
// printGap(gap);//打印左边margin
int beginNum = ex(2, level - 1);
for (BSTNode<K, V> node : l) {
while (beginNum != node.num) {
//打印gap
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * gap; i++) {
res.append(" ");
}
res.append("**");
//打印gap
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * gap; i++) {
res.append(" ");
}
res.append(" ");
beginNum++;
}
//打印gap
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * gap; i++) {
res.append(" ");
}
res.append(node.key);
//打印gap
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * gap; i++) {
res.append(" ");
}
res.append(" "); beginNum++;
}
level++;
res.append("\n");
}
return res.toString();
} private void printGap(int margin) {
for (int i = 0; i < margin; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
} private void printGap(int gap, String s, int gap1) {
for (int i = 0; i < gap; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.printf("%2s", s);
for (int i = 0; i < gap; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
} } public static int ex(int a, int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return a;
int temp = a; // a 的 1 次方
int res = 1;
int exponent = 1;
while ((exponent << 1) < n) {
temp = temp * temp;
exponent = exponent << 1;
} res *= ex(a, n - exponent); return res * temp;
}
}
二叉查找树(BST)的实现的更多相关文章
- 二叉查找树(BST)
二叉查找树(BST):使用中序遍历可以得到一个有序的序列
- 查找系列合集-二叉查找树BST
一. 二叉树 1. 什么是二叉树? 在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构. 通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree). 二叉树常 ...
- 二叉查找树BST 模板
二叉查找树BST 就是二叉搜索树 二叉排序树. 就是满足 左儿子<父节点<右儿子 的一颗树,插入和查询复杂度最好情况都是logN的,写起来很简单. 根据BST的性质可以很好的解决这些东 ...
- [学习笔记] 二叉查找树/BST
平衡树前传之BST 二叉查找树(\(BST\)),是一个类似于堆的数据结构, 并且,它也是平衡树的基础. 因此,让我们来了解一下二叉查找树吧. (其实本篇是作为放在平衡树前的前置知识的,但为了避免重复 ...
- 【查找结构 2】二叉查找树 [BST]
当所有的静态查找结构添加和删除一个数据的时候,整个结构都需要重建.这对于常常需要在查找过程中动态改变数据而言,是灾难性的.因此人们就必须去寻找高效的动态查找结构,我们在这讨论一个非常常用的动态查找树— ...
- 3.2 符号表之二叉查找树BST
一.插入和查找 1.二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)是一棵二叉树,并且每个结点都含有一个Comparable的键,保证每个结点的键都大于其左子树中任意结点的键而小于其右子树的任意结点 ...
- 从一段简单算法题来谈二叉查找树(BST)的基础算法
先给出一道很简单,喜闻乐见的二叉树算法题: 给出一个二叉查找树和一个目标值,如果其中有两个元素的和等于目标值则返回真,否则返回假. 例如: Input: 5 / \ 3 6 / \ \ 2 4 7 T ...
- 二叉查找树BST
每棵子树头节点的值都比各自左子树上所有节点值要大,也都比各自右子树上所有节点值要小. 二叉查找树的中序遍历序列一定是从小到大排列的. 一个节点的后继节点是指,这个节点在中序遍历序列中的下一个节点.相应 ...
- K:二叉查找树(BST)
相关介绍: 二叉查找树(英语:Binary Search Tree),也称二叉搜索树.有序二叉树(英语:ordered binary tree),排序二叉树(英语:sorted binary tre ...
随机推荐
- python2 使用pip安装psycopg2出现错误:Command "python setup.py egg_info" failed with error code 1 in /tmp/pip-install-mvzdNj/psycopg2/
公司业务需求,开发语言python2,需要使用数据库:postgresql,需要安装模块psycopg2这个模块, 使用pip install psycopg2 报错: Command "p ...
- Cannot resolve class or package 'mysql’
一:当使用Spring Boot 2.0 整合MySQL的时候配置可能会出现这个故障 目前开始选用新的名称:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 二:其次,爆红产生错误分析 其实这个问题是 ...
- jQuery配合html2canvas 使用时 报错 Uncaught (in promise) Provided element is not within a Document
报错代码: 这个函数运行时 function download(){ var element = $("#demo"); //jquery 获取元素 //这里将会报错 html2c ...
- <!特别的一天>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="gb2312/"> <title&g ...
- spring boot 2.0 配置双数据源 MySQL 和 SqlServer
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaofengfeng/p/9552816.html 安装 org.mybatis.spring.boot:mybatis-spring-boo ...
- 路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索--2019OKR规划
一.前言 加入博客园半年多,认识了很多优秀上进,乐于分享的人,我的男神:EdisonZhou,还有张队长,叶伟民,腾飞,梁桐铭 等等. 半年来写了26篇随笔,我的第一篇随笔 C# DynamicObj ...
- Nginx 自定义添加Response Headers 修改server
之前说过如何隐藏Response Headers中 X-Powered-By 修改php.ini expose_php = Off service php-fpm reload 隐藏Nginx版本号 ...
- python全栈开发day113-DBUtils(pymysql数据连接池)、Request管理上下文分析
1.DBUtils(pymysql数据连接池) import pymysql from DBUtils.PooledDB import PooledDB POOL = PooledDB( creato ...
- HTC VIVE固定头显位置
用此方法可以限制HTC VIVE头显定位(即固定头显位置,但是视角是不固定的). UnityEngine.XR.InputTracking.disablePositionalTracking = fa ...
- Learning English with EnglishClass101.com---10 Habits of highly Effective Learners
you can find it on YouTube:Learning English with EnglishClass101.com 10 Habits of highly Effective L ...
