几个简单排序算法的Python实现
先引用这哥们的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41239584/article/details/82193879
一,冒泡排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:稳定
冒泡排序我就不多讲了,大体上就是比较相邻的两个数,每次把较大的数沉底。流程图大致上如下:
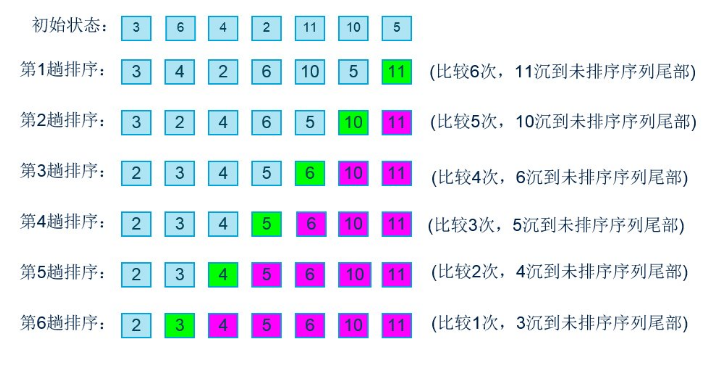
图是截得别人的,只是说明一下,代码没有参看别人的,写的不好,有更好的写法可以一起探讨。下面是代码:
def bubble(list):
#print(list)
for index in range(1,len(list)): #比较6趟
print(" index: %d" %index)
for index2 in range(len(list)-1,0,-1):
print("index2 = %d:" %index2)
if list[len(list) - index2-1] > list[len(list) - index2]:
temp = list[len(list) - index2-1]
list[len(list) - index2 - 1] = list[len(list) - index2]
list[len(list) - index2] = temp
print(list)
list = [3, 6, 4, 2, 11, 10, 5,12,1,7,10]
bubble(list)
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.25):
'''
若list长度为n则迭代n-1次,每次迭代只要有前面大于后面便交换
'''
def buble_sort(list): n =
while len(list)-n:
for i in range(len(list)-):
if list[i] > list[i+]:
list[i],list[i+] = list[i+],list[i]
n +=
print(n-,":",list) l = [,,,,,,,]
buble_sort(l)
=================再精简一下===================
def bubble(list):
for i in range(len(list)-1):
for j in range(len(list)-1):
if list[j] > list[j+1]:
list[j + 1],list[j] =list[j], list[j + 1]
print(list)
bubble([3, 6, 4, 2, 11, 10, 5,20])
二,选择排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:不稳定
如:8,9,8,6,7中第四个数6位最小的,将与第一个8交换,这时候第一个8就变为了第二个了,因此不稳定。
选择排序大体上就是每次在列表中找出最小的数,拿出来,然后再把拿出最小值后的列表在找最小数,就是这个思路。如图:

def xuanze(list):
list2 = []
for index in range(1,len(list)):
print("第 %d 次排序list,list2分别为:" %index)
min = list[0] #最小值
for i in list: #这里的i是里面的数值,而不是序号,print(i)可验证
#print(i)
if i < min:
min = i
#print(list.index(min)) #知道值求位置
locate = list.index(min) #最小值的序号
temp = list[0] #以下三行是交换
list[0] = list[locate]
list[locate] = temp print(list)
list2.append(list[0])
list.remove(list[0])
'''当交换位置后的list第一个值被remove出去后,
此时的list是[56,80,91,20]了,依此类推,这里是
本算法利用list最好玩的地方,可以少写一个for'''
print(list2) print("最终的list2:")
list2.append(list[0])
print(list2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
list = [56,12,80,91,20,33,89,99]
xuanze(list)
17:06:26 2018-05-24
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.25):
def selection_sort(list):
new_list = []
while len(list):
min = list[]
for i in range(,len(list)):
if list[i] < min:
min= list[i]
new_list.append(min)
list.remove(min)
print(new_list) l = [,,,,,]
selection_sort(l)
三,插入排序
时间复杂度:O(n2)
稳定性:稳定
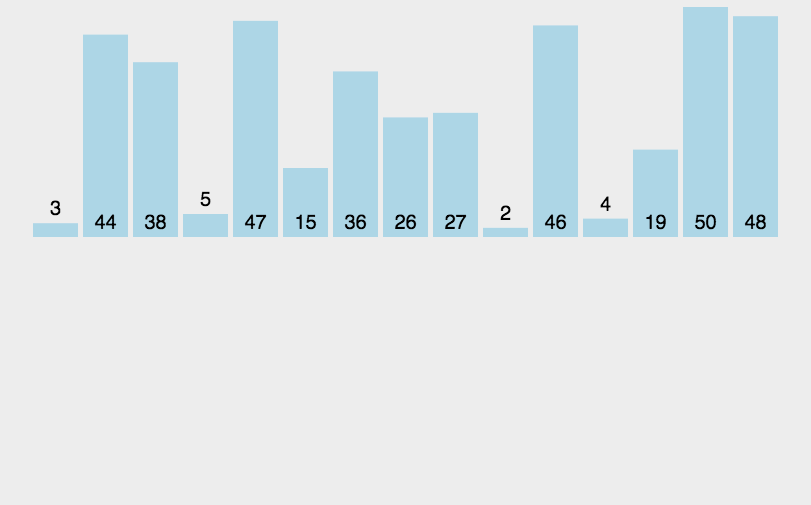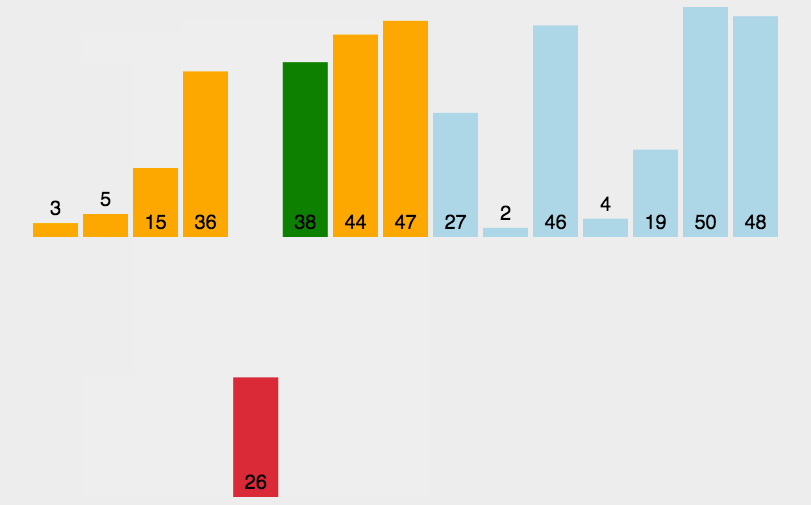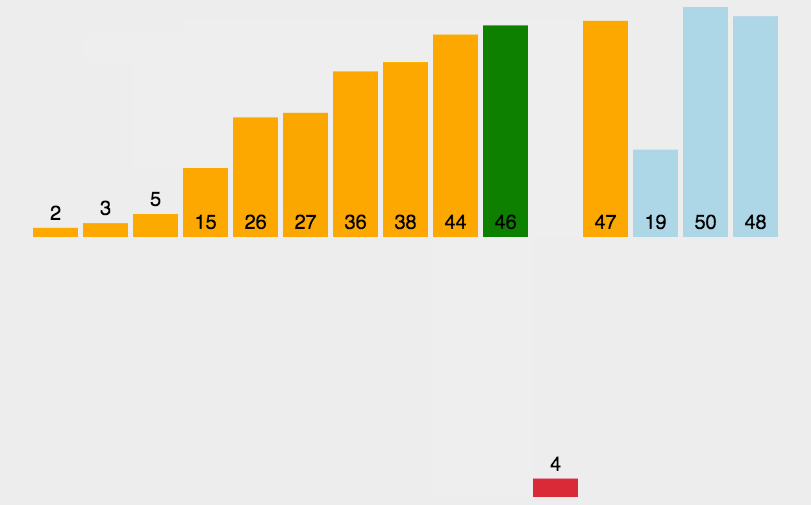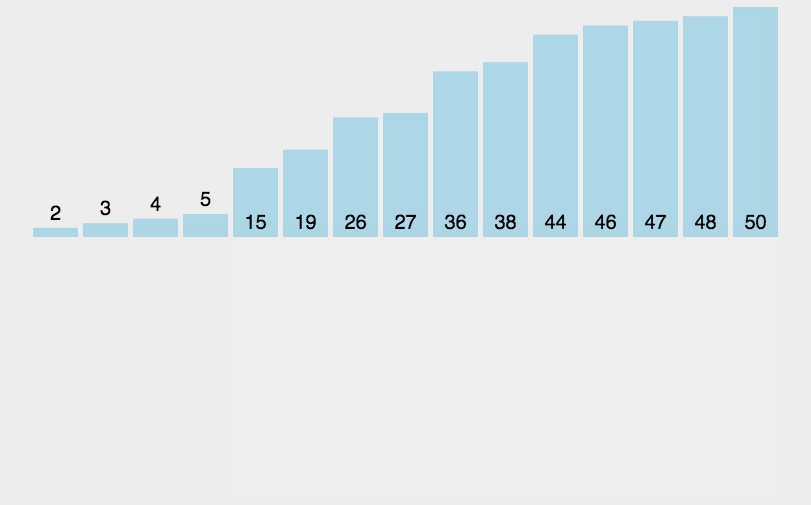
基本就是这个样子吧,看示意图能看明白,不再赘述。代码如下:
def charu(list):
num = len(list)
for i in range(1,num):
for j in range(0,i):
print("i=",i,"j=",j," list[i]=",list[i],"list[j]=",list[j])
if list[i] < list[j]:
temp = list[i]
list.remove(list[i])
list.insert(j,temp)
print(list)
break
list = [3,44,39,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48] #13个数
charu(list)
这里添加了新的解法(2019.6.26):
def insertion_sort(list):
for i in range(,len(list)):
for j in range(,i):
temp = list[i]
if temp < list[j]:
list.pop(i)
list.insert(j,temp)
return list l = [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]
insertion_sort(l)
四,归并排序
O(n*logn),稳定
归并用到了分治的思想。
def merge_sort(list):
if len(list) == :
return list
else:
mid = len(list)//2 #地板除
left = list[:mid]
right = list[mid:]
return merge(left,right)
#合并两个排好的list
def merge(left,right):
left.extend(right)
sort_list = sorted(left)
return sort_list result = merge_sort([,,,,,,,])
print(result)
五,快速排序
O(n*logn) 不稳定
引用:https://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6684558
'''
基本思想:
.先从数列中取出一个数作为基准数。
.分区过程,将比这个数大的数全放到它的右边,小于或等于它的数全放到它的左边。
.再对左右区间重复第二步,直到各区间只有一个数。
'''
def quick_sort(list):
if len(list) == :
return list
else:
base = list[]
left = []
right = []
for i in list:
if i>=base:
right.append(i)
else:
left.append(i)
return combine(left,right)
#合并两个排好的list
def combine(left,right):
left.extend(right)
sort_list = sorted(left)
return sort_list l = [,,,,,,,,]
result = quick_sort(l)
print(result) ====================================
def quicksort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
return quicksort(left) + middle + quicksort(right)
print(quicksort([3,6,8,10,1,2,1]))
六,希尔排序
不稳定
def shell_sort(list,gap):
#导入的list的长度
length = len(list)
#gap为0则停止,不为0则继续迭代
if gap == 0:
return list
else:
#list_container用于装按照gap打散(分组)后的列表
list_container = []
for i in range(0,gap):
temp_list = []
for j in range(i,length,gap):
temp_list.append(list[j])
# print(temp_list)
list_sep = sort(temp_list)
list_container.append(list_sep)
print("按照对应gap划分出的列表:",list_container) sorted_list = sort_all_list(list_container, length, gap)
print("调用sort_all_list后:",sorted_list)
#gap减小以达到最终迭代终止条件
gap = gap//2
#最后调用自己以迭代
return shell_sort(sorted_list, gap) def sort(list1):
return sorted(list1)
#把按照gap打散(分组)后的列表排到一个理好顺序的list中
def sort_all_list(list2,length,gap):
new_list = []
for mm in range(length):
new_list.append(0)
#把l2每个数组按照每隔gap组成一个new_list
for list in list2:
N = list2.index(list)
for i in range(N,length,gap):
num = int((i-N)/gap)
new_list[i] = list[num]
# print("sort_all_list:",new_list)
return new_list l = [9,1,3,6,87,12,64,9,11,65,7]
#初始gap
if len(l) % 2 == 0:
gap = int(len(l) / 2)
else:
gap = int((len(l) - 1) / 2)
shell_sort(l,gap)
七,堆排序
堆排序是不稳定的,因为建堆后的堆顶要和最后一个数交换。但我这里的稳定性这里是稳定的,因为第我没用这个方法,而是在42pop出最大值,然后再把pop后的list进行建堆,再pop,所以不用交换。后期我会改进。
def adjuste_tree(non_leaf,list):
#先验证non_leaf是否有右子节点。若相等则有右子树,否则没有。 还得分大于3和小于等于3.
if list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ] or list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ]:
if (list[ * non_leaf + ] > list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [ * non_leaf + ], [ * non_leaf + ])
elif (list[ * non_leaf + ] < list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[ * non_leaf + ],[ * non_leaf + ])
return list def Heap_sort(list):
#,建堆,以找出最大值(因为不管怎样都能找出最大根,即使下面排的不对)
#第一个非叶子节点为len/-
n = int(len(list) / - )
for non_leaf in range(n,-,-):
#若节点小于他的子节点。
adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) #,取出根再调整堆 #,重复2直到只剩下一个数 list =[,,,,,,,,,]
Heap_sort(list)
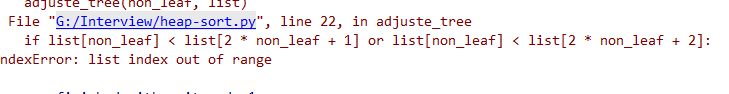
这里的错误是因为在第3行没有管它有没右子树,所以我们要加上这一步。
现在,我们吧24行的list随便加一个数使他除叶子节点外都有右节点,经过多次验证,发现得出的结果没问题,因此我们字需要关注他‘第一个非叶子结点’没有右子节点时候的情形:
def adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list):
# 先验证最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点。
# 若相等则有右子树,否则没有。
# 还得分大于3和小于等于3. if non_leaf == int(len(list)/-): #是否是最后一个非叶子节点
if *non_leaf+ == len(list)-: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点
if list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ] or list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ]:
if (list[ * non_leaf + ] > list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [ * non_leaf + ], [ * non_leaf + ])
elif (list[ * non_leaf + ] < list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[ * non_leaf + ],[ * non_leaf + ])
else: #进入这里证明没有右子节点
if list[non_leaf] < list[*non_leaf+]: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否比它的左子节点大
list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf] = list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ]
else:
if list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ] or list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ]:
if (list[ * non_leaf + ] > list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [ * non_leaf + ], [ * non_leaf + ])
elif (list[ * non_leaf + ] < list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[ * non_leaf + ],[ * non_leaf + ])
print(non_leaf,list) def Heap_sort(list):
#,建堆,以找出最大值(因为不管怎样都能找出最大根,即使下面排的不对)
#第一个非叶子节点为len/-
n = int(len(list) / - )
for non_leaf in range(n,-,-):
#若节点小于他的子节点。
adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) #,取出根再调整堆 #,重复2直到只剩下一个数 list = [,,,,,,,,,]
Heap_sort(list)
这样一次建堆就一定能把最大值找出来,但是上层改变之后下层还是没变,不影响最后结果。
最后结果:
#调整树的三个节点,不能调整调整后的下层节点,但不影响结果
def adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list):
# 一定注意得先验证最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点。
if len(list) == or len(list) == :
return list
else:
if non_leaf == int(len(list)/-): #是否是最后一个非叶子节点
if *non_leaf+ == len(list)-: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否有右子节点
if list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ] or list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ]:
if (list[ * non_leaf + ] > list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Left:", list[non_leaf], [ * non_leaf + ], [ * non_leaf + ])
elif (list[ * non_leaf + ] < list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
# print("Right:",list[non_leaf],[ * non_leaf + ],[ * non_leaf + ])
else: #进入这里证明没有右子节点
if list[non_leaf] < list[*non_leaf+]: #这个最后一个非叶子节点是否比它的左子节点大
list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf] = list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ]
else:
if list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ] or list[non_leaf] < list[ * non_leaf + ]:
if (list[ * non_leaf + ] > list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf]
elif (list[ * non_leaf + ] < list[ * non_leaf + ]):
list[non_leaf], list[ * non_leaf + ] = list[ * non_leaf + ], list[non_leaf] def Heap_sort(list):
#,建堆,以找出最大值
#第一个非叶子节点为len/-
n = int(len(list) / - )
for non_leaf in range(n,-,-): #根节点序号为0时也要排序
#若节点小于他的子节点。
adjuste_tree(non_leaf, list) if __name__ == '__main__':
list = [, , , , , , , , , ]
soted_heap_list = [] #,取出根再调整堆
#,重复2直到只剩下一个数
while(len(list)):
Heap_sort(list)
soted_heap_list.append(list.pop())
print(soted_heap_list)
昨天太晚了,没做改进,今天上午来进行了修改,把调整树函数变为递归形式,使他能在换位后改变子节点的位置。
#调整树的三个节点,调整调整后的下层节点。
def adjuste_tree(heap,root):
HeapSize = len(heap)
#有右子节点 且 (左节点 > 根 or 右节点 > 根)
if *root+ <= len(heap)- and (heap[*root+] > heap[root] or heap[*root+] > heap[root]):
if heap[*root+] > heap[*root+]:
heap[ * root + ], heap[root] = heap[root], heap[ * root + ]
adjuste_tree(heap, * root + )
else:
heap[ * root + ], heap[root] = heap[root], heap[ * root + ]
adjuste_tree(heap, * root + )
# 无右子节点 且 (左节点 > 根)
if *root+ <= len(heap) and (heap[*root+] > heap[root]):
heap[ * root + ],heap[root] = heap[root],heap[ * root + ]
adjuste_tree(heap, * root + ) def Heap_sort(list):
#,建堆,以找出最大值
#第一个非叶子节点为len/-
n = int(len(list) / - )
for non_leaf in range(n,-,-): #根节点序号为0时也要排序
#若节点小于他的子节点。
adjuste_tree(list,non_leaf) if __name__ == '__main__':
list = [, , , , , , , , , ]
soted_heap_list = [] #,取出根再调整堆
#,重复2直到只剩下一个数
while(len(list)):
Heap_sort(list)
soted_heap_list.append(list.pop())
print(soted_heap_list)
几个简单排序算法的Python实现的更多相关文章
- 常用排序算法的python实现和性能分析
常用排序算法的python实现和性能分析 一年一度的换工作高峰又到了,HR大概每天都塞几份简历过来,基本上一天安排两个面试的话,当天就只能加班干活了.趁着面试别人的机会,自己也把一些基础算法和一些面试 ...
- 简单排序算法 C++类实现
简单排序算法: 冒泡排序 插入排序 选择排序 .h代码: // // SortClass.h // sort and selection // // Created by wasdns on 16/1 ...
- 简单排序算法设计(Java)
总共有八种排序算法,还是慢慢看吧 1.简单排序算法 简单排序算法就是设置标兵,逐个比较数,然后查找插入位置,插入 public static void p(int[] a){ for(int i=0; ...
- 八大排序算法的 Python 实现
转载: 八大排序算法的 Python 实现 本文用Python实现了插入排序.希尔排序.冒泡排序.快速排序.直接选择排序.堆排序.归并排序.基数排序. 1.插入排序 描述 插入排序的基本操作就是将一个 ...
- 十大经典排序算法总结 (Python)
作业部落:https://www.zybuluo.com/listenviolet/note/1399285 以上链接是自己在作业部落编辑的排序算法总结- Github: https://github ...
- 一些排序算法的Python实现
''' Created on 2016/12/16 Created by freeol.cn 一些排序算法的Python实现 @author: 拽拽绅士 ''' '''值交换''' def swap( ...
- 写代码?程序猿?你不能不懂的八大排序算法的Python实现
信息获取后通常需要进行处理,处理后的信息其目的是便于人们的应用.信息处理方法有多种,通常由数据的排序,查找,插入,删除等操作.本章介绍几种简单的数据排序算法和高效的排序算法. 本章主要涉及到的知识点有 ...
- python实现简单排序算法
算法 递归两个特点: 调用自身 有穷调用 计算规模越来越小,直至最后结束 用装饰器修饰一个递归函数时会出现问题,这个问题产生的原因是递归的函数也不停的使用装饰器.解决方法是,只让装饰器调用一次即可,那 ...
- 八大排序算法的python实现(八)简单选择排序
代码: #coding:utf-8 #author:徐卜灵 # L = [6, 3, 2, 32, 5, 4] def Select_sort(L): for i in range(0,len(L)) ...
随机推荐
- Springboot 6.Springboot 返回cookies信息的验证和post接口开发及常见错误解决
在介绍之前先将一个小插件:lombok ,在prefrence里面点击plugins,然后搜索lombok,进行install就可以了 首先将pom文件里面的lombok引进来 <depend ...
- Java EE 开发环境搭建
1 Windows 1.1 JDK 下载: 下载地址:https://developer.oracle.com/java 安装文件:jdk-8u201-windows-x64.exe JDK 并不是越 ...
- Mycat的读写分离
1. Mycat实现读写分离的部署: https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/5447566.html springboot动态数据源的原理以及配置: Spring内置了 ...
- 关于Java____________Object类
一说Java 不聊聊Object 如何说你了解Java 不多说 具体看源码去 下面是Object的方法 以及方法的作用如下 protected Object clone () ...
- JDBC 关闭数据库连接与自动提交【转】
// Jdbc关闭数据库连接时,会隐含一个提交事务的操作 private final static String DB_DRIVER = "oracle.jdbc.driver.Oracle ...
- 第一节: 结合EF的本地缓存属性来介绍【EF增删改操作】的几种形式
一. 背景 说起EF的增删改操作,相信很多人都会说,有两种方式:① 通过方法操作 和 ② 通过状态控制. 相信你在使用EF进行删除或修改操作的时候,可能会遇到以下错误:“ The object c ...
- [Android] 免费天气预报接口
[Android] 免费天气预报接口 这是 国家气象局提供的天气预报接口 [免费] 当然,网上有很多的收费API或者每天定次数的接口 使用 国家气象局 的步骤如下: 1.首先获取城市ID号 北京:10 ...
- 【easy】215. Kth Largest Element in an Array 第K大的数
class Solution { public: int quicksort(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end, int k){ int ...
- QPS/TPS/并发量/系统吞吐量概念和公式
1.概念 我们在日常工作中经常会听到QPS/TPS这些名词,也会经常被别人问起说你的系统吞吐量有多大.一个系统的吞度量(承压能力)与request对CPU的消耗.外部接口.IO等等紧密关联,单个req ...
- java中的stream的泛型方法的使用示例
本文章使用jdk8测试 ,并结合使用lambda测试 测试前准备一些测试数据: class ObjectDemo { private Integer id; private String name; ...
