C++ 迷宫寻路问题
迷宫寻路应该是栈结构的一个非常经典的应用了, 最近看数据结构算法应用时看到了这个问题, 想起来在校求学时参加算法竞赛有遇到过相关问题, 感觉十分亲切, 在此求解并分享过程, 如有疏漏, 欢迎指正
问题描述: 非常简洁明了的问题, 即对于一个由1,0构成的矩阵, 找到一条用0连接起来的从(1,1)到(10,10)的路径
思路: 用栈结构存储路径, 每经过一个点, 将点坐标存入栈, 并在矩阵中将此坐标点值置1, 循环直至找到点(10,10), 若中途没找到可以继续前进的点且栈为空, 则说明当前迷宫无解
代码如下:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stack>
- //坐标
- typedef struct _struct_pos
- {
- _struct_pos()
- {
- x = ;
- y = ;
- }
- int x;
- int y;
- }Pos;
- //地图
- int g_maze_arr[][] = {{,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,},
- {,,,,,,,,,,,}};
- //路径栈
- std::stack<Pos> g_stack_path;
- /***************************************************************
- *
- */
- void print_pos(const Pos &pos)
- {
- std::cout << "[" << pos.x
- << "," << pos.y
- << "]" << std::endl;
- }
- //检查出口
- bool find_next(const Pos &curr_pos, Pos &next_pos)
- {
- //当前坐标
- int x = curr_pos.x;
- int y = curr_pos.y;
- //生成四个方向的坐标
- Pos top, down, left, right;
- top.x = x;
- top.y = y - ;
- down.x = x;
- down.y = y + ;
- left.x = x - ;
- left.y = y;
- right.x = x + ;
- right.y = y;
- //判断四个方向有无通路
- if (g_maze_arr[top.x][top.y] == )
- {
- next_pos.x = top.x;
- next_pos.y = top.y;
- std::cout << "find way : ";
- print_pos(next_pos);
- return true;
- }
- else if (g_maze_arr[down.x][down.y] == )
- {
- next_pos.x = down.x;
- next_pos.y = down.y;
- std::cout << "find way : ";
- print_pos(next_pos);
- return true;
- }
- else if (g_maze_arr[left.x][left.y] == )
- {
- next_pos.x = left.x;
- next_pos.y = left.y;
- std::cout << "find way : ";
- print_pos(next_pos);
- return true;
- }
- else if (g_maze_arr[right.x][right.y] == )
- {
- next_pos.x = right.x;
- next_pos.y = right.y;
- std::cout << "find way : ";
- print_pos(next_pos);
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- std::cout << "no way find in :";
- print_pos(curr_pos);
- return false;
- }
- }
- //寻找路径
- bool find_path()
- {
- Pos st_curr_pos, st_next_pos;
- //起点
- st_curr_pos.x = ;
- st_curr_pos.y = ;
- g_maze_arr[][] = ;
- //不为终点坐标,继续查找路径
- while ((st_curr_pos.x != ) || (st_curr_pos.y != ))
- {
- //找到下一路径
- if (find_next(st_curr_pos, st_next_pos))
- {
- //记录下一个位置并置标记为1
- g_stack_path.push(st_next_pos);
- st_curr_pos = st_next_pos;
- g_maze_arr[st_next_pos.x][st_next_pos.y] = ;
- }
- //无路可走
- else
- {
- //路径栈为空,且无路可退,此迷宫无解
- if (g_stack_path.empty())
- {
- return false;
- }
- //根据栈内信息,回退一步
- else
- {
- st_curr_pos = g_stack_path.top();
- g_stack_path.pop();
- }
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- //输出路径
- void print_path()
- {
- while (!g_stack_path.empty())
- {
- Pos st_curr_pos = g_stack_path.top();
- std::cout << "[" << st_curr_pos.x
- << "," << st_curr_pos.y
- << "]" << std::endl;
- g_stack_path.pop();
- }
- }
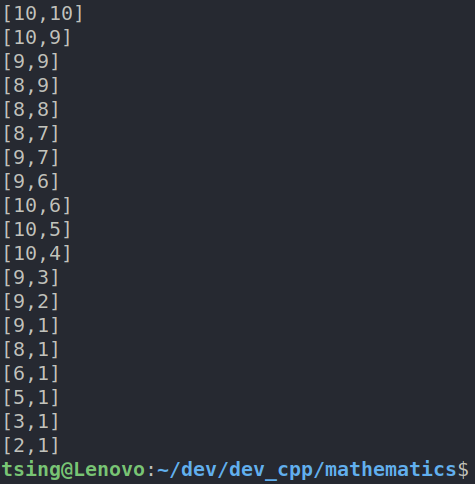
测试如下:

结果
C++ 迷宫寻路问题的更多相关文章
- PTA7-1 迷宫寻路 (20分)
7-1 迷宫寻路 (20分) 给定一个M行N列的迷宫图,其中 "0"表示可通路,"1"表示障碍物,无法通行.在迷宫中只允许在水平或上下四个方向的通路上行走,走过 ...
- NEFU 558 迷宫寻路
题目链接 简单搜索题 #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespac ...
- HTML 迷宫
今天补个遗,将很久以前研究 HTML5 的时候写的生成迷宫.迷宫寻路程序整理出来. 下载链接在文章最后. 简介 为什么要做这个 HTML5 迷宫程序?因为我喜欢.我愿意.也是向老程序员学习(见第5节) ...
- AI-随机迷宫&迷宫求解
本文记录了,人工智能中简单的搜索策略中的路径搜索策略中的A*算法,来实现迷宫寻路的问题.(这只是一次本人的课外作业) 完整的程序源码已经发送到我的Git.这里只记录了我的思路和感想以及收获. 产生随机 ...
- 【转】A*寻路算法 C++实现
头文件:AStarPathFinding #ifndef ASTARPATHFINDING_H #define ASTARPATHFINDING_H #include <queue>//为 ...
- PTA-迷宫寻路(输出最短路径)
给定一个M行N列的迷宫图,其中 "0"表示可通路,"1"表示障碍物,无法通行.在迷宫中只允许在水平或上下四个方向的通路上行走,走过的位置不能重复走. 5行8列的 ...
- 用Java语言编写的迷宫小游戏软件
可查看本项目的github 源码链接,撒娇打滚求 star 哦~~ღ( ´・ᴗ・ ` )比心 本仓库代码是经过 eclipse 编译运行过的,一般情况下将本仓库代码下载下来之后,使用 eclipse ...
- 【小白学游戏常用算法】二、A*启发式搜索算法
在上一篇博客中,我们一起学习了随机迷宫算法,在本篇博客中,我们将一起了解一下寻路算法中常用的A*算法. 通常情况下,迷宫寻路算法可以使用深度优先或者广度优先算法,但是由于效率的原因,不会直接使用这些算 ...
- canvas——路径搜索
在前一篇博客中随机生成迷宫,现在就以随机生成的迷宫为地图,开始寻找路径. 迷宫寻路也可以使用DFS,BFS,但常见的是A*算法,它是启发式搜索算法的一种,效率相比前两者也更高.接下来以A*算法为例,迷 ...
随机推荐
- Perl:理解正则中“.”可匹配出回车符(“\n”)外任意字符的例子,配合 $^I 关键字
要把下面文件的内容改了, Program name: graniteAuthor: Gilbert BatesCompany: RockSoftDepartment: R&DPhone: +1 ...
- sklearn包源码分析(二)——ensemble(未完成)
网络资源 sklearn包tree模型importance解析
- day13-面向对象
#解决同一类问题,使用面向对象的思想.类是制造对象的模具,类是抽象的,我们能知道它有哪些属性(name,age,saraly),但不知道具体的属性值. #看下面代码:类Penson制造了实例化对象re ...
- 浏览器CA认证流程
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22771739/article/details/86479411 首先说说证书的签发过程: 服务方 S 向第三方机构CA提交公钥.组织信息.个 ...
- Linux命令:ldd
1.ldd不是一个可执行程序,而是一个shell脚本. zlf@ubuntu:~/$ which ldd /usr/bin/ldd zlf@ubuntu:~/$ file /usr/bin/ldd / ...
- LG_2967_[USACO09DEC]视频游戏的麻烦Video Game Troubles
题目描述 Farmer John's cows love their video games! FJ noticed that after playing these games that his c ...
- WAIC | 奇点云携「酷炫AI应用」亮相2019世界人工智能大会
你是否还在疑惑“人工智能可否改变世界?” 那么,你该有一些危机感了. 机器视觉.自然语言处理.智能语音.机器人问诊.智慧驾驶……这些AI技术及应用早已渗入了我们日常生活的点滴. 29日,以「智联世界, ...
- 导出Wireless组中的成员
get-adgroupmember -Identity wireless |export-csv -path C:\Group.csv -Encoding UTF8
- [LC] 110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. For this problem, a height-balanced binary ...
- [LC] 167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
Given an array of integers that is already sorted in ascending order, find two numbers such that the ...
