翻译——3_Gaussian Process Regression
使用不同的机器学习方法进行预测
上篇2_Linear Regression and Support Vector Regression
高斯过程回归
%matplotlib inline
import requests
from StringIO import StringIO
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd # pandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # module for plotting
import datetime as dt # module for manipulating dates and times
import numpy.linalg as lin # module for performing linear algebra operations
from __future__ import division
import matplotlib
import sklearn.decomposition
import sklearn.metrics
from sklearn import gaussian_process
from sklearn import cross_validation
pd.options.display.mpl_style = 'default'
从数据预处理中读取数据
# Read in data from Preprocessing results
hourlyElectricityWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/hourlyElectricityWithFeatures.xlsx')
hourlyChilledWaterWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/hourlyChilledWaterWithFeatures.xlsx')
hourlySteamWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/hourlySteamWithFeatures.xlsx')
dailyElectricityWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/dailyElectricityWithFeatures.xlsx')
dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures.xlsx')
dailySteamWithFeatures = pd.read_excel('Data/dailySteamWithFeatures.xlsx')
# An example of Dataframe
dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures.head()
| chilledWater-TonDays | startDay | endDay | RH-% | T-C | Tdew-C | pressure-mbar | solarRadiation-W/m2 | windDirection | windSpeed-m/s | humidityRatio-kg/kg | coolingDegrees | heatingDegrees | dehumidification | occupancy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 | 0.961857 | 2012-01-01 | 2012-01-02 | 76.652174 | 7.173913 | 3.073913 | 1004.956522 | 95.260870 | 236.086957 | 4.118361 | 0.004796 | 0 | 7.826087 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2012-01-02 | 0.981725 | 2012-01-02 | 2012-01-03 | 55.958333 | 5.833333 | -2.937500 | 994.625000 | 87.333333 | 253.750000 | 5.914357 | 0.003415 | 0 | 9.166667 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2012-01-03 | 1.003672 | 2012-01-03 | 2012-01-04 | 42.500000 | -3.208333 | -12.975000 | 1002.125000 | 95.708333 | 302.916667 | 6.250005 | 0.001327 | 0 | 18.208333 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2012-01-04 | 1.483192 | 2012-01-04 | 2012-01-05 | 41.541667 | -7.083333 | -16.958333 | 1008.250000 | 98.750000 | 286.666667 | 5.127319 | 0.000890 | 0 | 22.083333 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2012-01-05 | 3.465091 | 2012-01-05 | 2012-01-06 | 46.916667 | -0.583333 | -9.866667 | 1002.041667 | 90.750000 | 258.333333 | 5.162041 | 0.001746 | 0 | 15.583333 | 0 | 0.3 |
以上是我们的数据样本。
每日预测:
每日用电
获取训练/验证和测试集。dataframe显示功能和目标。
def addDailyTimeFeatures(df):
df['weekday'] = df.index.weekday
df['day'] = df.index.dayofyear
df['week'] = df.index.weekofyear
return df
dailyElectricityWithFeatures = addDailyTimeFeatures(dailyElectricityWithFeatures)
df = dailyElectricityWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week',
'occupancy', 'electricity-kWh']]
#df.to_excel('Data/trainSet.xlsx')
trainSet = df['2012-01':'2013-06']
testSet_dailyElectricity = df['2013-07':'2014-10']
#normalizer = np.max(trainSet)
#trainSet = trainSet / normalizer
#testSet = testSet / normalizer
trainX_dailyElectricity = trainSet.values[:,0:-1]
trainY_dailyElectricity = trainSet.values[:,4]
testX_dailyElectricity = testSet_dailyElectricity.values[:,0:-1]
testY_dailyElectricity = testSet_dailyElectricity.values[:,4]
trainSet.head()
| weekday | day | week | occupancy | electricity-kWh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.0 | 2800.244977 |
| 2012-01-02 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 3168.974047 |
| 2012-01-03 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.3 | 5194.533376 |
| 2012-01-04 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | 5354.861935 |
| 2012-01-05 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 5496.223993 |
以上是在预测每日用电时使用的特性。
交叉验证以获得输入参数 theta , nuggest
实际上有一些后台测试。首先做一个粗糙的网格serach参数,这里没有显示。之后,就可以得到精细网格搜索的参数范围,如下图所示。
def crossValidation_all(theta, nugget, nfold, trainX, trainY):
thetaU = theta * 2
thetaL = theta/2
scores = np.zeros((len(nugget) * len(theta), nfold))
labels = ["" for x in range(len(nugget) * len(theta))]
k = 0
for j in range(len(theta)):
for i in range(len(nugget)):
gp = gaussian_process.GaussianProcess(theta0 = theta[j], nugget = nugget[i])
scores[k, :] = cross_validation.cross_val_score(gp,
trainX, trainY,
scoring='r2', cv = nfold)
labels[k] = str(theta[j]) + '|' + str(nugget[i])
k = k + 1
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8))
plt.boxplot(scores.T, sym='b+', labels = labels, whis = 0.5)
plt.ylim([0,1])
plt.title('R2 score as a function of nugget')
plt.ylabel('R2 Score')
plt.xlabel('Choice of theta | nugget')
plt.show()
theta = np.arange(1, 8, 2)
nfold = 10
nugget = np.arange(0.01, 0.2, 0.03)
crossValidation_all(theta, nugget, nfold, trainX_dailyElectricity, trainY_dailyElectricity)
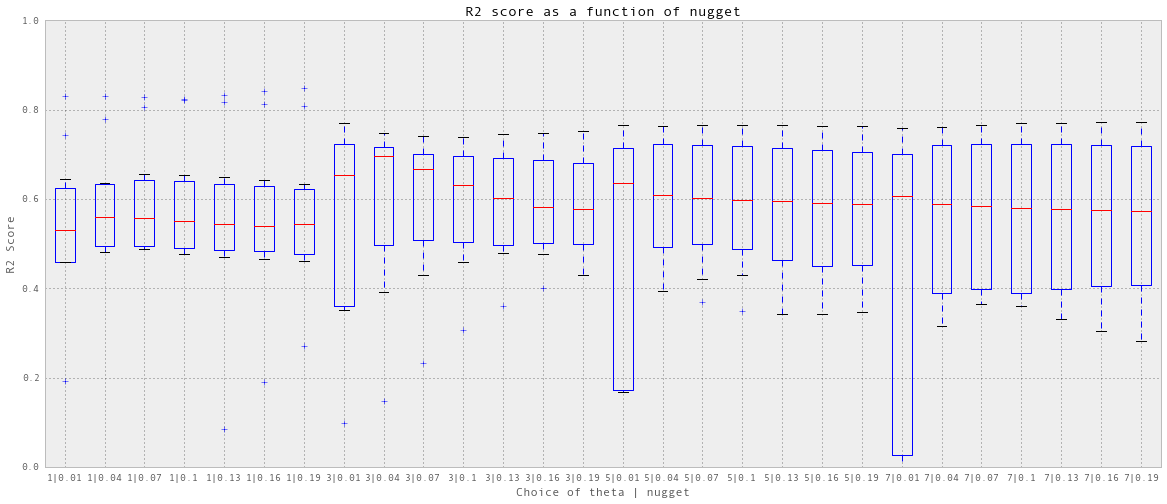
我选择theta = 3, nuggest = 0.04,这是最好的中位数预测精度。
预测,计算精度和可视化
def predictAll(theta, nugget, trainX, trainY, testX, testY, testSet, title):
gp = gaussian_process.GaussianProcess(theta0=theta, nugget =nugget)
gp.fit(trainX, trainY)
predictedY, MSE = gp.predict(testX, eval_MSE = True)
sigma = np.sqrt(MSE)
results = testSet.copy()
results['predictedY'] = predictedY
results['sigma'] = sigma
print "Train score R2:", gp.score(trainX, trainY)
print "Test score R2:", sklearn.metrics.r2_score(testY, predictedY)
plt.figure(figsize = (9,8))
plt.scatter(testY, predictedY)
plt.plot([min(testY), max(testY)], [min(testY), max(testY)], 'r')
plt.xlim([min(testY), max(testY)])
plt.ylim([min(testY), max(testY)])
plt.title('Predicted vs. observed: ' + title)
plt.xlabel('Observed')
plt.ylabel('Predicted')
plt.show()
return gp, results
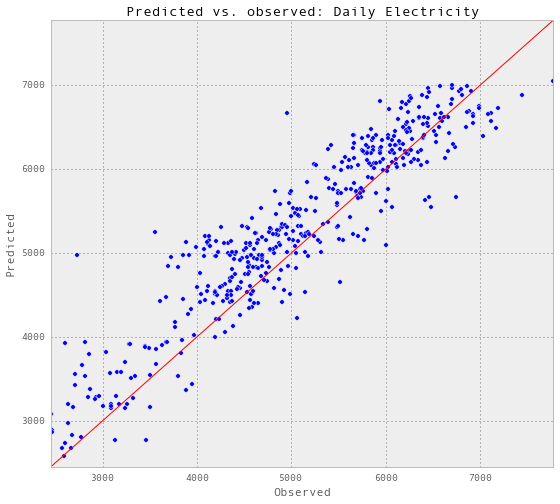
gp_dailyElectricity, results_dailyElectricity = predictAll(3, 0.04,
trainX_dailyElectricity,
trainY_dailyElectricity,
testX_dailyElectricity,
testY_dailyElectricity,
testSet_dailyElectricity,
'Daily Electricity')
Train score R2: 0.922109831389
Test score R2: 0.822408541698
def plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma):
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (20,6))
plt.plot(testY, 'r.', markersize=10, label=u'Observations')
plt.plot(predictedY, 'b-', label=u'Prediction')
x = range(len(testY))
plt.fill(np.concatenate([x, x[::-1]]),
np.concatenate([predictedY - 1.9600 * sigma,
(predictedY + 1.9600 * sigma)[::-1]]),
alpha=.5, fc='b', ec='None', label='95% confidence interval')
subset = results_dailyElectricity['2013-12':'2014-06']
testY = subset['electricity-kWh']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Electricity (kWh)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Daily Electricity Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = pd.DataFrame(data = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),10)], columns=['datetime'])
xTickLabels['date'] = xTickLabels['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 10))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels['date'], fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()

以上是部分预测的可视化。
每日用电预测相当成功。
每日冷水
获取训练/验证和测试集。dataframe显示功能和目标。
dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures = addDailyTimeFeatures(dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures)
df = dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week', 'occupancy',
'coolingDegrees', 'T-C', 'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'dehumidification', 'chilledWater-TonDays']]
#df.to_excel('Data/trainSet.xlsx')
trainSet = df['2012-01':'2013-06']
testSet_dailyChilledWater = df['2013-07':'2014-10']
trainX_dailyChilledWater = trainSet.values[:,0:-1]
trainY_dailyChilledWater = trainSet.values[:,8]
testX_dailyChilledWater = testSet_dailyChilledWater.values[:,0:-1]
testY_dailyChilledWater = testSet_dailyChilledWater.values[:,8]
trainSet.head()
| weekday | day | week | occupancy | coolingDegrees | T-C | humidityRatio-kg/kg | dehumidification | chilledWater-TonDays | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.0 | 0 | 7.173913 | 0.004796 | 0 | 0.961857 |
| 2012-01-02 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 5.833333 | 0.003415 | 0 | 0.981725 |
| 2012-01-03 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -3.208333 | 0.001327 | 0 | 1.003672 |
| 2012-01-04 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -7.083333 | 0.000890 | 0 | 1.483192 |
| 2012-01-05 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -0.583333 | 0.001746 | 0 | 3.465091 |
以上是用于日常冷水预测的特征。
同样,需要对冷水进行交叉验证。
交叉验证以获得输入参数
def crossValidation(theta, nugget, nfold, trainX, trainY):
scores = np.zeros((len(theta), nfold))
for i in range(len(theta)):
gp = gaussian_process.GaussianProcess(theta0 = theta[i], nugget = nugget)
scores[i, :] = cross_validation.cross_val_score(gp, trainX, trainY, scoring='r2', cv = nfold)
plt.boxplot(scores.T, sym='b+', labels = theta, whis = 0.5)
#plt.ylim(ylim)
plt.title('R2 score as a function of theta0')
plt.ylabel('R2 Score')
plt.xlabel('Choice of theta0')
plt.show()
theta = np.arange(0.001, 0.1, 0.02)
nugget = 0.05
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 3, trainX_dailyChilledWater, trainY_dailyChilledWater)
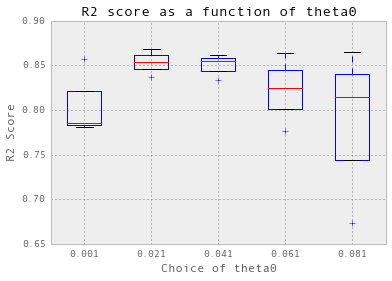
选择 theta = 0.021.
交叉验证实际上并不适用于冷冻水。首先,我必须使用三倍交叉验证,而不是十倍。此外,为了简化过程,从现在开始,我只显示针对theta的初始值的交叉验证结果:theta0。 我在后台搜索了nugget。
预测,计算精度和可视化
theta = 0.021
nugget =0.05
# Predict
gp, results_dailyChilledWater = predictAll(theta, nugget,
trainX_dailyChilledWater,
trainY_dailyChilledWater,
testX_dailyChilledWater,
testY_dailyChilledWater,
testSet_dailyChilledWater,
'Daily Chilled Water')
# Visualize
subset = results_dailyChilledWater['2014-08':'2014-10']
testY = subset['chilledWater-TonDays']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Chilled water (ton-days)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Daily Chilled Water Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
#plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = pd.DataFrame(data = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),7)],
columns=['datetime'])
xTickLabels['date'] = xTickLabels['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 7))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels['date'], fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()
Train score R2: 0.91483040513
Test score R2: 0.901408621289

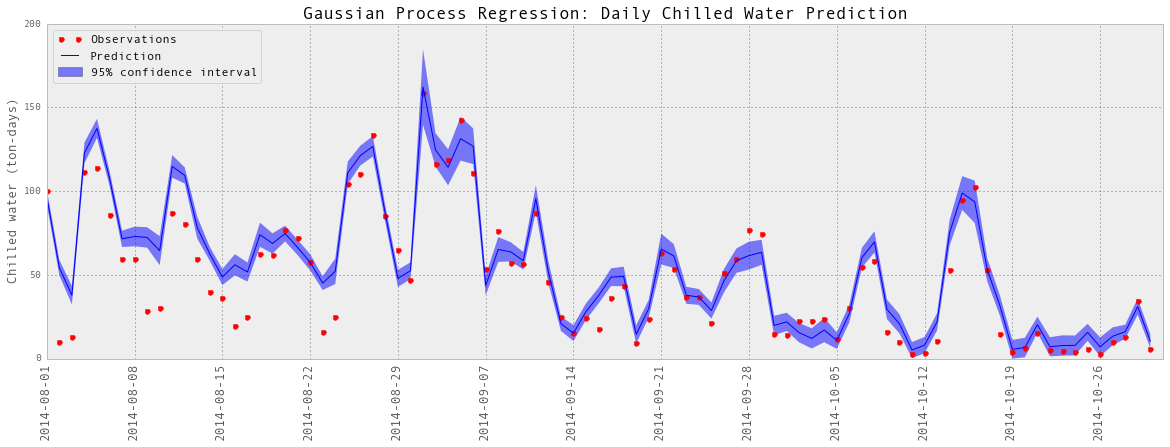
以上是部分预测的可视化。
预测又相当成功。
再增加一个特性:电量预测
为了提高预测精度,又增加了一个特性,即耗电量预测。预测的电量是根据前面电力部分中描述的时间特性产生的。这描述了入住计划。需要训练数据集中的实际用电量进行训练,然后将用电量作为测试数据集的特征进行预测。因此,这种预测方法仍然只需要时间和天气信息以及历史用电量来预测未来的用电量
dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures['predictedElectricity'] = gp_dailyElectricity.predict(
dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week', 'occupancy']].values)
df = dailyChilledWaterWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week',
'occupancy',
'coolingDegrees', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'dehumidification',
'predictedElectricity',
'chilledWater-TonDays']]
#df.to_excel('Data/trainSet.xlsx')
trainSet = df['2012-01':'2013-06']
testSet_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = df['2013-07':'2014-10']
trainX_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = trainSet.values[:,0:-1]
trainY_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = trainSet.values[:,9]
testX_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = testSet_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures.values[:,0:-1]
testY_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = testSet_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures.values[:,9]
trainSet.head()
| weekday | day | week | occupancy | coolingDegrees | T-C | humidityRatio-kg/kg | dehumidification | predictedElectricity | chilledWater-TonDays | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.0 | 0 | 7.173913 | 0.004796 | 0 | 2883.784617 | 0.961857 |
| 2012-01-02 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 5.833333 | 0.003415 | 0 | 4231.128909 | 0.981725 |
| 2012-01-03 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -3.208333 | 0.001327 | 0 | 5013.703046 | 1.003672 |
| 2012-01-04 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -7.083333 | 0.000890 | 0 | 4985.929899 | 1.483192 |
| 2012-01-05 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | -0.583333 | 0.001746 | 0 | 5106.976841 | 3.465091 |
交叉验证
theta = np.arange(0.001, 0.15, 0.02)
nugget = 0.05
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 3, trainX_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures, trainY_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures)
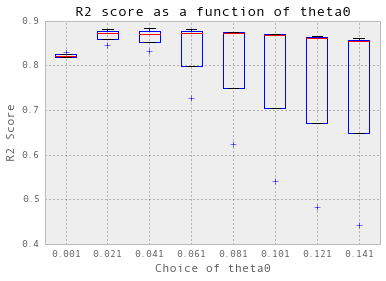
选择 theta =0.021.
预测,计算精度和可视化
# Predict
gp, results_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures = predictAll(
0.021, 0.05,
trainX_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures,
trainY_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures,
testX_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures,
testY_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures,
testSet_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures,
'Daily Chilled Water')
# Visualize
subset = results_dailyChilledWaterMoreFeatures['2014-08':'2014-10']
testY = subset['chilledWater-TonDays']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Chilled water (ton-days)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Daily Chilled Water Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
#plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = pd.DataFrame(data = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),7)],
columns=['datetime'])
xTickLabels['date'] = xTickLabels['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 7))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels['date'], fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()
Train score R2: 0.937952834542
Test score R2: 0.926978705167
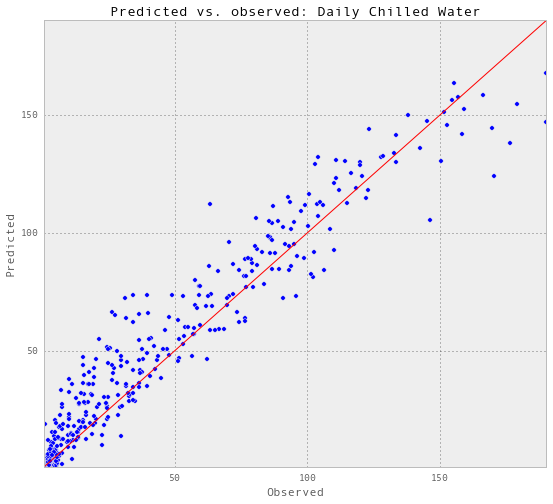
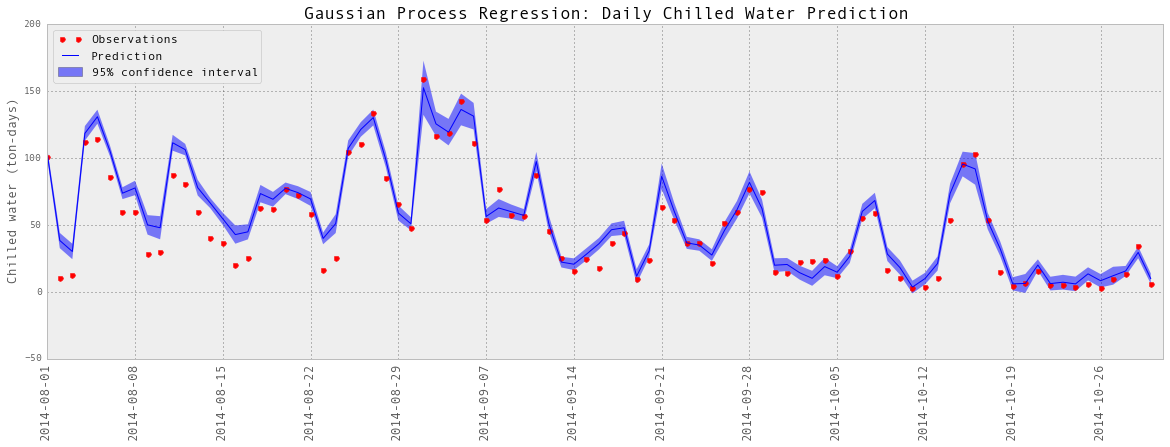
以上是部分预测的可视化。
根据R2的得分,准确性确实提高了一点。因此,我将把预测的电量包括在预测中。
热水
获取训练/验证和测试集。dataframe显示功能和目标。
dailySteamWithFeatures = addDailyTimeFeatures(dailySteamWithFeatures)
dailySteamWithFeatures['predictedElectricity'] = gp_dailyElectricity.predict(
dailySteamWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week', 'occupancy']].values)
df = dailySteamWithFeatures[['weekday', 'day', 'week', 'occupancy',
'heatingDegrees', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg', 'predictedElectricity', 'steam-LBS']]
#df.to_excel('Data/trainSet.xlsx')
trainSet = df['2012-01':'2013-06']
testSet_dailySteam = df['2013-07':'2014-10']
trainX_dailySteam = trainSet.values[:,0:-1]
trainY_dailySteam = trainSet.values[:,8]
testX_dailySteam = testSet_dailySteam.values[:,0:-1]
testY_dailySteam = testSet_dailySteam.values[:,8]
trainSet.head()
| weekday | day | week | occupancy | heatingDegrees | T-C | humidityRatio-kg/kg | predictedElectricity | steam-LBS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.0 | 7.826087 | 7.173913 | 0.004796 | 2883.784617 | 17256.468099 |
| 2012-01-02 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 9.166667 | 5.833333 | 0.003415 | 4231.128909 | 17078.440755 |
| 2012-01-03 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.3 | 18.208333 | -3.208333 | 0.001327 | 5013.703046 | 59997.969401 |
| 2012-01-04 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | 22.083333 | -7.083333 | 0.000890 | 4985.929899 | 56104.878906 |
| 2012-01-05 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 15.583333 | -0.583333 | 0.001746 | 5106.976841 | 45231.708984 |
交叉验证以获得输入参数
theta = np.arange(0.06, 0.15, 0.01)
nugget = 0.05
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 3, trainX_dailySteam, trainY_dailySteam)

选择theta = 0.1.
预测,计算精度和可视化
# Predict
gp, results_dailySteam = predictAll(0.1, 0.05, trainX_dailySteam, trainY_dailySteam,
testX_dailySteam, testY_dailySteam, testSet_dailySteam, 'Daily Steam')
# Visualize
subset = results_dailySteam['2013-10':'2014-02']
testY = subset['steam-LBS']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Steam (LBS)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Daily Steam Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
#plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = pd.DataFrame(data = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),10)],
columns=['datetime'])
xTickLabels['date'] = xTickLabels['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 10))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels['date'], fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()
Train score R2: 0.96729657748
Test score R2: 0.933120481633


以上是部分预测的可视化。
每小时的预测
我用同样的方法来训练和测试每小时的模型。因为随着数据点数量的增加,计算成本显著增加。在大型数据集上进行交叉验证是不可能的,因为我们没有太多的时间进行项目。因此,我只使用一小组训练/验证数据来获取参数,然后使用完整的数据集进行训练和测试,并让我的计算机连夜运行。
每小时用电量
获取训练/验证和测试集。先尝试小样本。dataframe显示特性和目标。
def addHourlyTimeFeatures(df):
df['hour'] = df.index.hour
df['weekday'] = df.index.weekday
df['day'] = df.index.dayofyear
df['week'] = df.index.weekofyear
return df
hourlyElectricityWithFeatures = addHourlyTimeFeatures(hourlyElectricityWithFeatures)
df_hourlyElectricity = hourlyElectricityWithFeatures[['hour', 'weekday', 'day',
'week', 'cosHour',
'occupancy', 'electricity-kWh']]
#df_hourlyElectricity.to_excel('Data/trainSet_hourlyElectricity.xlsx')
def setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd, indY):
trainSet = df[trainStart : trainEnd]
testSet = df[testStart : testEnd]
trainX = trainSet.values[:,0:-1]
trainY = trainSet.values[:,indY]
testX = testSet.values[:,0:-1]
testY = testSet.values[:,indY]
return trainX, trainY, testX, testY, testSet
trainStart = '2013-02'
trainEnd = '2013-05'
testStart = '2014-03'
testEnd = '2014-04'
df = df_hourlyElectricity;
trainX_hourlyElectricity, trainY_hourlyElectricity, \
testX_hourlyElectricity, testY_hourlyElectricity, \
testSet_hourlyElectricity = setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart,
trainEnd, testStart, testEnd, 6)
df_hourlyElectricity.head()
| hour | weekday | day | week | cosHour | occupancy | electricity-kWh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 01:00:00 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.866025 | 0 | 111.479277 |
| 2012-01-01 02:00:00 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.965926 | 0 | 117.989395 |
| 2012-01-01 03:00:00 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 1.000000 | 0 | 119.010131 |
| 2012-01-01 04:00:00 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.965926 | 0 | 116.005587 |
| 2012-01-01 05:00:00 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0.866025 | 0 | 111.132977 |
交叉验证以获得输入参数
nugget = 0.008
theta = np.arange(0.05, 0.5, 0.05)
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 10, trainX_hourlyElectricity, trainY_hourlyElectricity)
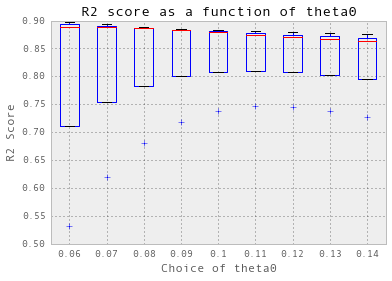
预测,计算精度和可视化
gp_hourlyElectricity, results_hourlyElectricity = predictAll(0.1, 0.008,
trainX_hourlyElectricity,
trainY_hourlyElectricity,
testX_hourlyElectricity,
testY_hourlyElectricity,
testSet_hourlyElectricity,
'Hourly Electricity (Partial)')
Train score R2: 0.957912601164
Test score R2: 0.893873175566

subset = results_hourlyElectricity['2014-03-08 23:00:00':'2014-03-15']
testY = subset['electricity-kWh']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Electricity (kWh)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Hourly Electricity Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
#plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),6)]
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 6))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels, fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()
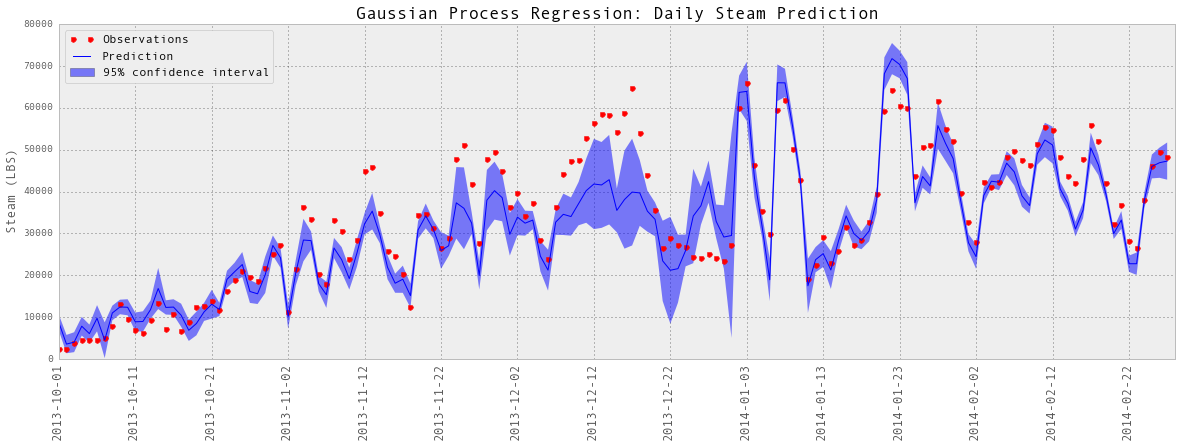
以上是部分预测的可视化。
训练和测试每小时的数据
每小时电量的最终预测精度。
trainStart = '2012-01'
trainEnd = '2013-06'
testStart = '2013-07'
testEnd = '2014-10'
results_allHourlyElectricity = pd.read_excel('Data/results_allHourlyElectricity.xlsx')
def plotR2(df, energyType, title):
testY = df[energyType]
predictedY = df['predictedY']
print "Test score R2:", sklearn.metrics.r2_score(testY, predictedY)
plt.figure(figsize = (9,8))
plt.scatter(testY, predictedY)
plt.plot([min(testY), max(testY)], [min(testY), max(testY)], 'r')
plt.xlim([min(testY), max(testY)])
plt.ylim([min(testY), max(testY)])
plt.title('Predicted vs. observed: ' + title)
plt.xlabel('Observed')
plt.ylabel('Predicted')
plt.show()
plotR2(results_allHourlyElectricity, 'electricity-kWh', 'All Hourly Electricity')
Test score R2: 0.882986662109
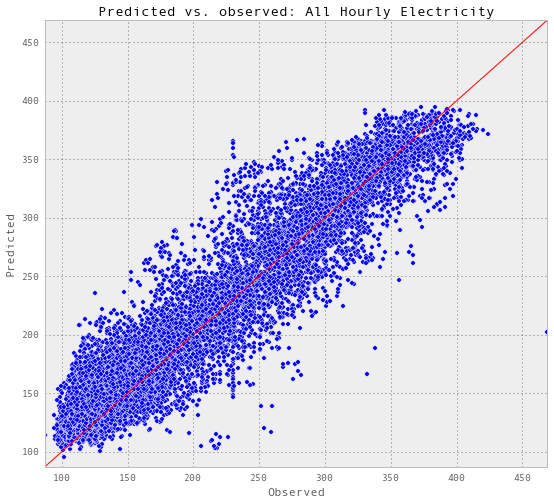
每小时用冷水
获取训练/验证和测试集。先尝试小样本。dataframe显示特性和目标。
trainStart = '2013-08'
trainEnd = '2013-10'
testStart = '2014-08'
testEnd = '2014-10'
def getPredictedElectricity(trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd):
trainX, trainY, testX, testY, testSet = setTrainTestSets(df_hourlyElectricity,
trainStart, trainEnd,
testStart, testEnd, 6)
gp = gaussian_process.GaussianProcess(theta0 = 0.15, nugget = 0.008)
gp.fit(trainX, trainY)
trainSet = df_hourlyElectricity[trainStart : trainEnd]
predictedElectricity = pd.DataFrame(data = np.zeros(len(trainSet)),
index = trainSet.index,
columns = ['predictedElectricity'])
predictedElectricity = \
predictedElectricity.append(pd.DataFrame(data = np.zeros(len(testSet)),
index = testSet.index,
columns = ['predictedElectricity']))
predictedElectricity.loc[trainStart:trainEnd,
'predictedElectricity'] = gp.predict(trainX)
predictedElectricity.loc[testStart:testEnd,
'predictedElectricity'] = gp.predict(testX)
return predictedElectricity
predictedElectricity = getPredictedElectricity(trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd)
hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures = \ hourlyChilledWaterWithFeatures.join(predictedElectricity, how = 'inner')
hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures = addHourlyTimeFeatures(hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures)
df_hourlyChilledWater = hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures[['hour', 'cosHour',
'weekday', 'day', 'week',
'occupancy', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'predictedElectricity',
'chilledWater-TonDays']]
df = df_hourlyChilledWater;
trainX_hourlyChilledWater, \
trainY_hourlyChilledWater, \
testX_hourlyChilledWater, \
testY_hourlyChilledWater, \
testSet_hourlyChilledWater = setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart, trainEnd,
testStart, testEnd, 9)
df_hourlyChilledWater.head()
| hour | cosHour | weekday | day | week | occupancy | T-C | humidityRatio-kg/kg | predictedElectricity | chilledWater-TonDays | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013-08-01 00:00:00 | 0 | 0.707107 | 3 | 213 | 31 | 0.5 | 17.7 | 0.010765 | 123.431454 | 0.200647 |
| 2013-08-01 01:00:00 | 1 | 0.866025 | 3 | 213 | 31 | 0.5 | 17.8 | 0.012102 | 119.266616 | 0.183318 |
| 2013-08-01 02:00:00 | 2 | 0.965926 | 3 | 213 | 31 | 0.5 | 17.7 | 0.012026 | 121.821887 | 0.183318 |
| 2013-08-01 03:00:00 | 3 | 1.000000 | 3 | 213 | 31 | 0.5 | 17.6 | 0.011962 | 124.888675 | 0.183318 |
| 2013-08-01 04:00:00 | 4 | 0.965926 | 3 | 213 | 31 | 0.5 | 17.7 | 0.011912 | 124.824413 | 0.183318 |
交叉验证以获得输入参数
nugget = 0.01
theta = np.arange(0.001, 0.05, 0.01)
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 5, trainX_hourlyChilledWater, trainY_hourlyChilledWater)
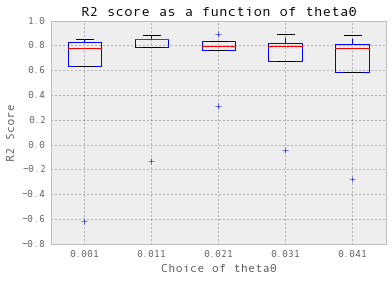
预测,计算精度和可视化
gp_hourlyChilledWater, results_hourlyChilledWater = predictAll(0.011, 0.01,
trainX_hourlyChilledWater,
trainY_hourlyChilledWater,
testX_hourlyChilledWater,
testY_hourlyChilledWater,
testSet_hourlyChilledWater,
'Hourly Chilled Water (Particial)')
Train score R2: 0.914352370778
Test score R2: 0.865202975683
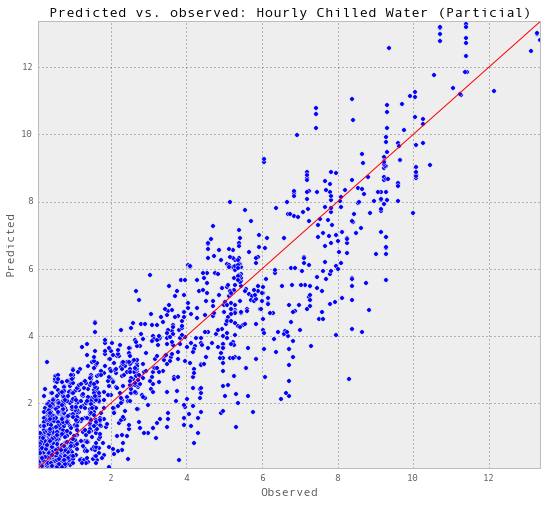
subset = results_hourlyChilledWater['2014-08-24':'2014-08-30']
testY = subset['chilledWater-TonDays']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Chilled water (ton-days)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Hourly Chilled Water Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
#plt.ylim([1000,8000])
xTickLabels = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),6)]
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 6))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels, fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()
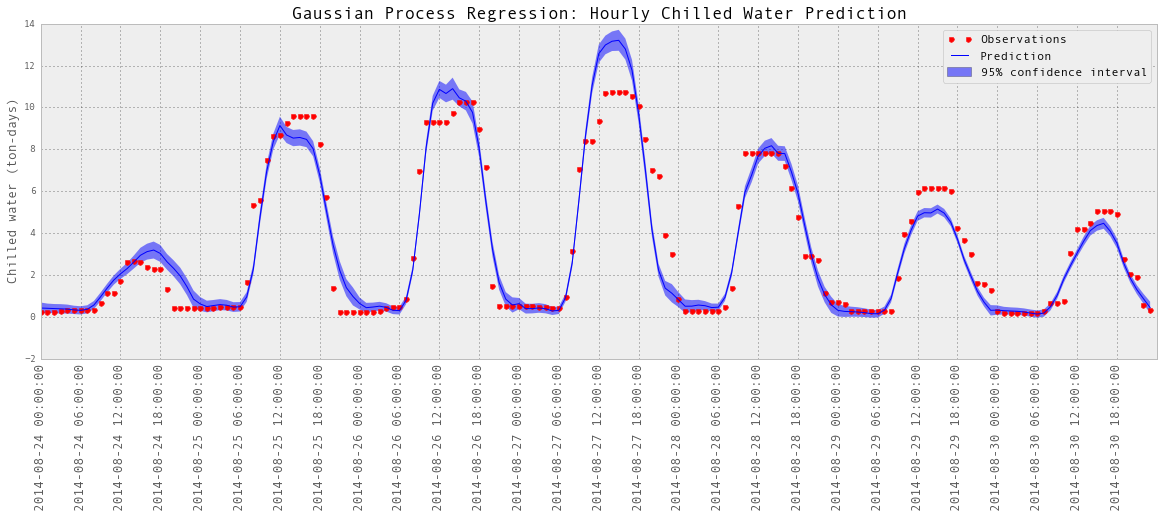
以上是部分预测的可视化。
训练和测试每小时的数据
警告:这可能需要很长时间才能执行代码。
# This could take forever.
trainStart = '2012-01'
trainEnd = '2013-06'
testStart = '2013-07'
testEnd = '2014-10'
predictedElectricity = getPredictedElectricity(trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd)
# Chilled water
hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures = hourlyChilledWaterWithFeatures.join(predictedElectricity, how = 'inner')
hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures = addHourlyTimeFeatures(hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures)
df_hourlyChilledWater = hourlyChilledWaterWithMoreFeatures[['hour', 'cosHour',
'weekday', 'day',
'week', 'occupancy', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'predictedElectricity',
'chilledWater-TonDays']]
df = df_hourlyChilledWater;
trainX_hourlyChilledWater, \
trainY_hourlyChilledWater, \
testX_hourlyChilledWater, \
testY_hourlyChilledWater, \
testSet_hourlyChilledWater = setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart, trainEnd,
testStart, testEnd, 9)
gp_hourlyChilledWater, results_hourlyChilledWater = predictAll(0.011, 0.01,
trainX_hourlyChilledWater,
trainY_hourlyChilledWater,
testX_hourlyChilledWater,
testY_hourlyChilledWater,
testSet_hourlyChilledWater)
results_hourlyChilledWater.to_excel('Data/results_allHourlyChilledWater.xlsx')
每小时冷水预报的最终精度。
results_allHourlyChilledWater = pd.read_excel('Data/results_allHourlyChilledWater.xlsx')
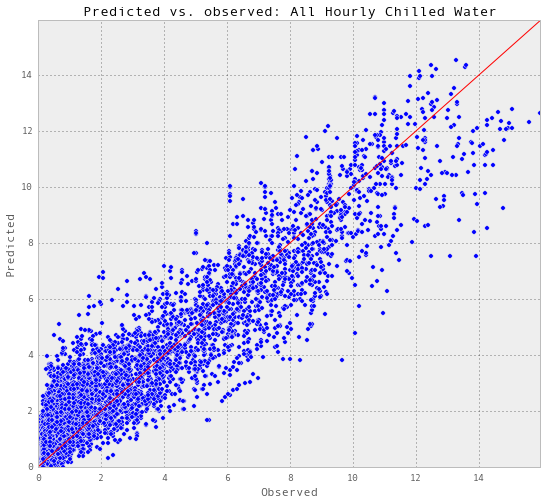
plotR2(results_allHourlyChilledWater, 'chilledWater-TonDays', 'All Hourly Chilled Water')
Test score R2: 0.887195665411
每小时用热水
获取训练/验证和测试集。先尝试小样本。dataframe显示特性和目标。
trainStart = '2012-01'
trainEnd = '2012-03'
testStart = '2014-01'
testEnd = '2014-03'
predictedElectricity = getPredictedElectricity(trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd)
hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures = hourlySteamWithFeatures.join(predictedElectricity,
how = 'inner')
hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures = addHourlyTimeFeatures(hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures)
df_hourlySteam = hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures[['hour', 'cosHour', 'weekday',
'day', 'week', 'occupancy', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'predictedElectricity', 'steam-LBS']]
df = df_hourlySteam;
trainX_hourlySteam,
trainY_hourlySteam,
testX_hourlySteam,
testY_hourlySteam, \
testSet_hourlySteam = setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd, 9)
df_hourlySteam.head()
| hour | cosHour | weekday | day | week | occupancy | T-C | humidityRatio-kg/kg | predictedElectricity | steam-LBS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012-01-01 01:00:00 | 1 | 0.866025 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0 | 4 | 0.004396 | 117.502720 | 513.102214 |
| 2012-01-01 02:00:00 | 2 | 0.965926 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0 | 4 | 0.004391 | 114.720226 | 1353.371311 |
| 2012-01-01 03:00:00 | 3 | 1.000000 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0 | 5 | 0.004380 | 113.079503 | 1494.904514 |
| 2012-01-01 04:00:00 | 4 | 0.965926 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0 | 6 | 0.004401 | 112.428146 | 490.090061 |
| 2012-01-01 05:00:00 | 5 | 0.866025 | 6 | 1 | 52 | 0 | 4 | 0.004382 | 113.892620 | 473.258464 |
交叉验证以获得输入参数
nugget = 0.01
theta = np.arange(0.001, 0.014, 0.002)
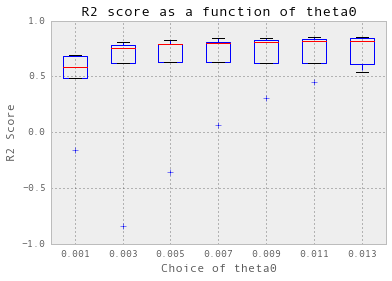
crossValidation(theta, nugget, 5, trainX_hourlySteam, trainY_hourlySteam)
训练和测试每小时的数据
gp_hourlySteam, results_hourlySteam = predictAll(0.007, 0.01,
trainX_hourlySteam, trainY_hourlySteam,
testX_hourlySteam, testY_hourlySteam, testSet_hourlySteam, 'Hourly Steam (Particial)')
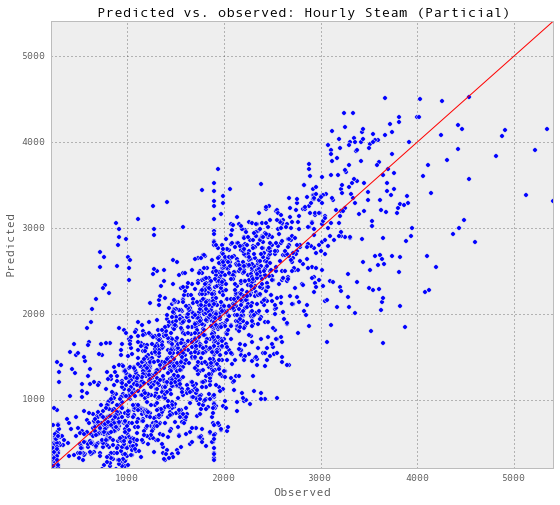
Train score R2: 0.844826486064
Test score R2: 0.570427290315
subset = results_hourlySteam['2014-01-26':'2014-02-01']
testY = subset['steam-LBS']
predictedY = subset['predictedY']
sigma = subset['sigma']
plotGP(testY, predictedY, sigma)
plt.ylabel('Steam (LBS)', fontsize = 13)
plt.title('Gaussian Process Regression: Hourly Steam Prediction', fontsize = 17)
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlim([0, len(testY)])
xTickLabels = subset.index[np.arange(0,len(subset.index),6)]
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(subset), 6))
ax.set_xticklabels(labels = xTickLabels, fontsize = 13, rotation = 90)
plt.show()

以上是部分预测的可视化。
尝试训练和测试每小时的热水
警告:这可能需要很长时间才能执行代码。
# Warning: this could take forever to execute the code.
trainStart = '2012-01'
trainEnd = '2013-06'
testStart = '2013-07'
testEnd = '2014-10'
predictedElectricity = getPredictedElectricity(trainStart, trainEnd, testStart, testEnd)
# Steam
hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures = hourlySteamWithFeatures.join(predictedElectricity,
how = 'inner')
hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures = addHourlyTimeFeatures(hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures)
df_hourlySteam = hourlySteamWithMoreFeatures[['hour', 'cosHour', 'weekday',
'day', 'week', 'occupancy', 'T-C',
'humidityRatio-kg/kg',
'predictedElectricity', 'steam-LBS']]
df = df_hourlySteam;
trainX_hourlySteam, trainY_hourlySteam, testX_hourlySteam, testY_hourlySteam, \
testSet_hourlySteam = setTrainTestSets(df, trainStart, trainEnd,
testStart, testEnd, 9)
gp_hourlySteam, results_hourlySteam = predictAll(0.007, 0.01,
trainX_hourlySteam, trainY_hourlySteam,
testX_hourlySteam, testY_hourlySteam,
testSet_hourlySteam)
results_hourlySteam.to_excel('Data/results_allHourlySteam.xlsx')
Final accuracy for hourly steam prediction.
results_allHourlySteam = pd.read_excel('Data/results_allHourlySteam.xlsx')
plotR2(results_allHourlySteam, 'steam-LBS', 'All Hourly Steam')
Test score R2: 0.84405417838

每小时的预测不如每天的好。但是R2的值仍然是0.85。
总结
高斯过程回归的整体性能非常好。GP的优点是提供了预测的不确定范围。缺点是对于大型数据集来说,它的计算开销非常大。
下篇4_Random Forests and K-Nearest Neighbours
翻译——3_Gaussian Process Regression的更多相关文章
- 翻译——2_Linear Regression and Support Vector Regression
续上篇 1_Project Overview, Data Wrangling and Exploratory Analysis 使用不同的机器学习方法进行预测 线性回归 在这本笔记本中,将训练一个线性 ...
- Scalaz(50)- scalaz-stream: 安全的无穷运算-running infinite stream freely
scalaz-stream支持无穷数据流(infinite stream),这本身是它强大的功能之一,试想有多少系统需要通过无穷运算才能得以实现.这是因为外界的输入是不可预料的,对于系统本身就是无穷的 ...
- The Model Complexity Myth
The Model Complexity Myth (or, Yes You Can Fit Models With More Parameters Than Data Points) An oft- ...
- Summary on Visual Tracking: Paper List, Benchmarks and Top Groups
Summary on Visual Tracking: Paper List, Benchmarks and Top Groups 2018-07-26 10:32:15 This blog is c ...
- 机器学习理论基础学习18---高斯过程回归(GPR)
一.高斯(分布)过程(随机过程)是什么? 一维高斯分布 多维高斯分布 无限维高斯分布 高斯网络 高斯过程 简单的说,就是一系列关于连续域(时间或空间)的随机变量的联合,而且针对每一个时间或是空间点 ...
- Resources in Visual Tracking
这个应该是目前最全的Tracking相关的文章了 一.Surveyand benchmark: 1. PAMI2014:VisualTracking_ An Experimental Sur ...
- ECCV 2014 Results (16 Jun, 2014) 结果已出
Accepted Papers Title Primary Subject Area ID 3D computer vision 93 UPnP: An optimal O(n) soluti ...
- CVPR 2015 papers
CVPR2015 Papers震撼来袭! CVPR 2015的文章可以下载了,如果链接无法下载,可以在Google上通过搜索paper名字下载(友情提示:可以使用filetype:pdf命令). Go ...
- nodejs api 中文文档
文档首页 英文版文档 本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用 3.0 未本地化版本许可协议进行许可. Node.js v0.10.18 手册 & 文档 索引 | 在单一页面中浏览 | JSON格 ...
随机推荐
- 用 Python 编写一个天气查询应用
效果预览: 一.获取天气信息 使用python获取天气有两种方式. 1)是通过爬虫的方式获取天气预报网站的HTML页面,然后使用xpath或者bs4解析HTML界面的内容. 2)另一种方式是根据天气预 ...
- java 图片上传
代码是最有力量的,嘎嘎 @CrossOrigin@ApiOperation(value = "上传图片", notes = "上传图片", httpMethod ...
- oracle,uuid为主键,插入时直接更新id
uuid为主键,插入时自动更新 -- Create table create table TECHNOLOGYCOMPANY ( ID VARCHAR2(32) default SYS_GUID() ...
- MQTT 协议学习:005-发布消息 与 对应报文 (PUBLISH、PUBACK、PUBREC、PUBREL)
背景 当有订阅者订阅了有关的主题以后,通过发布消息的消息的动作,可以让订阅者收到对应主题的消息. 根据不同的QoS 等级,通信的动作也略有不同. PUBLISH – 发布消息 报文 PUBLISH控制 ...
- Docker Yearning + Inception SQL审核平台搭建
[一]安装[1.1]系统环境系统环境:CentOS Linux release 7.6.1708 (Core)系统内存:4G系统内核:1Python:3.6.4关闭iptables and selin ...
- 【问题管理】-- Tomcat8部署项目加载静态资源html页面编码错误
1.问题背景及解决方式 最近在回顾Tomcat部署Web项目,自己简单地从Tomcat的下载安装及配置server.xml文件入手,学习Tomcat的项目部署,在自己使用IDEA创建了一个简单地web ...
- java核心-多线程-零碎知识收集
1.不能使用Integer作为并发锁 原因:synchronized(Integer)时,当值发生改变时,基本上每次锁住的都是不同的对象实例,想要保证线程安全,推荐使用AtomicInteger之类会 ...
- Swift 元组 Tuple
let infoArray:[Any] = ["jack",18,1.88] let infoName=infoArray[0] as!String //此处为Any类型强转为St ...
- HDU 1542 线段树离散化+扫描线 平面面积计算
也是很久之前的题目,一直没做 做完之后觉得基本的离散化和扫描线还是不难的,由于本题要离散x点的坐标,最后要计算被覆盖的x轴上的长度,所以不能用普通的建树法,建树建到r-l==1的时候就停止,表示某段而 ...
- select2 智能补全模糊查询select2的下拉选择框使用
我们在上篇文章中已经在SpringMVC基础框架的基础上应用了BootStrap的后台框架,在此基础上记录select2的使用. 应用bootstrap模板 基础项目源码下载地址为: SpringMV ...
