Chapter 8 The Simplest Plug-in Solution
This chapter introduces the simplest plug-in solution that are applicable to the four major components. This solution involves the following aspects:
1) Combine the dex of all plugins to solve the problem of loading plug-in's class.
2) Declare the four major components of the plugin in the host app’s AndroidManifest file. It’s a nuisance for hundreds of activities in the plug-in.
3) Merge all the resources in the plug-in into the host's resources in one time. Of course, this may result in conflict of resource ids.
8.1 Declaring Components in a Plug-in in Android Manifest
As we mentioned earlier, the four major components in the plug-in are just ordinary classes that the system does not recognize at all.
To make the host app to recognize them, you must declare the four major components in the host app's AndroidManifest.xml.
Then there is the simplest plug-in solution in history. The four components in the plug-in are declared in the host app.
Look at the example ZeusStudy1.0, as shown in the figure below. Plugin1 has a TestService1 component
.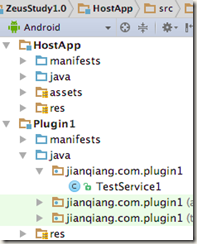
Figure 8-1 Project structure of Plugin1
Correspondingly, in the Host app’s AndroidManifest file, the statement is as follows:
<service android:name="jianqiang.com.plugin1.TestService1" />
8.2 Combine the dex
Host app loads classes in plug-ins, there are two methods to make it. [1]
1.Use the class of plug-in’s ClassLoader;
2.Combine the dexs of host app and plug-in.
The second one is simpler.
Once the plug-in dex is merged into the host's dex, then the ClassLoader corresponding to the host App loads all the classes in the plug-in as follows:
public final class BaseDexClassLoaderHookHelper {
public static void patchClassLoader(ClassLoader cl, File apkFile, File optDexFile)
throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Obtain BaseDexClassLoader : pathList
Object pathListObj = RefInvoke.getFieldObject(DexClassLoader.class.getSuperclass(), cl, "pathList");
// Obtain PathList: Element[] dexElements
Object[] dexElements = (Object[]) RefInvoke.getFieldObject(pathListObj, "dexElements");
// Element type
Class<?> elementClass = dexElements.getClass().getComponentType();
// Create an array to replace the original array
Object[] newElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(elementClass, dexElements.length + 1);
// Construct a plugin Element(File file, boolean isDirectory, File zip, DexFile dexFile) This constructor
Class[] p1 = {File.class, boolean.class, File.class, DexFile.class};
Object[] v1 = {apkFile, false, apkFile, DexFile.loadDex(apkFile.getCanonicalPath(), optDexFile.getAbsolutePath(), 0)};
Object o = RefInvoke.createObject(elementClass, p1, v1);
Object[] toAddElementArray = new Object[] { o };
// Copy the original elements
System.arraycopy(dexElements, 0, newElements, 0, dexElements.length);
// The element of the plugin is copied in
System.arraycopy(toAddElementArray, 0, newElements, dexElements.length, toAddElementArray.length);
// replace
RefInvoke.setFieldObject(pathListObj, "dexElements", newElements);
}
}
8.3 Start the Service of plug-in
Combined with the previous two parts, the host App can start a service that in plug-in.
Intent intent = new Intent();
String serviceName = "jianqiang.com.plugin1.TestService1";
intent.setClassName(this, serviceName);
startService(intent);
8.4Activity resources [2]
Not just Service, four major components can be implemented as plug-in program. Both ContentProvider and Receiver are relatively simple, you can try to implement it by yourself.
Service, ContentProvider, and Receiver just need to merge dex, because they have no resources.
The solution for Activity here is a bit complicated.
Activity is heavily dependent on resources. Therefore, if you want to implement the plug-in of the Activity, you must solve the problem of loading the resources in the plug-in.
Chapter 7 introduced the relationship between AssetManager and Resources. AssetManager has an addAssetPath method that can populate the plugin's path all at once, and then generates a "super" Resource based on this "super" AssetManager.
Save this Super Resources in the global variable PluginManager. After you find the plugin or the host resource, you can find it too.
The above logic is implemented as follows (located in MyApplication):
private static void reloadInstalledPluginResources() {
try {
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
Method addAssetPath = AssetManager.class.getMethod("addAssetPath", String.class);
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager, mBaseContext.getPackageResourcePath());
addAssetPath.invoke(assetManager, pluginItem1.pluginPath);
Resources newResources = new Resources(assetManager,
mBaseContext.getResources().getDisplayMetrics(),
mBaseContext.getResources().getConfiguration());
RefInvoke.setFieldObject (mBaseContext, "mResources", newResources);
// This is the main need to replace, if you do not support the plug-in runtime update, just leave this one
RefInvoke.setFieldObject (mPackageInfo, "mResources", newResources);
mNowResources = newResources;
// Need to clean up the mTheme object, otherwise it will report an error when loading resources through inflate mode
// If the activity dynamically loads the plugin, you need to set the activity's mTheme object to null RefInvoke.setFieldObject (mBaseContext, "mTheme", null);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
The plug-in Activity must implement the base class ZeusBaseActivity. In this base class, the getResource method is overridden, thereby ensuring that the plug-in Activity is fetched from the "super" Resources each time it fetches resources.
public class ZeusBaseActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
return PluginManager.mNowResources;
}
}
Here is the code for TestActivity1 in plug-in which called Plugin1. It uses the layout xml resource called activity_test1 in the plug-in:
public class TestActivity1 extends ZeusBaseActivity {
private final static String TAG = "TestActivity1";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test1);
findViewById(R.id.button1).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
try {
Intent intent = new Intent();
String activityName = "jianqiang.com.hostapp.ActivityA";
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("jianqiang.com.hostapp", activityName));
startActivity(intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
At this point, the simplest plug-in solution of activity is complete, and we can even jump from the plug-in activity to the activity in the host.
However, there has a fatal problem: The four major components in the plugin must be declared in the host's AndroidManifest file beforehand and cannot be added.
In fact, for most of the App, rarely use Service, Receiver and ContentProvider, so the plug-in has these three components, is also typically updated logic, and will not add new.
However, there are many activities in the plug-in, and also add new, at this moment, we cannot pre-empt in the host AndroidManifest file.
This issue will be completely resolved in Chapter 9.
8.5Summary
This chapter introduces the simplest plug-in solution. Although the plug-in can be successfully loaded, there are many problems:
1) Because the plugin and host resources are merged together, the resource ids will conflict.
2) Activity in the plug-in cannot be expected in advance, especially add new Activity1 in the plug-in.
These problems will be solved in the subsequent chapters.
[1] This section example code, please refer to https://github.com/Baobaojianqiang/ZeusStudy1.0
[2] This section example code, please refer to https://github.com/Baobaojianqiang/ZeusStudy1.1
Chapter 8 The Simplest Plug-in Solution的更多相关文章
- C++ 之 策略模式
1 会飞的鸭子 Duck 基类,包含两个成员函数 swim() 和 display():派生类 MallardDuck,RedheadDuck 和 RubberDuck,各自重写 display() ...
- (转)几种范数的解释 l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, … , l-infinity Norm
几种范数的解释 l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, - , l-infinity Norm from Rorasa's blog l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, ...
- 如何创建Asp.net MVC ViewModel
ASP.NET MVC View Model Patterns Since MVC has been released I have observed much confusion about how ...
- C#主要字典集合性能对比[转]
A post I made a couple days ago about the side-effect of concurrency (the concurrent collections in ...
- 2D Rotated Rectangle Collision
Introduction While working on a project for school, I found it necessary to perform a collision chec ...
- TIJ——Chapter One:Introduction to Objects
///:~容我对这个系列美其名曰"读书笔记",其实shi在练习英文哈:-) Introduction to Objects Object-oriented programming( ...
- Think Python - Chapter 18 - Inheritance
In this chapter I present classes to represent playing cards, decks of cards, and poker hands.If you ...
- Think Python - Chapter 11 - Dictionaries
Dictionaries A dictionary is like a list, but more general. In a list, the indices have to be intege ...
- Chapter 4: Spring and AOP:Spring's AOP Framework -- draft
Spring's AOP Framework Let's begin by looking at Spring's own AOP framework - a proxy-based framewor ...
随机推荐
- [SSM项目]Eclipse 搭建marven-web项目 hello world!
配置的种种 (仅第一次)eclipse配置好tomcat.jdk.marven: 建立项目:建立mvn project-选择mvn-web 消除警告和错误: 解决错误1-项目propriety-Jav ...
- Java多线程02(线程安全、线程同步、等待唤醒机制)
Java多线程2(线程安全.线程同步.等待唤醒机制.单例设计模式) 1.线程安全 如果有多个线程在同时运行,而这些线程可能会同时运行这段代码.程序每次运行结果和单线程运行的结果是一样的,而且其他的变量 ...
- 监控服务器配置(五)-----Redis_exporter安装配置
1.下载redis_exporter安装包(linux版)到 /opt/minitor/redis_exporter . 下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download ...
- 识别手机浏览器代码【C#和JS两种语言】
C# 识别手机浏览器代码: public static bool MobileBrowserDetect() { bool bismobile = false; try { #region 包含and ...
- Flask 单元测试 unittest
import unittest 单元测试 app = Flask(__name__) -------------------------------------------- import unite ...
- springmvc webservlet 异步请求总结
1:每次请求会启动一个新线程 上边在debug状态下, 每次请求一次,生成一个新的 thread 在此已经是245了 出现一个现象在debug模式下, 每次请求生成的线程,自动在红框那个位置停了下来 ...
- java 得到项目路径
JavaEXTTomcatJSPWeb 一 相对路径的获得 说明:相对路径(即不写明时候到底相对谁)均可通过以下方式获得(不论是一般的java项目还是web项目) String relativel ...
- oracle自带总页数分页sql
string strSQL = string.Format(@"select * from( with temp as (select * from * where {0} order by ...
- jQuery基础方法:each(),map(),index(),is()
jQuery的each()方法和forEach()的区别: each()返回调用自身的jQuery对象,可用于链式调用 $('div').each(function(idx){ //找到所有div元素 ...
- [转]windows中断与共享的连接(samba)
问题:window下当成功登录到samba服务器上的共享的目录的时候,若要是再系想登录此服务器上另外一个共享目录时,会弹出登录窗口. 但是不管输入的用户名和密码对错都会提示. “不允许一个用户使用一个 ...
