Java 容器源码分析之 Deque 与 ArrayDeque
Queue 也是 Java 集合框架中定义的一种接口,直接继承自 Collection 接口。除了基本的 Collection 接口规定测操作外,Queue 接口还定义一组针对队列的特殊操作。通常来说,Queue 是按照先进先出(FIFO)的方式来管理其中的元素的,但是优先队列是一个例外。
Deque 接口继承自 Queue接口,但 Deque 支持同时从两端添加或移除元素,因此又被成为双端队列。鉴于此,Deque 接口的实现可以被当作 FIFO队列使用,也可以当作LIFO队列(栈)来使用。官方也是推荐使用 Deque 的实现来替代 Stack。
ArrayDeque 是 Deque 接口的一种具体实现,是依赖于可变数组来实现的。ArrayDeque 没有容量限制,可根据需求自动进行扩容。ArrayDeque不支持值为 null 的元素。
下面基于JDK 8中的实现对 ArrayDeque 加以分析。
方法概览
1 |
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
|
Deque 提供了双端的插入与移除操作,如下表:
| First Element (Head) | Last Element (Tail) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throws exception | Special value | Throws exception | Special value | |
| Insert | addFirst(e) | offerFirst(e) | addLast(e) | offerLast(e) |
| Remove | removeFirst() | pollFirst() | removeLast() | pollLast() |
| Examine | getFirst() | peekFirst() | getLast() | peekLast() |
Deque 和 Queue 方法的的对应关系如下:
| Queue Method | Equivalent Deque Method |
|---|---|
| add(e) | addLast(e) |
| offer(e) | offerLast(e) |
| remove() | removeFirst() |
| poll() | pollFirst() |
| element() | getFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
Deque 和 Stack 方法的对应关系如下:
| Stack Method | Equivalent Deque Method |
|---|---|
| push(e) | addFirst(e) |
| pop() | removeFirst() |
| peek() | peekFirst() |
ArrayList 实现了 Deque 接口中的所有方法。因为 ArrayList 会根据需求自动扩充容量,因而在插入元素的时候不会抛出IllegalStateException异常。
底层结构
1 |
//用数组存储元素 |
在 ArrayDeque 底部是使用数组存储元素,同时还使用了两个索引来表征当前数组的状态,分别是 head 和 tail。head 是头部元素的索引,但注意 tail 不是尾部元素的索引,而是尾部元素的下一位,即下一个将要被加入的元素的索引。
初始化
ArrayDeque 提供了三个构造方法,分别是默认容量,指定容量及依据给定的集合中的元素进行创建。默认容量为16。
1 |
public ArrayDeque() {
|
ArrayDeque 对数组的大小(即队列的容量)有特殊的要求,必须是 2^n。通过 allocateElements方法计算初始容量:
1 |
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
|
>>>是无符号右移操作,|是位或操作,经过五次右移和位或操作可以保证得到大小为2^k-1的数。看一下这个例子:
1 |
0 0 0 0 1 ? ? ? ? ? //n |
在进行5次位移操作和位或操作后就可以得到2^k-1,最后加1即可。这个实现还是很巧妙的。
添加元素
向末尾添加元素:
1 |
public void addLast(E e) {
|
这段代码中,(tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head这句有点难以理解。其实,在 ArrayDeque 中数组是当作环形来使用的,索引0看作是紧挨着索引(length-1)之后的。参考下面的图片:
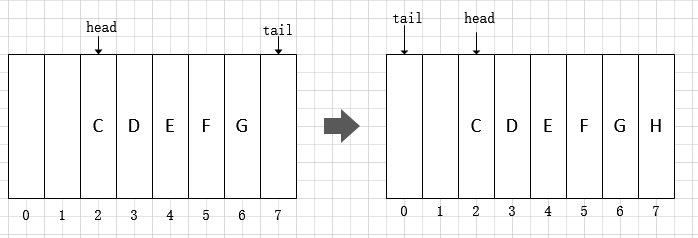
那么为什么(tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)就能保证按照环形取得正确的下一个索引值呢?这就和前面说到的 ArrayDeque 对容量的特殊要求有关了。下面对其正确性加以验证:
1 |
length = 2^n,二进制表示为: 第 n 位为1,低位 (n-1位) 全为0 |
可见,在容量保证为 2^n 的情况下,仅仅通过位与操作就可以完成环形索引的计算,而不需要进行边界的判断,在实现上更为高效。
向头部添加元素的代码如下:
1 |
public void addFirst(E e) {
|
其它的诸如add,offer,offerFirst,offerLast等方法都是基于上面这两个方法实现的,不再赘述。
扩容
在每次添加元素后,如果头索引和尾部索引相遇,则说明数组空间已满,需要进行扩容操作。 ArrayDeque 每次扩容都会在原有的容量上翻倍,这也是对容量必须是2的幂次方的保证。
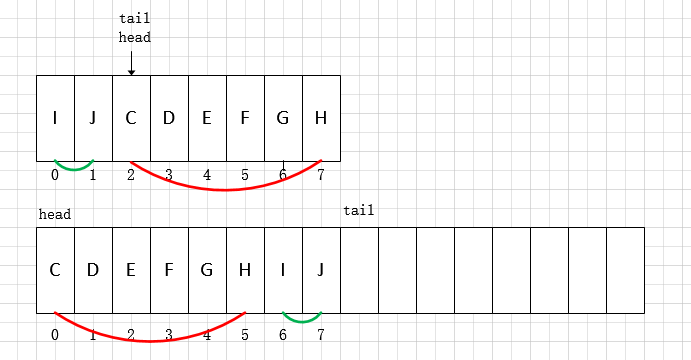
1 |
private void doubleCapacity() {
|
移除元素
ArrayDeque支持从头尾两端移除元素,remove方法是通过poll来实现的。因为是基于数组的,在了解了环的原理后这段代码就比较容易理解了。
1 |
public E pollFirst() {
|
获取队头和队尾的元素
1 |
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
|
迭代器
ArrayDeque 在迭代是检查并发修改并没有使用类似于 ArrayList 等容器中使用的 modCount,而是通过尾部索引的来确定的。具体参考 next 方法中的注释。但是这样不一定能保证检测到所有的并发修改情况,加入先移除了尾部元素,又添加了一个尾部元素,这种情况下迭代器是没法检测出来的。
1 |
private class DeqIterator implements Iterator<E> {
|
除了 DeqIterator,还有一个反向的迭代器 DescendingIterator,顺序和 DeqIterator 相反。
小结
ArrayDeque 是 Deque 接口的一种具体实现,是依赖于可变数组来实现的。ArrayDeque 没有容量限制,可根据需求自动进行扩容。ArrayDeque 可以作为栈来使用,效率要高于 Stack;ArrayDeque 也可以作为队列来使用,效率相较于基于双向链表的 LinkedList 也要更好一些。注意,ArrayDeque 不支持为 null 的元素。
Java 容器源码分析之 Deque 与 ArrayDeque的更多相关文章
- 基于JDK1.8,Java容器源码分析
容器源码分析 如果没有特别说明,以下源码分析基于 JDK 1.8. 在 IDEA 中 double shift 调出 Search EveryWhere,查找源码文件,找到之后就可以阅读源码. Lis ...
- Java 容器源码分析之1.7HashMap
以下内容基于jdk1.7.0_79源码: 什么是HashMap 基于哈希表的一个Map接口实现,存储的对象是一个键值对对象(Entry<K,V>): HashMap补充说明 基于数组和链表 ...
- Java 容器源码分析之Map-Set-List
HashMap 的实现原理 HashMap 概述 HashMap 是基于哈希表的 Map 接口的非同步实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键.此类不保证映射的顺序 ...
- java容器源码分析及常见面试题笔记
概览 容器主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两种,Collection 存储着对象的集合,而 Map 存储着键值对(两个对象)的映射表. List Arraylist: Object数组 ...
- Java 容器源码分析之 ArrayList
概览 ArrayList是最常使用的集合类之一了.在JDK文档中对ArrayList的描述是:ArrayList是对list接口的一种基于可变数组的实现.ArrayList类的声明如下: 12 pub ...
- Java 容器源码分析之ConcurrentHashMap
深入浅出ConcurrentHashMap(1.8) 前言 HashMap是我们平时开发过程中用的比较多的集合,但它是非线程安全的,在涉及到多线程并发的情况,进行put操作有可能会引起死循环,导致CP ...
- Java 容器源码分析之 TreeMap
TreeMap 是一种基于红黑树实现的 Key-Value 结构.在使用集合视图在 HashMap 中迭代时,是不能保证迭代顺序的: LinkedHashMap 使用了双向链表,保证按照插入顺序或者访 ...
- Java 容器源码分析之 LinkedHashMap
同 HashMap 一样,LinkedHashMap 也是对 Map 接口的一种基于链表和哈希表的实现.实际上, LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类,其扩展了 HashMap 增加 ...
- Java 容器源码分析之1.8HashMap方法讲解
前言:Java8之后新增挺多新东西,在网上找了些相关资料,关于HashMap在自己被血虐之后痛定思痛决定整理一下相关知识方便自己看.图和有些内容参考的这个文章:http://www.importnew ...
随机推荐
- jquery学习总结24-36
一.jquery的自定义事件 1.自定义事件不能通过eventName()来添加,只能通过on来绑定 2.自定义事件需要通过trigger(自动触发)来进行触发 二.jauery事件命名空间 1.事件 ...
- eclipse下Spring环境构建及插件
首先获取spring tool suite插件 获取地址http://spring.io/tools/sts/ 然后打开eclipse选择菜单栏Help下Install new software添加我 ...
- Python开发——15.协程与I/O模型
一.协程(Coroutine) 1.知识背景 协程又称微线程,是一种用户态的轻量级线程.子程序,或者称为函数,在所有语言中都是层级调用,比如A调用B,B在执行过程中又调用了C,C执行完毕返回,B执行完 ...
- Paper | 量化CV任务的关联性,寻找最佳迁移策略(Taskonomy)
目录 1. 问题 2. 方法 3. 实验设计 3.1. 解决词典内部(一组已知)任务的能力 3.2. 解决新任务(少量标记数据)的能力 4. 讨论和启发 论文:Taskonomy: Disentang ...
- SJCP认证题前五十题填坑
在做Java的SJCP认证试题时自己整理了一些Java基础细节知识点,以下是知识点陈列 1.标签机制:标签起作用的唯一的地方刚好在迭代语句之前(不然编译错误) continue label1 直接转到 ...
- ICO图标下载地址
http://findicons.com/ http://www.iconfont.cn/
- Linux 区别 chown和chmod的用法
chown用法用来更改某个目录或文件的用户名和用户组的chown 用户名:组名 文件路径(可以是就对路径也可以是相对路径)例1:chown root:root /tmp/tmp1就是把tmp下的tmp ...
- day_12函数默认值,数据类型的补充,函数对象名称空间与作用域,函数的嵌套定义
复习, 昨天讲了字符串的比较,按照从左往右比较每一个字符,通过字符对应的ASCII码进行比较 函数的参数,‘ 实参与形参 形参:在函数定义时()中出现的参数 实参,在函数调用时()中出现的参数 实参的 ...
- 关于c++的一篇随笔
众所周知c++是一门极其深奥的学科,正因为其深奥之处,才会让人们觉得学习起来特别难.当然,我想说我自己也不例外,想起当初就像一场噩梦一样,直到今日还历历在目.尽管如此,c++还是一门相当有魅力的课程, ...
- spring 读取yaml配置文件
从Spring框架4.1.0增加了对YAML的支持,Spring框架4.1.0 maven POM具有Snakeyaml依赖性 . 您可以在Spring Boot应用中使用两种方式加载YAML: 1 ...
