leetcode 0217
✅ 682. 棒球比赛
描述
你现在是棒球比赛记录员。给定一个字符串列表,每个字符串可以是以下四种类型之一:1.整数(一轮的得分):直接表示您在本轮中获得的积分数。2. "+"(一轮的得分):表示本轮获得的得分是前两轮有效 回合得分的总和。3. "D"(一轮的得分):表示本轮获得的得分是前一轮有效 回合得分的两倍。# stack.top() *= 24. "C"(一个操作,这不是一个回合的分数):表示您获得的最后一个有效 回合的分数是无效的,应该被移除。# tt 对应队列的pop每一轮的操作都是永久性的,可能会对前一轮和后一轮产生影响。你需要返回你在所有回合中得分的总和。示例 1:输入: ["5","2","C","D","+"]输出: 30解释:第1轮:你可以得到5分。总和是:5。第2轮:你可以得到2分。总和是:7。操作1:第2轮的数据无效。总和是:5。第3轮:你可以得到10分(第2轮的数据已被删除)。总数是:15。第4轮:你可以得到5 + 10 = 15分。总数是:30。示例 2:输入: ["5","-2","4","C","D","9","+","+"]输出: 27解释:第1轮:你可以得到5分。总和是:5。第2轮:你可以得到-2分。总数是:3。第3轮:你可以得到4分。总和是:7。操作1:第3轮的数据无效。总数是:3。第4轮:你可以得到-4分(第三轮的数据已被删除)。总和是:-1。第5轮:你可以得到9分。总数是:8。第6轮:你可以得到-4 + 9 = 5分。总数是13。第7轮:你可以得到9 + 5 = 14分。总数是27。注意:输入列表的大小将介于1和1000之间。列表中的每个整数都将介于-30000和30000之间
解答
多个 if 去判断 字符 就好了吧?
cpp
注意: stoi
注意: 你要好好记得 参数 : vector<string>& ops 里面的每一个都是string ,so use: “”
Line 13: Char 31: error: no match for 'operator==' (operand types are '__gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<std::allocator<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >::value_type' {aka 'std::__cxx11::basic_string<char>'} and 'char')} else if (ops[i] == 'D') { // tt change it to "D" will be fine
class Solution {public:int calPoints(vector<string>& ops) {int ret = 0;stack<int> s;for (int i = 0; i < ops.size(); i++) {if(ops[i] == "+") {int a = s.top();s.pop();int b = s.top();s.push(a);s.push(a + b);} else if (ops[i] == "D") {int a = s.top();s.push(2 * a);} else if (ops[i] == "C") {s.pop();} else {s.push(stoi(ops[i]));// stoi will cause one char in ops convert to an integer.}}while(!s.empty()) {ret += s.top();s.pop();}return ret;}};/*执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了71.81%的用户内存消耗 :9.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.10%的用户*/
py
class Solution:def calPoints(self, ops: List[str]) -> int:scores = []for i in ops:if i == '+':scores += [sum(scores[-2:])]# this will add last two in list# list0 can be append by list1 + list2,so u got: [1,2,3] = [1] + [2,3]elif i == 'D':scores += [scores[-1] * 2]elif i == 'C':scores.pop()else:scores += [int(i)]return sum(scores)'''执行用时 :40 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了84.49%的用户内存消耗 :13.1 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了44.70%的用户'''
✅ 999. 车的可用捕获量
描述
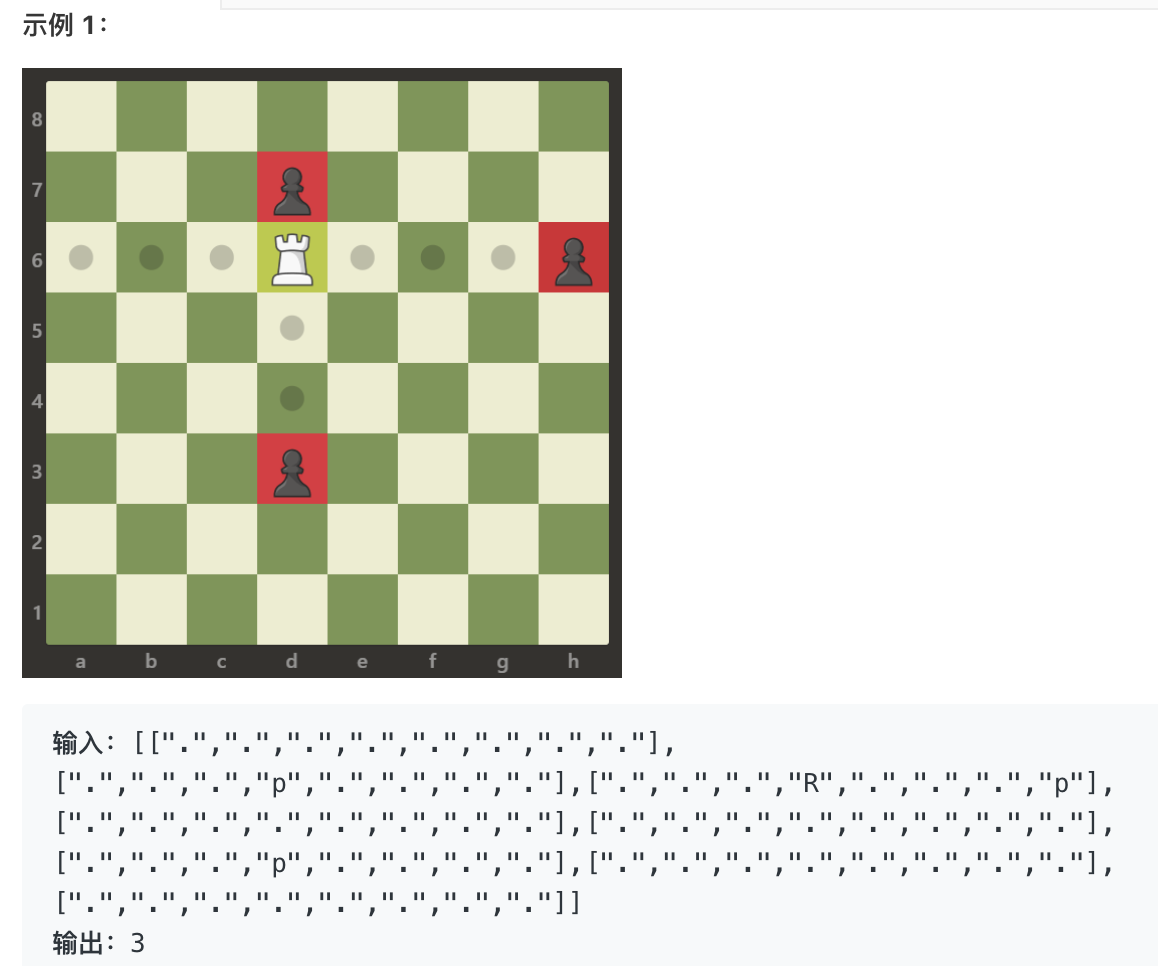
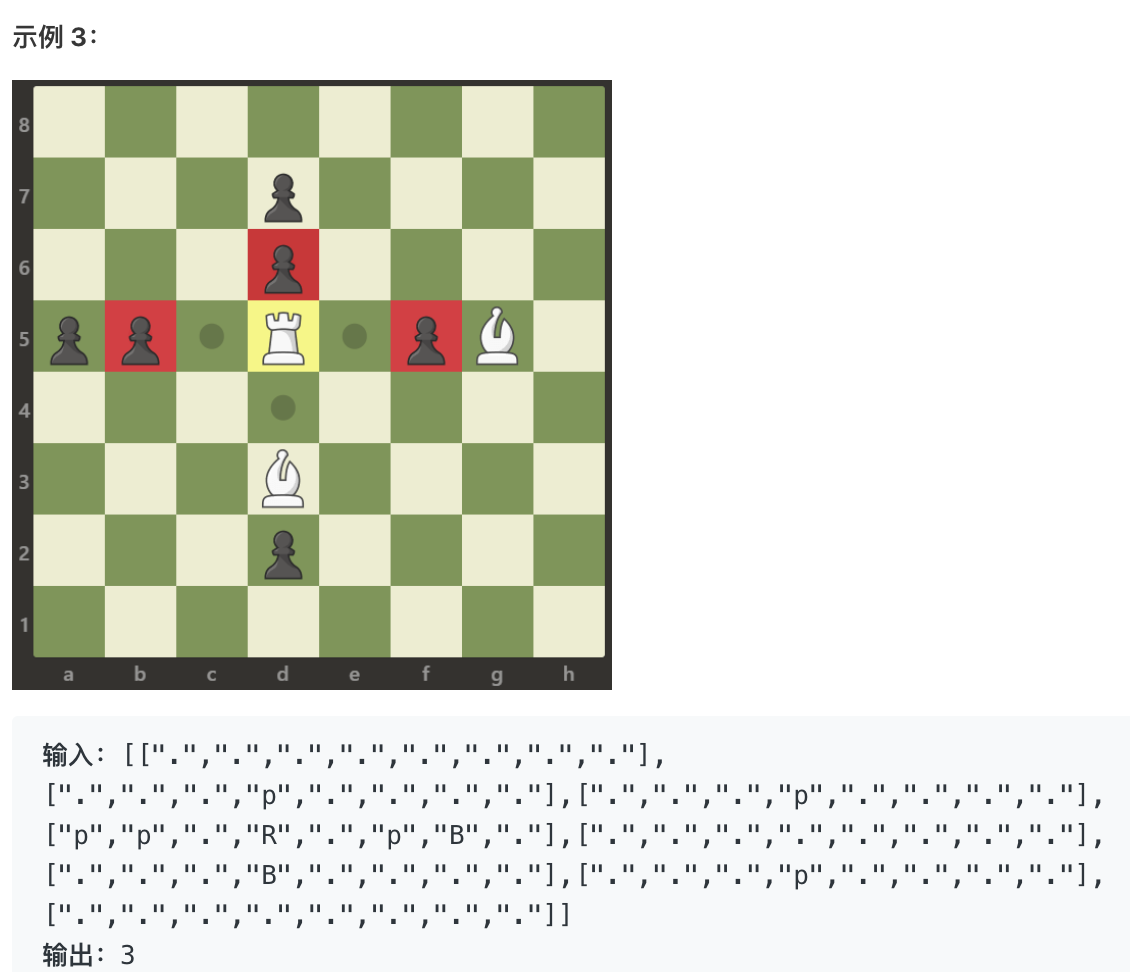
在一个 8 x 8 的棋盘上,有一个白色车(rook)。也可能有 空方块,白色的象(bishop)和黑色的卒(pawn)。它们分别以字符 “R”,“.”,“B” 和 “p” 给出。大写字符表示白棋,小写字符表示黑棋。车按国际象棋中的规则移动:它选择四个基本方向中的一个(北,东,西和南),然后朝那个方向移动,直到它选择停止、到达棋盘的边缘或移动到同一方格来捕获该方格上颜色相反的卒。另外,车不能与其他友方(白色)象进入同一个方格。返回车能够在一次移动中捕获到的卒的数量。

解答
c
int numRookCaptures(char** board, int boardSize, int* boardColSize){int x,y,res=0;// 找 车for(int i=0;i<8;i++){for(int j=0;j<8;j++){if(board[i][j]=='R'){x=i;y=j;break;}}}// 四个方向开车for(int i=x+1;i<8;i++){if(board[i][y]=='B')break;if(board[i][y]=='p'){res++;break;}}for(int i=x-1;i>=0;i--){if(board[i][y]=='B')break;if(board[i][y]=='p'){res++;break;}}for(int i=y+1;i<8;i++){if(board[x][i]=='B')break;if(board[x][i]=='p'){res++;break;}}for(int i=y-1;i>=0;i--){if(board[x][i]=='B')break;if(board[x][i]=='p'){res++;break;}}return res;}
other java todo
class Solution {public int numRookCaptures(char[][] board) {for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){for(int j=0;j<board[i].length;j++){//找到R的位置if(board[i][j]=='R'){//以R 为原点建立坐标系//依次向上找,向下找,向右找,向左找return cap(board,i,j,0,1)+cap(board,i,j,0,-1)+cap(board,i,j,1,0)+cap(board,i,j,-1,0);}}}return 0;}public int cap(char[][] a,int x,int y,int dx,int dy){/*参数说明*a为原数组矩阵*x,y为R的坐标*dx,dy为增长步长*/while(x>=0 && x<a.length && y>=0 && y<a[x].length && a[x][y]!='B'){if(a[x][y]=='p'){return 1;}x+=dx;y+=dy;}return 0;}
py
class Solution:def numRookCaptures(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> int:#首先找到车所在的行和列output = 0col = Nonerow = Nonefor i in range(len(board)):if 'R' in board[i]:row = ibreakcol = board[row].index('R')# 值得注意 list.index(some_ele)# 找到了 车 的 row and col# 接下来 从 行,从列找 车能捕获 的 卒# 行:s = ''.join(board[row])# now s is??? guess == board[row]s = s.replace('.', '')# replace all 空方块('.') with really empty ''# countif 'pR' in s:output += 1if 'Rp' in s:output += 1# col:s = ''.join(traversedRow[col] for traversedRow in board)s = s.replace('.', '')# replace all 空方块('.') with really empty ''# countif 'pR' in s:output += 1if 'Rp' in s:output += 1return output'''执行用时 :32 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了81.42%的用户内存消耗 :13 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了51.13%的用户'''
✅ 118. 杨辉三角
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pascals-triangle/
描述
pascal triangle
在杨辉三角中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。示例:输入: 5输出:[[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]
解答
cpp
//c:/*** Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().*/int** generate(int numRows, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){*returnSize = numRows;*returnColumnSizes = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * numRows);//存贮每行有几个数字; 比如,第一行 1 个,第二行 2个。后面有 赋值int **ret = (int **) malloc(sizeof(int *) * numRows);//我被返回,我每行存int ptrfor(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = i + 1;ret[i] = (int *) malloc (sizeof(int) * (i + 1));//每行分配i+1 个空间大小ret[i][0] = 1;ret[i][i] = 1;//开头 ,结尾 已经 赋值为1 ,ok// 然后,我依次加到下面的行// 注意:第一行不会执行 这个forfor(int j = 1; j < i; j++) {ret[i][j] = ret[i - 1][j] + ret[i - 1][j - 1];//add zheng top, and left top}}return ret;}/*执行用时 :4 ms, 在所有 C 提交中击败了76.92%的用户内存消耗 :7.2 MB, 在所有 C 提交中击败了75.09%的用户*///c++class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {vector<vector<int>> vec;for(int i= 0;i < numRows;i++){vec.push_back(vector<int> (i+1,1));//初始化为 i + 1 那么大,每个元素为1if(i > 1){for(int j = 1; j < i; j++){vec[i][j] = vec[i-1][j-1] + vec[i-1][j];}}}return vec;}};/*执行用时 :4 ms, 在所有 C 提交中击败了76.92%的用户内存消耗 :7.2 MB, 在所有 C 提交中击败了75.09%的用户*/
py
class Solution:def generate(self, numRows: int) -> List[List[int]]:ret = []for i in range(numRows):now = [1] * (i+1)if i >= 2:for n in range (1, i):now[n] = pre[n - 1] + pre[n]ret += [now] # add now(the list [3,4,5]) as one single list elepre = nowreturn ret'''执行用时 :28 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了90.60%的用户内存消耗 :12.9 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了50.43%的用户'''
✅ 258. 各位相加
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-digits
描述
给定一个非负整数 num,反复将各个位上的数字相加,直到结果为一位数。示例:输入: 38输出: 2解释: 各位相加的过程为:3 + 8 = 11, 1 + 1 = 2。 由于 2 是一位数,所以返回 2。进阶:你可以不使用循环或者递归,且在 O(1) 时间复杂度内解决这个问题吗?
解答
X = 100a + 10b + c = 99a + 9b + (a+b+c);所以对9取余即可。
接受降维打击吧 各位: return 1 + (num - 1) % 9;
cpp
//递归class Solution {public:int addDigits(int num) {if(num < 10) {return num;}int newInt = 0;while(num != 0) {newInt += num % 10;num /= 10;}return addDigits(newInt);}};/*执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了30.57%的用户内存消耗 :8.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了39.39%的用户*/
py
找到规律:理解todo
除了传统的单纯循环,还可以找规律。假如一个三位数'abc',其值大小为s1 = 100 * a + 10 * b + 1 * c,经过一次各位相加后,变为s2 = a + b + c,减小的差值为(s1 -s2) = 99 * a + 9 * b 差值可以被9整除,每一个循环都这样,缩小了9的倍数。当num小于9,即只有一位时,直接返回num,大于9时,如果能被9整除,则返回9(因为不可能返回0也不可能返回两位数及以上的值),如果不能被整除,就返回被9除的余数。
class Solution:def addDigits(self, num: int) -> int:if num > 9:num = num % 9if num == 0:return 9return num
leetcode 0217的更多相关文章
- 我为什么要写LeetCode的博客?
# 增强学习成果 有一个研究成果,在学习中传授他人知识和讨论是最高效的做法,而看书则是最低效的做法(具体研究成果没找到地址).我写LeetCode博客主要目的是增强学习成果.当然,我也想出名,然而不知 ...
- LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
终于将LeetCode的免费题刷完了,真是漫长的第一遍啊,估计很多题都忘的差不多了,这次开个题目汇总贴,并附上每道题目的解题连接,方便之后查阅吧~ 477 Total Hamming Distance ...
- [LeetCode] Longest Substring with At Least K Repeating Characters 至少有K个重复字符的最长子字符串
Find the length of the longest substring T of a given string (consists of lowercase letters only) su ...
- Leetcode 笔记 113 - Path Sum II
题目链接:Path Sum II | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each ...
- Leetcode 笔记 112 - Path Sum
题目链接:Path Sum | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf ...
- Leetcode 笔记 110 - Balanced Binary Tree
题目链接:Balanced Binary Tree | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. For ...
- Leetcode 笔记 100 - Same Tree
题目链接:Same Tree | LeetCode OJ Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are equal or ...
- Leetcode 笔记 99 - Recover Binary Search Tree
题目链接:Recover Binary Search Tree | LeetCode OJ Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped ...
- Leetcode 笔记 98 - Validate Binary Search Tree
题目链接:Validate Binary Search Tree | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binar ...
随机推荐
- OSI七层协议详解
一.简介 开放系统互连参考模型 (Open System Interconnect 简称OSI)是国际标准化组织(ISO)和国际电报电话咨询委员会(CCITT)联合制定的开放系统互连参考模型,为开放式 ...
- DFA 简易正则表达式匹配
一个只能匹配非常简单的(字母 . + *)共 4 种状态的正则表达式语法的自动机(注意,仅限 DFA,没考虑 NFA): 好久之前写的了,记得有个 bug 一直没解决... #include < ...
- Unity相机跟随
固定相机跟随 这种相机有一个参考对象,它会保持与该参考对象固定的位置,跟随改参考对象发生移动 using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; public c ...
- Java学习笔记(九)面向对象---模板方法设计模式
理解 在定义功能时功能的一部分是确定的,但是有一部分是不确定的,而确定的部分在使用不确定的部分,那么就将不确定的部分暴露出去,由该类的子类完成. 举例 需求 获取一段程序的运行时间 代码 abstra ...
- 【代码审计】seacms 前台Getshell分析
一.漏洞分析 漏洞触发点search.php 211-213行 跟进parseIf 函数 ./include/main.class.php 这里要注意 3118行的位置,可以看到未做任何处理的eval ...
- Go_栈
1. 栈的介绍 2. 栈的应用 3. 栈入门 package main import ( "fmt" "errors" ) //使用数组来模拟一个栈的使用 ty ...
- flask 2 进阶
# 创建项目 jinja2 语法基础 # pycharm 里面 创建 new project -->pure python 之后选择路径 选择解释器 以及虚拟环境问题 from flask im ...
- Intersection over Union(IoU) algorithms
IoU算法可用与评估两个多维度数据的相似度,举一个实际应用,做CV,目标检测,我们需要评估模型的识别准确率,不同于二元类问题,普通的评估算法不合适,于是用到了这个算法,这个算法简单易懂,评估效果也不错 ...
- Anaconda"无法定位程序输入点 OPENSSL_sk_new_reserve 于动态链接库Anaconda3\Library\bin\libssl-1_1-x64.dll上"的解决办法
Anaconda"无法定位程序输入点 OPENSSL_sk_new_reserve 于动态链接库Anaconda3\Library\bin\libssl-1_1-x64.dll上" ...
- itest(爱测试) 4.3.0 发布,开源BUG 跟踪管理 & 敏捷测试管理软件
itest 简介:查看简介 test 开源敏捷测试管理,testOps 践行者.可按测试包分配测试用例执行,也可建测试迭代(含任务,测试包,BUG)来组织测试工作,也有测试环境管理,还有很常用的测试度 ...
