吴裕雄 python 机器学习——核化PCAKernelPCA模型
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,decomposition def load_data():
'''
加载用于降维的数据
'''
# 使用 scikit-learn 自带的 iris 数据集
iris=datasets.load_iris()
return iris.data,iris.target #核化PCAKernelPCA模型
def test_KPCA(*data):
X,y=data
kernels=['linear','poly','rbf','sigmoid']
# 依次测试四种核函数
for kernel in kernels:
kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=None,kernel=kernel)
kpca.fit(X)
print('kernel=%s --> lambdas: %s'% (kernel,kpca.lambdas_)) # 产生用于降维的数据集
X,y=load_data()
# 调用 test_KPCA
test_KPCA(X,y)

...................

....................
def plot_KPCA(*data):
'''
绘制经过 KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点
'''
X,y=data
kernels=['linear','poly','rbf','sigmoid']
fig=plt.figure()
# 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色
colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) for i,kernel in enumerate(kernels):
kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel=kernel)
kpca.fit(X)
# 原始数据集转换到二维
X_r=kpca.transform(X)
## 两行两列,每个单元显示一种核函数的 KernelPCA 的效果图
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,2,i+1)
for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors):
position=y==label
ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label,
color=color)
ax.set_xlabel("X[0]")
ax.set_ylabel("X[1]")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title("kernel=%s"%kernel)
plt.suptitle("KPCA")
plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA
plot_KPCA(X,y)

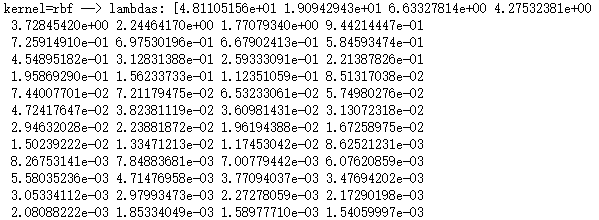
def plot_KPCA_poly(*data):
'''
绘制经过 使用 poly 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点
'''
X,y=data
fig=plt.figure()
# 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色
colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2))
# poly 核的参数组成的列表。
# 每个元素是个元组,代表一组参数(依次为:p 值, gamma 值, r 值)
# p 取值为:3,10
# gamma 取值为 :1,10
# r 取值为:1,10
# 排列组合一共 8 种组合
Params=[(3,1,1),(3,10,1),(3,1,10),(3,10,10),(10,1,1),(10,10,1),(10,1,10),(10,10,10)]
for i,(p,gamma,r) in enumerate(Params):
# poly 核,目标为2维
kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='poly',gamma=gamma,degree=p,coef0=r)
kpca.fit(X)
# 原始数据集转换到二维
X_r=kpca.transform(X)
## 两行四列,每个单元显示核函数为 poly 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,4,i+1)
for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors):
position=y==label
ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label,
color=color)
ax.set_xlabel("X[0]")
# 隐藏 x 轴刻度
ax.set_xticks([])
# 隐藏 y 轴刻度
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_ylabel("X[1]")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title(r"$ (%s (x \cdot z+1)+%s)^{%s}$"%(gamma,r,p))
plt.suptitle("KPCA-Poly")
plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_poly
plot_KPCA_poly(X,y)
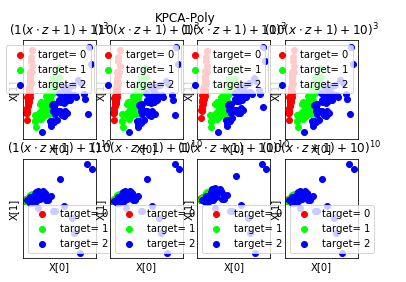
def plot_KPCA_rbf(*data):
'''
绘制经过 使用 rbf 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点
'''
X,y=data
fig=plt.figure()
# 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色
colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2))
# rbf 核的参数组成的列表。每个参数就是 gamma值
Gammas=[0.5,1,4,10]
for i,gamma in enumerate(Gammas):
kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='rbf',gamma=gamma)
kpca.fit(X)
# 原始数据集转换到二维
X_r=kpca.transform(X)
## 两行两列,每个单元显示核函数为 rbf 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,2,i+1)
for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors):
position=y==label
ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label,
color=color)
ax.set_xlabel("X[0]")
# 隐藏 x 轴刻度
ax.set_xticks([])
# 隐藏 y 轴刻度
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_ylabel("X[1]")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title(r"$\exp(-%s||x-z||^2)$"%gamma)
plt.suptitle("KPCA-rbf")
plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_rbf
plot_KPCA_rbf(X,y)
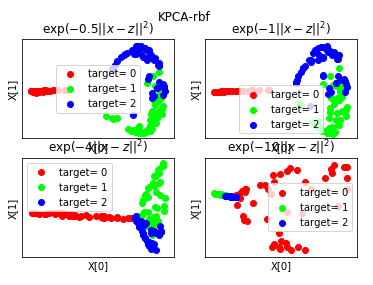
def plot_KPCA_sigmoid(*data):
'''
绘制经过 使用 sigmoid 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点
'''
X,y=data
fig=plt.figure()
# 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色
colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2))
# sigmoid 核的参数组成的列表。
Params=[(0.01,0.1),(0.01,0.2),(0.1,0.1),(0.1,0.2),(0.2,0.1),(0.2,0.2)]
# 每个元素就是一种参数组合(依次为 gamma,coef0)
# gamma 取值为: 0.01,0.1,0.2
# coef0 取值为: 0.1,0.2
# 排列组合一共有 6 种组合
for i,(gamma,r) in enumerate(Params):
kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='sigmoid',gamma=gamma,coef0=r)
kpca.fit(X)
# 原始数据集转换到二维
X_r=kpca.transform(X)
## 三行两列,每个单元显示核函数为 sigmoid 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图
ax=fig.add_subplot(3,2,i+1)
for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors):
position=y==label
ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label,
color=color)
ax.set_xlabel("X[0]")
# 隐藏 x 轴刻度
ax.set_xticks([])
# 隐藏 y 轴刻度
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_ylabel("X[1]")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title(r"$\tanh(%s(x\cdot z)+%s)$"%(gamma,r))
plt.suptitle("KPCA-sigmoid")
plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_sigmoid
plot_KPCA_sigmoid(X,y)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——核化PCAKernelPCA模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——分类决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——回归决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——线性回归模型
import numpy as np from sklearn import datasets,linear_model from sklearn.model_selection import tra ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——K均值聚类KMeans模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import cluster from sklearn.metrics ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——混合高斯聚类GMM模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import mixture from sklearn.metrics ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——层次聚类AgglomerativeClustering模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import cluster from sklearn.metrics ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——密度聚类DBSCAN模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import cluster from sklearn.metrics ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——等度量映射Isomap降维模型
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datas ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机非线性回归SVR模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm fr ...
随机推荐
- c++ stl在竞赛里的使用总结
SET bzoj2761: [JLOI2011]不重复数字 这题... count() 的用法,返回这个值出现的次数,但是在set里只会出现0次和1次,这个可以判断某个值是否在set里出现过 还有si ...
- AntDesign(React)学习-14 使用UMI提供的antd模板
1.UMI提供了可视化antd模板,可以直接添加到项目中修改用 比如将个人中心添加到项目中 2.选择个人中心,确定 3.成功 4.打开项目 5.Route文件也自动添加 根路由有exact:true后 ...
- Django学习笔记4
Referto https://docs.djangoproject.com/zh-hans/2.2/intro/tutorial04/ Since we have the abstract conc ...
- 3ds Max File Format (Part 5: How it all links together; ReferenceMaker, INode)
At this point, you should start to familiarize yourself a bit with the publicly available 3ds Max AP ...
- python3读取、写入、追加写入excel文件
由于excel版本不同,python处理的时候选择的库页不同. 一.操作对应版本表格需要用到的库 1.操作xls格式的表格文件,需要用到的库如下: 读取:xlrd 写入:xlwt 修改(追加写入):x ...
- g++运行c++程序提示main()找不到
/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/5/../../../x86_64-linux-gnu/crt1.o: In function `_start': (.text+0x20) ...
- 题解 【Codefoeces687B】Remainders Game
题意: 给出c1,c2,...cn,问对于任何一个正整数x,给出x%c1,x%c2,...的值x%k的值是否确定; 思路: 中国剩余定理.详见https://blog.csdn.net/acdream ...
- Linux - Shell - 字符串截取
概述 简述 字符串 截取 背景 之前因为要给文件 批量重命名, 做过字符串截取 当时做好了, 也说了要写点东西 结果忘了 现在又要尝试批量 重命名 才发现之前的东西已经忘了好多 要是当时把博客写下来, ...
- LED Decorative Light Supplier - LED Environmental Decorative Lighting Application
Creating ambient lighting in the home can bridge the gap between the internal world and the outside ...
- 三、ZigBee无线网络工具
CC2530概述 CC2530是德州仪器Ti公司用于2.4-GHz IEEE 802.15.4.ZigBee 和 RF4CE 应用的一个真正的片上系统(SoC)解决方案,是作为ZigBee无线传 感网 ...
