python — 表的操作(二)
1.单表查询
单表查询语法:
select distinct 字段1,字段2... from 表名
where 条件
group by field
having 筛选
order by field
limit 限制条数
关键字执行的优先级:
from
where
group by
select
distinct
having
order by
limit

1.1 简单查询
1.select语句:
- select * from 表;
- select 字段,字段.. from 表;
- select distinct 字段,字段.. from 表; # 按照查出来的字段去重
- select 字段*5 from 表; # 给查出来的字段做四则运算 (字段时int类型)
- select 字段 as 新名字,字段 as 新名字 from 表; # 给查出来的字段重命名
- select 字段 新名字 from 表;给查出来的字段重命名
2.定义显示的格式 concat
1.concat() 函数 用于字符串拼接
例:select concat('姓名: ',emp_name,' 年薪: ', salary*12) as annual_salary
from employee;2.concat_ws() 第一个参数为分隔符
例:select concat_ws(':',emp_name,salary*12) as annual_salary
from employee;
1.2 where语句
where语句不能与聚合函数合用
1.比较运算
> 、< 、= 、>= 、<= 、!= 或<> (不等于)
用于数值比较(不会用于做字符串的比较)
2.范围筛选
1.多选一 :字段名 in (值1,值2,值3)
in (值1,值2,值3) 相当于 or
例:select * from employee where salary in (20000,30000,3000,19000,18000,17000)
2.在一个模糊的范围里
1.在一个数值区间 between 值1 and 值2
# 查薪资在1w-2w之间的所有人的名字
select emp_name from employee where salary between 10000 and 20000;
2.字符串的模糊查询 like
通配符 % 匹配任意长度的任意内容
select * from employee where emp_name like '程%';# 查询以程开头的
select * from employee where emp_name like '%n';# 查询以n结尾的
select * from employee where emp_name like '%n%';# 查询包含n的
通配符 _ 匹配一个字符长度的任意内容
3.正则匹配 regexp 用于更加细粒度的匹配的时候
select * from 表 where 字段 regexp 正则表达式
select * from employee where emp_name regexp '^j[a-z]{5}'
查看岗位是teacher且名字是jin开头的员工姓名、年薪
select emp_name,salary*12 from employee where post='teacher' and emp_name like 'jin%'
select emp_name,salary*12 from employee where post='teacher' and emp_name regexp '^jin.*'
3.逻辑运算 - 条件的拼接
与 and
或 or
非 not
select * from employee where salary not in (20000,30000,3000,19000,18000,17000
4.身份运算符 - 关于null —— is null /is not null
查看岗位描述不为NULL的员工信息
select * from employee where post_comment is not null;
1.3 分组 group by
select *(或 字段名) from 表名 group by 字段名
select * from employee group by post
会把在group by后面的这个字段,也就是post字段中的每一个不同的项都保留下来,并且把值是这一项的的所有行归为一组
distinct 是基于分组完成的,所以一般去重用分组。
1.4 聚合
1.聚合:把很多行的同一个字段进行一些统计,最终的到一个结果
count(字段) — 统计这个字段有多少项
sum(字段) — 统计这个字段对应的数值的和
avg(字段) — 统计这个字段对应的数值的平均值
min(字段)
max(字段)
2.分组聚合
先分组在聚合
1.总是根据会重复的项来进行分组
2.分组总是和聚合函数一起用 最大 最小 平均 求和 有多少项
#求各个部门的人数
select post,count(*) from employee group by post;
#求公司里 男生 和女生的人数
select sex,count(id) from employee group by sex;
#求各部门的平均薪资
select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post;
#求各部门年龄最小的
select post,min(age) from employee group by post
求部门的最高薪资或者求公司的最高薪资都可以通过聚合函数取到,但是要得到对应的人,就必须通过多表查询
1.5 having 过滤
having 条件 # 过滤组 ,永远与group合用,是在group by 之后执行的。
执行顺序:总是先执行where ,再执行group by分组,所以相关先分组之后再根据分组做某些条件筛选的时候,where都用不上,只能用having来完成。
部门人数大于3的部门
select post from employee group by post having count(*) > 3
平均薪资大于10000的部门
select post from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000
select * from employee having age>18
注:普通的条件筛选不要用having,要使用where。
1.6 order by 查询排序
order by 某一个字段; 根据字段默认升序排列
order by 某一个字段 asc; 默认是升序 ,asc 从小到大
order by 某一个字段 desc; 指定降序排列 ,desc 从大到小
order by 第一个字段 asc,第二个字段 desc; 指定先根据第一个字段升序排列,在第一个字段相同的情况下,再根据第二个字段排列
1.7 LIMIT 限制查询的记录数
1.取前n个 : limit n == limit 0,n
- 考试成绩的前三名
- 入职时间最晚的前三个
2.分页 : limit m,n 从m+1开始取n个
- 员工展示的网页
- 18个员工
- 每一页展示5个员工
3.limit n offset m == limit m,n 从m+1开始取n个
1.8 总结
select distinct 需要显示的列 from 表
where 条件
group by 分组
having 过滤组条件
order by 排序
limit (offset) 前n 条
单表查询顺序:

2. 多表查询
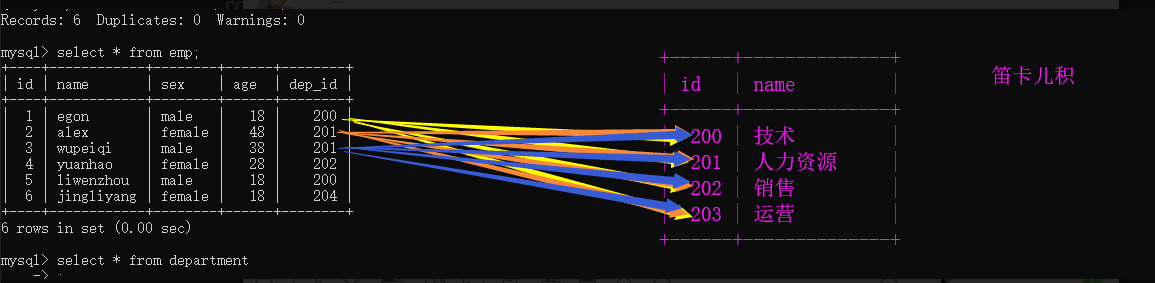
两张表是怎么连在一起的?
select * from emp,department;
2.1 连表查询
把两张表连在一起查
1.内链接 inner join
两张表条件不匹配的项不会出现在结果中
select * from emp inner join department on emp.dep_id = department.id;

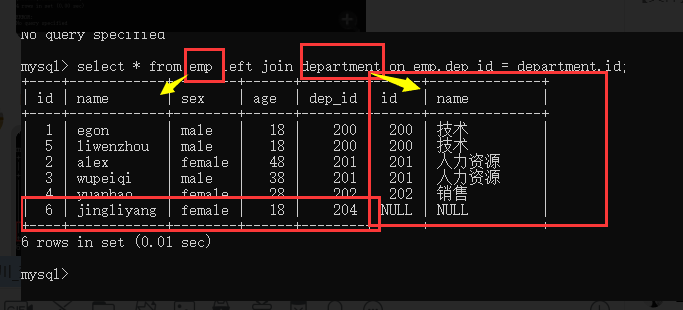
2.外连接
左外连接 left join
永远显示全量的左表中的数据
select * from emp left join department on emp.dep_id = department.id;
右外连接 right join
永远显示全量的右表中的数据
select * from emp right join department on emp.dep_id = department.id;
全外连接
全外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的和右边有左边没有的结果
注意:mysql不支持全外连接 full join
强调:mysql可以使用此种方式间接实现全外连接:
- select * from emp left join department on emp.dep_id = department.id
union
select * from department right join emp on emp.dep_id = department.id;
- select * from emp left join department on emp.dep_id = department.id
连接的语法:
- select 字段 from 表1 xxx join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
常用的连表查询:内链接 、左外链接
# 找技术部门的所有人的姓名
select * from emp inner join department on emp.dep_id = department.id;
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
select * from emp inner join department on emp.dep_id = department.id where department.name = '技术'
select emp.name from emp inner join department d on emp.dep_id = d.id where d.name = '技术'
# 找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门名称
select emp.name,d.name from emp inner join department as d on emp.dep_id = d.id where age>25;
# 根据age的升序顺序来连表查询emp和department
select * from emp inner join department as d on emp.dep_id = d.id order by age;
既可以用连表查询也可以用子查询时,优先使用连表查询,因为连表查询的效率高。
2.2 子查询
在查询一个结果的时候,依赖一个条件,这个条件也是一个sql语句
# 找技术部门的所有人的姓名
先找到部门表技术部门的部门id
select id from department where name = '技术';
再找emp表中部门id = 200
select name from emp where dep_id = (select id from department where name = '技术');
# 找到技术部门和销售部门所有人的姓名
先找到技术部门和销售部门的的部门id
select id from department where name = '技术' or name='销售'
找到emp表中部门id = 200或者202的人名
select name from emp where dep_id in (select id from department where name = '技术' or name='销售');
# 连表查询方法:
select emp.name from emp inner join department on emp.dep_id = department.id where department.name in ('技术','销售');
小练习
# 查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
部门名 department表
select name from department where id in (
select dep_id from emp group by dep_id having avg(age)>25
);
员工表
select dep_id,avg(age) from emp group by dep_id;
select dep_id from emp group by dep_id having avg(age)>25;
# 查看不足1人的部门名(子查询得到的是有人的部门id)
查emp表中有哪些部门id
select dep_id from emp group by dep_id;
再看department表中
select * from department where id not in (???)
select * from department where id not in (select dep_id from emp group by dep_id);
# 查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄
select * from emp where age>(select avg(age) from emp);
# 查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄
select dep_id,avg(age) from emp group by dep_id;
select * from emp inner join (select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) as d
on emp.dep_id = d.dep_id where emp.age > d.avg_age;
python — 表的操作(二)的更多相关文章
- python — 表的操作(一)
1. 创建表 创建表: create table t1 (id int,name char(4)); create table t2 (id int,name char(4)) engine=myis ...
- python 列表常用操作(二)
1.tuple 的 unpack a,b = t 2.格式化输出 print('您的输入:{},值为{}',format(a,b)) 3.日期计算 import datetime as dt impo ...
- MySQL库表详细操作
昨天我们初始了MySQL,今天我们先从库表方面详细说一下具体操作 一.库操作 1.创建数据库 1.1 语法 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf8; 1.2 数据库命名规则 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- MySQL数据库之 MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询
MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询 数据的准备 #建表 create table department( id int, name varchar(20) ); create table ...
- python 全栈开发,Day61(库的操作,表的操作,数据类型,数据类型(2),完整性约束)
昨日内容回顾 一.回顾 定义:mysql就是一个基于socket编写的C / S架构的软件 包含: ---服务端软件 - socket服务端 - 本地文件操作 - 解析指令(mysql语句) ---客 ...
- {MySQL的库、表的详细操作}一 库操作 二 表操作 三 行操作
MySQL的库.表的详细操作 MySQL数据库 本节目录 一 库操作 二 表操作 三 行操作 一 库操作 1.创建数据库 1.1 语法 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf ...
- 进击的Python【第十二章】:mysql介绍与简单操作,sqlachemy介绍与简单应用
进击的Python[第十二章]:mysql介绍与简单操作,sqlachemy介绍与简单应用 一.数据库介绍 什么是数据库? 数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织.存储和管理数据的仓库,每个数 ...
- Python之虚拟机操作:利用VIX二次开发,实现自己的pyvix(系列一)成果展示和python实例
在日常工作中,需要使用python脚本去自动化控制VMware虚拟机,现有的pyvix功能较少,而且不适合个人编程习惯,故萌发了开发一个berlin版本pyvix的想法,暂且叫其OpenPyVix.O ...
- SQL server学习(二)表结构操作、SQL函数、高级查询
数据库查询的基本格式为: select ----输出(显示)你要查询出来的值 from -----查询的依据 where -----筛选条件(对依据(数据库中存在的表)) group by ----- ...
随机推荐
- luogu P4168 蒲公英+ 分块学习笔记
传送门 题目描述 在乡下的小路旁种着许多蒲公英,而我们的问题正是与这些蒲公英有关. 为了简化起见,我们把所有的蒲公英看成一个长度为n的序列\((a_1,a_2..a_n)\),其中 \(a_i\)为一 ...
- Linux - /bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
问题 在Windows环境下用Notepad++写了个shell脚本,上传到Linux平台后运行报错如下: /bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or di ...
- CentOS7 升级Python2.x到3.x
CentOS 7 中默认安装了 Python,版本比较低(2.7.5),为了使用新版 3.x,需要对旧版本进行升级.由于很多基本的命令.软件包都依赖旧版本,比如:yum.所以,在更新 Python 时 ...
- ICEM-一种三维Y型网格
原视频下载地址:https://yunpan.cn/cLHD9ewat8v9a 访问密码 0f0f
- yum安装nginx添加upstream_check_module模块
下载模块 upstream_check_module 查看yum安装nginx版本信息 # nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.17.0 built by gcc 4.8. ...
- DNN在推荐系统中的应用参考资料
参考资料 DSSM算法计算文本相似度:https://www.cnblogs.com/wmx24/p/10157154.html Deep Neural Network for YouTube Rec ...
- legend3---20、加东西之前要保证没有,删东西之前要保证有,无论前端后端
legend3---20.加东西之前要保证没有,删东西之前要保证有,无论前端后端 一.总结 一句话总结: 加东西之前要保证没有,删东西之前要保证有,无论前端后端 这是很好的编程习惯,可以避免很多错误, ...
- 关于Flutter启动项目白屏,报错[ERROR:flutter/shell/gpu/gpu_surface_gl.cc(58)] Failed to setup Skia Gr context.问题的解决方案
首先,环境如下: 1.系统:windows10 64位 Android SDK version: 28.0.3 Flutter SDK: v1.5.4-hotfix.2 模拟器: 网易Mu ...
- 初识kaggle,以及记录 kaggle的使用
1.简介:Kaggle是一个数据建模和数据分析竞赛的平台.企业和研究者可在其上发布数据,统计学者和数据挖掘专家可在其上进行竞赛,通过“众包”的形式以产生最好的模型.Kaggle可以分为Competit ...
- VS Code 使用技巧[转载]
原文:VS Code 快捷键(VS Code Shortcuts.pdf) 常用 General 按 Press 功能 Function Ctrl + Shift + P,F1 显示命令面板 Show ...
