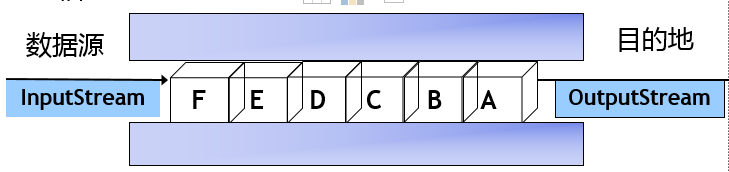
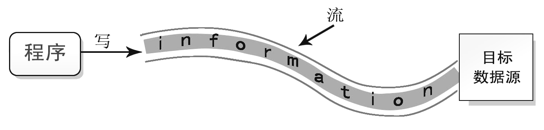
15_IO流
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
package cn.sxt01.fileinputstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:读取c.txt中的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\c.txt");
// 【1】构建输入流(管道)
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
System.out.println(fis);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【2】读取一个字节
int r = 0;
try {
r = fis.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println((char)r);
// 【3】关闭流
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt01.fileinputstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:读取c.txt中的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\c.txt");
// 【1】构建输入流(管道)
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
System.out.println(fis);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【2】读取一个字节
int len = 0; // 读取到缓冲区中的字节个数
byte[] buf = new byte[2]; // 字节缓冲区
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
while( (len=fis.read(buf)) != -1 ) {
String tmp = new String(buf,0,len);
sb.append(tmp);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(sb);
// 【3】关闭流
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt01.fileouputstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:写入helloworld 到d.txt中的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt");
// 【1】创建输出流(管道)
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//【2】写入信息到输出流
try {
fos.write('h');
fos.write('e');
fos.write('l');
fos.write('l');
fos.write('o');
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】刷新缓冲区
try {
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt01.fileouputstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:写入helloworld 到d.txt中的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt");
// 【1】创建输出流(管道)
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//【2】写入信息到输出流
try {
String str = "hello world中国";
// 默认gbk编码
/*byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
fos.write(buf);*/
byte[] buf = str.getBytes("utf8");
fos.write(buf);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】刷新缓冲区
try {
fos.flush();
// 【4】关闭文件
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt03.filereader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt");
// 【1】建立字符输入流
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【2】一次读取一个字符
int r = 0;
try {
/*r = fr.read();
r = fr.read();
r = fr.read();
r = fr.read();
r = fr.read();
r = fr.read();
System.out.println(r);*/
/*
中国abc\r\n
中国你好你好
*/
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (r=fr.read()) != -1 ) {
sb.append((char)r);
}
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】关闭输入流
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt03.filereader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt");
// 【1】建立字符输入流
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【2】一次读取多个字符
int len = 0;
char[] cbuf = new char[2];
try {
/*
len = fr.read(cbuf);
len = fr.read(cbuf);
len = fr.read(cbuf);
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cbuf));
*/
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (len=fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
sb.append(cbuf, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】关闭输入流
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt03.filewriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\e.txt");
FileWriter fw = null;
// 【1】建立输出流管道
try {
/*
* append:表示写入文件的方式
* true:追加 false:覆盖
*/
fw = new FileWriter(file,false);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【2】写入
try {
// 写入一个字符
/*fw.write('中');
fw.write('国');*/
// 写入一个字符数组
/*char[] cbuf = {'中','国','\r','\n','a','b','c'};
fw.write(cbuf);*/
// 写入一个字符串
fw.write("中国abc");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】刷新
try {
fw.flush();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
 |
|
package cn.sxt04.outputstramwriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
// 需求:写入 “中国abc” 以utf8编码写入
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\g.txt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "utf8");
osw.write('中');
char[] cbuf = {'国','a'};
osw.write(cbuf);
osw.write("中国abc");
osw.flush();
osw.close();
}
}
|
|
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
// 需求:读取g.txt的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\g.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf8");
/*int r = isr.read();
System.out.println((char)r);*/
char[] cbuf = new char[2];
int len = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (len=isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
sb.append(cbuf,0,len);
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
|
|
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
// 需求:读取win手动创建的utf8编码的h.txt的内容
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\h.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf8");
/*int r = isr.read();
System.out.println((char)r);*/
char[] cbuf = new char[2];
int len = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (len=isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
sb.append(cbuf,0,len);
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt01.bufferedreader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\i.txt");
// ctrl+t:查看类继承关系
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
// 一次读取一行
/*
String str = br.readLine();
str = br.readLine();
str = br.readLine();
str = br.readLine();
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
*/
String line;
while( (line=br.readLine() ) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
reader.close();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt01.bufferedwriter;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
// 需求:以utf8存入一首诗
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\k.txt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "utf8");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
bw.write("床前明月光,");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("疑似地上霜。");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
bw.close();
osw.close();
out.close();
}
}
|
 |
|
package cn.sxt02.inout;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 从控制台输入一个字符并打印
InputStream in = System.in;
// 【1】一次读取一个字节:(输入/数据源是键盘)
// int r = in.read();
// System.out.println((char)r);
// 【2】一次读取多个字节
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
len = in.read(buf);
// 默认控制台是gbk编码
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt02.inout;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 思考:为什么会乱码?
File file = new java.io.File("d:\\javatest\\i.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 标准输出流(gbk)
PrintStream ps = System.out;
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[2];
while( (len=fis.read(buf)) != -1 ) {
ps.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt02.inout;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 通过打印流写入数据到一个文件(gbk)
/*File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\m.txt");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(file);
ps.write('a');
ps.write('b');
ps.close();*/
// 通过打印流写入一个utf8编码的文件
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\m1.txt");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(file,"utf8");
ps.println("abc中国");
ps.close();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt02.inout;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.write('a');
ps.write('b');
ps.flush();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt02.inout;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream ps = System.out;
/*ps.write('a');
ps.write('b');*/
// 自动调用flush方法
/*byte[] buf = {'a','b'};
ps.write(buf);*/
// 自动调用flush方法
/*ps.write('a');
ps.write('b');
ps.write('\n');*/
// 自动调用flush方法
ps.println("ab");
// sps.flush();
}
}
|
|
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 字符输出流
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(System.out);
pw.println("hello");
pw.println("中国");
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt04.serializable;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
User user = new User("001", "二狗", "123", 20);
/**
* 思路:
* 序列化:把对象个各个属性按照有规律的格式拼接成字符串,把字符串写入文件。
* 反序列化:把文件中的字符串读取为内存中,按序列化格式把字符串拆开得到很多属性值,然后初始化对象。
*/
// String info = user.getId()+"-"+user.getName()+"-"+user.getPwd()+"-"+user.getAge();
// System.out.println(info);
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\n1.sxt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
oos.writeObject(user);
oos.close();
out.close();
}
}
|
|
package cn.sxt04.serializable;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\n1.sxt");
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
User user = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
|
|
Exception in thread "main" java.io.InvalidClassException: cn.sxt04.serializable.User; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 4281284299154400224, local class serialVersionUID = 8687762707351138232
at java.io.ObjectStreamClass.initNonProxy(ObjectStreamClass.java:687)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readNonProxyDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1876)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readClassDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1745)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readOrdinaryObject(ObjectInputStream.java:2033)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject0(ObjectInputStream.java:1567)
at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject(ObjectInputStream.java:427)
at cn.sxt04.serializable.Test02.main(Test02.java:19)
|
 |
|
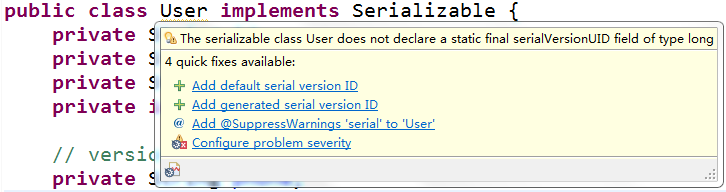
public class User implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String id;
private String name;
private transient String pwd;
private int age;
private String phone;
|
15_IO流的更多相关文章
- day20<IO流>
IO流(IO流概述及其分类) IO流(FileInputStream) IO流(read()方法返回值为什么是int) IO流(FileOutputStream) IO流(FileOutputStre ...
- 【Java基础】【22IO(其他流)&Properties】
22.01_IO流(序列流)(了解) 1.什么是序列流 序列流可以把多个字节输入流整合成一个, 从序列流中读取数据时, 将从被整合的第一个流开始读, 读完一个之后继续读第二个, 以此类推. 2.使用方 ...
- 【Java基础】【21IO(字符流)&字符流其他内容&递归】
21.01_IO流(字符流FileReader) 1.字符流是什么 字符流是可以直接读写字符的IO流 字符流读取字符, 就要先读取到字节数据, 然后转为字符. 如果要写出字符, 需要把字符转为字节再写 ...
- java-IO流-其他流
###22.01_IO流(序列流)(了解) * 1.什么是序列流 * 序列流可以把多个字节输入流整合成一个, 从序列流中读取数据时, 将从被整合的第一个流开始读, 读完一个之后继续读第二个, ...
- 阶段01Java基础day22IO流03
22.01_IO流(序列流) 1.什么是序列流 序列流可以把多个字节输入流整合成一个, 从序列流中读取数据时, 将从被整合的第一个流开始读, 读完一个之后继续读第二个, 以此类推. 2.使用方式 整合 ...
- 阶段01Java基础day21IO流02
21.01_IO流(字符流FileReader) 1.字符流是什么 字符流是可以直接读写字符的IO流 字符流读取字符, 就要先读取到字节数据, 然后转为字符. 如果要写出字符, 需要把字符转为字节再写 ...
- day22<IO流+>
IO流(序列流) IO流(序列流整合多个) IO流(内存输出流) IO流(内存输出流之黑马面试题) IO流(对象操作流ObjecOutputStream) IO流(对象操作流ObjectInputSt ...
- day21<IO流+&FIle递归>
IO流(字符流FileReader) IO流(字符流FileWriter) IO流(字符流的拷贝) IO流(什么情况下使用字符流) IO流(字符流是否可以拷贝非纯文本的文件) IO流(自定义字符数组的 ...
- 【Java基础】【20IO(字节流)】
20.01_IO流(IO流概述及其分类) 1.概念 IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输 Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式 Java用于操作流的类都在IO包中 流按流向分为两种:输入流,输出流. 流按操 ...
随机推荐
- Java8函数式编程的宏观总结
1.java8优势通过将行为进行抽象,java8提供了批量处理数据的并行类库,使得代码可以在多核CPU上高效运行. 2.函数式编程的核心使用不可变值和函数,函数对一个值进行处理,映射成另一个值. 3. ...
- Centos-7修改yum源(阿里yum源)
国外地址yum源下载慢,下到一半就断了,就这个原因就修改它为国内yum源地址 国内yum源: 阿里centos7 yum源:http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos- ...
- vscode远程代码同步
参考资料: https://blog.csdn.net/u012560340/article/details/83030680 https://github.com/liximomo/vscode-s ...
- qt 创建程序目录
voidinitDir() { QStringuserFilePath=QStandardPaths::writableLocation(QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocati ...
- SQL优化 | 避免全表扫描
1. 对返回的行无任何限定条件,即没有where 子句 2. 未对数据表与任何索引主列相对应的行限定条件 例如:在City-State-Zip列创建了三列复合索引,那么仅对State列限定条件不能使用 ...
- gitment初始化评论跳回博客首页
表现 众所周知,gitment评论系统需要初始化以创建对应的issue,可是我在点击login with github的时候,总是跳向博客首页!WTF!什么鬼?这样不程序啊? 排查 1.F12查看lo ...
- vue开发环境、正式环境的配置及原理
修改prod.env.js里的内容,修改后的内容如下: 'use strict' module.exports = { NODE_ENV: '"production"', EVN_ ...
- Android向系统日历添加日程提醒事件
在项目开发过程中,有时会有预约提醒.定时提醒等需求,这时我们可以使用系统日历来辅助提醒.通过向系统日历中写入事件.设置提醒方式(闹钟),实现到达某个特定的时间自动提醒的功能.这样做的好处是由于提醒功能 ...
- Oracle存在则更新,不存在则插入应用-merge
转: Oracle存在则更新,不存在则插入应用-merge 2017年01月11日 14:15:26 周星猩 阅读数 11354更多 分类专栏: Oracle 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循C ...
- java类什么时候加载?,加载类的原理机制是怎么样的?
java类什么时候加载?,加载原理机制是怎么样的? 答: 很多人都不是很清楚java的class类什么时候加载在运行内存中,其实类加载的时间是发生在一下几种情况: 1.实例化对象时,就像sprin ...
