MapReduce中的Join算法
在关系型数据库中Join是非常常见的操作,各种优化手段已经到了极致。在海量数据的环境下,不可避免的也会碰到这种类型的需求,例如在数据分析时需要从不同的数据源中获取数据。不同于传统的单机模式,在分布式存储下采用MapReduce编程模型,也有相应的处理措施和优化方法。
我们先简要地描述待解决的问题。假设有两个数据集:气象站数据库和天气记录数据库
气象站的示例数据,如下
|
Station ID |
Station Name |
|
011990-99999 |
SIHCCAJAVRI |
|
012650-99999 |
TRNSET-HANSMOEN |
天气记录的示例数据,如下
|
Station ID |
Timestamp |
Temperature |
|
012650-99999 |
194903241200 |
111 |
|
012650-99999 |
194903241800 |
78 |
|
011990-99999 |
195005150700 |
0 |
|
011990-99999 |
195005151200 |
22 |
|
011990-99999 |
195005151800 |
-11 |
假设我们想要如下结果
|
Station ID |
Station Name |
Timestamp |
Temperature |
|
011990-99999 |
SIHCCAJAVRI |
195005150700 |
0 |
|
011990-99999 |
SIHCCAJAVRI |
195005151200 |
22 |
|
011990-99999 |
SIHCCAJAVRI |
195005151800 |
-11 |
|
012650-99999 |
TYNSET-HANSMOEN |
194903241200 |
111 |
|
012650-99999 |
TYNSET-HANSMOEN |
194903241800 |
78 |
想想看,我们该怎么通过MapReduce实现上面的需求?
MapReduce连接操作的实现技术取决于数据集的规模及分区方式。如果一个数据集很大而另外一个数据集很小,以至于小的数据集可以分发到集群中的每一个节点之中,然后在mapper阶段读取大数据集中的数据;到reducer时,reduce获取本节点上的数据(也就是小数据集中的数据)并完成连接操作;我们以上面的天气数据连接来做具体阐述,假设气象站数据集很少,那将气象站数据集分发到集群中的每个节点中,在mapper阶段读取天气记录数据,在reduce阶段读取本节点上的气象站数据,然后通过气象站数据中的气象站ID和天气数据中的气象ID做连接,从而完成气象站数据和天气记录数据的连接。在这种情况下,我们就用到了Hadoop的分布式缓存机制,它能够在任务运行过程中及时地将文件和存档复制到任务节点以供使用。为了节约网络宽带,在每一个作业中,各个文件通常只需要复制到一个节点一次
如果两个数据集的规模均很大,以至于没有哪个数据集可以被完全复制到集群的每个节点中,我们仍然可以使用 MapReduce来进行连接,至于到底采用map端连接(连接操作如果由mapper执行,则称为 “map 端连接”)还是reduce端连接(连接操作如果由reducer执行,则称为“reduce端连接”),则取决于数据的组织方式。下面我们分别介绍map端连接和reduce端连接。
map 端连接
在两个大规模输入数据集到达map函数之前就应该执行连接操作。为达到该目的,各map的输入数据必须先分区并且以特定方式排序。各个输入数据集被划分成相同数量的分区,并且均按相同的键(连接键)排序。同一键的所有记录均会放在同一分区之中。听起来似乎要求非常严格,但这的确合乎MapReduce作业的输出。
map端连接操作可以连接多个作业的输出,只要这些作业的reducer数量相同、键相同并且输出文件是不可切分的(例如,小于一个 HDFS 块)。在上面讲的天气例子中,如果气象站文件以气象站ID部分排序,天气记录也以气象站ID部分排序,而且reducer的数量相同,则就满足了执行map端连接的前提条件。
利用 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.join 包中的CompositeInputFormat类来运行一个 map 端连接。CompositeInputFormat类的输入源和连接类型(内连接或外连接)可以通过一个连接表达式进行配置,连接表达式的语法简单。此种方法不常用,这里不再赘述。
reduce 端连接
由于reduce端连接并不要求输入数据集符合特定结构,因而reduce端连接比 map 端连接更为常用。但是,由于两个数据集均需经过MapReduce的shuffle过程, 所以reduce 端连接的效率往往要低一些。基本思路是mapper为各个记录标记源,并且使用连接键作为 map 输出键,使键相同的记录放在同一reducer中。 我们通过下面两种技术实现reduce端连接。
1、多输入
数据集的输入源往往有多种格式,因此可以使用 MultipleInputs 类来方便地解析各个数据源。MultipleInputs的用法,在“MapReduce输入格式”已经介绍过,这里就不再赘述。
2、二次排序
如前所述,reducer在两个数据源中选出键相同的记录并不介意这些记录是否已排好序。此外,为了更好地执行连接操作,先将某一个数据源传输到reducer会非常重要。还以上面的天气数据连接为例,当天气记录发送到reducer的时候,与这些记录有相同键的气象站信息最好也已经放在reducer,使得reducer能够将气象站名称填到天气记录之中就马上输出。虽然也可以不指定数据传输次序,并将待处理的记录缓存在内存之中,但应该尽量避免这种情况,因为其中任何一组的记录数量可能非常庞大,远远超出reducer的可用内存容量。 因此我们用到二次排序技术,对map阶段输出的每个键的值进行排序,实现这一效果。
下面我们分别介绍两种实现方式分布式缓存机制、reduce端连接
1、分布式缓存机制
1、用法
Hadoop 命令行选项中,有三个命令可以实现文件分发到任务的各个节点。
1)可以使用-files选项指定待分发的文件,文件内包含以逗号隔开的URL列表。文件可以存放在本地文件系统、HDFS、或其它Hadoop可读文件系统之中。如果尚未指定文件系统,则这些文件被默认是本地的。即使默认文件系统并非本地文件系统,这也是成立的。
2)可以使用-archives选项向自己的任务中复制存档文件,比如JAR文件、ZIP 文件、tar文件和gzipped tar文件,这些文件会被解档到任务节点。
3)可以使用-libjars选项将JAR文件添加到mapper和reducer任务的类路径中。如果作业JAR文件中并非包含很多库JAR文件,使用-libjars选项是很方便的。
2、工作机制
当启动一个作业,Hadoop会把由-files、-archives、和-libjars等选项所指定的文件复制到分布式文件系统之中。接着,在任务运行之前,tasktracker将文件从分布式文件系统复制到本地磁盘(缓存)使任务能够访问文件。此时,这些文件就被视为“本地化” 了。从任务的角度来看, 这些文件就已经在那儿了,它并不关心这些文件是否来自 HDFS 。此外,有-libjars指定的文件会在任务启动前添加到任务的类路径(classpath)中。
3、分布式缓存API
由于可以通过Hadoop命令行间接使用分布式缓存,所以大多数应用不需要使用分布式缓存API。然而,一些应用程序需要用到分布式缓存的更高级的特性,这就需要直接使用API了。 API包括两部分:将数据放到缓存中的方法,以及从缓存中读取数据的方法。
1)首先掌握数据放到缓存中的方法,以下列举 Job 中可将数据放入到缓存中的相关方法:
public void addCacheFile(URI uri);
public void addCacheArchive(URI uri);// 以上两组方法将文件或存档添加到分布式缓存
public void setCacheFiles(URI[] files);
public void setCacheArchives(URI[] archives);// 以上两组方法将一次性向分布式缓存中添加一组文件或存档
public void addFileToClassPath(Path file);
public void addArchiveToClassPath(Path archive);// 以上两组方法将文件或存档添加到 MapReduce 任务的类路径
在缓存中可以存放两类对象:文件(files)和存档(achives)。文件被直接放置在任务节点上,而存档则会被解档之后再将具体文件放置在任务节点上。
2)其次掌握在map或者reduce任务中,使用API从缓存中读取数据。
public Path[] getLocalCacheFiles() throws IOException;
public Path[] getLocalCacheArchives() throws IOException;
public Path[] getFileClassPaths();
public Path[] getArchiveClassPaths();
我们可以使用 getLocalCacheFiles()和getLocalCacheArchives()方法获取缓存中的文件或者存档的引用。当处理存档时,将会返回一个包含解档文件的目录。相应的,用户可以通过 getFileClassPaths()和getArchivesClassPaths()方法获取被添加到任务的类路径下的文件和文档。
下面我们仍然以前面的气象站数据和天气记录数据为例,使用分布式缓存API,完成两个数据集的连接操作。完整的 MapReduce 程序如下所示。
package com.buaa.distributedgache; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Hashtable; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa.distributedgache
* @ClassName JoinRecordWithStationName
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-25 19:34:57
*/
public class JoinRecordWithStationName extends Configured implements Tool { public static class TemperatureMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] arr = value.toString().split("\t", 2);
if (arr.length == 2) {
context.write(new Text(arr[0]), value);
}
}
} public static class TemperatureReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
// 定义Hashtable存放缓存数据
private Hashtable<String, String> table = new Hashtable<String, String>(); /**
* 获取分布式缓存文件
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 返回本地文件路径
Path[] localPaths = (Path[]) context.getLocalCacheFiles();
if (localPaths.length == 0) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Distributed cache file not found.");
} // 获取本地 FileSystem实例
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.getLocal(context.getConfiguration());
// 打开输入流
FSDataInputStream in = fs.open(new Path(localPaths[0].toString()));
// 创建BufferedReader读取器
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
// 按行读取并解析气象站数据
String infoAddr = null;
while ((infoAddr = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] records = infoAddr.split("\t");
// key为stationID,value为stationName
table.put(records[0], records[1]);
}
} public void reduce(Text key, Iterable< Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 天气记录根据stationId获取stationName
String stationName = table.get(key.toString());
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(new Text(stationName), value);
}
}
} @Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 读取配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // 判断路径是否存在,如果存在,则删除
Path mypath = new Path(args[2]);
FileSystem hdfs = mypath.getFileSystem(conf);
if (hdfs.isDirectory(mypath)) {
hdfs.delete(mypath, true);
} // 获取一个job实例
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf,"join");
// 主类
job.setJarByClass(JoinRecordWithStationName.class); // 设置record.txt文件作为输入
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
// 添加station.txt到分布式缓存
job.addCacheFile(new URI(args[1]));
// 输出目录
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[2])); // mapper
job.setMapperClass(TemperatureMapper.class);
// reduce
job.setReducerClass(TemperatureReducer.class); // 输出key类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 输出value类型
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); return job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] args0 = {
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/record.txt",
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/station.txt",
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/out/"
};
int ec = ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new JoinRecordWithStationName(), args0);
System.exit(ec);
}
}
添加分布式缓存文件相对简单,只需使用job.addCacheFile(new URI(cacheFilePath))方法添加缓存文件即可。需要注意的是,在获取获取缓存文件时,文件将以“本地的”Path 对象的形式返回。为了读取文件,用户需要首先使用getLocal()方法获得一个Hadoop本地FileSystem实例。本程序中,我们在Reduce的setup()方法中获取缓存文件。
以下是输出结果,达到我们预期的效果。
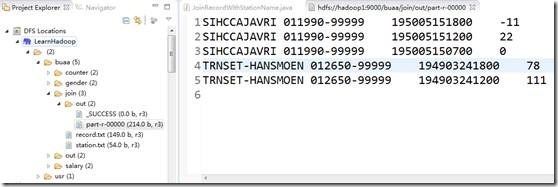
2、Reduce端连接
我们使用 TextPair 类构建组合键,包括气象站ID 和“标记”。在这里,“标记” 是一个虚拟的字段,其唯一目的是对记录排序,使气象站记录比天气记录先到达。一种简单的做法就是:对于气象站记录,设置“标记”的值设为 0;对于天气记录,设置“标记”的值设为1,代码如下所示
package com.buaa.secondarysort; import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa
* @ClassName TextPair
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-24 22:54:05
*/
public class TextPair implements WritableComparable<TextPair>{
// Text类型的实例变量first
private Text first;
// Text类型的实例变量second
private Text second; public TextPair(){
set(new Text(),new Text());
} public TextPair(String first,String second){
set(new Text(first),new Text(second));
} public void set(Text first,Text second){
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
} @Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
first.readFields(in);
second.readFields(in);
} @Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
first.write(out);
second.write(out);
} public int hashCode() {
return first.hashCode() * 163 + second.hashCode();
} public boolean equals(TextPair tp) {
return first.equals(tp.first) && second.equals(tp.second);
} public String toStirng() {
return first + "\t" + second;
} @Override
public int compareTo(TextPair o) {
if(!first.equals(o.first)){
return first.compareTo(o.first);
}else if(!second.equals(o.second)){
return second.compareTo(o.second);
} return 0;
} public Text getFirst() {
return first;
} public void setFirst(Text first) {
this.first = first;
} public Text getSecond() {
return second;
} public void setSecond(Text second) {
this.second = second;
}
}
JoinStationMapper处理来自气象站数据,代码如下所示。
package com.buaa.secondarysort; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa
* @ClassName JoinStationMapper
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-24 22:55:42
*/
public class JoinStationMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, TextPair, Text> {
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
// 解析气象站数据
String[] arr = line.split("\\s+"); if (arr.length == 2) {// 满足这种数据格式
// key=气象站id value=气象站名称
context.write(new TextPair(arr[0], "0"), new Text(arr[1]));
}
}
}
JoinRecordMapper处理来自天气记录数据,代码如下所示
package com.buaa.secondarysort; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa
* @ClassName JoinRecordMapper
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-24 22:56:55
*/
public class JoinRecordMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,TextPair,Text>{
protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String line = value.toString();
// 解析天气记录数据
String[] arr = line.split("\\s+",2); if(arr.length == 2){
//key=气象站id value=天气记录数据
context.write(new TextPair(arr[0],"1"),new Text(arr[1]));
}
}
}
由于 TextPair 经过了二次排序,所以 reducer 会先接收到气象站数据。因此从中抽取气象站名称,并将其作为后续每条输出记录的一部分写到输出文件。JoinReducer 的代码如下所示。
package com.buaa.secondarysort; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa
* @ClassName JoinReducer
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-24 22:54:24
*/
public class JoinReducer extends Reducer< TextPair,Text,Text,Text>{
protected void reduce(TextPair key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
Iterator<Text> iter = values.iterator();
// 气象站名称
Text stationName = new Text(iter.next()); while(iter.hasNext()){
// 天气记录的每条数据
Text record = iter.next(); Text outValue = new Text(stationName.toString() + "\t" + record.toString()); context.write(key.getFirst(),outValue);
}
}
}
下面我们定义作业的驱动类 JoinRecordWithStationName,在该类中,关键在于根据组合键的第一个字段(即气象站 ID)进行分区和分组,JoinRecordWithStationName 类的代码如下所示。
package com.buaa.secondarysort; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.MultipleInputs;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner; /**
* @ProjectName JoinDemo
* @PackageName com.buaa
* @ClassName JoinRecordWithStationName
* @Description TODO
* @Author 刘吉超
* @Date 2016-05-24 22:57:24
*/
public class JoinRecordWithStationName extends Configured implements Tool {
public static class KeyPartitioner extends Partitioner<TextPair, Text> {
public int getPartition(TextPair key, Text value, int numPartitions) {
return (key.getFirst().hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numPartitions;
}
} public static class GroupComparator extends WritableComparator {
protected GroupComparator() {
super(TextPair.class, true);
} @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable wc1, WritableComparable wc2) {
TextPair tp1 = (TextPair) wc1;
TextPair tp2 = (TextPair) wc2; return tp1.getFirst().compareTo(tp2.getFirst());
}
} public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 读取配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // 判断路径是否存在,如果存在,则删除
Path mypath = new Path(args[2]);
FileSystem hdfs = mypath.getFileSystem(conf);
if (hdfs.isDirectory(mypath)) {
hdfs.delete(mypath, true);
} // 新建一个任务
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "join");
// 主类
job.setJarByClass(JoinRecordWithStationName.class); // 天气记录数据源
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]), TextInputFormat.class, JoinRecordMapper.class);
// 气象站数据源
MultipleInputs.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[1]), TextInputFormat.class, JoinStationMapper.class);
// 输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[2])); // 自定义分区
job.setPartitionerClass(KeyPartitioner.class);
// 自定义分组
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupComparator.class); // 指定Reducer
job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class); // map key输出类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(TextPair.class);
// reduce key输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] args0 = {
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/record.txt",
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/station.txt",
"hdfs://hadoop1:9000/buaa/join/out/"
};
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new JoinRecordWithStationName(), args0);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}
以下是输出结果,也达到我们预期的效果。
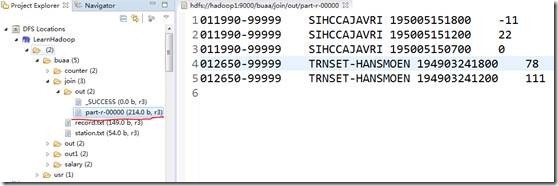
如果,您认为阅读这篇博客让您有些收获,不妨点击一下右下角的【推荐】。
如果,您希望更容易地发现我的新博客,不妨点击一下左下角的【关注我】。
如果,您对我的博客所讲述的内容有兴趣,请继续关注我的后续博客,我是【刘超★ljc】。
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
MapReduce中的Join算法的更多相关文章
- Mapreduce中的join操作
一.背景 MapReduce提供了表连接操作其中包括Map端join.Reduce端join还有半连接,现在我们要讨论的是Map端join,Map端join是指数据到达map处理函数之前进行合并的,效 ...
- Hadoop学习笔记—12.MapReduce中的常见算法
一.MapReduce中有哪些常见算法 (1)经典之王:单词计数 这个是MapReduce的经典案例,经典的不能再经典了! (2)数据去重 "数据去重"主要是为了掌握和利用并行化思 ...
- MapReduce中的Join
一. MR中的join的两种方式: 1.reduce side join(面试题) reduce side join是一种最简单的join方式,其主要思想如下: 在map阶段,map函数同时读取两个文 ...
- 使用map端连接结合分布式缓存机制实现Join算法
前面我们介绍了MapReduce中的Join算法,我们提到了可以通过map端连接或reduce端连接实现join算法,在文章中,我们只给出了reduce端连接的例子,下面我们说说使用map端连接结合分 ...
- (转)MapReduce中的两表join几种方案简介
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/leoleocmm/article/details/8602081 1. 概述 在传统数据库(如:MYSQL)中,JOIN操作是非常常见且非常耗时的.而 ...
- (转)MapReduce 中的两表 join 几种方案简介
1. 概述 在传统数据库(如:MYSQL)中,JOIN操作是非常常见且非常耗时的.而在HADOOP中进行JOIN操作,同样常见且耗时,由于Hadoop的独特设计思想,当进行JOIN操作时,有一些特殊的 ...
- MapReduce 中的两表 join 几种方案简介
转自:http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/95186 MapSideJoin例子:http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/1 ...
- MapReduce 中的两表 join 方案解析
1. 概述 在传统数据库(如:MYSQL)中,JOIN操作是非常常见且非常耗时的.而在HADOOP中进行JOIN操作,同样常见且耗时,由于Hadoop的独特设计思想,当进行JOIN操作时,有一些特殊的 ...
- MapReduce的模式、算法和用例
英文原文:<MapReduce Patterns, Algorithms, and Use Cases> https://highlyscalable.wordpress.com/2012 ...
随机推荐
- Android使用Dom解析xml
一.理论准备 二.上代码 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> < ...
- 关于MATLAB中的tic toc的问题
关于MATLAB中的tic toc的问题 其一) MATLAB实际单位时间计时函数的具体应用,在编写程序时,经常需要获知代码的执行实际时间,这就需要在程序中用到计时函数,matlab中提供了以下三种方 ...
- Word Puzzles
poj1204:http://poj.org/problem?id=1204 题意:给你n*m的字符串矩阵,然后p个查询,每个查询会给出一个字符串,然后问你在矩阵中能否通过8个方向搜索到这个字符串,输 ...
- EMMC 简要介绍
一直想写一篇关于EMMC的文章,但是因为之前弄了很多PPT,所以一直提不起兴趣,索性直接把之前的一个介绍EMMC的PPT贴出来给大家看看,有什么问题可以直接跟帖,我会第一时间进行解答,谢谢
- Service知识点总结
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/krislight/article Service可以看作一个后台服务,但并非是开启另外的线程,Service还是在主线程中运行.所以需避免耗 ...
- Android 颜色Color
Android中使用4个数字来表示颜色,分别是alpha.红(red).绿(green).蓝(blue)四个颜色值(ARGB).每个数字取值0-255,因此一个颜色可以用一个整数来表示.为了运行效率, ...
- LREM key count value
LREM key count value Available since 1.0.0. Time complexity: O(N) where N is the length of the list. ...
- java 常量池
在jvm规范中,每个类型都有自己的常量池.常量池是某类型所用常量的一个有序集合,包括直接常量(基本类型,String)和对其他类型.字段.方法的符号引用.之所以是符号引用而不是像c语言那样,编译时直接 ...
- JavaScript用JQuery呼叫Server端方法
准备好Server端的方法 [System.Web.Services.WebMethod] public static string VeryUserName(string name) { strin ...
- team geek
1. 转载自http://book.douban.com/review/6007037/,版权归丸子(^.^)v所有. New Google employees (we call “Nooglers” ...
