Linux内核--链表结构(一)
一、前言
Linux内核链表结构是一种双向循环链表结构,与传统的链表结构不同,Linux内核链表结构仅包含前驱和后继指针,不包含数据域。使用链表结构,仅需在结构体成员中包含list_head*成员就行;链表结构的定义在linux/list.h头文件。
二、链表初始化
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
宏LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)和LIST_HEAD(name)的作用在于初始化一个链表头节点,并使其前驱指针和后继指针指向自身;内联函数INIT_LIST_HEAD同理;
三、添加节点
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
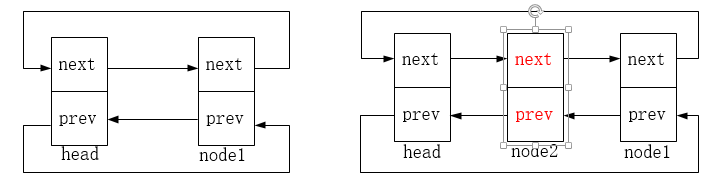
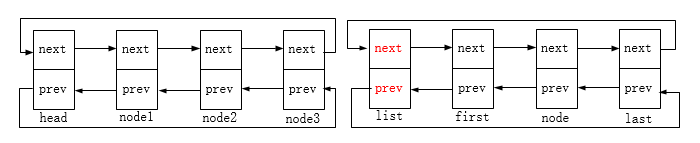
list_add:在头节点后插入节点,图示如下,node2为新增的节点:
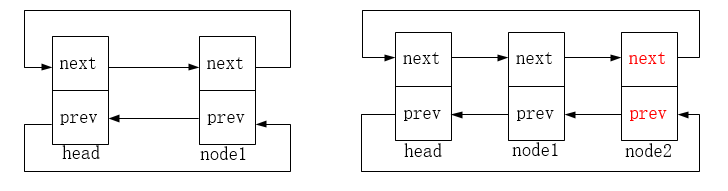
list_add_tail在头节点前插入节点,图示如下,node2为新增的节点:
四、删除节点
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
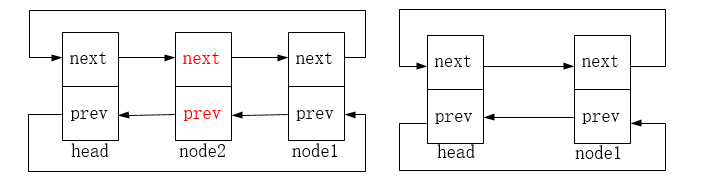
list_del:删除链表中的entry节点,entry节点的前驱后继指针指向LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2两个特殊值,这样设置是为了保证不在链表中的节点项不可访问,对LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2的访问都将引起页故障。
list_del_init:删除原链表中的entry节点,然后重新初始化entry节点为头节点(使其前驱后继指针都指向自身)。
/*
* Architectures might want to move the poison pointer offset
* into some well-recognized area such as 0xdead000000000000,
* that is also not mappable by user-space exploits:
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE
# define POISON_POINTER_DELTA _AC(CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE, UL)
#else
# define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0
#endif /*
* These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults
* under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses
* non-initialized list entries.
*/
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
链表删除的图示如下:
五、节点替换
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
} static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
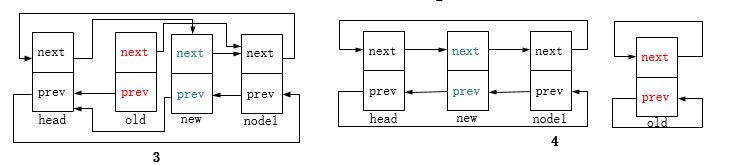
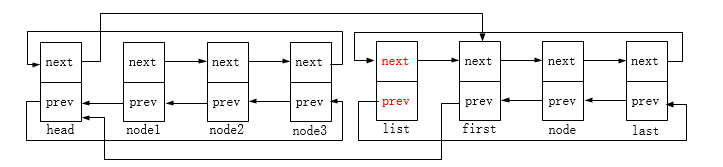
list_replace:将旧节点替换为新节点,函数头两句对应下图2,新节点next指针指向node1,node1节点的prev指针指向新节点。后两句对应图3,新节点prev指针指向head,head节点的next指针指向新节点。此时old节点的next和prev指针指向仍保留着;
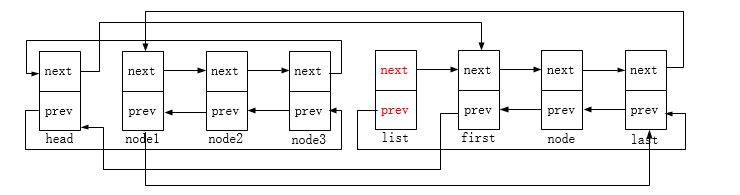
list_replace_init:将旧节点替换为新节点,并将旧节点重新初始化为头节点(前驱后继指针指向自身),对应下图4。

六、移动节点
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add(list, head);
}
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
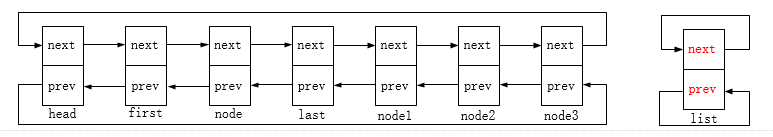
list_move:将list节点移动至head节点后(对应下图示的node1节点移动);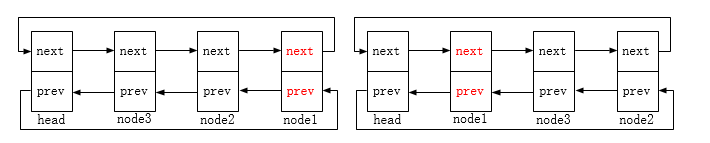
list_move_tail:将list节点移动至head节点前(对应下图示的node2节点移动); 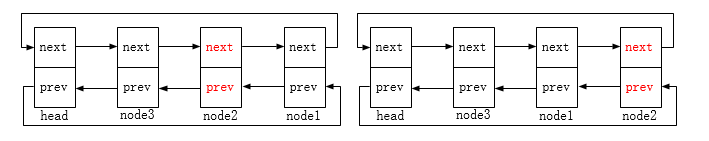
七、尾节点判断
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
链表的最后一个节点特性:其后继指针next必将指向头节点head
八、链表空判断
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *next = head->next;
return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}
list_empty和list_empty_careful都是判断链表是否为空。list_empty判断节点的后继指针next是否指向自身;list_empty_careful判断节点的后继指针和前驱指针是否均指向自身,其可用来判断链表是否为空且当前是否正在被修改。
九、链表旋转
static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first; if (!list_empty(head)) {
first = head->next;
list_move_tail(first, head);
}
}
list_rotate_left:链表节点向左移动,原先左边的节点向右移。相当于与前一节点互换位置。图示如下:
十、拆分链表
static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry;
entry->next = list;
head->next = new_first;
new_first->prev = head;
} /**
* list_cut_position - cut a list into two
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
* and if so we won't cut the list
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and
* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should
* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list
* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about
* losing its data.
*
*/
static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{
if (list_empty(head))
return;
if (list_is_singular(head) &&
(head->next != entry && head != entry))
return;
if (entry == head)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
else
__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
}
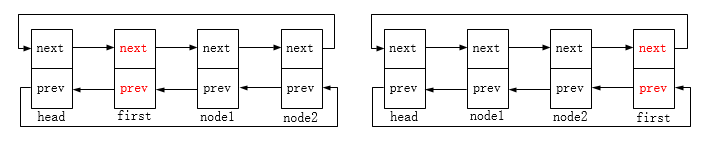
链表初始状态如下:
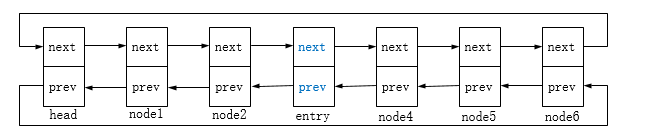
插入list节点:
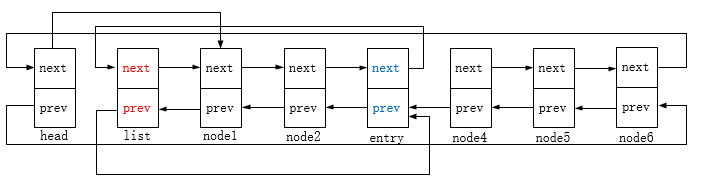
修改head和entry->next(这里是node4)节点的前驱后继指向:
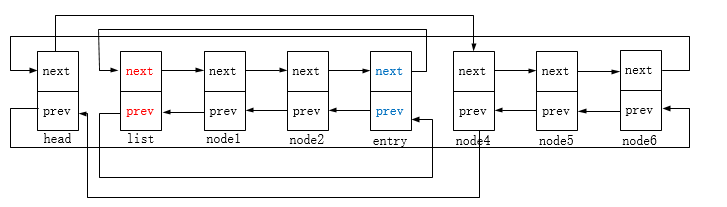
即:
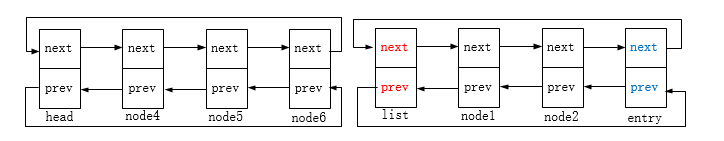
函数参数list是指要加进来的链表,head是指要拆分的链表头节点,entry则是位于head指向的链表中的某个节点;
函数的作用是将head(不包括head节点)到entry的链表拆分下来,添加到list所指向的链表后;
如果链表为空或entry指向的就是头节点,亦或者链表仅单个节点且entry这个节点不在这个链表内(不指向head亦不指向head->next),则不能拆分。
十一、判断链表是否仅含单个节点
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
判断条件为链表不为空,且头指针的前驱和后继均指向同个节点
十二、合并链表
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev; first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first; last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
} /**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
} /**
* list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
} /**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
} /**
* list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
链表初始状态:
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
这里prev即head节点
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
这里next即node1节点
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
最后一步,把list节点重新初始化为头节点,使其前驱后继指针指向自身。
上述图示描述了list_splice_init的链表合并过程,函数的作用是把list链表(除list节点自身)插入到head节点后(即head和head->next之间),并重新初始化list节点;
list_splice_tail_init则是与list_splice_init的区别仅是插入的位置不同,其是插入到head节点之前(即head->prev和head之间)。
Linux内核--链表结构(一)的更多相关文章
- Linux内核--链表结构(二)
Linux内核链表定义了一系列用于链表遍历的宏,本章详细描述. 一.container_of和offsetof 首先介绍两个很好用的宏container_of和offsetof.offsetof宏用于 ...
- C语言 Linux内核链表(企业级链表)
//Linux内核链表(企业级链表) #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> ...
- 深入分析 Linux 内核链表--转
引用地址:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/kernel/l-chain/index.html 一. 链表数据结构简介 链表是一种常用的组织有序数据 ...
- linux内核链表分析
一.常用的链表和内核链表的区别 1.1 常规链表结构 通常链表数据结构至少应包含两个域:数据域和指针域,数据域用于存储数据,指针域用于建立与下一个节点的联系.按照指针域的组织以及各个节 ...
- 深入分析 Linux 内核链表
转载:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/kernel/l-chain/ 一. 链表数据结构简介 链表是一种常用的组织有序数据的数据结构,它通过指 ...
- Linux 内核 链表 的简单模拟(2)
接上一篇Linux 内核 链表 的简单模拟(1) 第五章:Linux内核链表的遍历 /** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the & ...
- Linux 内核 链表 的简单模拟(1)
第零章:扯扯淡 出一个有意思的题目:用一个宏定义FIND求一个结构体struct里某个变量相对struc的编移量,如 struct student { int a; //FIND(struct stu ...
- linux内核链表的移植与使用
一. Linux内核链表为双向循环链表,和数据结构中所学链表类似,具体不再细讲.由于在内核中所实现的函数十分经典,所以移植出来方便后期应用程序中的使用. /********************* ...
- [国嵌攻略][108][Linux内核链表]
链表简介 链表是一种常见的数据结构,它通过指针将一系列数据节点连接成一条数据链.相对于数组,链表具有更好的动态性,建立链表时无需预先知道数据总量,可以随机分配空间,可以高效地在链表中的任意位置实时插入 ...
随机推荐
- [ Shell ] 两个 case 实现 GetOptions 效果
https://www.cnblogs.com/yeungchie/ 可以用 getopt,但我还是喜欢自己写这个过程,便于我够控制更多细节. 下面要实现的效果是,从命令行参数中分析,给 $libNa ...
- SMB共享配置
SMB 使用命令挂载和卸载SMB文件系统 自动挂载SMB文件系统 红帽企业 ...
- bzoj3545/bzoj3551 [ONTAK2010]Peaks/Peaks加强版
bzoj3545/bzoj3551 [ONTAK2010]Peaks/Peaks加强版 传送门:bzoj bzoj wdnmd为什么加强版不是权限题原题却是啊 3545: [ONTAK2010]Pe ...
- C++中的RAII介绍
摘要 RAII技术被认为是C++中管理资源的最佳方法,进一步引申,使用RAII技术也可以实现安全.简洁的状态管理,编写出优雅的异常安全的代码. 资源管理 RAII是C++的发明者Bjarne Stro ...
- idea在新窗口中打开
IntelliJ IDEA 2018.1.4 x64版本同时打开多个窗口可以进行如下设置,找到file--Settings...,然后会弹出下面的窗口:然后注意红框里的勾选项,最后确定Apply,OK ...
- 哪一个 bash 内置命令能够进行数学运算?
bash shell 的内置命令 let 可以进行整型数的数学运算. #! /bin/bash - - let c=a+b - -
- mysql问题排查与性能优化
MySQL 问题排查都有哪些手段? 使用 show processlist 命令查看当前所有连接信息. 使用 explain 命令查询 SQL 语句执行计划. 开启慢查询日志,查看慢查询的 SQL. ...
- 学习k8s(二)
kubernetes-国内拉取gcr.io\quay.io镜像方法 方法1: https://hub.docker.com/r/ibmcom/ 例如: gcr.io/google_containers ...
- 3.Spark设计与运行原理,基本操作
1.Spark已打造出结构一体化.功能多样化的大数据生态系统,请用图文阐述Spark生态系统的组成及各组件的功能. Spark生态系统主要包含Spark Core.Spark SQL.Spark St ...
- Python - Pycharm常用快捷键
1. 自动格式调整: pycharm有自动调整代码格式的快捷键,默认为Alt+Ctrl+L 2. 选中相同字符: 快捷键组合:Ctrl + Shift + Alt + J 3.批量缩进: 选择代码区域 ...
