svo笔记
使用
要想在ros中有更多的debug信息,要在global.h中把ros log的级别设为debug,最简单的就是把SVO_DEBUG_STREAM(x)改成ROS_INFO_STREAM(x)
#define SVO_DEBUG_STREAM(x) ROS_INFO_STREAM(x)
代码框架
一些状态的表示
enum Stage {
STAGE_PAUSED,
STAGE_FIRST_FRAME,
STAGE_SECOND_FRAME,
STAGE_DEFAULT_FRAME,
STAGE_RELOCALIZING
};
enum TrackingQuality {
TRACKING_INSUFFICIENT, TRACKING_BAD, TRACKING_GOOD
};
enum UpdateResult {
RESULT_NO_KEYFRAME, RESULT_IS_KEYFRAME, RESULT_FAILURE
};
主要的类
FrameHandlerMono::FrameHandlerMono(vk::AbstractCamera* cam) :
FrameHandlerBase(), //基类
cam_(cam), //相机模型
reprojector_(cam_, map_),
depth_filter_(NULL)
{
initialize();
}
void FrameHandlerMono::initialize()
{
//fast feature detector
feature_detection::DetectorPtr feature_detector(
new feature_detection::FastDetector(
cam_->width(), cam_->height(), Config::gridSize(), Config::nPyrLevels()));
//
DepthFilter::callback_t depth_filter_cb = boost::bind(
&MapPointCandidates::newCandidatePoint, &map_.point_candidates_, _1, _2);
//深度滤波线程
// 构造函数 DepthFilter(feature_detection::DetectorPtr feature_detector, callback_t seed_converged_cb);
depth_filter_ = new DepthFilter(feature_detector, depth_filter_cb);
depth_filter_->startThread();
}
整个就是一个状态机,不同的stage对应不同的处理函数
void FrameHandlerMono::addImage(const cv::Mat& img, const double timestamp)
{
// some cleanup from last iteration, can't do before because of visualization
core_kfs_.clear();
overlap_kfs_.clear();
// create new frame
new_frame_.reset(new Frame(cam_, img.clone(), timestamp));
// process frame
UpdateResult res = RESULT_FAILURE;
if(stage_ == STAGE_DEFAULT_FRAME)
res = processFrame();
else if(stage_ == STAGE_SECOND_FRAME)
//足够的视差
res = processSecondFrame();
else if(stage_ == STAGE_FIRST_FRAME)
//有足够的特征点就够
res = processFirstFrame();
else if(stage_ == STAGE_RELOCALIZING)
res = relocalizeFrame(SE3(Matrix3d::Identity(), Vector3d::Zero()),
map_.getClosestKeyframe(last_frame_));
// set last frame
last_frame_ = new_frame_;
new_frame_.reset();
}
FrameHandlerBase::UpdateResult FrameHandlerMono::processFrame()
{
// Set initial pose TODO use prior
//使用上一时刻的pose作为初始值
new_frame_->T_f_w_ = last_frame_->T_f_w_;
// sparse image align
// frame -- last frame,初始的估计
SparseImgAlign img_align(Config::kltMaxLevel(), Config::kltMinLevel(),
30, SparseImgAlign::GaussNewton, false, false);
size_t img_align_n_tracked = img_align.run(last_frame_, new_frame_);
// map reprojection & feature alignment
//frame -- map,优化点的位置,增加frame中的点,跟orbslam中的投影localmap相似
reprojector_.reprojectMap(new_frame_, overlap_kfs_);
const size_t repr_n_new_references = reprojector_.n_matches_;
const size_t repr_n_mps = reprojector_.n_trials_;
if(repr_n_new_references < Config::qualityMinFts())
{
new_frame_->T_f_w_ = last_frame_->T_f_w_; // reset to avoid crazy pose jumps
tracking_quality_ = TRACKING_INSUFFICIENT;
return RESULT_FAILURE;
}
// pose optimization
// pose的优化
pose_optimizer::optimizeGaussNewton(
Config::poseOptimThresh(), Config::poseOptimNumIter(), false,
new_frame_, sfba_thresh, sfba_error_init, sfba_error_final, sfba_n_edges_final);
if(sfba_n_edges_final < 20)
return RESULT_FAILURE;
// structure optimization
//点的优化
optimizeStructure(new_frame_, Config::structureOptimMaxPts(), Config::structureOptimNumIter());
// select keyframe
core_kfs_.insert(new_frame_);
setTrackingQuality(sfba_n_edges_final);
if(tracking_quality_ == TRACKING_INSUFFICIENT)
{
new_frame_->T_f_w_ = last_frame_->T_f_w_; // reset to avoid crazy pose jumps
return RESULT_FAILURE;
}
double depth_mean, depth_min;
frame_utils::getSceneDepth(*new_frame_, depth_mean, depth_min);
if(!needNewKf(depth_mean) || tracking_quality_ == TRACKING_BAD)
{
depth_filter_->addFrame(new_frame_);
return RESULT_NO_KEYFRAME;
}
new_frame_->setKeyframe();
// new keyframe selected
for(Features::iterator it=new_frame_->fts_.begin(); it!=new_frame_->fts_.end(); ++it)
if((*it)->point != NULL)
(*it)->point->addFrameRef(*it); //维护point看到的frame
map_.point_candidates_.addCandidatePointToFrame(new_frame_);
// optional bundle adjustment
#ifdef USE_BUNDLE_ADJUSTMENT
if(Config::lobaNumIter() > 0)
{
SVO_START_TIMER("local_ba");
setCoreKfs(Config::coreNKfs());
size_t loba_n_erredges_init, loba_n_erredges_fin;
double loba_err_init, loba_err_fin;
ba::localBA(new_frame_.get(), &core_kfs_, &map_,
loba_n_erredges_init, loba_n_erredges_fin,
loba_err_init, loba_err_fin);
SVO_STOP_TIMER("local_ba");
SVO_LOG4(loba_n_erredges_init, loba_n_erredges_fin, loba_err_init, loba_err_fin);
SVO_DEBUG_STREAM("Local BA:\t RemovedEdges {"<<loba_n_erredges_init<<", "<<loba_n_erredges_fin<<"} \t "
"Error {"<<loba_err_init<<", "<<loba_err_fin<<"}");
}
#endif
// init new depth-filters
depth_filter_->addKeyframe(new_frame_, depth_mean, 0.5*depth_min);
// if limited number of keyframes, remove the one furthest apart
if(Config::maxNKfs() > 2 && map_.size() >= Config::maxNKfs())
{
FramePtr furthest_frame = map_.getFurthestKeyframe(new_frame_->pos());
depth_filter_->removeKeyframe(furthest_frame); // TODO this interrupts the mapper thread, maybe we can solve this better
map_.safeDeleteFrame(furthest_frame);
}
// add keyframe to map
map_.addKeyframe(new_frame_);
return RESULT_IS_KEYFRAME;
}
FrameHandlerMono::UpdateResult FrameHandlerMono::relocalizeFrame(
const SE3& T_cur_ref,
FramePtr ref_keyframe)
{
SVO_WARN_STREAM_THROTTLE(1.0, "Relocalizing frame");
if(ref_keyframe == nullptr)
{
SVO_INFO_STREAM("No reference keyframe.");
return RESULT_FAILURE;
}
SparseImgAlign img_align(Config::kltMaxLevel(), Config::kltMinLevel(),
30, SparseImgAlign::GaussNewton, false, false);
size_t img_align_n_tracked = img_align.run(ref_keyframe, new_frame_);
if(img_align_n_tracked > 30)
{
SE3 T_f_w_last = last_frame_->T_f_w_;
last_frame_ = ref_keyframe;
FrameHandlerMono::UpdateResult res = processFrame();
if(res != RESULT_FAILURE)
{
stage_ = STAGE_DEFAULT_FRAME;
SVO_INFO_STREAM("Relocalization successful.");
}
else
new_frame_->T_f_w_ = T_f_w_last; // reset to last well localized pose
return res;
}
return RESULT_FAILURE;
}
Tracking 姿态估计
frame to frame

优化的变量使用红色表示,优化的residual变量使用蓝色表示
计算第k帧和第k−1帧中的特征点对的patch的灰度差, 点是上一时刻已经知道深度的点做投影,使用的是\(4\times4\)的patch,因为是跟上一帧进行对比,没有做affine transformation(仿射变换的)
使用inverse compositional,在最小二乘法中保持jacobian在更新的过程中保持不变,减少计算量

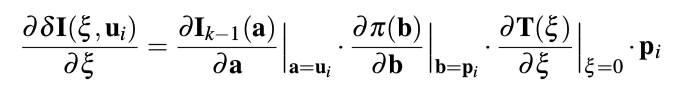
jacobian计算的过程中,reference patch \(I_{k-1}(u_i)\)和point \(p_i\)是保持不变的。所以计算的雅可比是不变的
更新的公式

class SparseImgAlign : public vk::NLLSSolver<6, SE3> //优化变量是6个自由度,se3空间表示的
{
public:
//计算不变的jacobian,和上一帧特征点对应的patch
void precomputeReferencePatches()
{
Matrix<double,2,6> frame_jac;
//
Frame::jacobian_xyz2uv(xyz_ref, frame_jac);
// cache the jacobian
jacobian_cache_.col(feature_counter*patch_area_ + pixel_counter) =
(dx*frame_jac.row(0) + dy*frame_jac.row(1))*(focal_length / (1<<level_));
}
double computeResiduals(const SE3& T_cur_from_ref,bool linearize_system,
bool compute_weight_scale)
{
const Vector6d J(jacobian_cache_.col(feature_counter*patch_area_ + pixel_counter));
//权重的设置 ,核函数 `robust_cost.h`
float weight = 1.0;
if (use_weights_) {
weight = weight_function_->value(res / scale_);
}
if (linearize_system) {
// compute Jacobian, weighted Hessian and weighted "steepest descend images" (times error)
const Vector6d J(
jacobian_cache_.col(
feature_counter * patch_area_
+ pixel_counter));
H_.noalias() += J * J.transpose() * weight;
Jres_.noalias() -= J * res * weight;
if (display_)
resimg_.at<float>((int) v_cur + y - patch_halfsize_,
(int) u_cur + x - patch_halfsize_) = res
/ 255.0;
}
}
int solve()
{
x_ = H_.ldlt().solve(Jres_);
if((bool) std::isnan((double) x_[0]))
return 0;
return 1;
}
//更新是在右边,并且是负的
void update(const ModelType& T_curold_from_ref, ModelType& T_curnew_from_ref) {
T_curnew_from_ref = T_curold_from_ref * SE3::exp(-x_);
}
};
frame to map
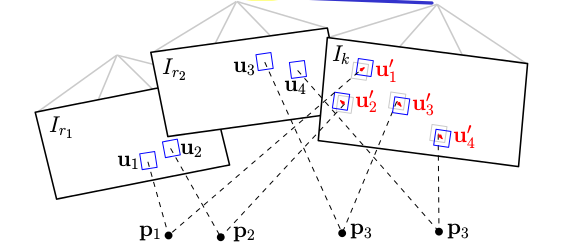
使用上一时刻求出的初始值,对每个当前帧能观察到的地图点p(已经收敛的深度估计),找到观察p角度最小的关键帧r上的对应点\(u_i\),优化得到p在当前帧上的投影\(u′i\)。
这一步中的patch采用的是8×8邻域,对应的距离比较大,要做仿射变换。这步不考虑极线约束,为了得到更精确的点位置估计
void Reprojector::reprojectMap(FramePtr frame,
std::vector<std::pair<FramePtr, std::size_t> >& overlap_kfs) {
//grid的顺序还做了一次随机的排序,数目是有要求的max_n_kfs,时间限制,实时性
resetGrid();
// Identify those Keyframes which share a common field of view.
//pair中的double是帧与帧之间的距离关系
list < pair<FramePtr, double> > close_kfs;
map_.getCloseKeyframes(frame, close_kfs);
// Sort KFs with overlap according to their closeness
close_kfs.sort(
boost::bind(&std::pair<FramePtr, double>::second, _1)
< boost::bind(&std::pair<FramePtr, double>::second, _2));
// Reproject all mappoints of the closest N kfs with overlap. We only store
// in which grid cell the points fall.
size_t n = 0;
overlap_kfs.reserve(options_.max_n_kfs);
for (auto it_frame = close_kfs.begin(), ite_frame = close_kfs.end();
it_frame != ite_frame && n < options_.max_n_kfs; ++it_frame, ++n) {
FramePtr ref_frame = it_frame->first;
overlap_kfs.push_back(pair<FramePtr, size_t>(ref_frame, 0));
// Try to reproject each mappoint that the other KF observes
for (auto it_ftr = ref_frame->fts_.begin(), ite_ftr =
ref_frame->fts_.end(); it_ftr != ite_ftr; ++it_ftr) {
// check if the feature has a mappoint assigned
//对应的深度要是已知的
if ((*it_ftr)->point == NULL)
continue;
// make sure we project a point only once
if ((*it_ftr)->point->last_projected_kf_id_ == frame->id_)
continue;
(*it_ftr)->point->last_projected_kf_id_ = frame->id_;
//改变grid变量 ,加入cell
if (reprojectPoint(frame, (*it_ftr)->point))
overlap_kfs.back().second++;
}
}
// Now project all point candidates
//
boost::unique_lock < boost::mutex > lock(map_.point_candidates_.mut_);
auto it = map_.point_candidates_.candidates_.begin();
while (it != map_.point_candidates_.candidates_.end()) {
if (!reprojectPoint(frame, it->first)) {
it->first->n_failed_reproj_ += 3;
if (it->first->n_failed_reproj_ > 30) {
map_.point_candidates_.deleteCandidate(*it);
it = map_.point_candidates_.candidates_.erase(it);
continue;
}
}
++it;
}
// Now we go through each grid cell and select one point to match.
// At the end, we should have at maximum one reprojected point per cell.
for (size_t i = 0; i < grid_.cells.size(); ++i) {
// we prefer good quality points over unkown quality (more likely to match)
// and unknown quality over candidates (position not optimized)
if (reprojectCell(*grid_.cells.at(grid_.cell_order[i]), frame))
++n_matches_;
if (n_matches_ > (size_t) Config::maxFts())
break;
}
}
bool Reprojector::reprojectCell(Cell& cell, FramePtr frame)
{
cell.sort(boost::bind(&Reprojector::pointQualityComparator, _1, _2));
Cell::iterator it=cell.begin();
while(it!=cell.end())
{
++n_trials_;
if(it->pt->type_ == Point::TYPE_DELETED)
{
it = cell.erase(it);
continue;
}
bool found_match = true;
if(options_.find_match_direct)
//优化点的坐标
found_match = matcher_.findMatchDirect(*it->pt, *frame, it->px);
if(!found_match)
{
it->pt->n_failed_reproj_++;
if(it->pt->type_ == Point::TYPE_UNKNOWN && it->pt->n_failed_reproj_ > 15)
map_.safeDeletePoint(it->pt);
if(it->pt->type_ == Point::TYPE_CANDIDATE && it->pt->n_failed_reproj_ > 30)
map_.point_candidates_.deleteCandidatePoint(it->pt);
it = cell.erase(it);
continue;
}
it->pt->n_succeeded_reproj_++;
if(it->pt->type_ == Point::TYPE_UNKNOWN && it->pt->n_succeeded_reproj_ > 10)
it->pt->type_ = Point::TYPE_GOOD;
Feature* new_feature = new Feature(frame.get(), it->px, matcher_.search_level_);
//
frame->addFeature(new_feature);
// Here we add a reference in the feature to the 3D point, the other way
// round is only done if this frame is selected as keyframe.
new_feature->point = it->pt;
if(matcher_.ref_ftr_->type == Feature::EDGELET)
{
new_feature->type = Feature::EDGELET;
new_feature->grad = matcher_.A_cur_ref_*matcher_.ref_ftr_->grad;
new_feature->grad.normalize();
}
// If the keyframe is selected and we reproject the rest, we don't have to
// check this point anymore.
it = cell.erase(it);
// Maximum one point per cell.
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Matcher::findMatchDirect(
const Point& pt,
const Frame& cur_frame,
Vector2d& px_cur)
{
//看到point的有最小的角度frame
if(!pt.getCloseViewObs(cur_frame.pos(), ref_ftr_))
return false;
// warp affine
warp::getWarpMatrixAffine(
*ref_ftr_->frame->cam_, *cur_frame.cam_, ref_ftr_->px, ref_ftr_->f,
(ref_ftr_->frame->pos() - pt.pos_).norm(),
cur_frame.T_f_w_ * ref_ftr_->frame->T_f_w_.inverse(), ref_ftr_->level, A_cur_ref_);
search_level_ = warp::getBestSearchLevel(A_cur_ref_, Config::nPyrLevels()-1);
warp::warpAffine(A_cur_ref_, ref_ftr_->frame->img_pyr_[ref_ftr_->level], ref_ftr_->px,
ref_ftr_->level, search_level_, halfpatch_size_+1, patch_with_border_);
createPatchFromPatchWithBorder();
// px_cur should be set
Vector2d px_scaled(px_cur/(1<<search_level_));
bool success = false;
if(ref_ftr_->type == Feature::EDGELET)
{
Vector2d dir_cur(A_cur_ref_*ref_ftr_->grad);
dir_cur.normalize();
success = feature_alignment::align1D(
cur_frame.img_pyr_[search_level_], dir_cur.cast<float>(),
patch_with_border_, patch_, options_.align_max_iter, px_scaled, h_inv_);
}
else
{
success = feature_alignment::align2D(
cur_frame.img_pyr_[search_level_], patch_with_border_, patch_,
options_.align_max_iter, px_scaled);
}
}
bundle adjustment
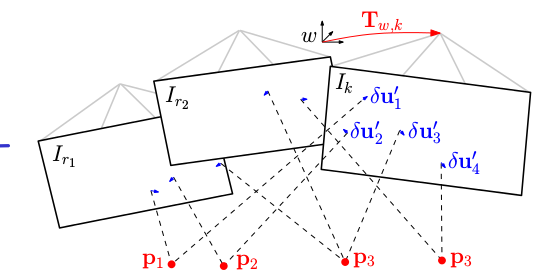
优化pose
void optimizeGaussNewton(
const double reproj_thresh,
const size_t n_iter,
const bool verbose,
FramePtr& frame,
double& estimated_scale,
double& error_init,
double& error_final,
size_t& num_obs)
{
for(size_t iter=0; iter<n_iter; iter++)
{
// overwrite scale
if(iter == 5)
scale = 0.85/frame->cam_->errorMultiplier2();
b.setZero();
A.setZero();
double new_chi2(0.0);
// compute residual
for(auto it=frame->fts_.begin(); it!=frame->fts_.end(); ++it)
{
if((*it)->point == NULL)
continue;
Matrix26d J;
Vector3d xyz_f(frame->T_f_w_ * (*it)->point->pos_);
Frame::jacobian_xyz2uv(xyz_f, J);
//residual 是特征点的u,v坐标
Vector2d e = vk::project2d((*it)->f) - vk::project2d(xyz_f);
double sqrt_inv_cov = 1.0 / (1<<(*it)->level);
e *= sqrt_inv_cov;
if(iter == 0)
chi2_vec_init.push_back(e.squaredNorm()); // just for debug
J *= sqrt_inv_cov;
double weight = weight_function.value(e.norm()/scale);
A.noalias() += J.transpose()*J*weight;
b.noalias() -= J.transpose()*e*weight;
new_chi2 += e.squaredNorm()*weight;
}
// solve linear system
const Vector6d dT(A.ldlt().solve(b));
// check if error increased
if((iter > 0 && new_chi2 > chi2) || (bool) std::isnan((double)dT[0]))
{
if(verbose)
std::cout << "it " << iter
<< "\t FAILURE \t new_chi2 = " << new_chi2 << std::endl;
frame->T_f_w_ = T_old; // roll-back
break;
}
// update the model
SE3 T_new = SE3::exp(dT)*frame->T_f_w_;
T_old = frame->T_f_w_;
frame->T_f_w_ = T_new;
chi2 = new_chi2;
if(verbose)
std::cout << "it " << iter
<< "\t Success \t new_chi2 = " << new_chi2
<< "\t norm(dT) = " << vk::norm_max(dT) << std::endl;
// stop when converged
if(vk::norm_max(dT) <= EPS)
break;
}
}
当前帧能看到的点(已知深度的)再次优化他的3d坐标点
void FrameHandlerBase::optimizeStructure(
FramePtr frame,
size_t max_n_pts,
int max_iter)
{
deque<Point*> pts;
for(Features::iterator it=frame->fts_.begin(); it!=frame->fts_.end(); ++it)
{
if((*it)->point != NULL)
pts.push_back((*it)->point);
}
max_n_pts = min(max_n_pts, pts.size());
nth_element(pts.begin(), pts.begin() + max_n_pts, pts.end(), ptLastOptimComparator);
for(deque<Point*>::iterator it=pts.begin(); it!=pts.begin()+max_n_pts; ++it)
{
(*it)->optimize(max_iter);
(*it)->last_structure_optim_ = frame->id_;
}
}
void Point::optimize(const size_t n_iter)
{
for(size_t i=0; i<n_iter; i++)
{
A.setZero();
b.setZero();
double new_chi2 = 0.0;
// compute residuals
for(auto it=obs_.begin(); it!=obs_.end(); ++it)
{
Matrix23d J;
const Vector3d p_in_f((*it)->frame->T_f_w_ * pos_);
Point::jacobian_xyz2uv(p_in_f, (*it)->frame->T_f_w_.rotation_matrix(), J);
const Vector2d e(vk::project2d((*it)->f) - vk::project2d(p_in_f));
new_chi2 += e.squaredNorm();
A.noalias() += J.transpose() * J;
b.noalias() -= J.transpose() * e;
}
// solve linear system
const Vector3d dp(A.ldlt().solve(b));
// update the model
Vector3d new_point = pos_ + dp;
}
}
Mapping 地图构建
深度估计
使用后验估计,假设深度值x的分布可以用高斯分布和均匀分布来联合表示
\]
其中\(\pi\)表示\(x\)为有效测量的概率,求以下的最大值
\]
相对于变量\(Z,\pi\),\(x_i\)的分布和\(Z,\pi\)无关
\]
作者证明,上面可以用Gaussian×Beta分布来近似
\]
迭代更新
\]
根据上式,在加入新的测量时,seed的近似后验概率分布也会得到更新。当\(\sigma_n\)小于给定阈值时,认为seed的深度估计已经收敛,计算其三维坐标,并加入地图。
keyframe对应的是
void DepthFilter::initializeSeeds(FramePtr frame) {
Features new_features;
feature_detector_->setExistingFeatures(frame->fts_);
feature_detector_->detect(frame.get(), frame->img_pyr_, Config::triangMinCornerScore(), new_features);
// initialize a seed for every new feature
seeds_updating_halt_ = true;
lock_t lock(seeds_mut_); // by locking the updateSeeds function stops
++Seed::batch_counter;
std::for_each(new_features.begin(), new_features.end(),
[&](Feature* ftr) { seeds_.push_back(Seed(ftr, new_keyframe_mean_depth_, new_keyframe_min_depth_));
});
if (options_.verbose)
SVO_INFO_STREAM( "DepthFilter: Initialized "<<new_features.size()<<" new seeds");
seeds_updating_halt_ = false;
}
非keyframe对应的是
void DepthFilter::updateSeeds(FramePtr frame)
{
}
void DepthFilter::updateSeed(const float x, const float tau2, Seed* seed)
{
// 合成正态分布的标准差
float norm_scale = sqrt(seed->sigma2 + tau2);
if(std::isnan(norm_scale))
return;
// 正态分布
boost::math::normal_distribution<float> nd(seed->mu, norm_scale);
// 公式(19)
float s2 = 1./(1./seed->sigma2 + 1./tau2);
// 公式(20)计算m.
float m = s2*(seed->mu/seed->sigma2 + x/tau2);
// 公式(21)计算C1.
float C1 = seed->a/(seed->a+seed->b) * boost::math::pdf(nd, x);
// 公式(22)计算C2。
float C2 = seed->b/(seed->a+seed->b) * 1./seed->z_range;
// 概率密度函数归一化
float normalization_constant = C1 + C2;
C1 /= normalization_constant;
C2 /= normalization_constant;
// 公式(25)
float f = C1*(seed->a+1.)/(seed->a+seed->b+1.) + C2*seed->a/(seed->a+seed->b+1.);
// 公式(26)
float e = C1*(seed->a+1.)*(seed->a+2.)/((seed->a+seed->b+1.)*(seed->a+seed->b+2.))
+ C2*seed->a*(seed->a+1.0f)/((seed->a+seed->b+1.0f)*(seed->a+seed->b+2.0f));
// update parameters.
// 公式(23)
float mu_new = C1*m+C2*seed->mu;
// 公式(24)变形
seed->sigma2 = C1*(s2 + m*m) + C2*(seed->sigma2 + seed->mu*seed->mu) - mu_new*mu_new;
seed->mu = mu_new;
// 公式(25)(26)联立求a'
seed->a = (e-f)/(f-e/f);
// 公式(25)求b'
seed->b = seed->a*(1.0f-f)/f;
}
资料
改进和不足的地方在博客园和知乎的那篇文章都提了,
svo笔记的更多相关文章
- SVO原理解析
最近空闲时间在研究Semi-Direct Monocular Visual Odometry(SVO)[1,2],觉得它值得写一写.另外,SVO的运算量相对较小,我想在手机上尝试实现它. 关于SVO的 ...
- 【英语魔法俱乐部——读书笔记】 3 高级句型-简化从句&倒装句(Reduced Clauses、Inverted Sentences) 【完结】
[英语魔法俱乐部——读书笔记] 3 高级句型-简化从句&倒装句(Reduced Clauses.Inverted Sentences):(3.1)从属从句简化的通则.(3.2)形容词从句简化. ...
- 【英语魔法俱乐部——读书笔记】 2 中级句型-复句&合句(Complex Sentences、Compound Sentences)
[英语魔法俱乐部——读书笔记] 2 中级句型-复句&合句(Complex Sentences.Compound Sentences):(2.1)名词从句.(2.2)副词从句.(2.3)关系从句 ...
- svo的一些博客解析
记录一边学习 白巧克力: svo代码笔记 http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/51083398 卢彦斌:svo原理解析 东北大学孙志明:s ...
- shell学习笔记
shell学习笔记 .查看/etc/shells,看看有几个可用的Shell . 曾经用过的命令存在.bash_history中,但是~/.bash_history记录的是前一次登录前记录的所有指令, ...
- SLAM学习笔记
ORB_SLAM2源码: 获得旋转矩阵,来自这里:http://www.cnblogs.com/shang-slam/p/6406584.html 关于Covisibility图来自:http://b ...
- SVO+PL-SVO+PL-StVO
PL-SVO是基于点.线特征的半直接法单目视觉里程计,我们先来介绍一下基于点特征的SVO,因为是在这个基础上提出的. [1]References: SVO: Fast Semi-Direct ...
- 三维重建7:Visual SLAM算法笔记
VSLAM研究了几十年,新的东西不是很多,三维重建的VSLAM方法可以用一篇文章总结一下. 此文是一个好的视觉SLAM综述,对视觉SLAM总结比较全面,是SLAM那本书的很好的补充.介绍了基于滤波器的 ...
- git-简单流程(学习笔记)
这是阅读廖雪峰的官方网站的笔记,用于自己以后回看 1.进入项目文件夹 初始化一个Git仓库,使用git init命令. 添加文件到Git仓库,分两步: 第一步,使用命令git add <file ...
随机推荐
- 《JavaScript高级程序设计》里对 call() 和 apply() 的解释 (116页)
每个函数都包含两个非继承而来的方法:apply()和call().这两个方法的用途都是在特定的作用域中调用函数,实际上等于设置函数体内this对象的值. apply(): 方法接受两个参数:一个是在其 ...
- 点击空白处隐藏指定dom元素(纯javascript方法)
<script type="text/javascript"> document.onclick = function (event) { event = event ...
- struts2.1.6教程九、文件上传下载(了解)
首先建立struts2UpDownLoad项目,搭建好struts2基本的开发环境. 上传实例 步骤一:upload.jsp代码如下: <s:form action="upload&q ...
- 四、 添加模型Model(ASP.NET MVC5 系列)
在这一章节中我们将添加一些classes类来管理数据库中的movies.这些classes类就是ASP.NET MVC应用程序中的"model". 我们将用.NET框架中的数据访问 ...
- ES学习笔记
ES学习 1. 安装 1.1 ES 安装配置 curl -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5. ...
- Tomcat 安装与配置
1. 将压缩文件“apache-tomcat-7.0.62.zip ”上传到linux系统目录:/home/下 2. 进入目录 cd /home/ 解压文件,执行如下命令:unzip apache-t ...
- HBuilder 安装使用教程
前段时间朋友让我帮忙打包一个 IPA 文件(使用 HTML5 开发的 Web 应用),了解到 HBuilder 这款 H5 开发神器.之前一直使用 WebStorm 开发 H5,闲来无事也学习下 HB ...
- 容器扩展属性 IExtenderProvider 实现WinForm通用数据验证组件
大家对如下的Tip组件使用应该不陌生,要想让窗体上的控件使用ToolTip功能,只需要拖动一个ToolTip组件到窗口,所有的控件就可以使用该功能,做信息提示. 本博文要记录的,就是通过容器扩展属性 ...
- poj3648
poj3648 题意 有一对新人结婚,n-1对夫妇去参加婚礼.有一个很长的座子,新娘与新郎坐在座子的两边(相反).接下来n-1对夫妇就坐,其中任何一对夫妇都不能坐在同一边,且(有一些人有奸情)这些有奸 ...
- javaSE_05Java中方法(函数)与重载、递归-思维导图
思维导图看不清楚时: 1)可以将图片另存为图片,保存在本地来查看 2)右击在新标签中打开放大查看
