React Fiber源码分析 第三篇(异步状态)
先附上流程图~
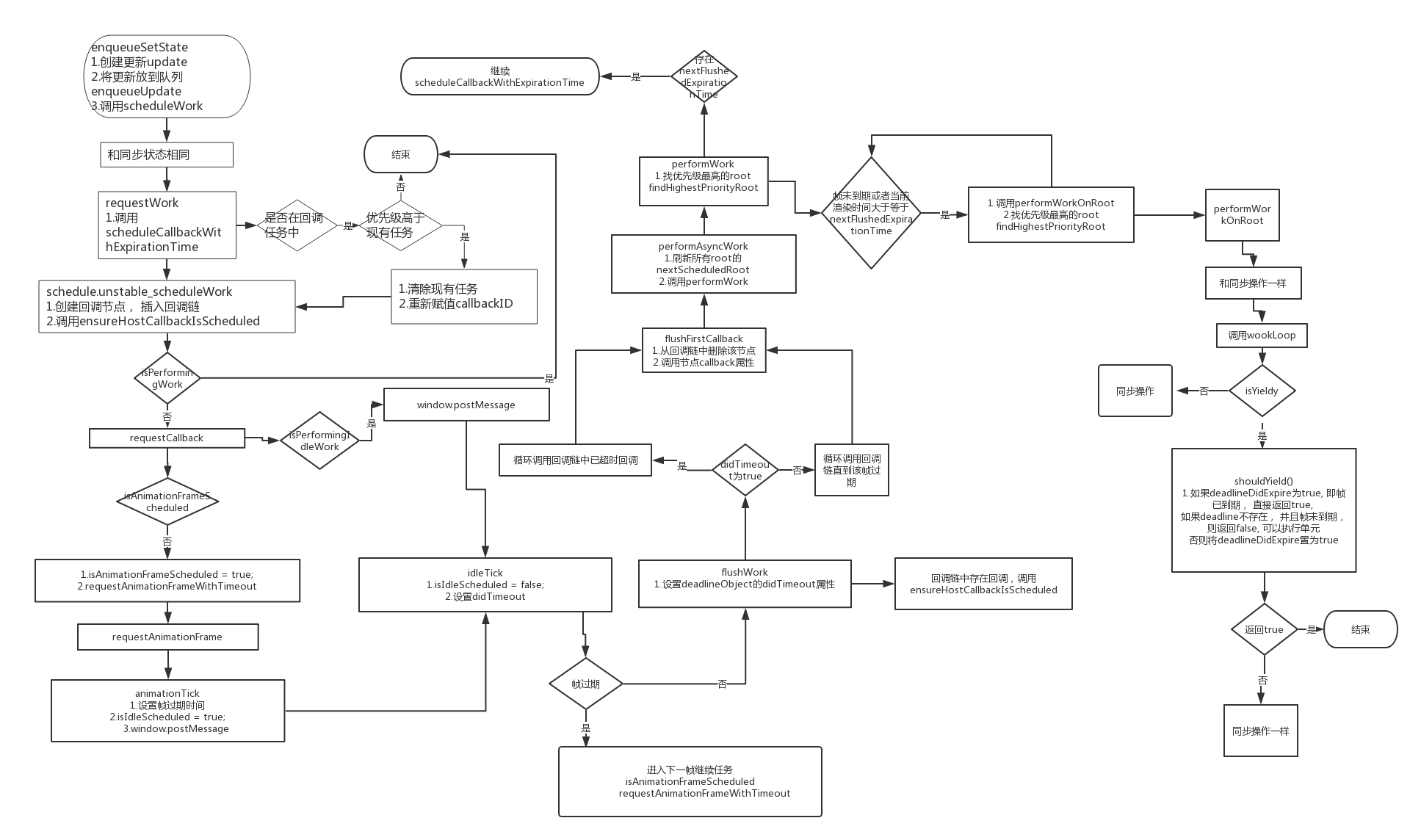
调用setState时, 会调用classComponentUpdater的enqueueSetState方法, 同时将新的state作为payload参数传进
enqueueSetState会先调用requestCurrentTime获取一个currentTime,
function requestCurrentTime() {
// 维护两个时间 一个renderingTime 一个currentSechedulerTime
// rederingTime 可以随时更新 currentSechedulerTime只有在没有新任务的时候才更新
if (isRendering) {
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (nextFlushedExpirationTime === NoWork || nextFlushedExpirationTime === Never) {
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
currentSchedulerTime = currentRendererTime;
return currentSchedulerTime;
}
return currentSheculerTime
通过获取到的currentTime, 调用computeExpirationForFiber,计算该fiber的优先级,
if (fiber.mode & AsyncMode) {
if (isBatchingInteractiveUpdates) {
// This is an interactive update
expirationTime = computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime);
} else {
// This is an async update
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration(currentTime);
}
...
}
这个函数其他点比较简单, 里面主要有下面 这个判断要说明一下, 如果是属于异步更新的话,会根据是 交互引起的更新 还是其他更新 来调用不同的函数computeInteractiveExpiration和computeAsyncExpiration,
可以看到这两个函数最后返回的都是computeExpirationBucket函数的结果, 只是入参不同, computeInteractiveExpiration的参数是500, 100, computeAsyncExpiration的参数是5000, 250, 然后看computeExpirationBucket函数可以看到, 第二个参数(500和5000)越大,则返回的expirationTime越大, 也就是说 computeInteractiveExpiration的更新优先级高于computeAsyncExpiration, 则交互的优先级高于其他
获得优先级后则和同步更新一样, 创建update并放进队列, 然后调用sheuduleWork
var classComponentUpdater = {
isMounted: isMounted,
enqueueSetState: function (inst, payload, callback) {
var fiber = get(inst);
// 获得优先级
var currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
var expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, fiber);
// 创建更新
var update = createUpdate(expirationTime);
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
},
接下来的步骤和同步一样, 直到同步调用的是performSyncWork函数, 而异步调用的是scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime函数
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime函数首先判断是否存在callback正在进行中, 判断现有expirationTime和其优先级,若优先级比较低则直接返回, 否则设置现在的fiber任务为新的callback,并把原来的回调从列表中移除
function scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime) {
if (callbackExpirationTime !== NoWork) {
// 判断优先级
if (expirationTime > callbackExpirationTime) {
// Existing callback has sufficient timeout. Exit.
return;
} else {
if (callbackID !== null) {
// 取消, 从回调列表中删除
schedule.unstable_cancelScheduledWork(callbackID);
}
}
// The request callback timer is already running. Don't start a new one.
}
// 设置新的callback和callbackExiporationTime
callbackExpirationTime = expirationTime;
var currentMs = schedule.unstable_now() - originalStartTimeMs;
var expirationTimeMs = expirationTimeToMs(expirationTime);
// 计算是否超时
var timeout = expirationTimeMs - currentMs;
callbackID = schedule.unstable_scheduleWork(performAsyncWork, { timeout: timeout });
}
接下来调用schedule.unstable_scheduleWork(performAsyncWork, { timeout: timeout })函数, 并生成一个节点, 存储回调函数和超时时间,插入到回调列表, 并根据超时排序, 调用ensureHostCallBackIsScheduled函数,最后返回该节点
function unstable_scheduleWork(callback, options) {
var currentTime = exports.unstable_now();
var timesOutAt;
// 获取超时时间
if (options !== undefined && options !== null && options.timeout !== null && options.timeout !== undefined) {
// Check for an explicit timeout
timesOutAt = currentTime + options.timeout;
} else {
// Compute an absolute timeout using the default constant.
timesOutAt = currentTime + DEFERRED_TIMEOUT;
}
// 生成一个节点, 存储回调函数和超时时间
var newNode = {
callback: callback,
timesOutAt: timesOutAt,
next: null,
previous: null
};
// 插入到回调列表, 并根据超时排序, 最后返回该节点
if (firstCallbackNode === null) {
// This is the first callback in the list.
firstCallbackNode = newNode.next = newNode.previous = newNode;
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled(firstCallbackNode);
} else {
...var previous = next.previous;
previous.next = next.previous = newNode;
newNode.next = next;
newNode.previous = previous;
}
return newNode;
}
ensureHostCallBackIsScheduled函数如名, 相对比较简单
function ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled() {
if (isPerformingWork) {
// Don't schedule work yet; wait until the next time we yield.
return;
}
// Schedule the host callback using the earliest timeout in the list.
var timesOutAt = firstCallbackNode.timesOutAt;
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
} else {
// Cancel the existing host callback.
cancelCallback();
}
requestCallback(flushWork, timesOutAt);
}
往下看requestCallback, 这里说的如果已经在执行任务的话, 就必须有一个错误被抛出(抛出的错误是啥??),同时不要等待下一帧, 尽快开始新事件
如果如果当前没有调度帧回调函数,我们需要进行一个调度帧回调函数, 并设置isAnimationFrameScheduled为true,
接着执行requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout;函数
requestCallback = function (callback, absoluteTimeout) {
scheduledCallback = callback;
timeoutTime = absoluteTimeout;
if (isPerformingIdleWork) {
// 如果已经在执行任务的话, 就必须有一个错误被抛出(抛出的错误是啥??),同时不要等待下一帧, 尽快开始新事件
window.postMessage(messageKey, '*');
} else if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {
isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);
}
};
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout函数就是执行一个异步操作, 执行完毕后, 假设此时又有N个回调任务进入, 同时原来的回调还没有进行, 则回到scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime函数上,
分为两个分支: 1. 假设优先级低于目前的回调任务, 则直接返回(已经把root加到root队列中)
2. 优先级高于目前的回调任务, 将目前的回调任务从列表中移除, 并将callBackID设为传入的回调, 接下来的路线与上面一致, 假设该传入的回调超时最早, 则会进入到cancelCallback函数,重 置各变量, 并进入到requestCallback函数, 此时除了赋值操作, 没有其他动作
到了这时候, 已经把新的回调替换正在进行的回调到回调列表。
函数正常执行, 调用callback, 即animationTick函数
cancelCallback = function () {
scheduledCallback = null;
isIdleScheduled = false;
timeoutTime = -1;
};
var ANIMATION_FRAME_TIMEOUT = 100;
var rAFID;
var rAFTimeoutID;
var requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout = function (callback) {
// schedule rAF and also a setTimeout
rAFID = localRequestAnimationFrame(function (timestamp) {
// cancel the setTimeout
localClearTimeout(rAFTimeoutID);
callback(timestamp);
});
rAFTimeoutID = localSetTimeout(function () {
// cancel the requestAnimationFrame
localCancelAnimationFrame(rAFID);
callback(exports.unstable_now());
}, ANIMATION_FRAME_TIMEOUT);
};
animationTick一个是把isAnimationFrameScheduled状态设为false, 即不在调度帧回调的状态, 同时计算帧到期时间frameDeadline , 判断是否在帧回调的状态, 否的话调用window.postMessage ,并设置isIdleScheduled状态为true
假设此时, 有N个回调进入, 分为两个情况: 1.假设优先级低于目前的回调任务, 则直接返回(已经把root加到root队列中)
2.优先级高于目前的回调任务, 将目前的回调任务从列表中移除, 并将callBackID设为传入的回调, 接下来的路线与上面一致,一直到animationTick函数,因为 postMessage比setTImeout更快执行,所以此时isIdleScheduled为false,和之前一样正常执行。
var animationTick = function (rafTime) {
isAnimationFrameScheduled = false;
...
...
// 每帧到期时间为33ms
frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime;
if (!isIdleScheduled) {
isIdleScheduled = true;
window.postMessage(messageKey, '*');
}
};
postMessage会执行idleTick , 首先把isIdleScheduled\didTimeout置为false,
先判断帧到期时间和超时时间是否小于当前时间, 如果是的话, 则置didTimeout为true,
如果帧到期, 但超时时间小于当前时间, 则置isAnimationFrameScheduled 为false, 并调用requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout, 即进入下一帧
如果帧未到期, 则调用callbak函数, 并把isPerformingIdleWork置为true
idleTick 会先执行callback, 完成后才将isPerformingIdleWork 置为false, 执行callback的时候会传入didTimeout作为参数, callback为flushWork
var idleTick = function (event) {
...
isIdleScheduled = false;
var currentTime = exports.unstable_now();
var didTimeout = false;
if (frameDeadline - currentTime <= 0) {
// 帧过期
if (timeoutTime !== -1 && timeoutTime <= currentTime) {
// 回调超时
didTimeout = true;
} else {
// No timeout.
if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {
// 到下一帧继续任务
isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);
}
// Exit without invoking the callback.
return;
}
}
timeoutTime = -1;
var callback = scheduledCallback;
scheduledCallback = null;
if (callback !== null) {
isPerformingIdleWork = true;
try {
callback(didTimeout);
} finally {
isPerformingIdleWork = false;
}
}
};
flushwork首先把isPerformingWork置为true, 然后把didTimeout赋值给deallinObject对象, 接下来进行判断
如果已经过了帧的结束期, 则判断链表中有哪个节点已超时, 并循环调用flushFirstCallback函数解决超时节点,
如果还没有过帧的结束期, 则调用flushFirstCallback函数处理链表中的第一个节点, 循环处理一直到该帧结束
最后, flushwork函数会将isPerformingWork置为false, 并判断是否还有任务 有则执行ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled函数
function flushWork(didTimeout) {
isPerformingWork = true;
deadlineObject.didTimeout = didTimeout;
try {
if (didTimeout) {
while (firstCallbackNode !== null) {
var currentTime = exports.unstable_now();
if (firstCallbackNode.timesOutAt <= currentTime) {
do {
flushFirstCallback();
} while (firstCallbackNode !== null && firstCallbackNode.timesOutAt <= currentTime);
continue;
}
break;
}
} else {
// Keep flushing callbacks until we run out of time in the frame.
if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {
do {
flushFirstCallback();
} while (firstCallbackNode !== null && getFrameDeadline() - exports.unstable_now() > 0);
}
}
} finally {
isPerformingWork = false;
if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {
// There's still work remaining. Request another callback.
ensureHostCallbackIsScheduled(firstCallbackNode);
} else {
isHostCallbackScheduled = false;
}
}
}
继续往下看, 则是flushFirstCallback函数,先把该节点从链表中清掉, 然后调用callback函数, 并带入deadlineObject作为参数
function flushFirstCallback(node) {
var flushedNode = firstCallbackNode;
//从链表中清理掉该节点, 这样哪怕出错了, 也能保留原链表状态
var next = firstCallbackNode.next;
if (firstCallbackNode === next) {
// This is the last callback in the list.
firstCallbackNode = null;
next = null;
} else {
var previous = firstCallbackNode.previous;
firstCallbackNode = previous.next = next;
next.previous = previous;
}
flushedNode.next = flushedNode.previous = null;
// Now it's safe to call the callback.
var callback = flushedNode.callback;
callback(deadlineObject);
}
接下来的就是performAsyncWork函数,如果didTimeout为true, 则表明至少有一个更新已过期, 迭代所有root任务, 把已过期的root的nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn重置为当前时间currentTime.
然后调用performWork(Nowork, dl)函数
function performAsyncWork(dl) {
if (dl.didTimeout) {
// 刷新所有root的nextEpirationTimeToWorkOn
if (firstScheduledRoot !== null) {
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
var root = firstScheduledRoot;
do {
didExpireAtExpirationTime(root, currentRendererTime);
// The root schedule is circular, so this is never null.
root = root.nextScheduledRoot;
} while (root !== firstScheduledRoot);
}
}
performWork(NoWork, dl);
}
performWork函数在之前已经分析过了, 这里主要看存在deadline时的操作, 在帧未到期 或者 当前渲染时间大于等于nextFlushedExpirationTime时才执行 performWorkOnRoot, 并将currentRendererTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime作为第三个参数传入, 一直循环处理任务,
最后清除callbackExpirationTime, callBackId, 同时, 如果还有任务的话, 则继续调用scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime);函数进入到回调
function performWork(minExpirationTime, dl) {
deadline = dl;
// Keep working on roots until there's no more work, or until we reach
// the deadline.
findHighestPriorityRoot();
if (deadline !== null) {
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
currentSchedulerTime = currentRendererTime;while (nextFlushedRoot !== null && nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork && (minExpirationTime === NoWork || minExpirationTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime) && (!deadlineDidExpire || currentRendererTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime)) {
performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, currentRendererTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime);
findHighestPriorityRoot();
recomputeCurrentRendererTime();
currentSchedulerTime = currentRendererTime;
}
}
if (deadline !== null) {
callbackExpirationTime = NoWork;
callbackID = null;
}
// If there's work left over, schedule a new callback.
if (nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork) {
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime);
}
// Clean-up.
deadline = null;
deadlineDidExpire = false;
finishRendering();
}
接下来看异步状态下的performWorkOnRoot函数。基本操作和同步一样, 在进入到renderRoot(root, _isYieldy, isExpired);函数时, 会根据是否已超时将isYieldy置为true或者false, 异步状态下未超时为false,
renderRoot和同步一样, 最后执行workLoop(isYieldy)
workLoop在未过期的情况下, 会执行shouldYield()函数来判断是否执行nextUnitOfWork, 和同步一样, 这里只需要关注shouldYied函数
function workLoop(isYieldy) {
if (!isYieldy) {
// Flush work without yielding
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
} else {
// Flush asynchronous work until the deadline runs out of time.
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYield()) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
}
}
}
shouldYield函数, 如果deadlineDidExpire为true, 即帧已到期, 直接返回true,
如果deadline不存在, 并且帧未到期, 则返回false, 可以执行单元
否则将deadlineDidExpire置为true
function shouldYield() {
if (deadlineDidExpire) {
return true;
}
if (deadline === null || deadline.timeRemaining() > timeHeuristicForUnitOfWork) {
// Disregard deadline.didTimeout. Only expired work should be flushed
// during a timeout. This path is only hit for non-expired work.
return false;
}
deadlineDidExpire = true;
return true;
}
完结~撒花
React Fiber源码分析 第三篇(异步状态)的更多相关文章
- React Fiber源码分析 (介绍)
写了分析源码的文章后, 总觉得缺少了什么, 在这里补一个整体的总结,输出个人的理解~ 文章的系列标题为Fiber源码分析, 那么什么是Fiber,官方给出的解释是: React Fiber是对核心算法 ...
- React Fiber源码分析 第二篇(同步模式)
先附上两张流程图 1.scheduleRootUpdate 这个函数主要执行了两个操作 1个是创建更新createUpdate并放到更新队列enqueueUpdate, 1个是执行sheculeW ...
- React Fiber源码分析 第一篇
先附上流程图一张 先由babel编译, 调用reactDOM.render,入参为element, container, callback, 打印出来可以看到element,container,cal ...
- JUC源码分析-线程池篇(三)ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
JUC源码分析-线程池篇(三)ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 继承自 ThreadPoolExecutor.它主要用来在 ...
- JUC源码分析-线程池篇(三)Timer
JUC源码分析-线程池篇(三)Timer Timer 是 java.util 包提供的一个定时任务调度器,在主线程之外起一个单独的线程执行指定的计划任务,可以指定执行一次或者反复执行多次. 1. Ti ...
- JUC源码分析-线程池篇(一):ThreadPoolExecutor
JUC源码分析-线程池篇(一):ThreadPoolExecutor Java 中的线程池是运用场景最多的并发框架,几乎所有需要异步或并发执行任务的程序都可以使用线程池.在开发过程中,合理地使用线程池 ...
- Spring MVC源码分析(三):SpringMVC的HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的体系结构设计与实现
概述在我的上一篇文章:Spring源码分析(三):DispatcherServlet的设计与实现中提到,DispatcherServlet在接收到客户端请求时,会遍历DispatcherServlet ...
- 鸿蒙内核源码分析(Shell编辑篇) | 两个任务,三个阶段 | 百篇博客分析OpenHarmony源码 | v71.01
子曰:"我非生而知之者,好古,敏以求之者也." <论语>:述而篇 百篇博客系列篇.本篇为: v71.xx 鸿蒙内核源码分析(Shell编辑篇) | 两个任务,三个阶段 ...
- 鸿蒙内核源码分析(字符设备篇) | 字节为单位读写的设备 | 百篇博客分析OpenHarmony源码 | v67.01
百篇博客系列篇.本篇为: v67.xx 鸿蒙内核源码分析(字符设备篇) | 字节为单位读写的设备 | 51.c.h.o 文件系统相关篇为: v62.xx 鸿蒙内核源码分析(文件概念篇) | 为什么说一 ...
随机推荐
- 通过Weeman+Ettercap配合拿下路由器管理权限
通过Weeman+Ettercap配合拿下路由器管理权限 本文转自>>>i春秋学院 本篇文章主要介绍如何在接入无线网络后如何拿到路由器的管理权限,至于如何得到路由器连接密码可以参考 ...
- Java学习图
- Docker学习笔记-Redis 安装
拉取官方的镜像 docker pull redis:3.2 查看 docker images redis 运行容器 docker run -p 6379:6379 -v $PWD/data:/data ...
- 第56节:ArrayList,LinkedList和String
import java.util.ArrayList; public class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Excepti ...
- 解决Java中There is no getter for property XXX'XXX' in 'class XXX'的问题
当你出现There is no getter for property XXX'XXX' in 'class XXX'时, 就是在你的这个类中没有找到你这个属性. 检查两个地方 1.你的返回值类型是否 ...
- react native项目启动需要做的操作
一.启动: 1.查看端口(默认8081是否被占用) netstat -ano 可以查看所有的进程 2.netstat -ano | findstr "8081" 查看某个端口 ...
- 运维笔记--ubuntu管理启动项
启动项 https://blog.csdn.net/sz457763638/article/details/78182700
- springMVC(2)---获取前段数据
springMVC(1)---获取前段数据 首先说明,如果你学过Struts2,那么在学springMVC就会简单很多,我也不最基础的开始写了,我前篇文章搭建了个ssm框架,算是springmvc入门 ...
- Android--Service之基础
前言 本篇博客聊一下Android下的Service组件,对于Service组件,有点类似于Windows下的服务.Service是Android四大组件中与Activity最相似的组件,它们的区别在 ...
- IDEA中MAVEN项目有多个子目录,如何加载构建
ddts这个项目有三个子目录,每个子目录下面也都有一个 pom.xml 此时需要 右键子目录的 pom.xml,选择Add as Maven Project,在上图中cli.core两个目 ...
