Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置
总结:
理解AOP@Before,@After,@AfterReturning,@AfterThrowing执行顺序
实现AOP的切面主要有以下几个要素:
使用@Aspect注解将一个java类定义为切面类
使用@Pointcut定义一个切入点,可以是一个规则表达式,比如下例中某个package下的所有函数,也可以是一个注解等。
根据需要在切入点不同位置的切入内容
使用@Before在切入点开始处切入内容
使用@After在切入点结尾处切入内容
使用@AfterReturning在切入点return内容之后切入内容(可以用来对处理返回值做一些加工处理)
使用@Around在切入点前后切入内容,并自己控制何时执行切入点自身的内容
使用@AfterThrowing用来处理当切入内容部分抛出异常之后的处理逻辑
try{
try{
doBefore();//对应@Before注解的方法切面逻辑
method.invoke();
}finally{
doAfter();//对应@After注解的方法切面逻辑
}
doAfterReturning();//对应@AfterReturning注解的方法切面逻辑
}catch(Exception e){
doAfterThrowing();//对应@AfterThrowing注解的方法切面逻辑
}
用过spring框架进行开发的人,多多少少会使用过它的AOP功能,都知道有@Before、@Around和@After等advice。最近,为了实现项目中的输出日志和权限控制这两个需求,我也使用到了AOP功能。我使用到了@Before、@Around这两个advice。但在,使用过程中,却对它们的执行顺序并不清楚。为了弄清楚在不同情况下,这些advice到底是以怎么样的一个顺序进行执行的,我作了个测试,在此将其记录下来,以供以后查看。
前提
- 对于AOP相关类(aspect、pointcut等)的概念,本文不作说明。
- 对于如何让spring框架扫描到AOP,本文也不作说明。
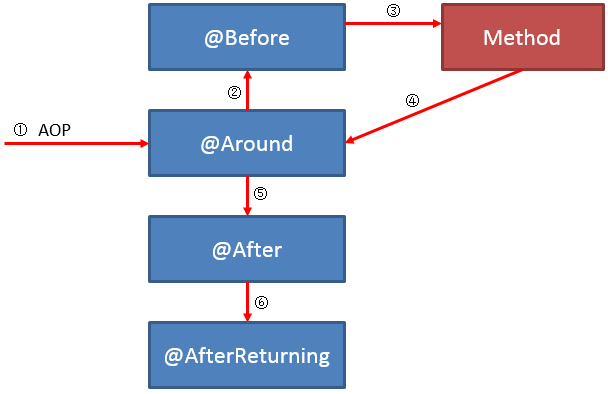
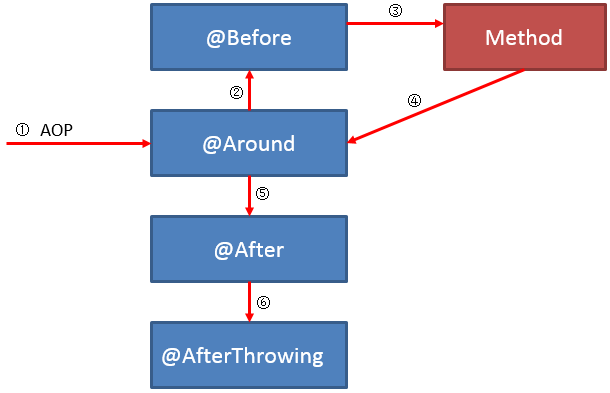
情况一: 一个方法只被一个Aspect类拦截
当一个方法只被一个Aspect拦截时,这个Aspect中的不同advice是按照怎样的顺序进行执行的呢?请看:
添加 PointCut类
该pointcut用来拦截test包下的所有类中的所有方法。
package test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; public class PointCuts { @Pointcut(value = "within(test.*)") public void aopDemo() { }
} package test; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; public class PointCuts
{ @Pointcut(value = "within(test.*)") public void aopDemo() { } }
添加Aspect类
该类中的advice将会用到上面的pointcut,使用方法请看各个advice的value属性。
package test;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class Aspect1 { @Before(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect1] before advise"); } @Around(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("[Aspect1] around advise 1"); pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("[Aspect1] around advise2"); } @AfterReturning(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect1] afterReturning advise"); } @AfterThrowing(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect1] afterThrowing advise"); } @After(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect1] after advise");
} }
添加测试用Controller
添加一个用于测试的controller,这个controller中只有一个方法,但是它会根据参数值的不同,会作出不同的处理:一种是正常返回一个对象,一种是抛出异常(因为我们要测试@AfterThrowing这个advice)
package test;
import test.exception.TestException; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping(value = "/aop") public class AopTestController { @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET) public Result test(@RequestParam boolean throwException) { // case 1 if (throwException) { System.out.println("throw an exception"); throw new TestException("mock a server exception");
} // case 2 System.out.println("test OK"); return new Result() {{ this.setId(); this.setName("mock a Result"); }}; } public static class Result { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } }
测试 正常情况
在浏览器直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=false
我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise test OK [Aspect1] around advise2 [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterReturning advise
测试 异常情况
在浏览器中直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=true
我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise throw an exception [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise
结论
在一个方法只被一个aspect类拦截时,aspect类内部的 advice 将按照以下的顺序进行执行:
正常情况:
异常情况:
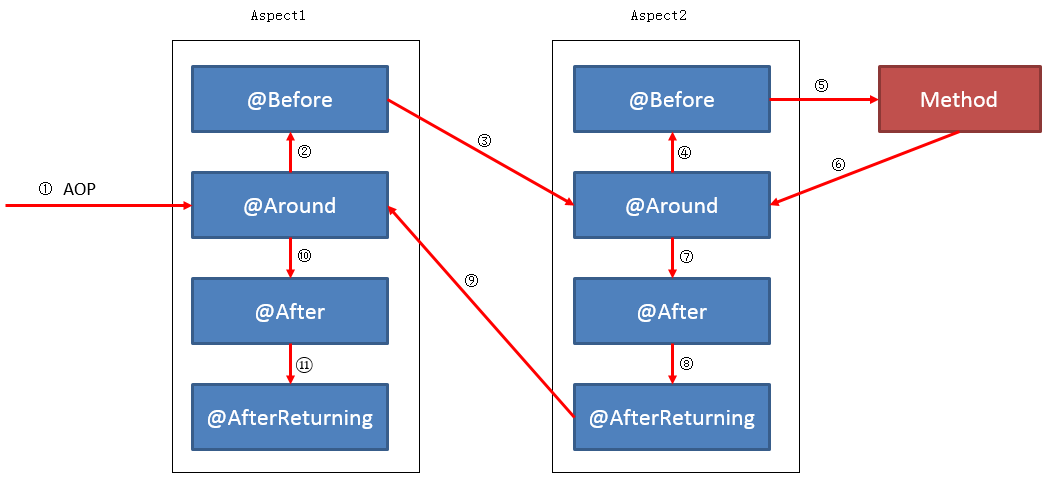
情况二: 同一个方法被多个Aspect类拦截
此处举例为被两个aspect类拦截。
有些情况下,对于两个不同的aspect类,不管它们的advice使用的是同一个pointcut,还是不同的pointcut,都有可能导致同一个方法被多个aspect类拦截。那么,在这种情况下,这多个Aspect类中的advice又是按照怎样的顺序进行执行的呢?请看:
pointcut类保持不变
添加一个新的aspect类
package test;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class Aspect2 { @Before(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect2] before advise"); } @Around(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("[Aspect2] around advise 1"); pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("[Aspect2] around advise2"); } @AfterReturning(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect2] afterReturning advise"); } @AfterThrowing(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect2] afterThrowing advise"); } @After(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()") public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("[Aspect2] after advise"); }
}
测试用Controller也不变
还是使用上面的那个Controller。但是现在 aspect1 和 aspect2 都会拦截该controller中的方法。
下面继续进行测试!
测试 正常情况
在浏览器直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=false
我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect2] around advise [Aspect2] before advise [Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise test OK [Aspect1] around advise2 [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterReturning advise [Aspect2] around advise2 [Aspect2] after advise [Aspect2] afterReturning advise
但是这个时候,我不能下定论说 aspect2 肯定就比 aspect1 先执行。
不信?你把服务务器重新启动一下,再试试,说不定你就会看到如下的执行结果:
[Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise [Aspect2] around advise [Aspect2] before advise test OK [Aspect2] around advise2 [Aspect2] after advise [Aspect2] afterReturning advise [Aspect1] around advise2 [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterReturning advise
也就是说,这种情况下, aspect1 和 aspect2 的执行顺序是未知的。那怎么解决呢?不急,下面会给出解决方案。
测试 异常情况
在浏览器中直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=true
我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect2] around advise [Aspect2] before advise [Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise throw an exception [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise [Aspect2] after advise [Aspect2] afterThrowing advise
同样地,如果把服务器重启,然后再测试的话,就可能会看到如下的结果:
[Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] before advise [Aspect2] around advise [Aspect2] before advise throw an exception [Aspect2] after advise [Aspect2] afterThrowing advise [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise
也就是说,同样地,异常情况下, aspect1 和 aspect2 的执行顺序也是未定的。
那么在 情况二 下,如何指定每个 aspect 的执行顺序呢?
方法有两种:
- 实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,实现它的getOrder()方法
- 给aspect添加@Order注解,该注解全称为:org.springframework.core.annotation.Order
不管采用上面的哪种方法,都是值越小的 aspect 越先执行。
比如,我们为 apsect1 和 aspect2 分别添加 @Order 注解,如下:
@Order()
@Component
@Aspect
public class Aspect1 {
// ...
}
@Order()
@Component
@Aspect
public class Aspect2 {
// ...
}
这样修改之后,可保证不管在任何情况下, aspect1 中的 advice 总是比 aspect2 中的 advice 先执行。如下图所示:
注意点
如果在同一个 aspect 类中,针对同一个 pointcut,定义了两个相同的 advice(比如,定义了两个 @Before),那么这两个 advice 的执行顺序是无法确定的,哪怕你给这两个 advice 添加了 @Order 这个注解,也不行。这点切记。
对于@Around这个advice,不管它有没有返回值,但是必须要方法内部,调用一下 pjp.proceed();否则,Controller 中的接口将没有机会被执行,从而也导致了 @Before这个advice不会被触发。比如,我们假设正常情况下,执行顺序为”aspect2 -> apsect1 -> controller”,如果,我们把 aspect1中的@Around中的 pjp.proceed();给删掉,那么,我们看到的输出结果将是:从结果可以发现, Controller 中的 接口 未被执行,aspect1 中的 @Before advice 也未被执行。
[Aspect2] around advise [Aspect2] before advise [Aspect1] around advise [Aspect1] around advise2 [Aspect1] after advise [Aspect1] afterReturning advise [Aspect2] around advise2 [Aspect2] after advise [Aspect2] afterReturning advise
参考:Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置
Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置的更多相关文章
- SSH深度历险(十) AOP原理及相关概念学习+AspectJ注解方式配置spring AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),是面向切面编程的技术.AOP基于IoC基础,是对OOP的有益补充. AOP之所以能得到广泛应用,主要是因为它将应用系统拆分分了2个部分 ...
- Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置(转)
用过spring框架进行开发的人,多多少少会使用过它的AOP功能,都知道有@Before.@Around和@After等advice.最近,为了实现项目中的输出日志和权限控制这两个需求,我也使用到了A ...
- Spring AOP 的@Aspect
Spring AOP 的@Aspect 转自:http://blog.csdn.net/tanghw/article/details/3862987 从Spring 2.0开始,可以使用基于sch ...
- 跟着刚哥学习Spring框架--通过注解方式配置Bean(四)
组件扫描:Spring能够从classpath下自动扫描,侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件. 特定组件包括: 1.@Component:基本注解,识别一个受Spring管理的组件 2.@Resposit ...
- spring bean的介绍以及xml和注解的配置方法
5.Bean 下边我们来了解一下Bean的: Bean的作用域Bean的生命周期Bean的自动装配Resources和ResourceLoader 5.1Bean容器的初始化 Bean容器的初始化 两 ...
- Spring声明式事务管理(基于注解方式实现)
----------------------siwuxie095 Spring 声明式事务管理(基于注解方式实现) 以转 ...
- spring学习笔记 星球日two - 注解方式配置bean
注解要放在要注解的对象的上方 @Autowired private Category category; <?xml version="1.0" encoding=" ...
- Spring boot 基于注解方式配置datasource
Spring boot 基于注解方式配置datasource 编辑 Xml配置 我们先来回顾下,使用xml配置数据源. 步骤: 先加载数据库相关配置文件; 配置数据源; 配置sqlSessionF ...
- Spring配置文件中bean标签中init-method和destroy-method和用注解方式配置
Person类: public class Person { private int i = 0; public Person(){ System.o ...
随机推荐
- WPF DataGrid 列宽填充表格方法
WPF中使DataGrid 列宽填充表格方法,设置ColumnWidth属性为ColumnWidth="*"即可. 源码: <DataGrid AutoGenerateCol ...
- CentOS 软件安装(yum 和 rpm)
CentOS 软件安装方法 常用的分为两种, - yum install 安装包名 : 类似于 Debian 的 “ apt-get install 安装包名 “ - rpm -i rmp文件名 :类 ...
- IDEA+'mvn' 不是内部或外部命令
问题描述: 提示'mvn' 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序或批处理文件. 或者提示 The JAVA_HOME environment variable is not defined corr ...
- 动态二维数组赋值及for循环遍历和toString遍历
package com.Summer_0421.cn; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author Summer * 动态二维数组赋值及for循环遍历和toStrin ...
- Linux并发与同步专题
并发访问:多个内核路径同时访问和操作数据,就有可能发生相互覆盖共享数据的情况,造成被访问数据的不一致. 临界区:访问和操作共享数据的代码段. 并发源:访问临界区的执行线程或代码路径. 在内核中产生并发 ...
- [LOJ#2386]. 「USACO 2018.01 Platinum」Cow at Large[点分治]
题意 题目链接 分析 假设当前的根为 rt ,我们能够在奶牛到达 \(u\) 之时拦住它,当且仅当到叶子节点到 \(u\) 的最短距离 \(mn_u \le dis_u\) .容易发现,合法的区域是许 ...
- .Net Core 在 Linux-Centos上的部署实战教程(二)
上篇我们说了 如何在Linux上部署.net core 但是有心的同学会发现你关闭掉终端网站就不能访问了,这个原因是因为直接 dotnet GetConfigFile.dll --server.ur ...
- 微信小程序支付异常:requestPayment:fail no permission
今天在调试微信小程序支付时碰到了这个问题,支付参数都正常生成了,在调用 wx.requestPayment 进行支付时遇到了这个报错,查了一下发现是开发者工具中 AppID 写错了,用的 AppID ...
- 蛙蛙推荐: TensorFlow Hello World 之平面拟合
tensorflow 已经发布了 2.0 alpha 版本,所以是时候学一波 tf 了.官方教程有个平面拟合的类似Hello World的例子,但没什么解释,新手理解起来比较困难. 所以本文对这个案例 ...
- 基于linux下的krpano的使用
鉴于目前网络上关于krpano的使用和介绍少之又少,结合自己的学习和使用经历,做个总结和记录. 1.安装 下载地址: linux https://krpano.com/forum/wbb/index. ...