Python GUI - tkinter
目录:
代码实例:
Python GUI编程(Tkinter)
Python 提供了多个图形开发界面的库,几个常用 Python GUI 库如下:
Tkinter: Tkinter 模块(Tk 接口)是 Python 的标准 Tk GUI 工具包的接口 .Tk 和 Tkinter 可以在大多数的 Unix 平台下使用,同样可以应用在 Windows 和 Macintosh 系统里。Tk8.0 的后续版本可以实现本地窗口风格,并良好地运行在绝大多数平台中。
wxPython:wxPython 是一款开源软件,是 Python 语言的一套优秀的 GUI 图形库,允许 Python 程序员很方便的创建完整的、功能键全的 GUI 用户界面。
Jython:Jython 程序可以和 Java 无缝集成。除了一些标准模块,Jython 使用 Java 的模块。Jython 几乎拥有标准的Python 中不依赖于 C 语言的全部模块。比如,Jython 的用户界面将使用 Swing,AWT或者 SWT。Jython 可以被动态或静态地编译成 Java 字节码。
Tkinter 编程
Tkinter 是 Python 的标准 GUI 库。Python 使用 Tkinter 可以快速的创建 GUI 应用程序。
由于 Tkinter 是内置到 python 的安装包中、只要安装好 Python 之后就能 import Tkinter 库、而且 IDLE 也是用 Tkinter 编写而成、对于简单的图形界面 Tkinter 还是能应付自如。
注意:Python3.x 版本使用的库名为 tkinter,即首写字母 T 为小写。
- import tkinter
- #创建一个GUI程序
- #1、导入 Tkinter 模块
- #2、创建控件
- #3、指定这个控件的 master, 即这个控件属于哪一个
- #4、告诉 GM(geometry manager) 有一个控件产生了。
主窗口常用操作:
- root.title('标题名')#修改框体的名字,也可在创建时使用className参数来命名;
- root.resizable(0,0) # 框体大小可调性,分别表示x,y方向的可变性;
- root.geometry('250x150')#指定主框体大小;
- root.quit() # 退出;
- root.update_idletasks()
- root.update()#刷新页面;
Tkinter 组件
Tkinter的提供各种控件,如按钮,标签和文本框,一个GUI应用程序中使用。这些控件通常被称为控件或者部件。
目前有15种Tkinter的部件。我们提出这些部件以及一个简短的介绍,在下面的表:
- (在Tkinter中窗口部件类没有分级;所有的窗口部件类在树中都是兄弟。)
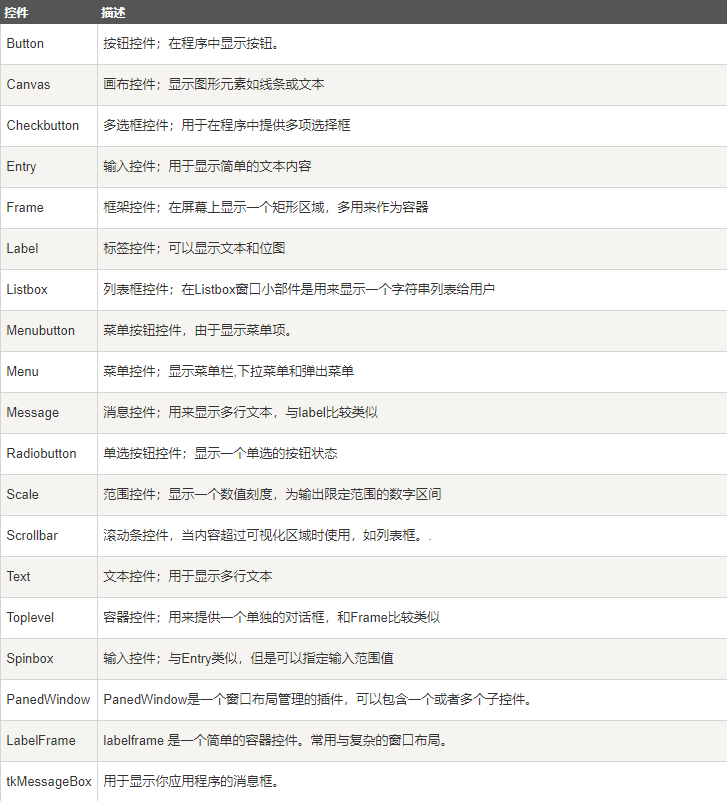
标准属性
标准属性也就是所有控件的共同属性,如大小,字体和颜色等等
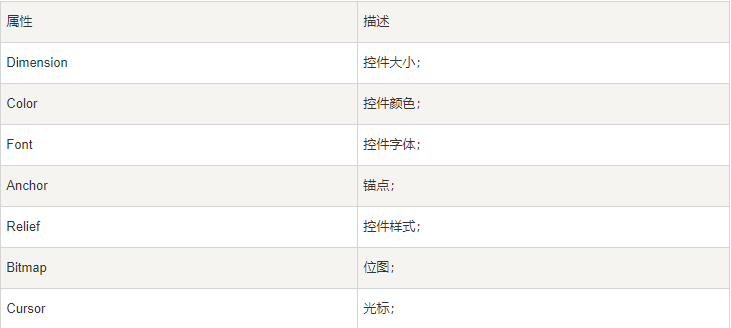
几何管理
Tkinter控件有特定的几何状态管理方法,管理整个控件区域组织,一下是Tkinter公开的几何管理类:包、网格、位置
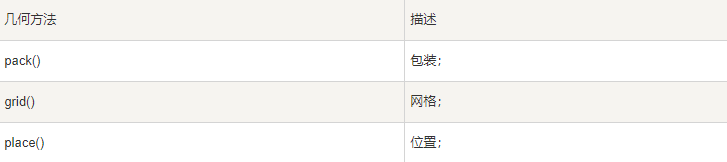
组件的放置和排版(pack,grid,place) 属性参数
- pack组件设置位置属性参数:
- after: 将组件置于其他组件之后;
- before: 将组件置于其他组件之前;
- anchor: 组件的对齐方式,顶对齐'n',底对齐's',左'w',右'e'
- side: 组件在主窗口的位置,可以为'top','bottom','left','right'(使用时tkinter.TOP,tkinter.E);
- fill 填充方式 (Y,垂直,X,水平)
- expand 1可扩展,0不可扩展
- grid组件使用行列的方法放置组件的位置,参数有:
- column: 组件所在的列起始位置;
- columnspam: 组件的列宽;
- row: 组件所在的行起始位置;
- rowspam: 组件的行宽;
- place组件可以直接使用坐标来放置组件,参数有:
- anchor: 组件对齐方式; NW N NE E SE S SW W CENTER
- x: 组件左上角的x坐标;
- y: 组件右上角的y坐标;
- relx: 组件相对于窗口的x坐标,应为0-1之间的小数;
- rely: 组件相对于窗口的y坐标,应为0-1之间的小数;
- width: 组件的宽度;
- heitht: 组件的高度;
- relwidth: 组件相对于窗口的宽度,0-1;
- relheight: 组件相对于窗口的高度,0-1;
代码实例:
1、 Label & Button
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/3/31 0:15
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : lable_button.py
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk() #根窗口
- root.title('Lable & Button') #主窗口标题
- root.geometry('800x600') #主窗口大小,中间的为英文字母x
- var = StringVar() #tk里面特定的字符串形式
- lable = Label(root, textvariable=var, bg='green', font=('Arial', 12),
- width=15, height=2)
- lable.pack()
- # lable.place() 安放到具体位置
- on_hit = False
- def hit_me():
- global on_hit #必须标出它是global的
- if on_hit == False:
- on_hit = True
- var.set('线性回归')
- else:
- on_hit = False
- var.set('')
- button = Button(root, text='执行', width=15, height=2, command=hit_me)
- button.pack()
- root.mainloop()
- anchor: 指定按钮上文本的位置;
- background(bg) 指定按钮的背景色;
- bitmap: 指定按钮上显示的位图;
- borderwidth(bd) 指定按钮边框的宽度;
- command: 指定按钮消息的回调函数;
- cursor: 指定鼠标移动到按钮上的指针样式;
- font: 指定按钮上文本的字体;
- foreground(fg) 指定按钮的前景色;
- height: 指定按钮的高度;
- image: 指定按钮上显示的图片;
- state: 指定按钮的状态(disabled);
- text: 指定按钮上显示的文本;
- width: 指定按钮的宽度
- padx 设置文本与按钮边框x的距离,还有pady;
- activeforeground 按下时前景色
- textvariable 可变文本,与StringVar等配合着用
Button按钮的参数
- Anchor 标签中文本的位置;
- background(bg) 背景色;
- foreground(fg) 前景色;
- borderwidth(bd) 边框宽度;
- width 标签宽度;
- height 标签高度;
- bitmap 标签中的位图;
- font 字体;
- image 标签中的图片;
- justify 多行文本的对齐方式;
- text 标签中的文本,可以使用'\n'表示换行
- textvariable 显示文本自动更新,与StringVar等配合着用
Label组件控制参数
2、 Entry & Text
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 0:30
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : entry_text.py
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk();
- root.title('Entry & Text')
- root.geometry('800x600')
- entry = Entry(root, show='*')
- entry.pack()
- def insert_point():
- var = entry.get()
- text.insert('insert', var)
- def insert_end():
- var = entry.get()
- # text.insert('end', var) 插入到末尾
- text.insert('2.2', var) #插入到第二行第三位
- b1 = Button(root, text='insert point', width=15, height=2, command=insert_point)
- b1.pack()
- b2 = Button(root, text='insert end', command=insert_end)
- b2.pack()
- text = Text(root, height=2)
- text.pack()
- root.mainloop()
- background(bg) 文本框背景色;
- foreground(fg) 前景色;
- selectbackground 选定文本背景色;
- selectforeground 选定文本前景色;
- borderwidth(bd) 文本框边框宽度;
- font 字体;
- show 文本框显示的字符,若为*,表示文本框为密码框;
- state 状态;
- width 文本框宽度
- textvariable 可变文本,与StringVar等配合着用
文本框tkinter.Entry,tkinter.Text控制参数
3、Listbox列表
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 0:45
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : listbox.py
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk();
- root.title('Listbox')
- root.geometry('400x300')
- var1 = StringVar()
- lable = Label(root, bg='yellow', width=4, textvariable=var1)
- lable.pack()
- def print_selection():
- value = lb.get(lb.curselection()) #得到光标选定的列表项
- var1.set(value)
- button = Button(root, text='print selection', width=15, height=2, command=print_selection)
- button.pack()
- var2 = StringVar()
- var2.set((11,22,33,55))
- lb = Listbox(root, listvariable=var2)
- list_items = [1,2,3,4]
- for item in list_items:
- lb.insert('end', item)
- lb.insert(1, 'first') #索引插入,第2位插入first
- lb.insert(2, 'second')
- lb.delete(2)#索引删除
- lb.pack()
- root.mainloop()
4、Radiobutton单选框
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 0:59
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : radiobutton.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("Radiobutton")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- var = tk.StringVar()
- lable = tk.Label(root, text='empty', bg='yellow', width=25 )
- lable.pack()
- def print_selection():
- lable.config(text='you have selected ' + var.get()) #lable重新设置text
- r1 = tk.Radiobutton(root, text='OptionA',
- variable=var, value='A',
- command=print_selection)
- r1.pack()
- r2 = tk.Radiobutton(root, text='OptionB',
- variable=var, value='B',
- command=print_selection)
- r2.pack()
- r3 = tk.Radiobutton(root, text='OptionC',
- variable=var, value='C',
- command=print_selection)
- r3.pack()
- root.mainloop()
- anchor 文本位置;
- background(bg) 背景色;
- foreground(fg) 前景色;
- borderwidth 边框宽度;
- width 组件的宽度;
- height 组件高度;
- bitmap 组件中的位图;
- image 组件中的图片;
- font 字体;
- justify 组件中多行文本的对齐方式;
- text 指定组件的文本;
- value 指定组件被选中中关联变量的值;
- variable 指定组件所关联的变量;
- indicatoron 特殊控制参数,当为0时,组件会被绘制成按钮形式;
- textvariable 可变文本显示,与StringVar等配合着用
单选框Radiobutton控制参数
5、Scale尺度
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 1:17
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : scale.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("Scale")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- lable = tk.Label(root, text='empty', bg='yellow', width=25 )
- lable.pack()
- def print_selection(v):
- lable.config(text='you have selected '+ v)
- #5-11是取值范围;HORIZONTAL指水平;length是长度200像素;showvalue为1是将value显示在scale上面;
- # tickinterval是标签的单位长度,比如隔3个数值显示一个单位;resolution=0.01保留2位小数
- # Scale中的执行函数是有默认传入值的,就是标签的值
- scale = tk.Scale(root, label='try me', from_=5, to=11,
- orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200,
- showvalue=1, tickinterval=3, resolution=0.01,
- command=print_selection)
- scale.pack()
- root.mainloop()
6、Checkbutton复选框
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 15:19
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : checkbutton.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title('Checkbutton')
- root.geometry('400x300')
- label = tk.Label(root, bg='yellow', width=20, text='Empty')
- label.pack()
- def print_selectioin():
- var = tk.StringVar()
- if var1.get() + var2.get() == 2:
- var = 'I love both'
- elif var1.get() + var2.get() == 0:
- var = 'I do not love either'
- else:
- if var1.get() == 1:
- var = 'I love Python'
- else:
- var = 'I love C++'
- label.config(text=var)
- var1 = tk.IntVar()
- var2 = tk.IntVar()
- c1 = tk.Checkbutton(root, text='Python', variable=var1, onvalue=1, offvalue=0,
- command=print_selectioin)
- c2 = tk.Checkbutton(root, text='C++', variable=var2, onvalue=1, offvalue=0,
- command=print_selectioin)
- c1.pack()
- c2.pack()
- root.mainloop()
- anchor 文本位置;
- background(bg) 背景色;
- foreground(fg) 前景色;
- borderwidth 边框宽度;
- width 组件的宽度;
- height 组件高度;
- bitmap 组件中的位图;
- image 组件中的图片;
- font 字体;
- justify 组件中多行文本的对齐方式;
- text 指定组件的文本;
- value 指定组件被选中中关联变量的值;
- variable 指定组件所关联的变量;
- indicatoron 特殊控制参数,当为0时,组件会被绘制成按钮形式;
- textvariable 可变文本显示,与StringVar等配合着用
复选框Checkbutton控制参数
7、Canvas 画布
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 16:02
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : canvas.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title('Canvas')
- root.geometry('400x300')
- canvas = tk.Canvas(root, bg='blue', height=100, width=200)
- image_file = tk.PhotoImage(file='../images/23.gif')
- image = canvas.create_image(10, 10, anchor='nw', image=image_file) #是图片锚定的点
- x0,y0,x1,y1 = 50,50,80,80
- line = canvas.create_line(x0,y0,x1,y1)
- oval = canvas.create_oval(x0,y0,x1,y1,fill='red') #x0,y0,x1,y1是圆的外接正方形
- arc = canvas.create_arc(x0+30,y0+30,x1+30,y1+30, start=0, extent=160)#0-160角度范围
- rect = canvas.create_rectangle(100,30,100+20,30+20)
- canvas.pack()
- def moveit():
- canvas.move(rect, 1, 2) #rect是正方形id,1是x方向移动,2是y方向移动
- button = tk.Button(root, text='move', command=moveit).pack()
- root.mainloop()
- background(bg) 背景色;
- foreground(fg) 前景色;
- borderwidth 组件边框宽度;
- width 组件宽度;
- height 高度;
- bitmap 位图;
- image 图片;
- 绘图的方法主要以下几种:
- create_arc 圆弧;
- create_bitmap 绘制位图,支持XBM;
- create_image 绘制图片,支持GIF(x,y,image,anchor);
- create_line 绘制支线;
- create_oval; 绘制椭圆;
- create_polygon 绘制多边形(坐标依次罗列,不用加括号,还有参数,fill,outline);
- create_rectangle 绘制矩形((a,b,c,d),值为左上角和右下角的坐标);
- create_text 绘制文字(字体参数font,);
- create_window 绘制窗口;
- delete 删除绘制的图形;
- itemconfig 修改图形属性,第一个参数为图形的ID,后边为想修改的参数;
- move 移动图像(1,4,0),1为图像对象,4为横移4像素,0为纵移像素,然后用root.update()刷新即可看到图像的移动,为了使多次移动变得可视,最好加上time.sleep()函数;
- 只要用create_方法画了一个图形,就会自动返回一个ID,创建一个图形时将它赋值给一个变量,需要ID时就可以使用这个变量名。
- coords(ID) 返回对象的位置的两个坐标(4个数字元组);
- 对于按钮组件、菜单组件等可以在创建组件时通过command参数指定其事件处理函数。方法为bind;或者用bind_class方法进行类绑定,bind_all方法将所有组件事件绑定到事件响应函数上。
组图组件Canvas控制参数
8、Menubar菜单
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 16:02
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : menubar.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("Menubar")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- label = tk.Label(root, text='', bg='yellow')
- label.pack()
- counter = 0
- def do_job():
- global counter
- label.config(text='do '+ str(counter)) #如果直接将pack()写在label定义的后面,则在这里就会出现label没有config属性的错误
- counter += 1
- menubar = tk.Menu(root)
- filemenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)#tearoff是指不可分割 它的值只有0和1,将tearoff设置为1以后,就是表明这个菜单是可以独立出来的,如果是0的话就不可以独立出来。代码演示一下即可。
- menubar.add_cascade(label='File', menu=filemenu)
- filemenu.add_command(label='New', command=do_job)
- filemenu.add_command(label='Open', command=do_job)
- filemenu.add_command(label='Save', command=do_job)
- filemenu.add_separator()
- filemenu.add_command(label='Exit',command=root.quit)
- editmenu = tk.Menu(menubar, tearoff=0)
- menubar.add_cascade(label='Edit', menu=editmenu)
- editmenu.add_command(label='Cut', command=do_job)
- editmenu.add_command(label='Copy', command=do_job)
- editmenu.add_command(label='Paste', command=do_job)
- submenu = tk.Menu(filemenu)
- filemenu.add_cascade(label='Import', menu=submenu, underline=0)
- submenu.add_command(label='Submenu1', command=do_job)
- root.config(menu = menubar) #将整个menubar添加到窗口
- root.mainloop()
- 参数:
- tearoff 分窗,0为在原窗,1为点击分为两个窗口
- bg,fg 背景,前景
- borderwidth 边框宽度
- font 字体
- activebackgound 点击时背景,同样有activeforeground,activeborderwidth,disabledforeground
- cursor
- postcommand
- selectcolor 选中时背景
- takefocus
- title
- type
- relief
- 方法:
- menu.add_cascade 添加子选项
- menu.add_command 添加命令(label参数为显示内容)
- menu.add_separator 添加分隔线
- menu.add_checkbutton 添加确认按钮
- delete 删除
菜单Menu的参数和方法
9、Frame框架
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 20:11
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : frame.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("Frame")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- tk.Label(root, text='on the window').pack()
- frm = tk.Frame(root)
- frm.pack()
- frm_l = tk.Frame(frm)
- frm_r = tk.Frame(frm)
- frm_l.pack(side='left') #固定到左侧(是针对父级的,不是主窗口)
- frm_r.pack(side='right')
- tk.Label(frm_l, text='on the frm_11').pack()
- tk.Label(frm_l, text='on the frm_12').pack()
- tk.Label(frm_r, text='on the frm_r').pack()
- root.mainloop()
10、messagebox弹窗
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/1 20:19
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : messagebox.py
- import tkinter as tk
- import tkinter.messagebox # messagebox必须加这行
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("messagebox")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- def hit_me():
- # tk.messagebox.showinfo(title='Hi', message='hahahha')
- # tk.messagebox.showwarning(title='Warning', message='nononon')
- # tk.messagebox.showerror(title='Error', message='fatal! never!!')
- # print(tk.messagebox.askquestion(title='Hi', message='nononon')) #return 'yes' / 'no'
- # print(tk.messagebox.askyesno(title='Hi', message='nononon')) # return True / False
- # print(tk.messagebox.askretrycancel(title='Hi', message='nononon')) # return True / False
- print(tk.messagebox.askokcancel(title='Hi', message='nononon')) # return True / False
- tk.Button(root, text='hit me', command=hit_me).pack()
- root.mainloop()
- messagebox._show函数的控制参数:
- default 指定消息框按钮;
- icon 指定消息框图标;
- message 指定消息框所显示的消息;
- parent 指定消息框的父组件;
- title 标题;
- type 类型;
- simpledialog模块参数:
- title 指定对话框的标题;
- prompt 显示的文字;
- initialvalue 指定输入框的初始值;
- filedialog 模块参数:
- filetype 指定文件类型;
- initialdir 指定默认目录;
- initialfile 指定默认文件;
- title 指定对话框标题
- colorchooser模块参数:
- initialcolor 指定初始化颜色;
- title 指定对话框标题;
弹窗参数
11、pack & gird & place几何管理
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/2 0:50
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : pack_grid_place.py
- import tkinter as tk
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("pack & grid & place")
- root.geometry('400x300')
- # tk.Label(root, text=1).pack(side='top')
- # tk.Label(root, text=2).pack(side='bottom')
- # tk.Label(root, text=3).pack(side='left')
- # tk.Label(root, text=4).pack(side='right')
- # for i in range(4):
- # for j in range(3):
- # tk.Label(root, text=1).grid(row=i, column=j, ipadx=10, ipady=10) #padx和pady是外部的x和y方向的扩展长度,ipadx和ipady是内部的
- tk.Label(root, text=1).place(x=10, y=100, anchor='nw')
- root.mainloop()
12、事件关联
- bind(sequence,func,add)——
- bind_class(className,sequence,func,add)
- bind_all(sequence,func,add)
- 事件参数:
- sequence 所绑定的事件;
- func 所绑定的事件处理函数;
- add 可选参数,为空字符或‘+’;
- className 所绑定的类;
- 鼠标键盘事件
- <Button-1> 鼠标左键按下,2表示中键,3表示右键;
- <ButtonPress-1> 同上;
- <ButtonRelease-1> 鼠标左键释放;
- <B1-Motion> 按住鼠标左键移动;
- <Double-Button-1> 双击左键;
- <Enter> 鼠标指针进入某一组件区域;
- <Leave> 鼠标指针离开某一组件区域;
- <MouseWheel> 滚动滚轮;
- <KeyPress-A> 按下A键,A可用其他键替代;
- <Alt-KeyPress-A> 同时按下alt和A;alt可用ctrl和shift替代;
- <Double-KeyPress-A> 快速按两下A;
- <Lock-KeyPress-A> 大写状态下按A;
- 窗口事件
- Activate 当组件由不可用转为可用时触发;
- Configure 当组件大小改变时触发;
- Deactivate 当组件由可用转变为不可用时触发;
- Destroy 当组件被销毁时触发;
- Expose 当组件从被遮挡状态中暴露出来时触发;
- Unmap 当组件由显示状态变为隐藏状态时触发;
- Map 当组件由隐藏状态变为显示状态时触发;
- FocusIn 当组件获得焦点时触发;
- FocusOut 当组件失去焦点时触发;
- Property 当窗体的属性被删除或改变时触发;
- Visibility 当组件变为可视状态时触发;
- 响应事件
- event对象(def function(event)):
- char 按键字符,仅对键盘事件有效;
- keycode 按键名,仅对键盘事件有效;
- keysym 按键编码,仅对键盘事件有效;
- num 鼠标按键,仅对鼠标事件有效;
- type 所触发的事件类型;
- widget 引起事件的组件;
- width,heigh 组件改变后的大小,仅Configure有效;
- x,y 鼠标当前位置,相对于窗口;
- x_root,y_root 鼠标当前位置,相对于整个屏幕
13、字体
- 一般格式:
- ('Times -10 bold')
- ('Times',10,'bold','italic') 依次表示字体、字号、加粗、倾斜
- 补充:
- config 重新配置
- label.config(font='Arial -%d bold' % scale.get())
- 依次为字体,大小(大小可为字号大小),加粗
- tkinter.StringVar 能自动刷新的字符串变量,可用set和get方法进行传值和取值,类似的还有IntVar,DoubleVar...
14、下拉列表Comobobox
- import tkinter as tk
- from tkinter import ttk #必须加这个
- def select_algorithm(*args):
- global algo_selected
- algo_selected = algorithm_combobox.get()
- print(algo_selected)
- algo_name = tk.StringVar()
- algorithm_combobox = ttk.Combobox(tools_frm, textvariable=algo_name, width=12)
- algorithm_combobox['value'] = ('选择算法', 'Classification', 'Clustering', 'Regression', 'Projections', 'Dynamical', 'Optimization') #'Reinforcenment Learning'
- algorithm_combobox['state'] = 'readonly'
- algorithm_combobox.current(0)
- algorithm_combobox.bind("<<ComboboxSelected>>", select_algorithm) #添加选择事件
- algorithm_combobox.grid(row=1, column=4)
15、文件选择框filedialog
- import tkinter as tk
- import tkinter.filedialog #必须加
- filename = tk.filedialog.askopenfilename(title='选择训练数据', filetypes=[('csv','*.csv')])
- # print(filename)
- if len(filename) != 0:
- data = np.loadtxt(filename, delimiter=',') # 训练数据
代码实战 - 登录窗口
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- # @Time : 2018/4/2 1:00
- # @Author : TanRong
- # @Software: PyCharm
- # @File : login.py
- import tkinter as tk
- import pickle
- import tkinter.messagebox
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title('Welcome to Login')
- root.geometry('450x300')
- # welcome image
- canvas = tk.Canvas(root, height=200, width=500)
- image_file = tk.PhotoImage(file='../images/welcome.gif')
- image = canvas.create_image(0,0, anchor='nw', image=image_file)
- canvas.pack(side='top')
- #输入框
- tk.Label(root, text='User name:').place(x=50, y=150)
- tk.Label(root, text='Password:').place(x=50, y=190)
- var_usr_name = tk.StringVar()
- var_usr_pwd = tk.StringVar()
- var_usr_name.set('loginPython@163.com')
- entry_usr_name = tk.Entry(root, textvariable=var_usr_name)
- entry_usr_name.place(x=160, y=150)
- entry_usr_pwd = tk.Entry(root, textvariable=var_usr_pwd, show='*')
- entry_usr_pwd.place(x=160, y=190)
- def usr_login():
- usr_name = var_usr_name.get()
- usr_pwd = var_usr_pwd.get()
- try:
- with open('usrs_info.pickle', 'rb') as usr_file:
- usrs_info = pickle.load(usr_file)
- except FileNotFoundError:
- with open('usrs_info.pickle', 'wb') as usr_file:
- usrs_info = {'admin':'admin'} #设置管理员信息
- pickle.dump(usrs_info, usr_file)
- if usr_name in usrs_info:
- if usr_pwd == usrs_info[usr_name]:
- tk.messagebox.showinfo(title='Welcome', message='How are you? '+ usr_name)
- else:
- tk.messagebox.showerror(title='Error', message='Error your password is wrong, try agein.')
- else:
- is_sign_up = tk.messagebox.askyesno(title='Welcome',
- message='You have not sign up. Sign up today?')
- if is_sign_up:
- usr_sign_up()
- def usr_sign_up():
- def sign_to_python():
- nname = new_name.get()
- npwd = new_pwd.get()
- npwd_confirm = new_pwd_confirm.get()
- with open('usrs_info.pickle', 'rb') as usr_file:
- exist_usr_info = pickle.load(usr_file)
- if npwd != npwd_confirm:
- tk.messagebox.showerror(title='Error', message='Password and Confirm Password must be same!')
- elif nname in exist_usr_info:
- tk.messagebox.showerror(title='Error', message='The user has already signed up!')
- else:
- exist_usr_info[nname] = npwd
- with open('usrs_info.pickle', 'wb') as usr_file:
- pickle.dump(exist_usr_info, usr_file)
- tk.messagebox.showinfo(title='Welcome', message='You have successfully signed up!')
- # global var_usr_name 无效
- # global var_usr_pwd
- # var_usr_name = nname
- # var_usr_pwd = ''
- window_sign_up.destroy()
- window_sign_up = tk.Toplevel(root)
- window_sign_up.geometry('350x200')
- window_sign_up.title('Sign up window')
- new_name = tk.StringVar()
- new_name.set('loginPython@163.com')
- tk.Label(window_sign_up, text='User name:').place(x=10, y=10)
- entry_new_name = tk.Entry(window_sign_up, textvariable=new_name)
- entry_new_name.place(x=150, y=10)
- new_pwd = tk.StringVar()
- tk.Label(window_sign_up, text='Password:').place(x=10, y=50)
- entry_new_pwd = tk.Entry(window_sign_up, textvariable=new_pwd)
- entry_new_pwd.place(x=150, y=50)
- new_pwd_confirm = tk.StringVar()
- tk.Label(window_sign_up, text='Confirm Password:').place(x=10, y=90)
- entry_usr_pwd_confirm = tk.Entry(window_sign_up, textvariable=new_pwd_confirm)
- entry_usr_pwd_confirm.place(x=150, y=90)
- btn_confirm_sign_up = tk.Button(window_sign_up, text='Sign up', command=sign_to_python)
- btn_confirm_sign_up.place(x=150, y=130)
- btn_login = tk.Button(root, text='Login', command=usr_login)
- btn_login.place(x=170, y=230)
- btn_sign_up = tk.Button(root, text='Sign up', command=usr_sign_up)
- btn_sign_up.place(x=270, y=230)
- root.mainloop()
- #filename:Caculater
- import tkinter,time,decimal,math,string
- root=tkinter.Tk()
- root.title('计算器')
- root.resizable(0,0)
- global cuncu, vartext, result, fuhao
- result = fuhao = None
- vartext = tkinter.StringVar()
- cuncu = []
- class anjianzhi:
- global cuncu, vartext, result, fuhao
- def __init__(self,anjian):
- self.anjian = anjian
- def jia(self):
- cuncu.append(self.anjian)
- vartext.set( ''.join(cuncu))
- def tui(self):
- cuncu.pop()
- vartext.set(''.join(cuncu))
- def clear(self):
- cuncu.clear()
- vartext.set('')
- result = None
- fuhao = None
- def zhengfu(self):
- if cuncu[0]:
- if cuncu[0] == '-':
- cuncu[0] = '+'
- elif cuncu[0] == '+':
- cuncu[0] = '-'
- else:
- cuncu.insert(0, '-')
- vartext.set(''.join(cuncu))
- def xiaoshudian(self):
- if cuncu.count('.') >= 1:
- pass
- else:
- if cuncu == [] :
- cuncu.append('')
- cuncu.append('.')
- vartext.set(''.join(cuncu))
- def yunshuan(self):
- global cuncu, vartext, result, fuhao
- if vartext.get() == '':
- pass
- else:
- get1 = decimal.Decimal(vartext.get())
- if self.anjian in ('1/x','sqrt'):
- if self.anjian == '1/x':
- result = 1/get1
- elif self.anjian == 'sqrt':
- result = math.sqrt(get1)
- elif self.anjian in ('+','-','*','/','='):
- if fuhao is not None:
- get1 = decimal.Decimal(result)
- get2 = decimal.Decimal(vartext.get())
- if fuhao == '+':
- result = get1 + get2
- elif fuhao == '-':
- result = get1 - get2
- elif fuhao == '*':
- result = get1 * get2
- elif fuhao == '/':
- result = get1 / get2
- else:
- result = get1
- if self.anjian == '=':
- fuhao = None
- else:
- fuhao = self.anjian
- print(fuhao)
- print(result)
- vartext.set(str(result))
- cuncu.clear()
- def copy1():
- # tkinter.Misc().clipboard_clear()
- tkinter.Misc().clipboard_append(string(vartext.get()))
- def buju(root):
- global cuncu, vartext, result, fuhao
- entry1 = tkinter.Label(root, width=30, height=2, bg='white', anchor='se', textvariable=vartext)
- entry1.grid(row=0, columnspan=5)
- buttonMC=tkinter.Button(root,text='MC',width=5)
- buttonMR=tkinter.Button(root,text='MR',width=5)
- buttonMS=tkinter.Button(root,text='MS',width=5)
- buttonM1=tkinter.Button(root,text='M+',width=5)
- buttonM2=tkinter.Button(root,text='M-',width=5)
- buttonMC.grid(row=1,column=0)
- buttonMR.grid(row=1,column=1)
- buttonMS.grid(row=1,column=2)
- buttonM1.grid(row=1,column=3)
- buttonM2.grid(row=1,column=4)
- buttonJ=tkinter.Button(root,text='←',width=5,command=anjianzhi('c').tui)
- buttonCE=tkinter.Button(root,text='CE',width=5)
- buttonC=tkinter.Button(root,text=' C ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('c').clear)
- button12=tkinter.Button(root,text='±',width=5,command=anjianzhi('c').zhengfu)
- buttonD=tkinter.Button(root,text='√',width=5,command=anjianzhi('sqrt').yunshuan)
- buttonJ.grid(row=2,column=0)
- buttonCE.grid(row=2,column=1)
- buttonC.grid(row=2,column=2)
- button12.grid(row=2,column=3)
- buttonD.grid(row=2,column=4)
- button7=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 7 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button8=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 8 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button9=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 9 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- buttonc=tkinter.Button(root, text=' / ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('/').yunshuan)
- buttonf= tkinter.Button(root, text=' % ',width=5)
- button7.grid(row=3,column=0)
- button8.grid(row=3,column=1)
- button9.grid(row=3,column=2)
- buttonc.grid(row=3,column=3)
- buttonf.grid(row=3,column=4)
- button4=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 4 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button5=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 5 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button6=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 6 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- buttonx=tkinter.Button(root,text=' * ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('*').yunshuan)
- buttonfs=tkinter.Button(root,text='1/x',width=5,command=anjianzhi('1/x').yunshuan)
- button4.grid(row=4,column=0)
- button5.grid(row=4,column=1)
- button6.grid(row=4,column=2)
- buttonx.grid(row=4,column=3)
- buttonfs.grid(row=4,column=4)
- button1 = tkinter.Button(root, text=' 1 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button2 = tkinter.Button(root, text=' 2 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button3 = tkinter.Button(root, text=' 3 ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- button_= tkinter.Button(root, text=' - ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('-').yunshuan)
- buttondy= tkinter.Button(root, text=' \n = \n ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('=').yunshuan)
- button1.grid(row=5, column=0)
- button2.grid(row=5, column=1)
- button3.grid(row=5, column=2)
- button_.grid(row=5, column=3)
- buttondy.grid(row=5, column=4,rowspan=2)
- button0=tkinter.Button(root,text=' 0 ',width=11,command=anjianzhi('').jia)
- buttonjh = tkinter.Button(root,text=' . ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('c').xiaoshudian)
- buttonjia=tkinter.Button(root,text=' + ',width=5,command=anjianzhi('+').yunshuan)
- button0.grid(row=6,column=0,columnspan=2)
- buttonjh.grid(row=6,column=2)
- buttonjia.grid(row=6,column=3)
- def caidan(root):
- menu=tkinter.Menu(root)
- submenu1=tkinter.Menu(menu,tearoff=0)
- menu.add_cascade(label='查看',menu=submenu1)
- submenu2 = tkinter.Menu(menu, tearoff=0)
- submenu2.add_command(label='复制')
- submenu2.add_command(label='粘贴')
- menu.add_cascade(label='编辑',menu=submenu2)
- submenu = tkinter.Menu(menu, tearoff=0)
- submenu.add_command(label='查看帮助')
- submenu.add_separator()
- submenu.add_command(label='关于计算机')
- menu.add_cascade(label='帮助',menu=submenu)
- root.config(menu=menu)
- buju(root)
- caidan(root)
- root.mainloop()
- 计算器
tkinter 计算器(不是我写的)
tkinter中的颜色:

参考链接: tkinter模块常用参数(python3):http://www.cnblogs.com/aland-1415/p/6849193.html
Python GUI - tkinter的更多相关文章
- Python GUI - Tkinter tkMessageBox
Python GUI - Tkinter tkMessageBox: tkMessageBox模块用于显示在您的应用程序的消息框.此模块提供了一个功能,您可以用它来显示适当的消息 tkMess ...
- python gui tkinter快速入门教程 | python tkinter tutorial
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/d5c57f56/,欢迎阅读最新内容! python tkinter tutorial Guide main ui messageb ...
- Python GUI——tkinter菜鸟编程(中)
8. Radiobutton 选项按钮:可以用鼠标单击方式选取,一次只能有一个选项被选取. Radiobutton(父对象,options,-) 常用options参数: anchor,bg,bitm ...
- python gui tkinter用法杂记
1.treeview遍历 iids = tree.selection() t = tree.get_children() for i in t: print(tree.item(i,'values') ...
- Python GUI tkinter 学习笔记(一)
第一个python程序 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- from Tkinter import * # 创建一个根窗口,其余的控件都在这个窗口之上 ...
- Python GUI tkinter 学习笔记(三)
草稿 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from Tkinter import * root = Tk() Label(root, text = "First").g ...
- Python GUI tkinter 学习笔记(二)
第二个程序 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from Tkinter import * class App: def __init__(self, master): # frame 创 ...
- Python GUI with Tkinter (from youtube) 在youtube上能找到很多编程视频...
Python GUI with Tkinter - 1 - Introduction以上链接是一个python tkinter视频系列的第一讲的链接.虽然英语不好,但是,程序还是看得懂的(照着做就可以 ...
- python GUI实战项目——tkinter库的简单实例
一.项目说明: 本次通过实现一个小的功能模块对Python GUI进行实践学习.项目来源于软件制造工程的作业.记录在这里以复习下思路和总结编码过程.所有的源代码和文件放在这里: 链接: https:/ ...
随机推荐
- response.setContentType()的String参数及对应类型
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="+ filename); res ...
- 一切皆Socket
“一切皆Socket!” 话虽些许夸张,但是事实也是,现在的网络编程几乎都是用的socket. ——有感于实际编程和开源项目研究. socket()函数介绍 socket函数介绍 函数原型 domai ...
- 洛谷P3247 [HNOI2016]最小公倍数 [分块,并查集]
洛谷 思路 显然,为了达到这个最小公倍数,只能走\(a,b\)不是很大的边. 即,当前询问的是\(A,B\),那么我们只能走\(a\leq A,b\leq B\)的边. 然而,为了达到这最小公倍数,又 ...
- java学习——异常处理
类 Throwable类 Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类.只有当对象是此类(或其子类之一)的实例时,才能通过 Java 虚拟机或者 Java throw语句抛出.类似地,只有此类 ...
- Confluence 6 MySQL 3.x 字符集编码问题
MySQL 3.x is 已知在大写和小写转换的时候有些问题(non-ASCII). 问题诊断 请按照 Troubleshooting Character Encodings 页面中的内容对问题进行诊 ...
- Confluence 6 中样式化字体
Confluence 提供了通过层叠样式表(CSS)调整页面展示情况的能力.本页面帮助你理解如何在 Confluence 中使用一些 CSS 样式修改字体样式和字体大小. 下面的代码为自定义的字体代码 ...
- IO 多路复用
IO 多路复用 多路复用也是要用单线程来处理客户端并发,与其他模型相比多出了select这个模块. 程序不再直接问操作系统要数据,而是先发起一个select调用,select会阻塞直到其中某个sock ...
- swoole 使用异步redis的前置条件
redis安装 官网下载redis 下载完成之后解压: 进入redis目录执行make: 进入src目录启动redis 启动成功如下: 启动后连接redis 编译安装hiredis 下载:https: ...
- strchr()
strchr()主要有2个最有用的用法: 第一个:搜索字符串在另一字符串中的第一次出现.并返回剩余的部分 $str = "hello_chrdai_1993"; $not_incl ...
- Metasploit 使用后门和Rootkit维持访问
1.内存攻击指的是攻击者利用软件的漏洞,构造恶意的输入导致软件在处理输入数据时出现非预期的错误,将输入数据写入内存中的某些敏感位置,从而劫持软件控制流,转而执行外部的指令代码,造成目标系统获取远程控制 ...
