Scrapy基础02
一、start_requests
def start_requests(self):
cls = self.__class__
if method_is_overridden(cls, Spider, 'make_requests_from_url'):
warnings.warn(
"Spider.make_requests_from_url method is deprecated; it "
"won't be called in future Scrapy releases. Please "
"override Spider.start_requests method instead (see %s.%s)." % (
cls.__module__, cls.__name__
),
)
for url in self.start_urls:
yield self.make_requests_from_url(url)
else:
for url in self.start_urls:
yield Request(url, dont_filter=True)
Scrapy初开始运行的时候是执行的是父类Spider里的start_requests方法
也可以自己重写:
import scrapy
from scrapy.http import Request class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'chouti'
allowed_domains = ['chouti.com']
start_urls = ['http://chouti.com/'] def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse) def parse(self, response):
pass
也可以用 return [Request(...)] 的形式替代 yield Reuest(...)
def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
# yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)
return [Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)]
因为源码里会对 start_requests()方法的返回值做一个 iter() 操作:
# from scrapy.crawler import Crawler def crawl(self, *args, **kwargs):
assert not self.crawling, "Crawling already taking place"
self.crawling = True try:
self.spider = self._create_spider(*args, **kwargs)
self.engine = self._create_engine()
start_requests = iter(self.spider.start_requests())
yield self.engine.open_spider(self.spider, start_requests)
yield defer.maybeDeferred(self.engine.start)
except Exception:
pass
...
所以:start_requests()方法 要么返回一个可迭代对象,要么返回一个生成器对象!!!
二、定义多个pipeline
如下所示:定义2个pipeline,类似Django里面的中间件,
按照优先级执行,300 400 代表优先级,越小越先执行;
# settings.py
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'day25spider.pipelines.Day25SpiderPipeline': 300,
'day25spider.pipelines.SecondPipeline': 400,
}
...
STORAGE_CONFIG = "chouti.json"
STORAGE_CONFIG2 = "chouti2.json"
DEPTH_LIMIT = 1
ENV = "debug"
# 爬虫文件:chouti.py import scrapy
from scrapy.http import Request
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from ..items import Day25SpiderItem class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'chouti'
allowed_domains = ['chouti.com']
start_urls = ['http://chouti.com/'] def start_requests(self):
for url in self.start_urls:
# yield Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)
return [Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)] def parse(self, response):
# print(response.body)
# print(response.text)
hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
item_list = hxs.xpath('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]')
# 找到首页所有消息的连接、标题、作业信息然后yield给pipeline进行持久化
for item in item_list:
link = item.xpath('./div[@class="news-content"]/div[@class="part1"]/a/@href').extract_first()
title = item.xpath('./div[@class="news-content"]/div[@class="part2"]/@share-title').extract_first()
author = item.xpath(
'./div[@class="news-content"]/div[@class="part2"]/a[@class="user-a"]/b/text()').extract_first()
yield Day25SpiderItem(link=link, title=title, author=author)
# items.py import scrapy class Day25SpiderItem(scrapy.Item):
link = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
author = scrapy.Field()
在执行第一个pipeline的时候,会做一个 if 'debug' == self.env ,
如果是 'debug' 环境就 raise DropItem() ,这样就会跳过后面的pipeline;
# pipelines.py from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem class Day25SpiderPipeline(object):
def __init__(self, file_path,env):
self.file_path = file_path # 文件路径
self.file_obj = None # 文件对象:用于读写操作
self.env = env # 运行环境 @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
"""
初始化时候,用于创建pipeline对象
:param crawler:
:return:
"""
val = crawler.settings.get('STORAGE_CONFIG')
env = crawler.settings.get('ENV')
return cls(val,env) def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(">>>> ", item)
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
self.file_obj.write(item.get('link') + "\n" + item.get('title') + "\n" + item.get('author') + "\n\n")
if 'debug' == self.env:
raise DropItem()
else:
return item def open_spider(self, spider):
"""
爬虫开始执行时,调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
# 如果不加:encoding='utf-8' 会导致文件里中文乱码
self.file_obj = open(self.file_path, mode='a+', encoding='utf-8') def close_spider(self, spider):
"""
爬虫关闭时,被调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
self.file_obj.close() class SecondPipeline(object):
def __init__(self, file_path):
self.file_path = file_path # 文件路径
self.file_obj = None # 文件对象:用于读写操作 @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
"""
初始化时候,用于创建pipeline对象
:param crawler:
:return:
"""
val = crawler.settings.get('STORAGE_CONFIG2')
return cls(val) def process_item(self, item, spider):
print(">>>> ", item)
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
self.file_obj.write(item.get('link') + "\n" + item.get('title') + "\n" + item.get('author') + "\n\n")
return item def open_spider(self, spider):
"""
爬虫开始执行时,调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
# 如果不加:encoding='utf-8' 会导致文件里中文乱码
self.file_obj = open(self.file_path, mode='a+', encoding='utf-8') def close_spider(self, spider):
"""
爬虫关闭时,被调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
if 'chouti' == spider.name:
self.file_obj.close()
三、url去重
Scrapy 默认是采用如下来实现url去重的:
yield Request(url, callback=self.parse, headers={}, cookies={},dont_filter=False)
# Scrapy默认的去重方法
# 在 from scrapy.dupefilter import RFPDupeFilter from __future__ import print_function
import os
import logging from scrapy.utils.job import job_dir
from scrapy.utils.request import request_fingerprint class BaseDupeFilter(object): @classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
return cls() def request_seen(self, request):
return False def open(self): # can return deferred
pass def close(self, reason): # can return a deferred
pass def log(self, request, spider): # log that a request has been filtered
pass class RFPDupeFilter(BaseDupeFilter):
"""Request Fingerprint duplicates filter""" def __init__(self, path=None, debug=False):
self.file = None
self.fingerprints = set()
self.logdupes = True
self.debug = debug
self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
if path:
self.file = open(os.path.join(path, 'requests.seen'), 'a+')
self.file.seek(0)
self.fingerprints.update(x.rstrip() for x in self.file) @classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
debug = settings.getbool('DUPEFILTER_DEBUG')
return cls(job_dir(settings), debug) def request_seen(self, request):
fp = self.request_fingerprint(request)
if fp in self.fingerprints:
return True
self.fingerprints.add(fp)
if self.file:
self.file.write(fp + os.linesep) def request_fingerprint(self, request):
return request_fingerprint(request) def close(self, reason):
if self.file:
self.file.close() def log(self, request, spider):
if self.debug:
msg = "Filtered duplicate request: %(request)s"
self.logger.debug(msg, {'request': request}, extra={'spider': spider})
elif self.logdupes:
msg = ("Filtered duplicate request: %(request)s"
" - no more duplicates will be shown"
" (see DUPEFILTER_DEBUG to show all duplicates)")
self.logger.debug(msg, {'request': request}, extra={'spider': spider})
self.logdupes = False spider.crawler.stats.inc_value('dupefilter/filtered', spider=spider)
# request_fingerprint源码 """
This module provides some useful functions for working with
scrapy.http.Request objects
""" from __future__ import print_function
import hashlib
import weakref
from six.moves.urllib.parse import urlunparse from w3lib.http import basic_auth_header
from scrapy.utils.python import to_bytes, to_native_str from w3lib.url import canonicalize_url
from scrapy.utils.httpobj import urlparse_cached _fingerprint_cache = weakref.WeakKeyDictionary()
def request_fingerprint(request, include_headers=None):
"""
Return the request fingerprint. The request fingerprint is a hash that uniquely identifies the resource the
request points to. For example, take the following two urls: http://www.example.com/query?id=111&cat=222
http://www.example.com/query?cat=222&id=111 Even though those are two different URLs both point to the same resource
and are equivalent (ie. they should return the same response). Another example are cookies used to store session ids. Suppose the
following page is only accesible to authenticated users: http://www.example.com/members/offers.html Lot of sites use a cookie to store the session id, which adds a random
component to the HTTP Request and thus should be ignored when calculating
the fingerprint. For this reason, request headers are ignored by default when calculating
the fingeprint. If you want to include specific headers use the
include_headers argument, which is a list of Request headers to include. """
if include_headers:
include_headers = tuple(to_bytes(h.lower())
for h in sorted(include_headers))
cache = _fingerprint_cache.setdefault(request, {})
if include_headers not in cache:
fp = hashlib.sha1()
fp.update(to_bytes(request.method))
fp.update(to_bytes(canonicalize_url(request.url)))
fp.update(request.body or b'')
if include_headers:
for hdr in include_headers:
if hdr in request.headers:
fp.update(hdr)
for v in request.headers.getlist(hdr):
fp.update(v)
cache[include_headers] = fp.hexdigest()
return cache[include_headers] def request_authenticate(request, username, password):
"""Autenticate the given request (in place) using the HTTP basic access
authentication mechanism (RFC 2617) and the given username and password
"""
request.headers['Authorization'] = basic_auth_header(username, password) def request_httprepr(request):
"""Return the raw HTTP representation (as bytes) of the given request.
This is provided only for reference since it's not the actual stream of
bytes that will be send when performing the request (that's controlled
by Twisted).
"""
parsed = urlparse_cached(request)
path = urlunparse(('', '', parsed.path or '/', parsed.params, parsed.query, ''))
s = to_bytes(request.method) + b" " + to_bytes(path) + b" HTTP/1.1\r\n"
s += b"Host: " + to_bytes(parsed.hostname or b'') + b"\r\n"
if request.headers:
s += request.headers.to_string() + b"\r\n"
s += b"\r\n"
s += request.body
return s def referer_str(request):
""" Return Referer HTTP header suitable for logging. """
referrer = request.headers.get('Referer')
if referrer is None:
return referrer
return to_native_str(referrer, errors='replace')
使用 request_fingerprint的示例:
from scrapy.utils.request import request_fingerprint
from scrapy.http import Request obj = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com',callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj2 = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com?a=1&b=2',callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj3 = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com?b=2&a=1',callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj4 = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com?b=2&a=1',headers={'Content-Type':'application/text'},callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj5 = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com?b=2&a=1',headers={'Content-Type':'application/text'},callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj6 = Request(url='http://www.baidu.com?b=2&a=1',headers={'Content-Type':'application/json'},callback=lambda x:x**2)
obj7 = Request(url='http://www.qq.com',callback=lambda x:x**2) fingerprint = request_fingerprint(obj)
fingerprint2 = request_fingerprint(obj2)
fingerprint3 = request_fingerprint(obj3)
fingerprint4 = request_fingerprint(obj4)
fingerprint5 = request_fingerprint(obj5,include_headers=['Content-Type'])
fingerprint6 = request_fingerprint(obj6,include_headers=['Content-Type'])
fingerprint7 = request_fingerprint(obj7) print(fingerprint)
print(fingerprint2)
print(fingerprint3)
print(fingerprint4)
print(fingerprint5)
print(fingerprint6)
print(fingerprint7) ###### 结果 ######
75d6587d87b3f4f3aa574b33dbd69ceeb9eafe7b
6b641a2d39886717fd794b75ef37ed73d06a716c
6b641a2d39886717fd794b75ef37ed73d06a716c
6b641a2d39886717fd794b75ef37ed73d06a716c
a00bfc032e3a3202184d6c20a5f5134900458fae
ad6b2ff37f5e73575d09159f5b4bea467d4c13e0
28853c538420894152718dadb9bdf109b333ccb5
cookie本质上是放到请求头里发到服务器端的,
所以 request_fingerprint() 方法只有 include_headers 参数,没有 include_cookie参数;
自定义去重方法:
# 第一步:创建去重文件
from scrapy.utils.request import request_fingerprint
class MyDupeFilter(object):
def __init__(self):
self.visited = set()
@classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
return cls()
def request_seen(self, request):
# print(request.url)
# print(request.callback)
fp = request_fingerprint(request)
if fp in self.visited:
return True # 返回True 表示已经爬过了
self.visited.add(fp)
def open(self): # can return deferred
pass
def close(self, reason): # can return a deferred
pass
def log(self, request, spider): # log that a request has been filtered
pass
# 第二步:配置settings.py
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = 'day25spider.my_filter.MyDupeFilter' # 自定义过滤插件
四、cookie
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6229292.html
# -*- coding: utf- -*-
import scrapy
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http.request import Request
from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar
from scrapy import FormRequest class ChouTiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令
name = "chouti"
# 允许的域名
allowed_domains = ["chouti.com"] cookie_dict = {}
has_request_set = {} def start_requests(self):
url = 'http://dig.chouti.com/'
# return [Request(url=url, callback=self.login)]
yield Request(url=url, callback=self.login) def login(self, response):
cookie_jar = CookieJar()
cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response, response.request)
for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items():
for i, j in v.items():
for m, n in j.items():
self.cookie_dict[m] = n.value req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/login',
method='POST',
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'},
body='phone=8615131255089&password=pppppppp&oneMonth=1',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.check_login
)
yield req def check_login(self, response):
req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/',
method='GET',
callback=self.show,
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
dont_filter=True
)
yield req def show(self, response):
# print(response)
hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
news_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]')
for new in news_list:
# temp = new.xpath('div/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract()
link_id = new.xpath('*/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract_first()
yield Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=%s' %(link_id,),
method='POST',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.do_favor
) page_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="dig_lcpage"]//a[re:test(@href, "/all/hot/recent/\d+")]/@href').extract()
for page in page_list: page_url = 'http://dig.chouti.com%s' % page
import hashlib
hash = hashlib.md5()
hash.update(bytes(page_url,encoding='utf-8'))
key = hash.hexdigest()
if key in self.has_request_set:
pass
else:
self.has_request_set[key] = page_url
yield Request(
url=page_url,
method='GET',
callback=self.show
) def do_favor(self, response):
print(response.text) 示例:自动登陆抽屉并点赞
自动登录抽屉并点赞
# 自动登录cookie并点赞 import json
import scrapy
from scrapy.http import Request
from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from ..items import Day25SpiderItem class ChoutiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'chouti'
allowed_domains = ['chouti.com'] cookie_dict = {} def start_requests(self):
url = 'http://dig.chouti.com/'
yield Request(url=url,callback=self.index,dont_filter=True)
# return [Request(url=url,callback=self.parse)] def index(self, response):
"""
:param response: 会拿到抽屉首页所有相关的内容
:return:
"""
# 第一步:GET请求,获取首页以及未授权的cookie信息
cookie_jar = CookieJar()
cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response,response.request)
# print(cookie_jar) # <scrapy.http.cookies.CookieJar object at 0x0000000004A32F98>
# print(cookie_jar._cookies) # cookie的详细内容
for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items():
for i, j in v.items():
for m, n in j.items():
self.cookie_dict[m] = n.value # 第二步:POST请求,发送用户名密码并携带未授权的cookie进行验证和授权
req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/login',
method='POST',
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'},
body='phone=8615066668888&password=xxxxxxxxxx&oneMonth=1',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.check_login,
dont_filter=True
)
yield req def check_login(self,response):
# 第三步:登录成功后去请求首页
print(response.text)
response = json.loads(response.text)
code = response['result']['code']
if '9999' == code:
req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/',
method='GET',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.do_favor,
dont_filter=True
)
yield req
else:
print("登陆失败") def do_favor(self,response):
# print(response.url)
# 第四步:获取首页所有的新闻id 并 执行点赞操作
hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
news_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]')
for new in news_list:
link_id = new.xpath('*/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract_first()
req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=%s' % (link_id,),
method='POST',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.do_favor_result,
dont_filter=True
)
yield req def do_favor_result(self,response):
# 第五步:输出点赞操作的结果
print(response.text)
五、自定制命令
- 在spiders同级创建任意目录,如:commands
- 在其中创建 crawlall.py 文件 (此处文件名就是自定义的命令)
- 在settings.py 中添加配置 COMMANDS_MODULE = '项目名称.目录名称'
- 在项目目录执行命令:scrapy crawlall
# ..commands/crawlall.py - 即 获取爬虫列表并执行所有的爬虫 from scrapy.commands import ScrapyCommand
from scrapy.crawler import Crawler
from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess
from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings class Command(ScrapyCommand): requires_project = True def syntax(self):
return '[options]' def short_desc(self):
return 'Runs all of the spiders' def run(self, args, opts):
spider_list = self.crawler_process.spiders.list()
for name in spider_list:
self.crawler_process.crawl(name, **opts.__dict__)
self.crawler_process.start()
# settings.py COMMANDS_MODULE = 'day25spider.commands'
所以,就可以知道爬虫启动的入口是什么
def run(self, args, opts):
self.crawler_process.crawl('chouti', **opts.__dict__)
self.crawler_process.start() 在 run() 里面打印下 print(type(self.crawler_process))
可以得到: <class 'scrapy.crawler.CrawlerProcess'> 所以 self.crawler_process 就是 scrapy.crawler.CrawlerProcess 类的一个对象
然后执行顺序就是:
scrapy.crawler.CrawlerProcess.crawl()
scrapy.crawler.Crawler.crawl()
scrapy.crawler.CrawlerProcess.start()
迭代器和生成器的补充
- 可迭代对象:具有 __iter__() 方法,并且执行后可以返回迭代器
- 迭代器:具有 __next__() 方法 并且逐一向后取值
- 生成器:函数中具有yield关键字
- 具有 __iter__() 返回的还是自己本身
- 具有 __next__()
六、下载中间件
在settings.py里配置上路径:
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'day25spider.middlewares.MyCustomDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
'day25spider.download_middlewares.DownMiddleware1': 543,
}
新建下载中间件:
class DownMiddleware1(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
"""
请求需要被下载时,经过所有下载器中间件的process_request调用
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
None,继续后续中间件去下载;
Response对象,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_response
Request对象,停止中间件的执行,将Request重新调度器
raise IgnoreRequest异常,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_exception
"""
pass def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
"""
spider处理完成,返回时调用
:param response:
:param result:
:param spider:
:return:
Response 对象:转交给其他中间件process_response
Request 对象:停止中间件,request会被重新调度下载
raise IgnoreRequest 异常:调用Request.errback
"""
print('response1')
return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
"""
当下载处理器(download handler)或 process_request() (下载中间件)抛出异常
:param response:
:param exception:
:param spider:
:return:
None:继续交给后续中间件处理异常;
Response对象:停止后续process_exception方法
Request对象:停止中间件,request将会被重新调用下载
"""
return None
下载中间件主要是 process_request() 方法里的返回值需要注意
process_request(self, request, spider) 应用:
- 自定义下载模块,而不是用scrapy自带的下载模块
- 定制请求头/cookie 避免每次请求都带上同样的重复代码:
request.headers['Content-Type'] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"
- 设置代理
关于代理的设置
- 第一种方式是scrapy默认的,需要环境变量里配置
from scrapy.downloadermiddlewares.httpproxy import HttpProxyMiddleware
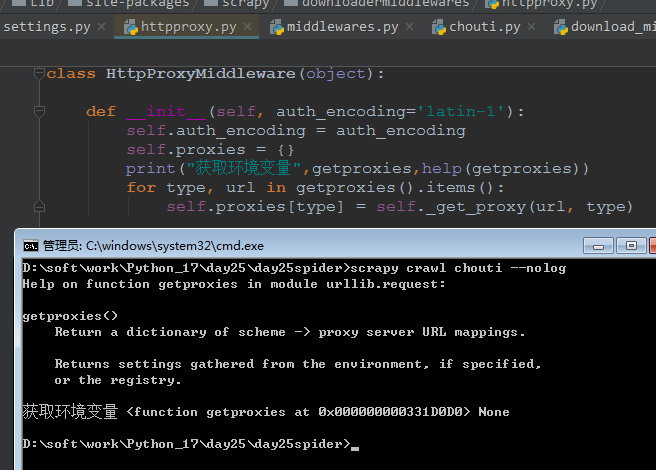
scrapy 默认采用的是 urllib.request.getproxies
# Proxy handling
def getproxies_environment():
"""Return a dictionary of scheme -> proxy server URL mappings. Scan the environment for variables named <scheme>_proxy;
this seems to be the standard convention. If you need a
different way, you can pass a proxies dictionary to the
[Fancy]URLopener constructor. """
proxies = {}
# in order to prefer lowercase variables, process environment in
# two passes: first matches any, second pass matches lowercase only
for name, value in os.environ.items():
name = name.lower()
if value and name[-6:] == '_proxy':
proxies[name[:-6]] = value
for name, value in os.environ.items():
if name[-6:] == '_proxy':
name = name.lower()
if value:
proxies[name[:-6]] = value
else:
proxies.pop(name[:-6], None)
return proxies
所以,这种需要使用 os.environ进行设置,且必须在程序最开始的时候设置:
# 爬虫文件 def start_requests(self):
import os
os.environ['http_proxy'] = "http://root:password@192.168.11.11:9999/"
os.environ['https_proxy'] = "http://192.168.11.11:9999/"
- 第二种则是可以通过自定义中间件
同样需要先在settings.py里注册,代理中间件如下:
import six
import base64
import random
# 用来兼容 Python2.x
def to_bytes(text, encoding=None, errors='strict'):
if isinstance(text, bytes):
return text
if not isinstance(text, six.string_types):
raise TypeError('to_bytes must receive a unicode, str or bytes '
'object, got %s' % type(text).__name__)
if encoding is None:
encoding = 'utf-8'
return text.encode(encoding, errors) class ProxyMiddleware(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
PROXIES = [
{'ip_port': '111.11.228.75:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '120.198.243.22:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '111.8.60.9:8123', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '101.71.27.120:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '122.96.59.104:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '122.224.249.122:8088', 'user_pass': ''},
]
proxy = random.choice(PROXIES)
if proxy['user_pass'] is not None:
request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port'])
encoded_user_pass = base64.encodestring(to_bytes(proxy['user_pass']))
request.headers['Proxy-Authorization'] = to_bytes('Basic ' + encoded_user_pass)
print("**************ProxyMiddleware have pass************" + proxy['ip_port'])
else:
print("**************ProxyMiddleware no pass************" + proxy['ip_port'])
request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port'])
把配置代理这一步写到中间件里,这样每个请求过来都会自动带上 代理
另外,此处的PROXIES 也可以换成是读文件或者去请求一个接口的形式获取代理信息
七、自定义扩展
自定义扩展,即利用信号在指定位置注册制定操作
# scrapy.signals 这里面给预留了很多的锚点
# 可以按照自己写扩展插件在某个锚点触发一些自定义操作 """
Scrapy signals These signals are documented in docs/topics/signals.rst. Please don't add new
signals here without documenting them there.
""" engine_started = object()
engine_stopped = object()
spider_opened = object()
spider_idle = object()
spider_closed = object()
spider_error = object()
request_scheduled = object()
request_dropped = object()
response_received = object()
response_downloaded = object()
item_scraped = object()
item_dropped = object() # for backwards compatibility
stats_spider_opened = spider_opened
stats_spider_closing = spider_closed
stats_spider_closed = spider_closed item_passed = item_scraped request_received = request_scheduled
在settings.py里注册:
EXTENSIONS = {
# 'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole': None,
'day25spider.extends.MyExtension':500,
}
扩展插件 extends.py :
from scrapy import signals class MyExtension(object):
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# val = crawler.settings.getint('EXTENDS_VAL')
val = crawler.settings.get('EXTENDS_VAL')
ext = cls(val) crawler.signals.connect(ext.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
crawler.signals.connect(ext.spider_closed, signal=signals.spider_closed)
crawler.signals.connect(ext.engine_started, signal=signals.engine_started)
crawler.signals.connect(ext.response_received, signal=signals.response_received)
crawler.signals.connect(ext.response_downloaded, signal=signals.response_downloaded) print(ext.value)
return ext def spider_opened(self, spider):
print('spider_opened') def spider_closed(self, spider):
print('spider_closed') def engine_started(self, spider):
print('engine_started') def response_received(self, spider):
print('response_received') def response_downloaded(self, spider):
print('response_downloaded')
...
更多参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6229292.html
Scrapy基础02的更多相关文章
- javascript基础02
javascript基础02 1.数据类型 数据类型的描述在上篇的扩展中有写到链接 由于ECMAScript数据类型具有动态性,因此的确没有再定义其他数据类型的必要.这句话很重要. 如果以后再数据类型 ...
- javaSE基础02
javaSE基础02 一.javac命令和java命令做什么事情? javac:负责编译,当执行javac时,会启动java的编译程序,对指定扩展名的.java文件进行编译,生成了jvm可以识别的字节 ...
- java基础学习05(面向对象基础02)
面向对象基础02 实现的目标 1.String类的使用2.掌握this关键字的使用3.掌握static关键字的使用4.了解内部类 String类 实例化String对象一个字符串就是一个String类 ...
- 0.Python 爬虫之Scrapy入门实践指南(Scrapy基础知识)
目录 0.0.Scrapy基础 0.1.Scrapy 框架图 0.2.Scrapy主要包括了以下组件: 0.3.Scrapy简单示例如下: 0.4.Scrapy运行流程如下: 0.5.还有什么? 0. ...
- 085 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 04 构造方法调用
085 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 04 构造方法调用 本文知识点:构造方法调用 说明:因为时间紧张,本人写博客过程中只是 ...
- 084 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 03 构造方法-this关键字
084 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 03 构造方法-this关键字 本文知识点:构造方法-this关键字 说明:因为时间紧 ...
- 083 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 02 构造方法-带参构造方法
083 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 02 构造方法-带参构造方法 本文知识点:构造方法-带参构造方法 说明:因为时间紧张, ...
- 082 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 01 构造方法-无参构造方法
082 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 02 构造方法介绍 01 构造方法-无参构造方法 本文知识点:构造方法-无参构造方法 说明:因为时间紧张, ...
- day32-线程基础02
线程基础02 3.继承Thread和实现Runnable的区别 从java的设计来看,通过继承Thread或者实现Runnable接口本身来创建线程本质上没有区别,从jdk帮助文档我们可以看到Thre ...
随机推荐
- FlatList
FlatList 之前使用的组件是ListView,当时要添加一个下拉刷新,上拉加载的功能,所以对ListView做了一些封装,但是后来看官方文档,不建议再使用ListView,因为效率问题,做过An ...
- hexo+next主题目录解析
默认目录结构: . ├── .deploy ├── public ├── scaffolds ├── scripts ├── source | ├── _drafts | └── _posts ├── ...
- iis默认文档
环境 W10 IIS10 输入网址后,显示一个默认首页,在IIS中,一般指定一个根目录下的文件例如index.html 如果要指定子目录下的文件, 例如让 /home/index.html 这个文件成 ...
- 「HNOI2016」最小公倍数 解题报告
「HNOI2016」最小公倍数 考虑暴力,对每个询问,处理出\(\le a,\le b\)的与询问点在一起的联通块,然后判断是否是一个联通块,且联通块\(a,b\)最大值是否满足要求. 然后很显然需要 ...
- Who Gets the Most Candies? POJ - 2886 (线段树)
按顺时针给出n个小孩,n个小孩每个人都有一个纸,然后每个人都有一个val,这个val等于自己的因子数,如果这个val是正的,那就顺时针的第val个孩子出去,如果是负的话,就逆时针的第val个孩子出去, ...
- 20165223 week6测试错题总结
由于时间预估错误及手机自身卡顿问题,虽然已经作答完成,却在最后提交时出现错误,错失提交时间,所以没能按时提交答案,也就没有纠错,以下仅凭印象列出错题: Q1:若超出JVM运行能力,如"byt ...
- 编写高质量代码:改善Java程序的151个建议 --[0~25]
警惕自增的陷阱 public class Client7 { public static void main(String[] args) { int count=0; for(int i=0; i& ...
- request.getRequestDispatcher 页面跳转,样式丢失。
在页面中引用样式和其它资源的时候,尽量不要用相对路径,因为"当前路径"这个概念在J2EE中是不稳定的. 所以最好都是绝对路径,类似于: <% String cp = requ ...
- 【CF1154】题解
A 直接模拟即可. B 对数组中的值进行排序去重.发现若去重之后的数组中有大于 3 个数时无解,因为无法找到一个点到数轴上四个点的距离均相等.若去重之后的数组中只有三个值,则判断中间的值是否到两边的值 ...
- 一文看懂npm、yarn、pnpm之间的区别
文作者对比了当前主流的包管理工具npm.yarn.pnpm之间的区别,并提出了合适的使用建议,以下为译文: NPM npm是Node.js能够如此成功的主要原因之一.npm团队做了很多的工作,以确保n ...
