Binary Space Partitioning
【Binary Space Partitioning】
BSP was discovered by John Carmack used BSP trees in Doom and Quake. Although the game Doom is now of some age virtually all the latest first person shooters still use BSP engines which really goes to show how this technique has stood the test of time.
Performing a for/next loop to sort all your levels polygons every frame would result in a performance level where you could probably bake a cake in between frame updates.
每帧对所有 Polygon 的排序会很卡。
Add to that collision detection of all the polygons in your level (having to check if you have hit each one) and then you could probably ice the cake as well.Not only that
每帧加上 Collision Detection 后会更卡。
对不透明物体,使用Z-Buff即可得正确的渲染结果。但对透明物体,Z-Buff就不管用了。对透明物体来说,不拆分物体,而仅仅依靠次序,是无法得到正确的渲染结果的。
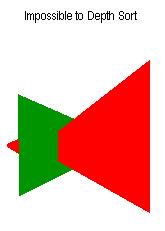
Storing a level in a BSP Tree can provide many benefits in other areas (collision detection,polygon culling).
Not only can a BSP tree be used for drawing all the polygons in your scene in the right order (WITHOUT the need for a Z-Buffer) but it can also be used (in my opinion more importantly) for culling any unseen objects from the fustrum at lightning speed.
最原始的 BSPNode 结构:
struct BSPNode
{
POLYGON *splitter;
BSPNode *FrontChild;
BSPNode *BackChild;
};
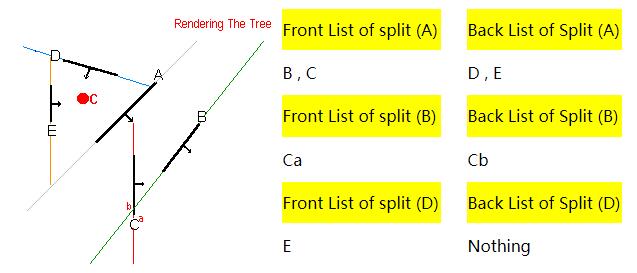
渲染BSP树:
void RenderBSP (NODE * CurrentNode)
{
int Result;
Result=ClassifyPoint(CameraPosition,CurrentNode->Polygon); if (Result==Front)
{
if (CurrentNode->BackChild!=NULL)
RenderBSP (CurrentNode->BackChild); DrawPolygon(CurrentNode->Polygon); if (CurrentNode->FrontChild!=NULL)
RenderBSP (CurrentNode->FrontChild);
}
else
{
if (CurrentNode->FrontChild!=NULL)
RenderBSP (CurrentNode->FrontChild); DrawPolygon(CurrentNode->Polygon); if (CurrentNode->BackChild!=NULL)
RenderBSP (CurrentNode->BackChild);
}
}
问题来了,如果有多边形完全与 Splitter 重叠,该怎么办?一种实现是,将这些重叠的多边形都加入当前 BSPNode,也即一个 BSPNode 可能包含多个物体。
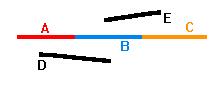
每一个物体有正反两面,当摄像机在物体背面时,看不见该物体。
WalkBSPTree
void WalkBspTree(NODE *Node,D3DVECTOR *pos)
{
POLYGON *shared;
int result=ClassifyPoint(pos,Node-> Splitter); if (result==CP_FRONT)
{
shared=Node-> Splitter->SameFacingShared;
if (Node-> Back!=NULL)
WalkBspTree(Node-> Back,pos); lpDevice-> DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST,D3DFVF_LVERTEX,
&Node-> Splitter-> VertexList[],
Node-> Splitter-> NumberOfVertices,
&Node-> Splitter->Indices[],
Node-> Splitter-> NumberOfIndices,
NULL); while (shared!=NULL)
{
lpDevice-> DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST,D3DFVF_LVERTEX,
&shared-> VertexList[],
shared-> NumberOfVertices,
&shared-> Indices[],
shared-> NumberOfIndices,
NULL);
shared=shared-> SameFacingShared;
} if (Node->Front!=NULL)
WalkBspTree(Node->Front,pos);
return ;
} // this means we are at back of node
shared=Node->Splitter->OppositeFacingShared; if (Node->Front!=NULL)
WalkBspTree(Node->Front,pos); while (shared!=NULL)
{
lpDevice-> DrawIndexedPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST,D3DFVF_LVERTEX,&shared-> VertexList[],shared-> NumberOfVertices,&shared-> Indices[],shared-> NumberOfIndices,NULL);
shared=shared-> OppositeFacingShared;
} if (Node-> Back!=NULL)
WalkBspTree(Node->Back,pos); return;
}
判定 Point 在 Plane 的 Front or Back:
int ClassifyPoint(D3DVECTOR *pos,POLYGON * Plane)
{
float result;
D3DVECTOR *vec1=(D3DVECTOR *)&Plane-> VertexList[];
D3DVECTOR Direction=(*vec1)-(*pos);
result=DotProduct(Direction,Plane->Normal); if (result< -0.001)
return CP_FRONT; if (result> 0.001)
return CP_BACK; return CP_ONPLANE;
}
判定 Polygon 在 Plane 的 Front or Back:
int ClassifyPoly(POLYGON *Plane,POLYGON * Poly)
{
int Infront=;
int Behind=;
int OnPlane=;
float result;
D3DVECTOR *vec1=(D3DVECTOR *)&Plane->VertexList[];
for (int a=;aNumberOfVertices;a++)
{
D3DVECTOR *vec2=(D3DVECTOR *)&Poly->VertexList[a];
D3DVECTOR Direction=(*vec1)-(*vec2);
result=DotProduct(Direction,Plane->Normal);
if (result> 0.001)
{
Behind++;
}
else if (result< -0.001)
{
Infront++;
}
else
{
OnPlane++;
Infront++;
Behind++;
}
}
if (OnPlane==Poly-> NumberOfVertices)
return CP_FRONT;// this would nomrally be CP_ONPLANE if (Behind==Poly-> NumberOfVertices)
return CP_BACK; if (Infront==Poly-> NumberOfVertices)
return CP_FRONT; return CP_SPANNING;
}
LineOfSight:

bool LineOfSight (D3DVECTOR *Start,D3DVECTOR *End, NODE *Node)
{
float temp;
D3DVECTOR intersection;
if (Node->IsLeaf==true)
{
return !Node->IsSolid;
} int PointA=ClassifyPoint(Start,Node->Splitter);
int PointB=ClassifyPoint(End,Node->Splitter); if (PointA==CP_ONPLANE && PointB==CP_ONPLANE)
{
return LineOfSight(Start,End,Node->Front);
} if (PointA==CP_FRONT && PointB==CP_BACK)
{
Get_Intersect (Start,End,(D3DVECTOR *) &Node->Splitter->VertexList[],&Node->Splitter->Normal,&intersection,&temp);
return LineOfSight(Start,&intersection,Node->Front) && LineOfSight(End,&intersection,Node->Back) ;
} if (PointA==CP_BACK && PointB==CP_FRONT)
{
Get_Intersect (Start,End,(D3DVECTOR *) &Node->Splitter->VertexList[],&Node->Splitter->Normal,&intersection,&temp);
return LineOfSight(End,&intersection,Node->Front) && LineOfSight(Start,&intersection,Node->Back) ;
} // if we get here one of the points is on the plane
if (PointA==CP_FRONT || PointB==CP_FRONT)
{
return LineOfSight(Start,End,Node->Front);
}
else
{
return LineOfSight(Start,End,Node->Back);
}
return true;
}
【Leaf BSP Tree】
1、First we choose a splitter from the Polygon List as we did before BUT instead of storing the polygon itself at the Node we only store the polygons Plane.
每个Node只存储 Polygon Plane.
2、The polygon is marked as having been used as a splitter but unlike the Node based compiler we do NOT remove the polygon from the list.We send it down its own front list and this polygon may still continue to be split by other Polygons Planes.
Polygonp被标记为已选中。不删除 polygon,只是加入到 FrontList中。可以被后续的Splitter分割。
3、If a polygon that has already been used as a Plane is split into two further down the tree then the polygon is removed as before and two new polygons are created but it is very important to realise that these splits inherit whether or not they have been used as a splitter from the parent.
被分割后的子Polygon,继承父Polygon的选中状态。
4、we check the Front list and the Back list and if all the polygons in any of the lists are ALL infront of one another then this list forms a convex hull and no longer has to be subdivided because if they are all in front of one another then none of them can be intersecting each other.This List (Front or Back) then becomes a Leaf.
每一个都在其它的正面。

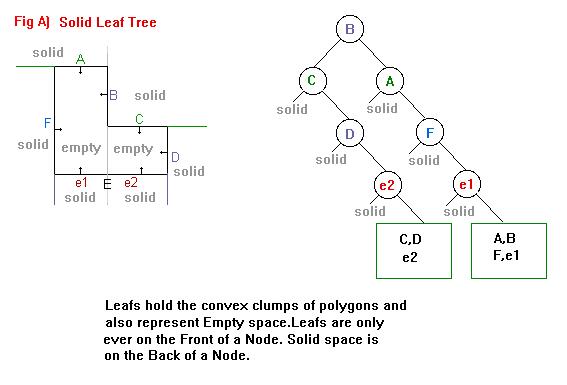
【Solid Leaf BSPTree】
1、A polygon is selected from the list and a Plane is created using the polygon info and stored in the newly created Node.This Plane is now the splitter for the current Node.We also mark the polygon that was selected and from which the Plane was created from as having been used as a splitter already so that it can not get choosen again.
选择 Polygon,根据 Polygon创建一个 Plane作为splitter,标记 Polygon 为选过状态。
2、loop though every polygon in the list (including the one that was used as the splitter) classify the polygon against the splitting Plane.
迭代当前 Polygon 在内的所有 Polygon。
Just as before if the Polygon is Behind the plane it gets added to the Back List and if it is in front of the plane it gets added to the Front List.If the polygon is ON (sharing) the plane then the Normal of the polygon is compared to the Normal split Plane.If the Polygons Normal is facing the same way as the Split Plane then the polygon is added to the Front List.If the Polygon Normal is facing in the opposite direction to the Split Plane then the polygon is added to the back list.
将所有的Pologon放入 Front、Back Listk中。On Plane Polygon 根据法线方向来判定。
3、 We check each Polygon in the Front list and if ALL the polygons have already been used as a Split Plane then this is a Convex Leaf and the polygons can be written to a leaf structure and attached to the current Nodes front.
当 Front List 中所有的 Polygon 都被选中过(即每一个都在每一个的前面),则形成了凸包,则将这些 Polygon 加入到一个Leaf中,这个Leaf叫 Convex Leaf。
4、We will see this in action in a moment.We now check the back list,if there are NO polygons left in the back list then we simply store a -1 in the Nodes Back Pointer.This means if we ever try to go down the back of this node we will know that the -1 means we can not because it is solid space.I
当Back 无物体时,Back List 存储为-1。
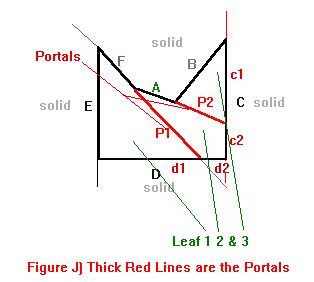
【Portal】
These portals will not be rendered or even kept after the PVS has been calculated but they are needed because if we can create a Portal to plug up the doorway then getting the dimensions of this Portal will get us the dimensions of the doorway which is exactly what we need.
As you can probably imagine creating portal Polygons to fit into all the gaps in our level is going to create many many portals.In otherwords if a room has 5 doorways we will need create a portal in each doorway and so on for every leaf .
Because of the nature of BSP trees portals between two leafs will always be on one of the Split planes in out tree.Above Portal 1 is on Node F's split plane and Portal 2 is on Node A's split plane.
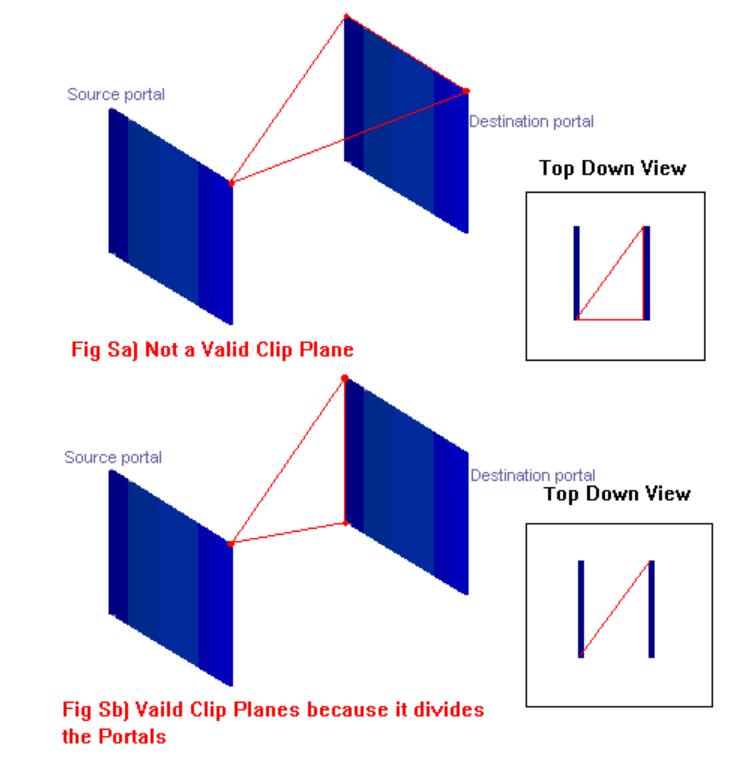
【Anti-Penumbra】
walk through each leaf in the tree and for every portal in that leaf create an ANTI-PENUMBRA between that Portal and every Portal in the Leafs adjoining that leaf and so on.

A Plane is considered to be an Anti-Penumbra plane if the plane clearly divides the Source Portal and the Destination portal.That is to say the Plane is accepted if the Source Portal lays of one side of the Plane and the Destination portal lays on the other.
参考:
1、https://www.cs.utah.edu/~jsnider/SeniorProj/BSP1/default.html
2、https://www.cs.utah.edu/~jsnider/SeniorProj/BSP/default.htm
Binary Space Partitioning的更多相关文章
- HDU #2966 In case of failure
Overview 给出平面上两两不重合的\(n\)个整点, 求每个点到它在其他\(n-1\)个点的最近临点的欧几里得距离的平方. Solution k-d tree 模板题. 关于k-d tree, ...
- K-D Tree
这篇随笔是对Wikipedia上k-d tree词条的摘录, 我认为解释得相当生动详细, 是一篇不可多得的好文. Overview A \(k\)-d tree (short for \(k\)-di ...
- Qt之图形视图框架
简述 图形视图(Graphics View)提供了一个平台,用于大量自定义2D图元的管理与交互,并提供了一个视图部件(view widget)来显示可以缩放和旋转的图元. 框架包括一个事件传播架构,支 ...
- Qt 学习之路:Graphics View Framework
Graphics View 提供了一种接口,用于管理大量自定义的 2D 图形元素,并与之进行交互:还提供了用于将这些元素进行可视化显示的观察组件,并支持缩放和旋转.我们通常所说的 Linux 的 KD ...
- qt Graphics View Framework(非重点)
Graphics View 提供了一种接口,用于管理大量自定义的 2D 图形元素,并与之进行交互:还提供了用于将这些元素进行可视化显示的观察组件,并支持缩放和旋转. 说明;Graphics View ...
- KD树
k-d树 在计算机科学里,k-d树( k-维树的缩写)是在k维欧几里德空间组织点的数据结构.k-d树可以使用在多种应用场合,如多维键值搜索(例:范围搜寻及最邻近搜索).k-d树是空间二分树(Binar ...
- Game Engine Architecture 1
[Game Engine Architecture 1] 1.This book is really just the beginning of a fascinating and potential ...
- 3D游戏引擎中常见的三维场景管理方法
对于一个有很多物体的3D场景来说,渲染这个场景最简单的方式就是用一个List将这些物体进行存储,并送入GPU进行渲染.当然,这种做法在效率上来说是相当低下的,因为真正需要渲染的物体应该是视椎体内的物体 ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(30):Graphics View Framework
Qt 学习之路 2(30):Graphics View Framework 豆子 2012年12月11日 Qt 学习之路 2 27条评论 Graphics View 提供了一种接口,用于管理大量自定义 ...
随机推荐
- mybatis(一、原理,一对多,多对一查询)
MyBatis框架及原理分析 MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架,其主要就完成2件事情: 封装JDBC操作 利用反射打通Java类与SQL语句之间的相互转换 ...
- centos安装VirtualBox增强包VBoxGuestAdditions
1.如果你的CentOS 版本早于 6,那么需要在 /etc/grub.conf 中添加一行 divider=10,以将这个参数传递给核心,以减少 idle CPU load. 2.#yum up ...
- PHP面试题学习
PHP 开发工程师笔试试卷 姓名 :__________ 第一部分为必答题,第二.三部分任选其一回答 一. PHP 开发部分 1.合并两个数组有几种方式,试比较它们的异同. 2.请写一个函数来检查用户 ...
- python __name__ 和__main__的使用领悟
__name__和__main__的使用 #hello.pydef sayHello(): str="hello" print(str); if __name__ == " ...
- Linux 下安装FastDFS v5.08 的php扩展
php扩展也需要依赖于FastDFS一些库文件,所以请先安装FastDFS,具体请看我之前的文章. 一.安装目录 php安装目录 /data/nmp/php FastDFS源码目录 /data/w ...
- DevExpress中barManager下的toolbar如何在panel中显示
如题,我的Dev Toolbar需要在一个pannel中显示,并且居于最顶部.可是好像默认情况下toolbar都是在窗体的最顶部的,如何设置才能使其位于一个panel的最顶部呢? 解决方案:经过测试, ...
- c++ CreateProcess调用dos命令
// test.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <windows.h> #include &l ...
- verilog 代码分析与仿真
verilog 代码分析与仿真 注意:使用vivado 自带的仿真工具, reg和wire等信号需要赋予初始值 边沿检测 module signal_test( input wire cmos_pcl ...
- ios下表单post使用gzip模式
使用afnetworking,服务器参考的这里 ios端,使用自己的序列化类 manager.requestSerializer = [MyHttpRequestSerializer new];[ma ...
- 初识docker-镜像
前言: 以前学习docker 都是零零碎碎的,只知道用,有些莫名其妙的报错自己也没有思路去解决,所以基于一本专业的介绍docker的书籍,重新开启学习,该博客就记录下我自己的学习过程吧. 1.dock ...
